Physiology ospe
1/71
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Made with love
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
Identify
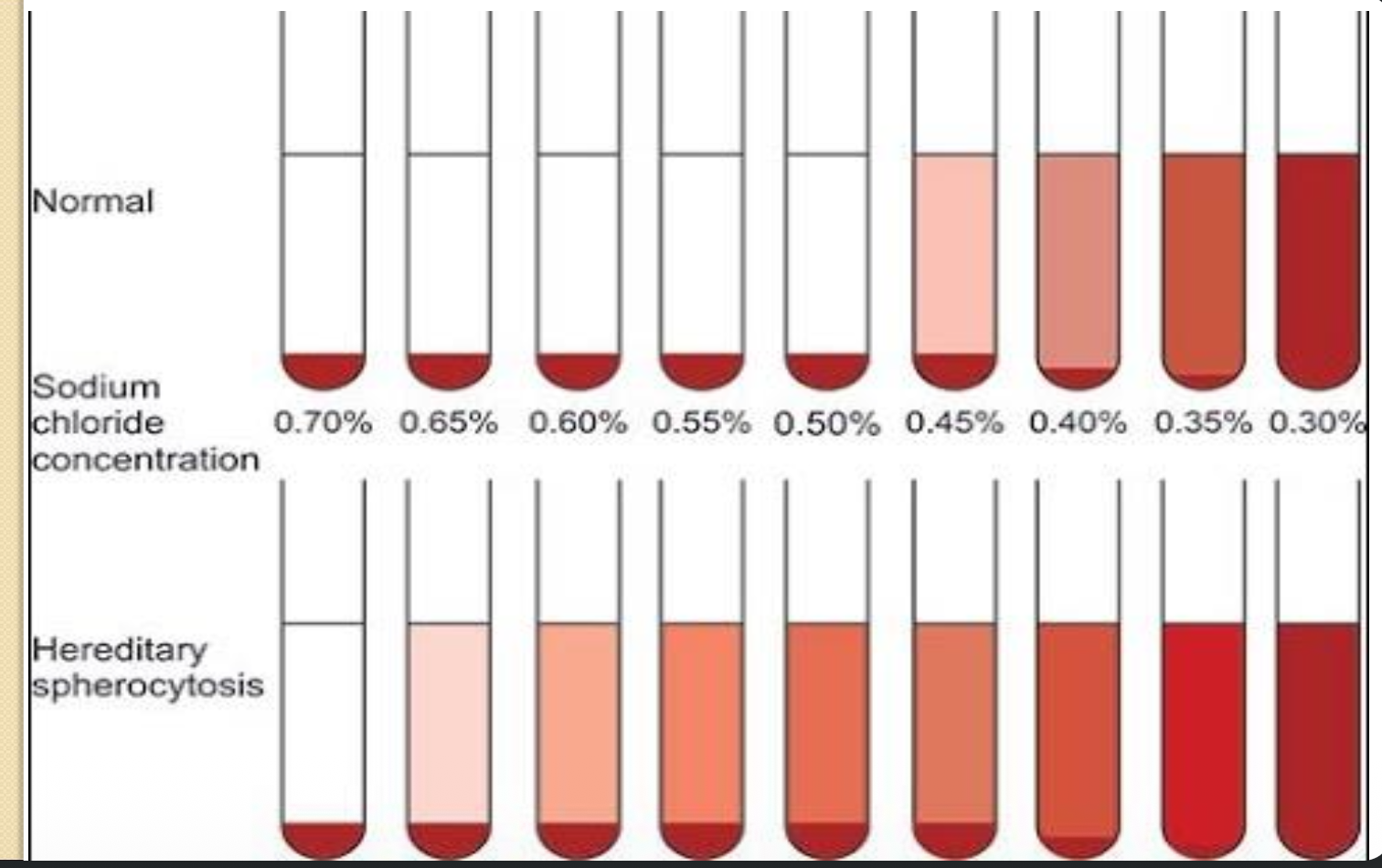
Osmotic fragility test
Mention 2 materials in osmotic fragility test
1. Distilled water.
2. NaCl solution of a concentration 1gm %
3. Test tubes and test tube rack.
4. Pipettes 1 ml and 5ml.
in OFT normally cells don’t heamolyse until concentration of NACL is below …..
0.45%
complete hemolysis occurs at ….. NaCl.
0.35%
mention two significance in OFT
used to diagnose hereditary spherocytosis
High osmotic fragility
Low osmotic fragility
hereditary spherocytosis →RBCs begin to hemolyse at …. and complete at ….
RBCs begin to hemolyse at 0.7% and complete at 0.5 %
in High osmotic fragility what it tend to increase and mention occurring disease
increased tendency to hemolysis
autoimmune hemolytic anemia, severe burns, chemical poisoning, or in
hemolytic disease of the newborn. ( erythroblastosis fetalis )
Low osmotic fragility RBCs begin at ….. and complete at ….
