Anatomy Final - Bishop
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
When you make a fist, your wrist will likely flex/extend?
Extend (bc extensors are engaged)
If you didn’t have Flexor Digitorum Superficialis, would you lose power or precision?
Power. (You would lose power but not precision bc Flexor digitorum profundus goes to the tips of the distal phalanges; FDS goes to the sides of middle phalanx)
If your patient makes a fist and a tendon pops out, what injury do they likely have?
Pulley injury (Usually an audible pop, caused by overloading the tendon; common in climbers)
What is the key to the gliding mechanism in finger flexors? (what helps it glide smoothly?)
Synovial fluid (tendons are in a sheath which contains synovial fluid)
What muscle pulls the extensor hood proximally?
a. FDP
b. FDS
c. ED
d. Lumbricals
c. Extensor digitorum
What muscle(s) extends the PIP and DIP joints since the ED can’t?
lumbricals
Dislocation most commonly happens when the GHJ is around ____ degrees.
a. 30
b. 45
b. 90
c. 120
b. 90 degrees
What position is the humerus going into when it is commonly dislocated?
a. flexion
b. extension
c. internal rotation
d. external rotation
d. external rotation (at 90 degrees, the humerus externally rotates as you abduct - this means the inferior glenohumeral ligament leaves a big hole in the front of the stability)
What muscle holds the clavicle and scapula together?
Trapezius (also levator scap and rhomboids)
What gives the GHJ stability when your arm is at your side?
a. inferior glenohumeral ligament
b. middle glenohumeral ligament
c. superior glenohumeral ligament
d. coracohumeral ligament
c. superior glenohumeral ligament
Which head of the biceps brachii is worse to tear, and why?
Long head because you lose shoulder flexion and shoulder stability
Your pt is a 4 year old child whose brother was holding his arm and swinging him in circles until the child started feeling pain and tenderness in his elbow. What was likely the mechanism of injury?
a. ulnar fracture
b. radial fracture
c. dislocation of radial head
d. dislocation of ulnar head
c. dislocation of radial head (this is also known as a "pulled elbow" or "nursemaid's elbow," which occurs when the child's elbow is pulled or stretched, often due to sudden lifting or swinging)
What is a common characteristic of ligaments that are triangular or “fan-shaped”?
they provide stability by resisting force in multiple directions
If there is an injury to the extensor mechanism of the wrist, what might be some of the symptoms?
a. inability to straighten fingers
b. inability to extend wrist
c. inability to bend wrist
d. both a and b
e. a b and c
d. both a and b (inability to straighten fingers and inability to extend wrist)
Which of the following might result from an injury to the extensor mechanism?
a. bouteonniere (buttonhole) deformity
b. swan neck
c. mallet finger
d. jersey finger
e. all of the above
e. all of the above
Which of the following is commonly associated with rheumatoid arthritis?
a. bouteonniere (buttonhole) deformity
b. swan neck
c. mallet finger
d. jersey finger
b. swan neck deformity (caused by hyperextension of the PIP joint and flexion of the DIP joint)

A sudden extension force ruptures the flexor digitorum profundus at the DIP joint. What condition is likely to result?
a. bouteonniere (buttonhole) deformity
b. swan neck
c. mallet finger
d. jersey finger
d. jersey finger (A “jersey finger” refers to a rupture of the flexor tendon, which is the tendon that bends the fingertip down. Its name comes from football athletes who have gripped the jersey of an opposing player who is trying to get away. As the player tries to free themselves, the finger gets unexpectedly straightened as it is still trying to flex and grip. This creates a tug of war, where the tendon is being pulled in two directions. This can result in the tendon separating from its bone insertion at the tip of the finger.)

If there is increased torsion, would your femoral heads be in front of or behind your acetabulum?
in front of the acetabulum
If someone has varus, or is bow-legged, do they likely have antetorsion of retrotorsion?
Retrotorsion (femur is rotated backwards, causing externally rotated legs with patella pointing outwards)
In which position does the hip have the greatest bony congruence/ligamentous/capsular tension?
a. flexion, adduction, lateral rotation
b. flexion, abduction, lateral rotation
b. extension, abduction, medial rotation
d. extension, adduction, medial rotation
b. flexion, abduction, lateral rotation (think criss cross); this is the close-packed position of the hip.
