
Looks like no one added any tags here yet for you.
Which tubes have no anticoagulant?
plain red/gold and tiger top (SST)
What tube for serology testing?
plain red/gold
What tubes for chemistry panels?
plain/red gold
What tube for hematology?
purple / EDTA
What tube for coagulation and platelet function?
light blue / sodium citrate
What tube for troponin?
green / heparin
What tube for ammonia?
green / heparin
what tube for blood bank testing?
purple / EDTA
what tube for acid-base imbalance?
green / heparin
what tube for arterial blood gasses?
green / heparin
what tube for blood alcohol testing?
gray / potassium oxalate
what tube for glucose?
gray / potassium oxalate
Serum
liquid portion of CLOTTED blood samples
(lack of free-floating clotting factors)
plasma
liquid portion of ANTICOAGULATED whole blood
(contains clotting factors/coagulation proteins)
What abnormalities are present when RBCs are hemolyzed in the sample?
increased level of serum potassium
RBC/WBC count is decreased
(inaccurate anemia and inaccurate electrolytes)
Which gauge needle is appropriate for venipuncture?
20-22 gauge
Which gauge of needle for blood donations or mass transfusions?
14-18 gauge
What size needle is not appropriate for routine blood collection? What are they used for?
smaller than 22 gauge (damages RBCs- hemolysis)
lidocaine, botox, small injections
Structure/Staffing of the clinical laboratory department
medical director- supervision & management, usually a pathologist
laboratory officer- administrative direction & quality control data, usually a medical technologist
testing personnel- medical technologist (MT) &medical laboratory technicians (MLT)
phlebotomists and laboratory assistants- specimen collection, basic lab procedures under supervision
What artery is most commonly used for arterial blood sample?
Radial artery in the wrist (FIRST CHOICE)
What PE test is necessary before using the radial artery for an arterial blood sample and why?
Modified Allen Test- to determine adequate circulation through ulnar artery.
In case radial artery is damaged, ulnar artery will still adequately circulate through the hand.
In the event that the radial artery cannot be used for arterial blood samples, what artery could you use instead?
brachial artery near basilica vein in antecubital area
How does eating affect venous blood samples?
increases serum glucose and triglyceride levels
What tests are performed after the patient has fasted?
CMP, liver functions
glucose and triglyceride/ lipid tests
What tests are elevated due to strenuous exercise/
How does strenuous exercise affect venous blood samples?
increases LD, CK, serum creatine, potassium, and WBC count.
Increased hematuria and proteinuria may be observed
How does emotional stress affect venous blood samples?
falsely increase WBC cont
How does hemolysis affect venous blood samples?
increases serum potassium, magnesium, phosphorous, LD, and acid phosphatatse
decreases RBC count and abnormal RBC indices
24 hour urine specimen collection
- first void is not kept. time is recorded.
- collect all urine voided over 24 hour time period
- last void at end of time period added to total volume
*must be refrigerated during collection to avoid bacteria overgrowth*
Types of urine tests
24 hour - quantitative procedure for analytes (protein, creatinine, calcium, cortisol)
random urine- routine urinalysis (UA); UTI, pyelonephritis, renal function, metabolic/systemic diseases
first morning urine - pregnancy test (inc. hCG)
clean catch midstream - microbiology (urine culture, antibiotic sensitive testing UCx)
What are the effects of improper urine storage?
inc bacterial growth, nitrite, pH, turbidity
dec glucose, ketones, bilirubin, urobilinogen
disintegration of cells, casts, crystals
color change
Causes of anemia?
increased destruction of RBCs - hemolytic anemias
decreased production of RBCs - aplastic anemias
excessive blood loss
aplastic anemia
destruction in bone marrow / failure to produce RBCs normally
pancytopenia
abnormal depression of all cellular elements of blood
-penia vs -cytosis/-philia
-penia: dec in number of cells
-cytosis / -penia: inc in number of cells
hematopoesis
formation of RBCs
hematopoesis locations
after birth, bone marrow is the only site
birth-20 years: long bone
after 20 years: flat bones, vertebrae, pelvis
Peripheral blood smear
-EDTA anticoagulated blood on glass slide stained with Wright-Giemsa stain (purple)
-examined for WBC types & percentage, abnormal RBC morphology, platelet count estimate and clumping
How are reference ranges determined?