Tell me also about hemolysis
RBCs begin at 0.4% and complete at 0.2%
Increased resistance to hemolysis
Identify
Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR)
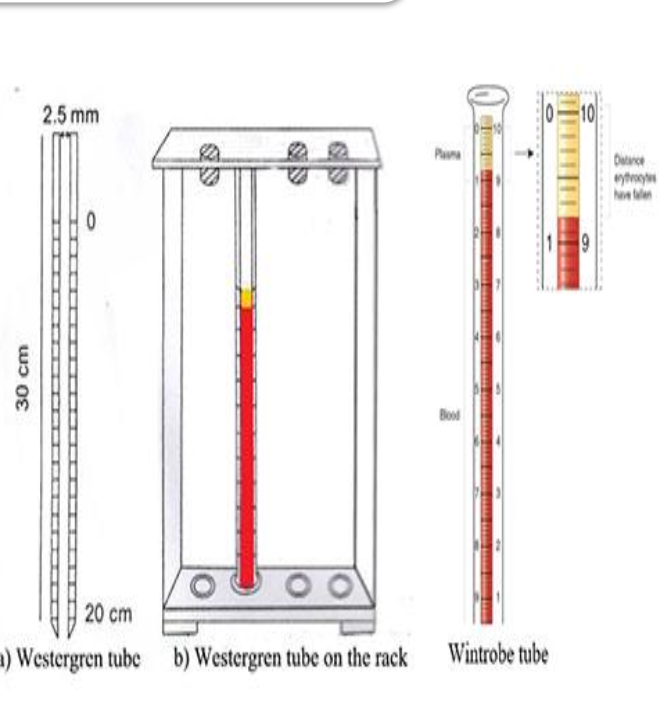
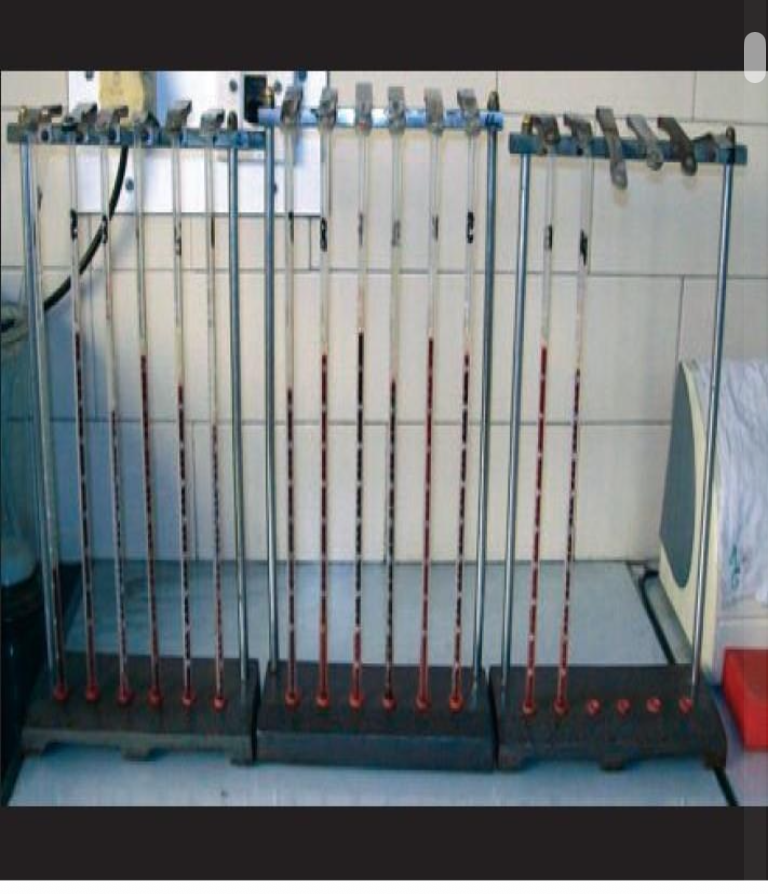
Westergren on left ( tube and rack )
wintrobe on right

identify
ESR ( westernberg method )

identify
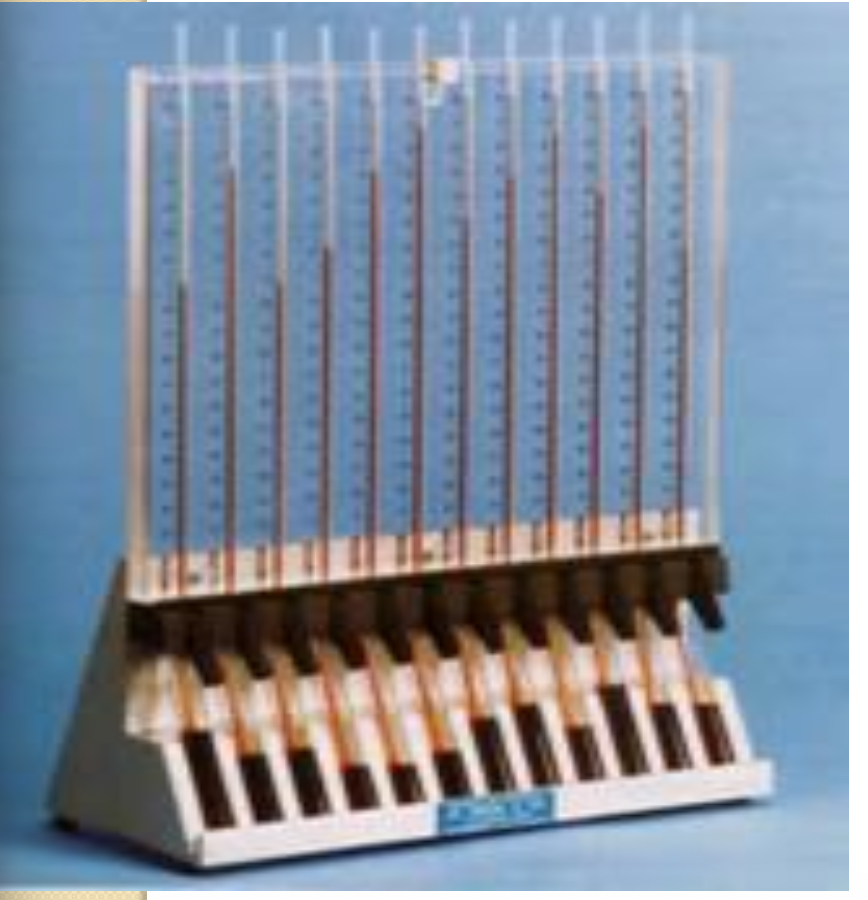
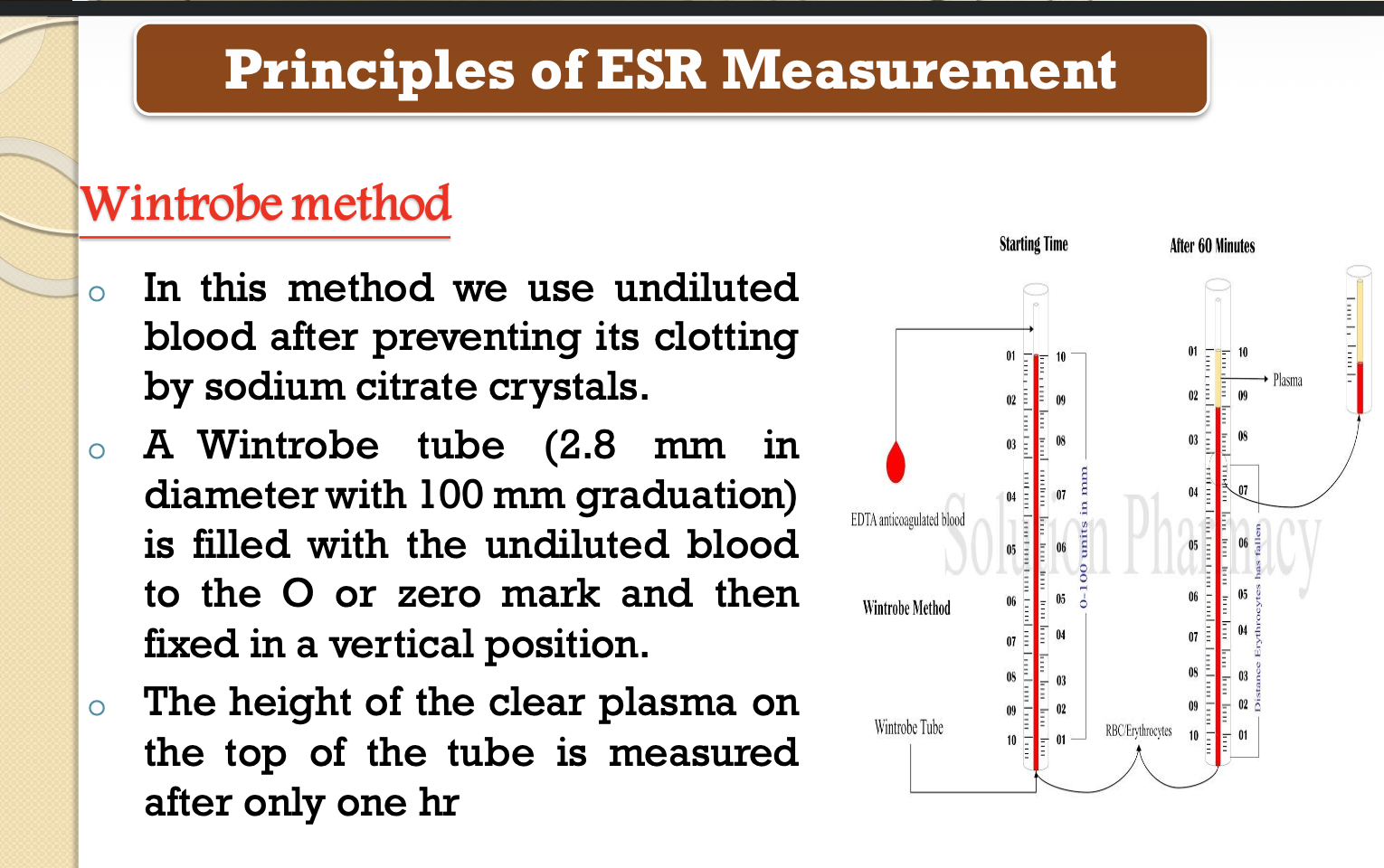
ESR ( wintrobe method )
mention definition and methods of ESR
Def —> It is the rate of the downward descent of RBCs in a vertical column of blood
It is measured by 2 methods
1. Westergren method.
2. Wintrobe method
what rate of RBCs decent depends on ?
A —- Plasma viscosity
B —- Rouleaux Formation
what is the Rouleaux Formation means ?
Means clumping of RBCs together to form clumps like a coins
This will increase the weight of RBCs and decrease frictional resistance, so it increases ESR
Materials of Westergren Method ?
Westergren tubes
Special racks
3.8% sodium citrate
5 ml sterile syringes and test tubes
diameterاعرف الفرق بين الطريقتين كويس في شكل الانابيب وال
ومترقمه لغايه كام
Normal values of ESR in Westergren method
in Male first hour — 3-5mm second hour — 6-10mm
in Female first hour — 8-10 mm second hour — 16-20mm
Normal Values of ESR in Wintrobe method
Male 15mm /hour.
Female 20mm /hour.