You notice your patient walking with a hip drop, also called a Trendelenburg gait. Which muscles would most likely be the cause of his weakness?
a. hip extensors
b. hip flexors
c. hip adductors
d. hip abductors
d. hip abductors (commonly glute med)
You noticed your patient has a very weak L gluteus medius. What walking pattern might she adopt?
a. Dragging her feet
b. Walking on her toes
c. Leaning to her left
d. Leaning to her right
C. Leaning to her left (pts put one foot on the ground and lean to their weak side with weak hip abductors)
What plane(s) does the knee move in?
a. frontal
b. sagittal
c. transverse
d. frontal and sagittal
e. frontal and transverse
f. frontal, transverse, and sagittal
d. frontal and sagittal (flx/ext is in the frontal plane and ER/IR is in the frontal plane)
The medial femoral condyle is bigger than the lateral femoral condyle, meaning as the tibia moves on the femur in open-chain movement, the tibia will ______ relative to the femur
a. flex
b. extend
c. internally rotate
d. externally rotate
d. externally rotate (Think of the knee extension machine. When you extend your knee, do your toes tend to point inward or outward?….hint: it’s outward)
Your patient is unable to fully extend her knee. What motion is she likely missing in her knee?
a. abduction
b. adduction
c. internal rotation
d. external rotation
d. external rotation (this happens in the last couple of degrees of extension)
Is your tibiofemoral joint in the close-packed position when the knee is straight or bent?
straight (don’t need a lot of muscle activity to keep your leg straight when standing. When bent, you have to activate quads the whole time, which puts pressure on your patella)
To keep the tibiofemoral joint right under the femoral head, do we rest in a varus or valgus position so weight goes right through center of the knee?
Valgus
A meniscus cannot heal from an injury UNLESS it is injured in what region?
a. inner 1/3
b. inner 2/3
c. outer 1/3
d. outer 2/3
c. outer 1/3 (this is the only part of the meniscus that receives blood supply)
Which knee ligaments are extra-articular (outside the joint)? Choose all that apply.
a. ACL
b. MCL.
c. PCL
d. LCL
e. ALL
MCL, LCL, ALL
Which ligaments are comprised of different bundles, allowing the ligaments to be taut throughout the range of knee flexion and extension?
a. ACL
b. MCL.
c. PCL
d. LCL
e. ALL
ACL and PCL (these are the intra-articular joints)
Name 3 ligaments that help with stability as you go into extension of tibiofemoral joint? (hint: not talking about ACL, LCL, MCL, or PCL)
Arcuate popliteal ligament
Oblique popliteal ligament
Meniscofemoral ligaments
(acronym: AMO)
Name the primary, secondary, and dynamic restraint of anterior joint stability in the knee.
Primary: ACL
Secondary: MCL
Dynamic restraint: Hamstrings
Name the primary, secondary, and dynamic restraints of posterior joint stability
primary: PCL
secondary: LCL and arcuate ligament (acronym: LA)
dynamic: quadriceps
Name the primary, secondary, and dynamic restraints of medial joint stability
primary: MCL
OPL (oblique popliteal ligament) - when knee ext (acronym: MO)
secondary: ACL
dynamic: pes anserine
Name the primary, secondary, and dynamic restraints of lateral joint stability.
primary: LCL and ALL (anterolateral ligament)
arcuate ligament (when knee extended) (LALA)
secondary: ACL & PCL
dynamic: biceps femoris
Name the primary and dynamic restraint of internal rotation
Primary: ACL, PCL
Dynamic restraint: biceps femoris
Name the primary and dynamic restraint of external rotation
primary: MCL, LCL
dynamic: popliteus
What bursa stops quadriceps from rubbing against the femur?
a. infrapatellar
b. suprapatellar
c. subpopliteal
d. gastrocnemius
e. prepatellar
b. suprapatellar
What bursa protects the most anterior surface of the patella?
a. infrapatellar
b. suprapatellar
c. subpopliteal
d. gastrocnemius
e. prepatellar
e. prepatellar
What bursa stops patella tendon/ligaments from rubbing backwards/forwards on tibia?
a. infrapatellar
b. suprapatellar
c. subpopliteal
d. gastrocnemius
e. prepatellar
a. infrapatellar
Tibia moves __________ relatively to the femur to flex the knee and ________ relative to the femur to extend the knee.
a. anterior; anterior
b. anterior; posterior
c. posterior; anterior
d. posterior; posterior
c. posterior; anterior
Tibia moves posterior relatively to the femur to flex the knee and anterior relative to the femur to extend the knee.
As the (concave/convex) surface of the tibia moves posteriorly, it has to slide posteriorly relatively to the femur.
concave
In open-chain flexion of the knee, tibial plateaus glide _________ on the femoral condyles and spin _________.
a. anteriorly; medially
b. anteriorly; externally
c. posteriorly; medially
d. posteriorly; externally
c. posteriorly, medially (0-20)
In open-chain flexion of the knee, tibial plateaus glide posteriorly on the femoral condyles and spin medially.