collect from large population and determine range
erythrocyte vs leukocyte vs thrombocyte
erythrocyte- red blood cell
erythrocyte- white blood cell
thrombocyte- platelet
WBC differential
stained with wrights stain then identified and classified w/ microscope
result report as relative count (percentage of each type)
Never Let Monkeys Eat Bananas
neutrophils
lymphocytes
monocytes
eosinophil
basophil
reticulocyte
polychromatic erythrocyte (immature RBC)
matures in 1-2 days in periphery
what does reticulocyte count indicate?
RBC production in bone marrow
seen in peripheral samples
What increases retic count?
-hemolytic anemias (sickle cell anemia, G-6-PD deficiency, autoimmune antibody formation)
-acute or chronic bleeding
-following treatment for iron deficiency anemia
-following treatment of factor deficiency anemias (hemophilia a/b, von willebrand’s disease)
What decreases retic count?
-aplastic anemia
-ineffective erythropoiesis
reticulocyte appearance with wrights stain
more than considered normal
stain differently than mature rbcs
Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR)
detects inflammation
very non-specific
replaced with C-reactive protein (CRP) at most facilities
What causes increased destruction of RBCs?
What does tissue hypoxia result from?
reduced oxygen carrying capacity of carboxyhemoglobin / decrease in oxygen delivery to body tissues
What does tissue hypoxia cause? Which organ and hormone?
****in kidneys- stimulates inc erythropoietin production
Lifespan of RBC
120 days
Where does destruction of RBCs occur?
by macrophages in spleen
RBC indices
MCV- size of cell (always 80-100)
MCH- weight of Hgb per cell
MCHC- concentration of Hgb per cell
RDW- range of sizes of cells
term for increased variability of cell sizes on peripheral smear?
anisocytosis
Microcytic
MCV less than 80
Normocytic
MCV 80-100
Macrocytic
MCV greater than 100
most common cause of megaloblastic anemia
low vitamin B12 and low folate
Which RBC indices is indicative of megaloblastic anemia?
MCV >100 (macrocytic)
What do toxic granulation and vacuoles indicate?
acute bacterial infections
What type of cell is this and what does it indicate?
Reactive lymphocyte- abundant, pale blue staining unevenly, appears “soft” and is easily indented by surrounding RBCs, abnormally shaped and borders less defined
indicates viral infections (infectious mononucleosis, hepatitis, pneumonia, mumps, etc), pertussis (whooping cough), toxoplasmosis
absolute leukocyte count
WBC ct x leukocyte diff
Megakarocytes
produces platelets through megakaryopoiesis
(CFU-Meg/stem cell → megakaryoblast → magakaryocyte → platelets)
C-reactive protein test
why is G6PD deficiency significant?
exposure of RBCs in affected persons to oxidizing drugs causes RBCs to lyse (hemolytic anemia)
What is a bone marrow aspirate indicated for?