physiological factors increases ESR
1. Old age
2. Females
3. Pregnancy
4. During menstruation
5. Muscle exercise
physiological factors decreases ESR
1. Newborn
2. Males
3. High altitudes
pathological factors increases ESR
1. Acute inflammation such as tonsillitis
2. Chronic infections such as T.B.
3. Malignancy
4. Tissue trauma
5. Fevers and Rheumatic fevers
pathological factors decreases ESR
1. Polycythemia
2. High cholesterol contents
3. Hyperviscosity of plasma
Clinical Significance of ESR ?
ESR is not a specific and diagnostic test but it is prognostic test
1. It detect the presence and severity of disease
It gives an idea about the activity of disease
It is used to follow up of disease and effect of treatment
Haemoglobin (Hb) represents ….. of RBC volume
consists of….. heme groups combined with … molecule of globin
34%
4
1
Normal value of HB
1. Adult male: 14-16 gm % (average 15gm %).
2. Adult female: 12-16 gm % (average 14gm %).
3. Newly born infant : 18 gm %
4. Children : 12 gm %

????
Sahli hemoglobinometer set
why we use it ?
determination of Hb content
Advantages of Sahli Method ?
1. The method is simple, quick, and fairly accurate.
2. It does not require any costly apparatus because it needs only direct color matching.
3. Its cost is minimal and can, therefore, be used in mass surveys.
Significance of Hb determination ?