During open-chain extension of the knee, tibial plateaus glide _________ on the femoral condyles and spin _________.
a. anteriorly; medially
b. anteriorly; externally
c. posteriorly; medially
d. posteriorly; externally
b. anteriorly, externally
During open-chain extension of the knee, tibial plateaus glide anteriorly on the femoral condyles and spin externally.
During closed-chain flexion of the knee, femoral condyles roll ________ and glide _________ on the tibial plateaus.
a. anterior; anterior
b. anterior, posterior
c. posterior; anterior
d. posterior; anterior
c. posterior, anterior
During closed-chain flexion of the knee, femoral condyles roll posterior and glide anterior on the tibial plateaus.
During closed-chain flexion of the knee, the femur spins ________; during closed chain extension of the knee, the femur spins __________.
a. externally; internally
b. externally, externally
c. internally; internally
d. internally; externally
externally; internally
During closed-chain flexion of the knee, the femur spins externally; during closed chain extension of the knee, the femur spins internally.
(Hint: Think about standing from a squat - this is closed-chain extension. We typically see valgus happen in this position, which is INTERNAL rotation)
What muscle unlocks the knee during active knee fkexion?
a. hamstrings
b. rectus femoris
c. popliteus
d. vastus medialis
c. popliteus
Knee is in loose packed position when knee is bent ____ degrees
a. 0
b. 45
c. 90
d. 120
c. 90 (in close-packed position, the tibia has more independent movement into IR and ER)
The axis of rotation of the knee happens at the ________.
a. medial tibial platea
b. lateral tibial plateau
c. medial femoral condyle
d. lateral femoral condyle
a. medial tibial plateau
T/F You can actively move your patella in isolation
F. You cannot, actively, move your patella in isolation. It’s like a “train on tracks” - It only moves bc tibia/femur moves and it’s attached to tendon
T/F The patella only moves on the sagittal plane.
F. Patella also moves on the frontal plane (not sure abt transverse)
Which of these are ways the patella moves? Choose all that apply
a. superior/inferior glide
b. medial/lateral glide
c. medial/lateral tilt
d. medial/lateral rotation
(all of them)
a. superior/inferior glide
b. medial/lateral glide
c. medial/lateral tilt
d. medial/lateral rotation
Which way does the patella move during tibiofemoral flexion?
a. superior roll
b. inferior roll
c. superior glide
d. inferior glide
d. inferior glide
What is the more STABLE configuration of the patellar tendon and how much contact does it have with the femur?
a. patella alta; too little congruence
b. patella alta; too much congruence
c. patella baja; too little congruence
d. patella baja; too much congruence
d. Patella baja - too much congruence.
(When the patella tendon is short (patella baja), it holds the patella down into femur a lot of the time. Therefore, it is more stable, but the greater contact with the femur means the chances of wear and tear are greater).
T/F. When you activate the quadriceps, you active all 4 of them. You cannot activate them individually
True! Quadriceps don’t have separate fibers. If you turn on quads, you turn on all the quads.
What provides passive stability to the patellofemoral joint? Choose all that apply.
a. patellofemoral ligaments
b. patellotibial ligaments
c. retinaculum
d. ilopatellar band of IT band
e. lateral femoral condyle
(all of them)
a. patellofemoral ligaments
b. patellotibial ligaments
c. retinaculum
d. ilopatellar band of IT band
e. lateral femoral condyle
What provides dynamic stability to the patellofemoral joint? Choose all that apply.
a. rectus femorus
b. vastus medialis
c. vastus intermedius
d. vastus lateralis
b. vastus medialis
d.
vastus lateralis
The area in contact between patella and femur (increases/decreases) as you flex your knee.
increases
The Q angle is the line from __________ to __________ and _________ to _________
ASIS to mid-patella and mid-patella to tibial tuberosity
The Q-angle is the estimate of the quadriceps influence in the
a. sagittal plane
b. frontal plane
c. transverse plane
d. all of the above
b. frontal plane
Is the Q angle typically higher in men or women, and why?
Women, bc women have a wider pelvis
A Q angle of over ____ degrees is often considered “abnormal” and results n in more laterally pulling forces of the quadriceps and patellofemoral stress.
a. 10
b. 15
c. 20
d. 30
c. 20
Pronation and supination happen at what planes? Choose all that apply.
a. sagittal plane
b. frontal plane
c. transverse plane
all 3 planes - sagittal, frontal, and transverse
What 3 movements happen during pronation?
