RAAS and Micturition
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Micturition, 500, 1
__ (term) = Urination
A full bladder comfortably able to hold __ mL of urine, at maximum _ L
internal sphincter, external sphincter
Micturition cycle
Urine passes through the __ __ to urethra
Then __ __ (voluntary) to release/void
Pontine Storage Area, Pontine Micturition Center
Neural control of micturition
The __ __ __ is a region of pons that inhibits act of urination
The __ __ __ is a region of pons that promotes act of urination
M3 Rs
Under normal circumstances, which ANS receptor type has the most significant influence on micturition?
Nephron, Minor calyx, Major calyx, papilla
Renal anatomy
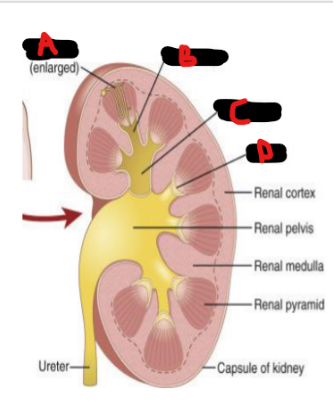
Ureters, detrusor muscle, internal sphincter, prostate, external sphincter, urethra, external urethra
Bladder anatomy
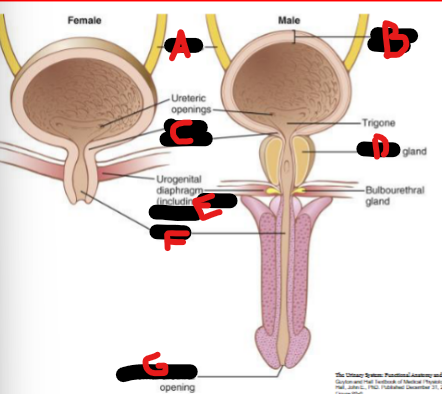
Collecting ducts, pelvis, ureter
Filtrate fluid in nephrons travel into the __ __ (nephron)
Empty into renal __ → Then directly proceed to the __
Peristalsis, renal stone, cramping
Ureters have smooth muscle that contract to move urine down to bladder via __
Strong … contractions in presence of __ __ to ureter produces a “__” abdominal pain
Collapsed, contracts, closed, reflux
Ureters course through detrusor muscle to prevent blackflow
Ureters are usually __ (expanded/collapsed), except when squeezing urine into bladder
When detrusor __ to urinate, it will squeeze the ureters __ (open/closed) = prevents __
Minimal (lesser), detrusor relaxation, internal sphincter contraction
Sympathetic Innervation of Bladder
__ influence compared to parasympathetic
Beta-2 Rs → __ __ (muscle contraction/constrict vs dilation/relax)
Alpha-1 Rs → __ __ (muscle contraction/constrict vs dilation/relax)
Primary, M3, detrusor constriction, internal sphincter dilation
Parasympathetic Innervation of Bladder
__ control, and done via __ Rs
Rs actions → __ __ and __ __ (muscle contraction/dilation)
Pudendal nerve, external, mechanoreceptors
Voluntary/somatic Innervation of Bladder
__ __ → Contraction of the __ sphincter
Sensory Innervation of Bladder
Stretch __ thru bladder wall and bladder neck
Pressure, mechano, micturition contractions, detrusor, external, micturition
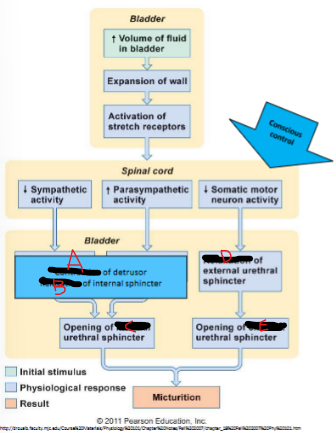
Micturition Reflex
Bladder __ increases and thus __receptors are stretched
Parasympathetic - Sends reflex of many small “__ __” to the __ and relax internal sphincter
Voluntary control of the __ sphincter allows patient to initiate or prevent __
Contraction, relaxation, internal, relaxation, external
Micturition Reflex
Renin
Produced by juxtaglomerular apparatus to raise BP/blood volume
Afferent arterial baroreceptors, Macula Densa, sympathetic
With Renin
__ __ __ sense a decreased afferent arteriole pressure
__ __ sense Na+ delivery with sodium cotransporter and tubular flow rates with cilia
__ (sympathetic/parasympathetic) stimulation involved
DCT, salt, Angiotensin II, aldosterone, ADH
After passing renin and still Low flow rate to the __ (part of nephron)
Result is increased __ retention and systemic volume and blood pressure
Done via __, __, and __
Systemic bp, renal artery stenosis, efferent arteriole
What stimuli can cause decreased afferent arteriole pressure?
Low __ __
Low flows and pressures to kidney (i.e. __ __ __)
__ __ dilation
Renin, angiotensin I, ACE, angiotensin II, RAAS, efferent arteriole constriction, afferent pressure
After decrease in afferent a is sensed by granular cells, what happens upon returning afferent arteriole pressure back to set point (RAAS)?
Increase __ → Increase __ __ → __ converts I to II → Increase __ __ → Activate __ → Systemic pressure and volume increase with __ __ __ (arteriole action) → Normalized __ __
Perfusion, juxtaglomerular
From RAAS/Goal of RAAS:
Water and salt retention, means an increased __ to __ apparatus
Aldosterone, Na-H+, efferent, increase, ADH, constriction
Angiotensin II receptor locations and actions
Adrenal cortex - produces __
Kidney - ___ exchange in PCT
Renal arterioles - constricts __ arteriole more to __ (increase/decrease) GFR
Hypothalamus - Produced __
Systemic arterioles - Direct vaso__
Contraction alkalosis
State where Na-H exchange occurring in low volume states in kidney
Adrenal cortex, PCT, renal arterioles, hypothalamus, systemic arterioles
5 targets of Angiotensin II
Endocrine - (2)
Renal anatomy - (2)
Systemic - (1)
Aldosterone
Produced by adrenal glands and in response to elevated K+ levels
Principal, DCT, H+, intercalated
Aldosterone
Acts at __ cells of late __ and collecting duct
Some increased __ secretion at __ cells
Lumen Na+, Na-K ATPase, lumen K+
Aldosterone’s 3 mechanisms lead to increased K+ secretion and increased Na+ reabsorption
More __ __ channels
More __ __ (enzyme) pumps and more activity
More __ __ channels
adrenal insufficiency, primary hyperaldosteronism
Pathophysiology of Aldosterone
Addison’s Disease from __ __
Conn’s syndrome from __ __
Hyponatremia, Hypernatremia
Is SIADH a problem of hyponatremia or hypernatremia?
What occurs from defective V2 receptors? - Large amounts of dilute urine (hypo/hypernatremia?)
Primary Hyperaldosteronism
Elevated aldosterone in absence of appropriate stimulus, renin should be suppressed
Hypertension, hypokalemia, metabolic alkalosis
HHM Triad in Conn Syndrome - (3)
Aldosterone, adrenal glands
Common causes of Conn syndrome
__-secreting tumors
Hyperplasia of the __ __
Increased osmotic, decreased blood
ADH
Osmoreceptors detect__ __ pressure
Baroreceptors detect __ __ pressure
(increased/decreased — pressure)
absorption of water, blood pressure
What would happen from mutation making V2 receptors less effective?
(1) Less __ of __ from kidneys
(2) Lowered __ __
Low renin
A patient has a history of Conn Syndrome. Which would be expected?
__ __ levels - RAAS component