Diagnosis of anemia, polycythemia
Calculations of some blood indices MCH ,MCHC
and useful in determination of the type of anemia hypochromic or normochromic
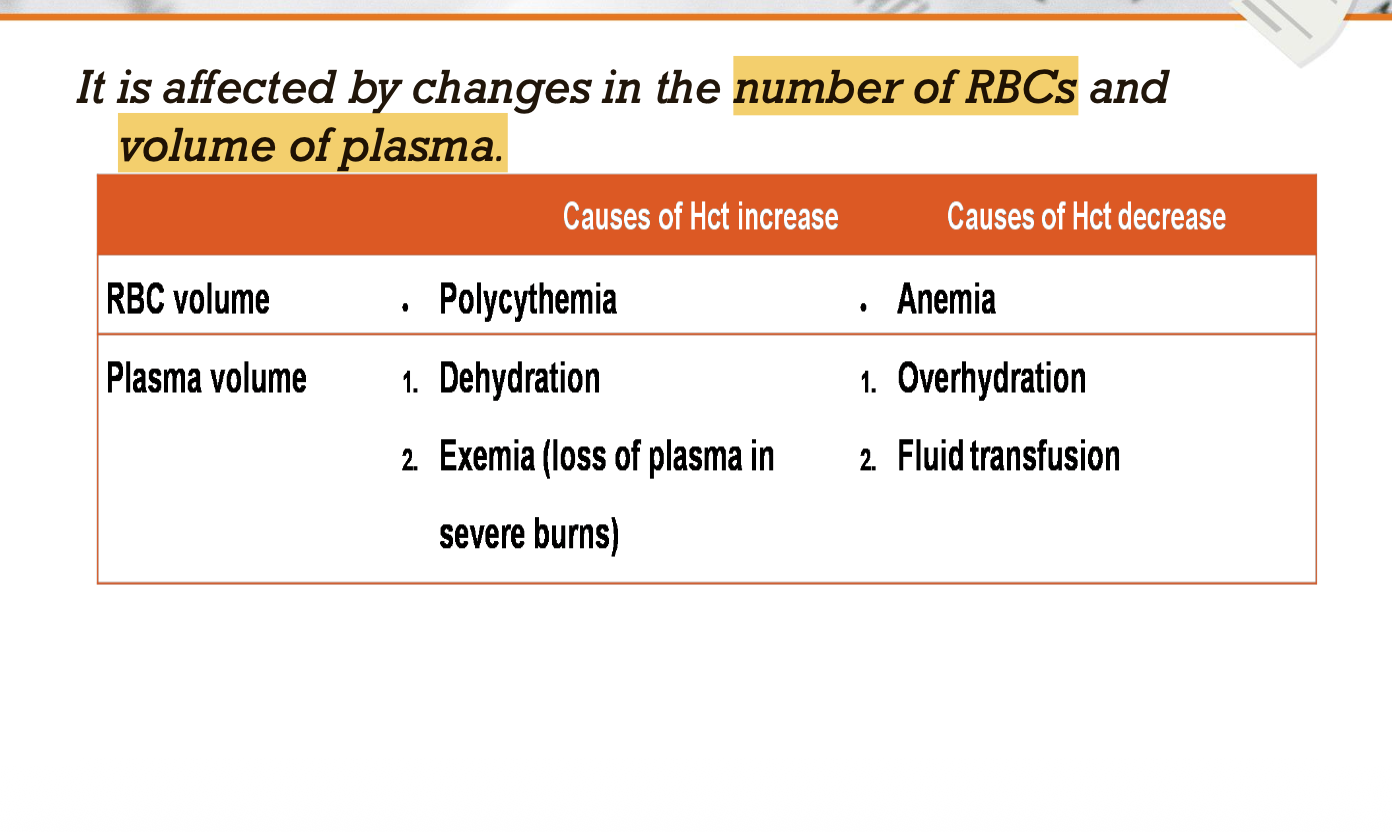
Definition of Hematocrite (HCT)
• It is the ratio of RBCs volume to total blood volume.
• RBCs volume/total blood volume x 100
other name ?
Packed Cell Volume (PCV)
Normal value of HCT
• Adult male : 42-48%
• Adult female: 38-42%.
• Newly born : 55%
• Children : 36%
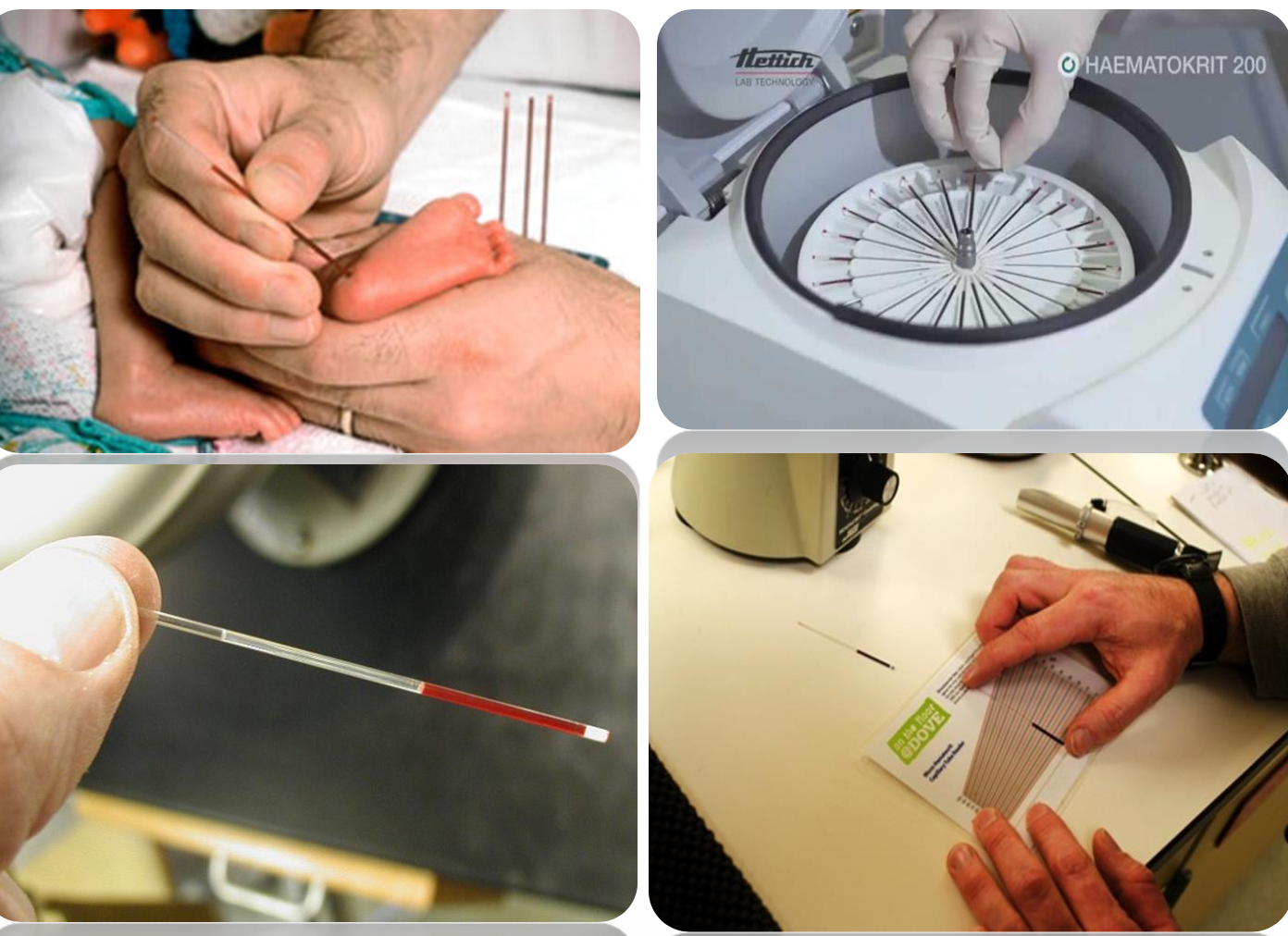
mention two methods of HCT measurement
A) Macrohematocrite method or (Wintrobe tube method)
B) Microhematocrite method or (Capillary tube method)
???
Macrohematocrite method

???
Microhematocrite method
in Macrohematocrite method
Venous blood anticoagulated with ….. or ……
Centrifuge the tube at …. r.p.m for …. minutes.
Venous blood anticoagulated with EDTA or Na citrate
Centrifuge the tube at 3000 r.p.m for 15 minutes
in Microhematocrite method
The tubes are centrifuged at a higher speed ….. r.p.m for …… minutes.