DF, Eversion, Abduction
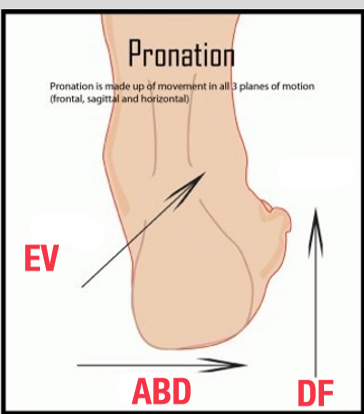
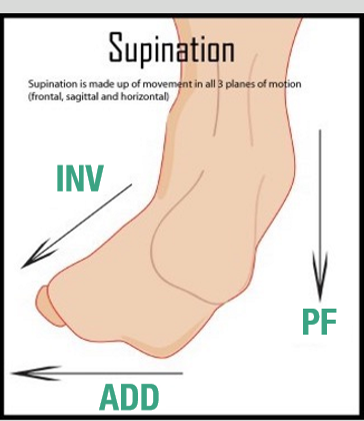
What 3 movements happen during supination?
PF, Inversion, ADDuction
Inversion/Eversion happen on what plane?
a. frontal
b. sagittal
c. transverse
c. transverse
Abduction and Adduction of the foot happen on what plane?
a. frontal
b. sagittal
c. transverse
a. frontal
During close-chain PRONATION, talus _____ & _______ while calcaneous _________.
During close-chain PRONATION, talus PF and ADD, while calcaneous everts.
During supination, talus _____ &_____ but calcaneous __________
During supination, talus DF & ABDucts but calcaneous inverts
the hamstrings are actively insufficient in what position?
Knee flexion, hip extension (quad stretch)
what position are hamstrings in passive insufficiency?
hip flexion, knee extension
Which muscle can extend the knee during close chain function of the leg? (starting from partial squat)
a. sartorius
b. tibialis anterior
c. psoas major
d. soleus
d. soleus
You ask patient to take a step forward with the RIGHT leg, and stop once the right foot hits the floor. In this position, you rightly observe:
a. ER of R hip
b. IR R hip
c. hip hike on L
d. 30 degrees of lumbar rotation to the R
a. ER of R hip
Ligaments of the hip joint are most taut in which position?
Extension, IR
T/F You have free movement btwn tarsal bones and calcaneous
T. That’s why if the calcaneous inverts, the front of foot can evert to keep toes on ground. Calcaneous moves separately from the toes
(Pronation/Supination) is associated with rigidity
Supination
(Pronation/supination) is associated with mobility
pronation
If the forefoot cannot compensate for rearfoot pronation, the ________ border of the forefoot will come off the ground.
a. anterior
b. posterior
c. medial
d. lateral
d. lateral
the plantar aponeurosis is stretched by toe (extension/flexion)
extension
what offsets femoral anteversion?
normal tibial torsion
Which joint is movement more restricted?
Talonavicular or calcaneocuboid?
Calcaneocuboid
What are the primary plantarflexors?
gastroc and soleus
what are strong dorsiflexors?
tibialis anterior and extensor hallicus longus
how do u determine is hip flexor tightness is caused by the iliopsoas or rectus femoris?
hip flexed above horizintal with 90 or more - iliopsoas only
knee in less than 90 degree of flx (i.e more extended) - then rectus femoris
If you do the Ober’s test with a bent knee what does it emphasize?
What does it emphasize with a straight leg?
Bent knee: tests the patellar portion of ITB
Straight leg: tests tibial portion of ITB
does a patella usually have more motion medially or laterally?
medially
a (smaller/larger) center edge angle has implications for predispositions to dislocation
smaller
a (smaller/bigger) center edge angle indicates more weightbearing contact btwn the humeral head and acetabulum
bigger
what is the normal angle of inclination
a. 60
b. 90
c.120
d. 150
c. 120
A decreased angle of inclination is known as (coxa cara/ coxa valga)
Coxa Vara
An increased angle of inclination is known as (coxa vara/coxa valga)
Coxa valga
We tend to see a (small/large) angle of inclination in younger kids.
large (almost 180 in younger kids)
You get decreased contact between acetabulum and femur with (coxa vara/ coxa valga)
Coxa valgaYo
u get less abduction btwn femur and pelvis with (coxa vara/coxa valga)
coxa varay
you have increased contact btwn femoral head and acetabulum with coxa vara/coxa valga
coxa vara
hip has the most ligament tension in the close-packed position, which is
extension, medial rotation, adduction/abduction
PPT results in flx/extension of hip?
flexion
you could flex your hip by anterior pelvic tilt or posterior pelvic tilt?
anterior pelvic tilt
Right hip ihking causes ____ of R hip and ___ of L hip
ADD R, ABD L