Concept 6.1: Biologists use microscopes and biochemistry to study cells
1/8
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
Microscope
An instrument used to magnify objects to small to be seen by the naked eye
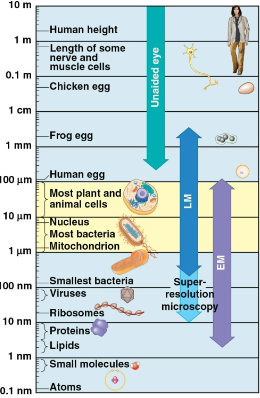
Light microscope (LM)
A microscope where visible light is passed through a specimen and then through glass lenses, which magnify the image
Magnification
The ratio of an object’s image size to its real size
Resolution
The measure of the clarity of the image
Organelles
The membrane-enclosed structures in eukaryotic cells, such as mitochondria which aids ATP and cellular respiration
Light microscopy cannot study these due to low resolutions despite staining or labeling
Scanning electron microscopes (SEMs)
Electron microscope that focuses a beam of electrons onto the surface of a specimen, providing images that look 3-D
Transmission electron microscopes (TEMs)
Electron microscope that focuses a beam of electrons through a specimen, used to study internal cell structures
Electron microscopes (EMs)
Microscopes that transmit electrons to view closer details, can be cost prohibitive and includes scanning electron microscopes and transmission electron microscopes
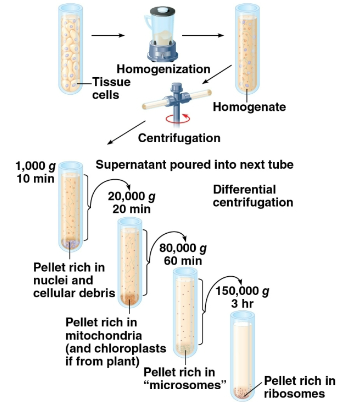
Cell fractionation
The use of centrifuges to fractionate cells into their component parts of organelles, helping determine the functions of organelles based on structure