The tubes are centrifuged at a higher speed 6000 r.p.m for 5 minutes.
advantage for Microhematocrite method
Microhaematocrit is easier, more accurate and use a small amount of blood (commonly used in newly born infants)
Factors affecting hematocrite ?
Significance of hematocrite measurement ?
1. Diagnosis of anemia, polycythemia.
2. Calculation of blood indices (MCV, MCHC).
3. Calculation of renal blood flow, blood volume.
Significance of hematocrite measurement ? مش بالغلط
Calculation of renal blood flow
Hbديه مهمه جدا لان ده اللي بيفرق بينها وبين ال
MCV ? Formula ?
It measure the average volume of single RBC

normal value ?
mention other conditions
90±7 fl
MCV is high (above 97 micro3 ) → macrocytic
MCV is low (below 83 micro3) → microcytic
normal → normocytic
MCH ? formula ?
Expresses the average amount of Hb present in single RBC

significance in MCH
➢Normochromic cell: 30±3 pg.
➢Hypochromic cell: below 27 pg.
MCHC ? Formula ?
Expresses the %ratio of Hb concentration in a single RBC in relation to its volume
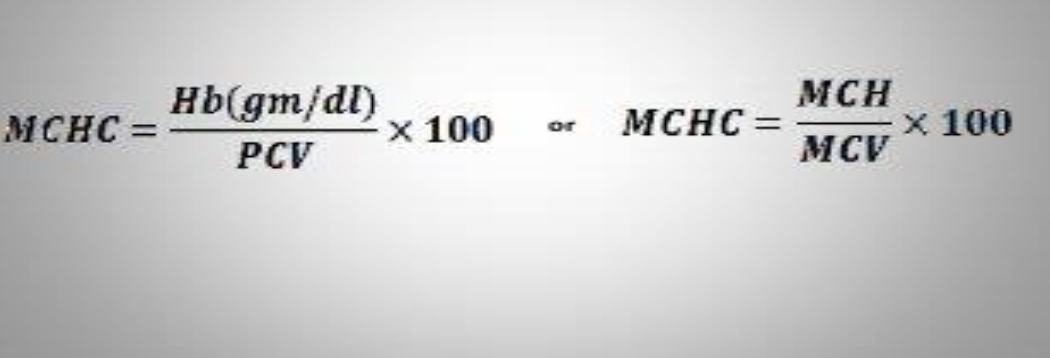
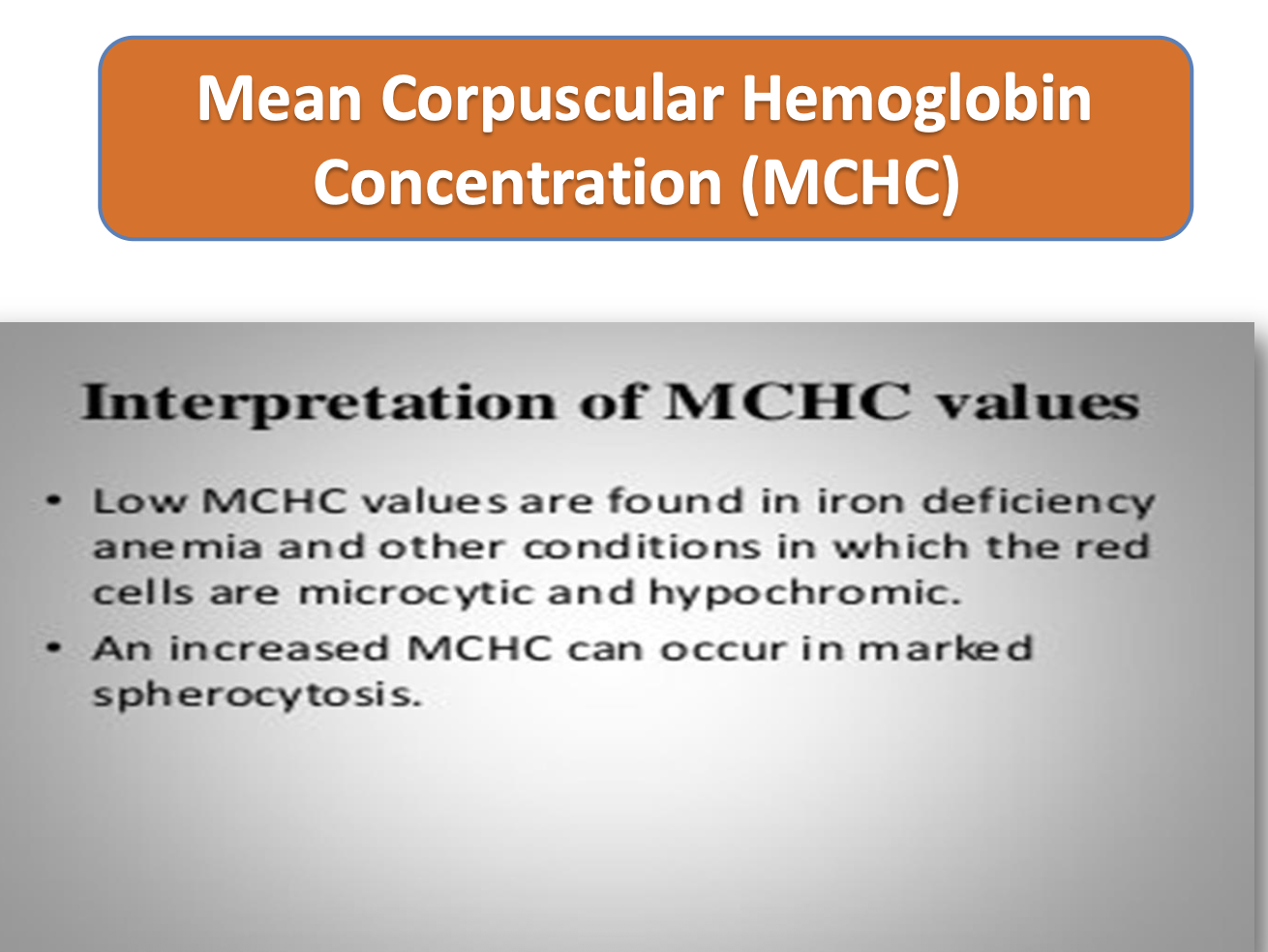
Significance of MCHC ?
• Normochromic cell: 30- 36 gm%
• Hypochromic cell: below 30 gm%
info
➢ There is no hyperchromic RBC because, it contains the maximal concentration of Hb.
➢A large cell may contain more Hb, but its percentage saturation will not be more than 36%.
info 2
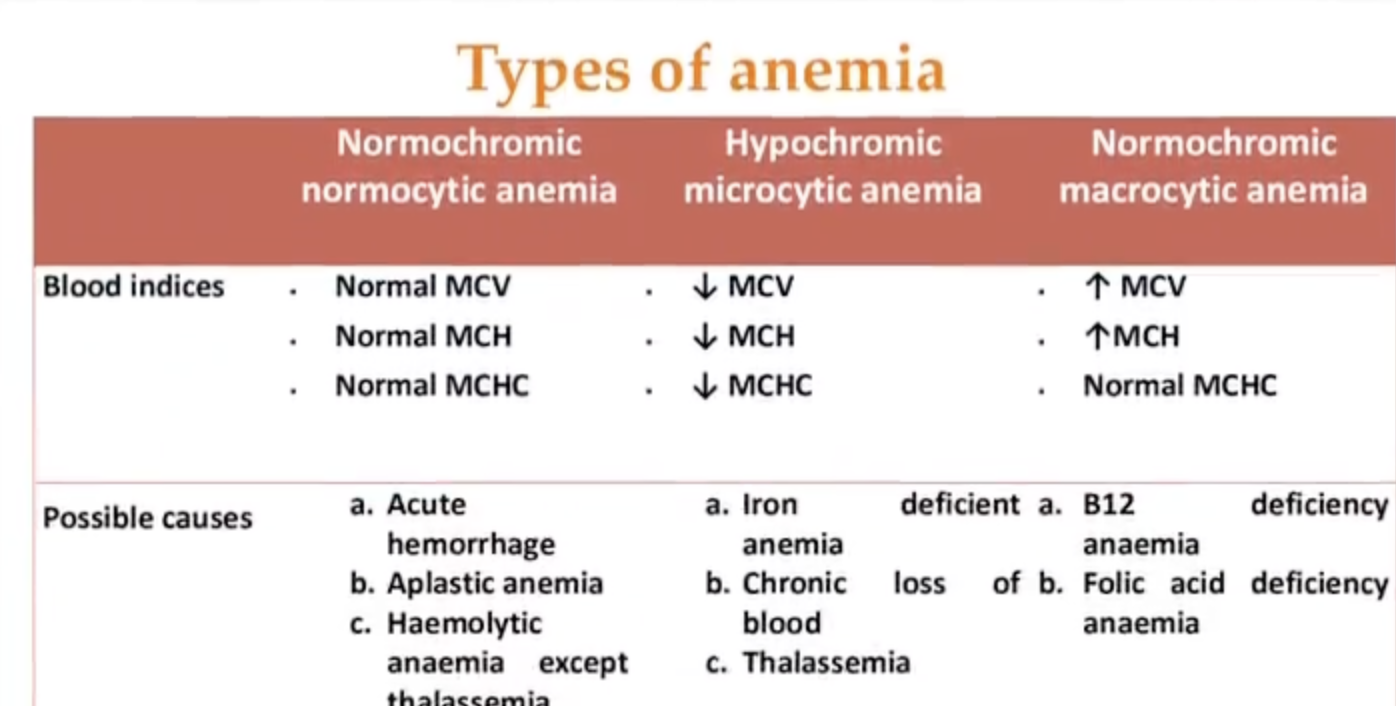
Types of anemia ? مهمه جدا الدكتور ماكده عليها
Mention the two systems related to the surface of red blood cell surface
ABO system
Rh system
النسب لكل جروب
وصور توضيحيه
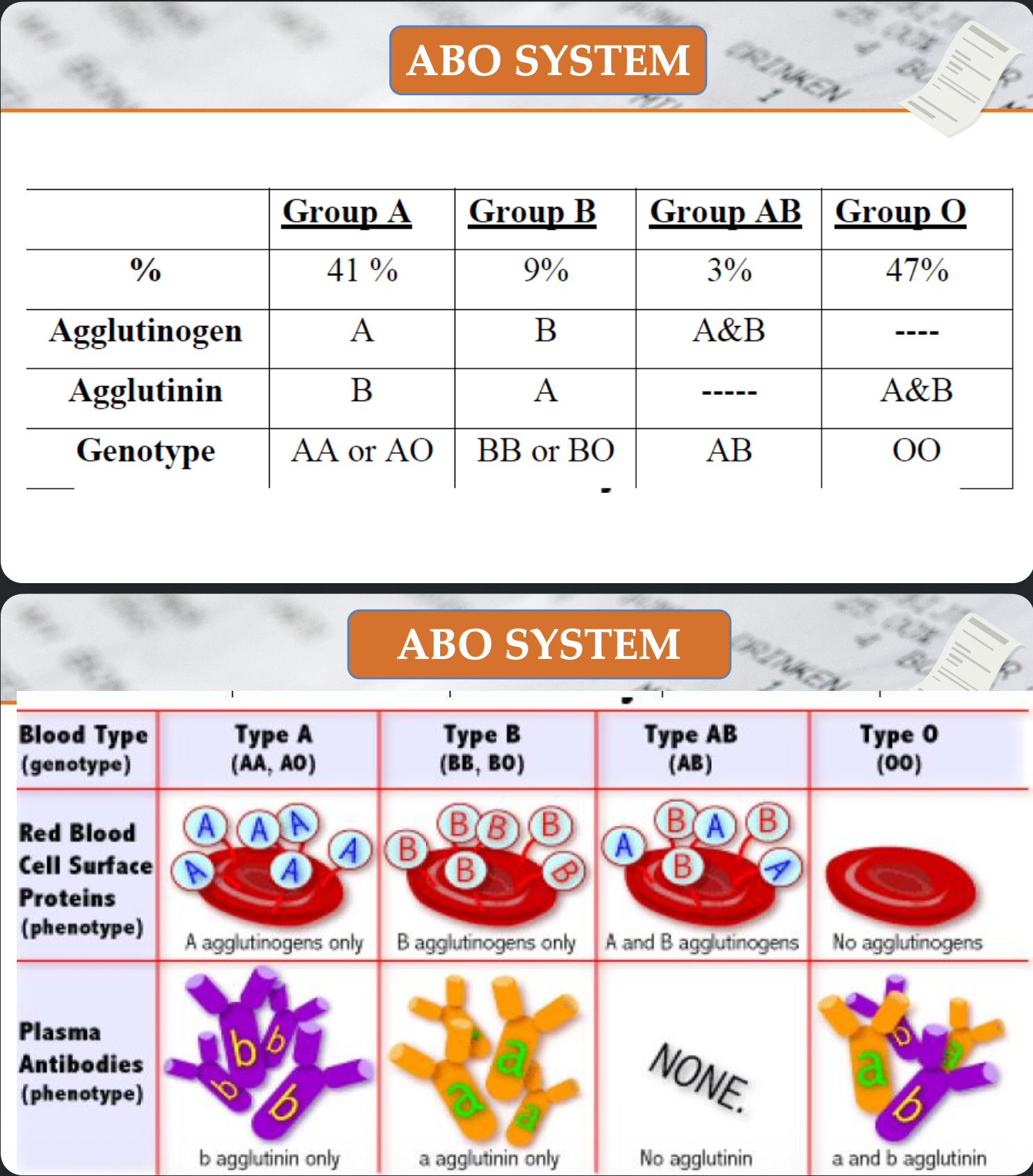
Importance of ABO system ?
1. Blood transfusion
2. Disputed parenthood
3. Medicolegal importance
4. Susceptibility to certain diseases
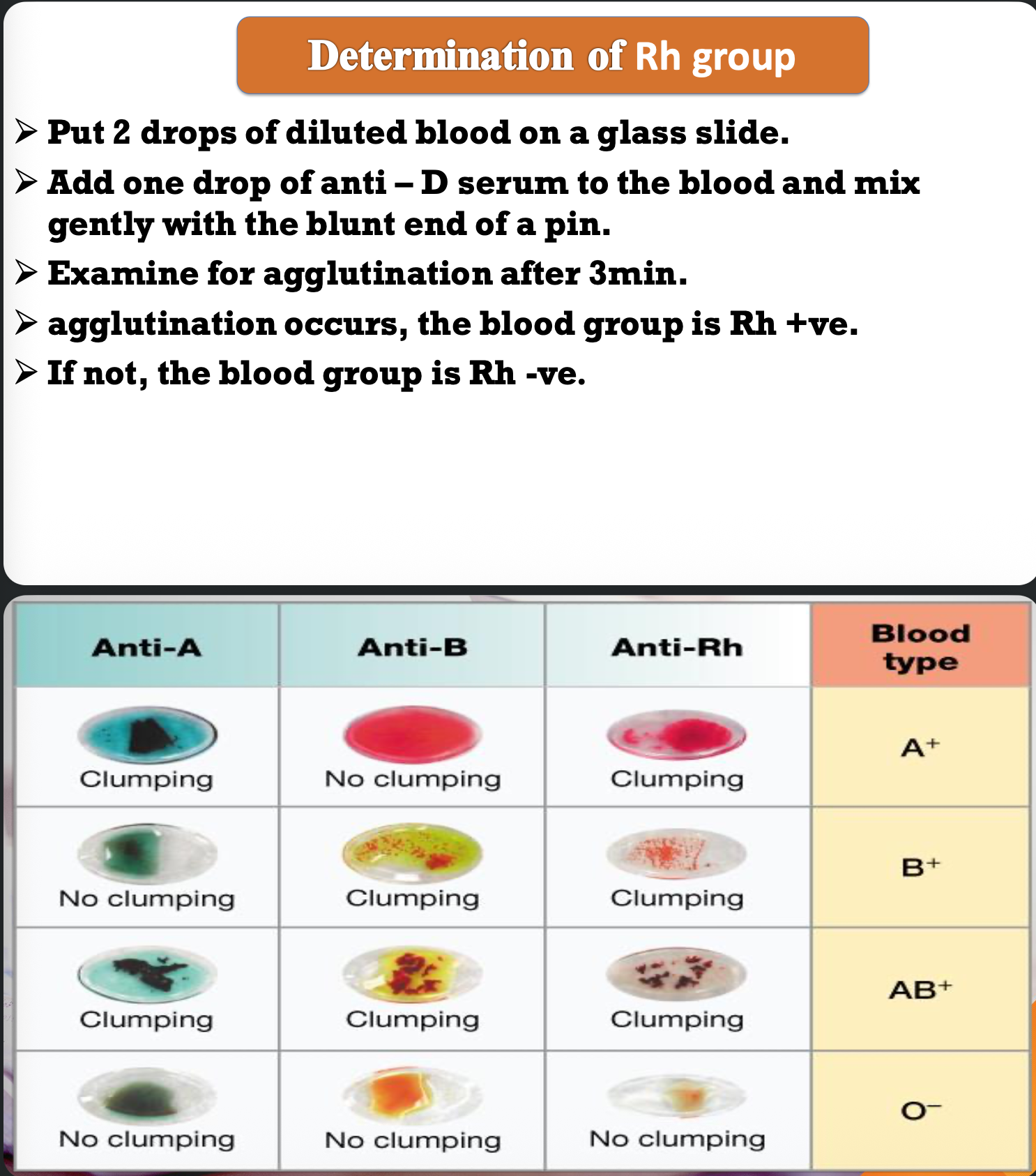
There are six common types of Rh antigens named …..,….,….,….,…,….,….,
There are six common types of Rh antigens named C, D, E, c, d, and e.
which type is most antigenic ?
type D-antigen
Presence of D-antigen→ Rh +ve.
Absence of D-antigen→ Rh -ve.
مين اشهر في المصريين
Rh positive
Is Rh have antibody ?
Noooo
Importance of Rh-factor ?
1- Blood transfusion
2- Hemolytic disease of the newborn (erythroblastosis foetalis)
Manifestation of erythroblastosis foetalis ?
1. Anemia.
2. Severe jaundice.
3. Many immature RBC’s (erythroblasts) in the foetal blood.
4. Kernicterus: it is a neurologic disease develops due to deposition of excess bilirubin in some brain centers (mainly motor areas) causing their damage
Neurologic disease develops due to deposition of excess bilirubin in some brain centers (mainly motor areas) causing their damage ?
Kernicterus
Treatment and Prevention ?

بص على دول
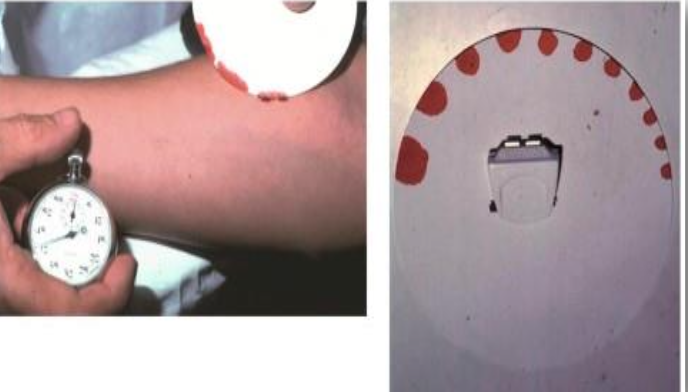
This test is used to measure ?
Bleeding time
def ?
from where we take the species ?
It is the time needed for bleeding to stop from small puncture
finger-tip ear-lobe
Significance of Bleeding time
time ?
measures ?
prolonged in…..?
normal in ….?
2-6 minutes
It measures the functions of platelets
prolonged in purpura and Von willbrand disease
usually normal in hemophilia
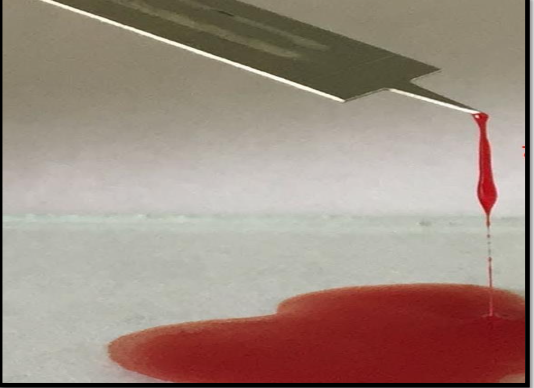
This test is used to measure ?
Clotting time
Significance of clotting Time
time ?
prolonged in ….?
normal in … ?
5-8 minutes
prolonged in hemophilia and other clotting factor disorders e.g. vit K deficiency, liver diseases, and use of oral anticoagulants
it is normal in purpura
to measure the extrinsic pathway of coagulation we use …. ?
Prothrombin time
significance of PT
time ?
prolonged in…. ?
Normally prothrombin time is 12-16 seconds.
it is prolonged if there is a deficiency of one or more factors of the extrinsic pathway of coagulation e.g. in liver diseases , oral anticoagulants and vitamin K deficiency
to measure the intrinsic pathway of coagulation we use …. ?
aPTT ( Activated partial thrombosisplastin Time )
Normal time for aPTT ?
25 -- 39 Seconds
اقلب
ادعو له بالرحمه ولكل الشهداء والجرحى والاسرى في غزه
وان يثبت الله قلوب اهاليهم