assess amount and nature of cell growth and maturation (uses red bone marrow from pelvis)
used to diagnose polycythemia vera, acute and chronic leukemias, myelodysplastic syndromes, aplastic anemia
how is anemia classified
based on RBC morphology- size and color intensity
what RBC morphology is associated with hereditary spherocytosis
spherocytes (appear microcytic and hyper chromic due to loss of central pale area)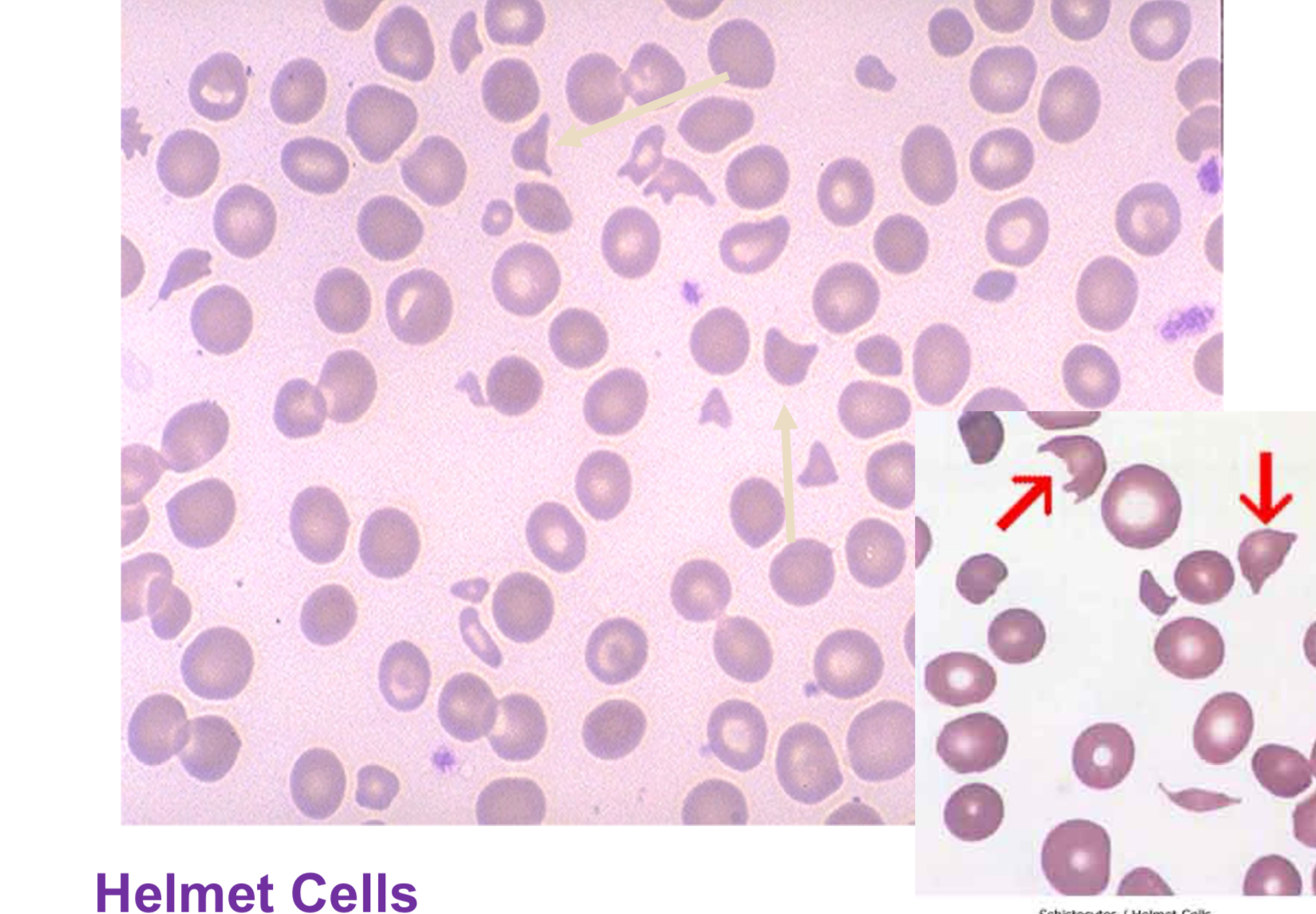
stomatocytes (rectangular or slit-like central pale area)
what RBC morphology is associated with G6PD deficiency
helmet/bite cells, blister cells (looks as if bite was taken out of it)
what RBC morphology is associated with DIC
schistocytes (small, bizarre shaped cell fragments)
what RBC morphology is associated with sickle cell crisis
schistocytes (small, bizarre shaped cell fragments)
what RBC morphology is associated with severe burns
schistocytes (small, bizarre shaped cell fragments)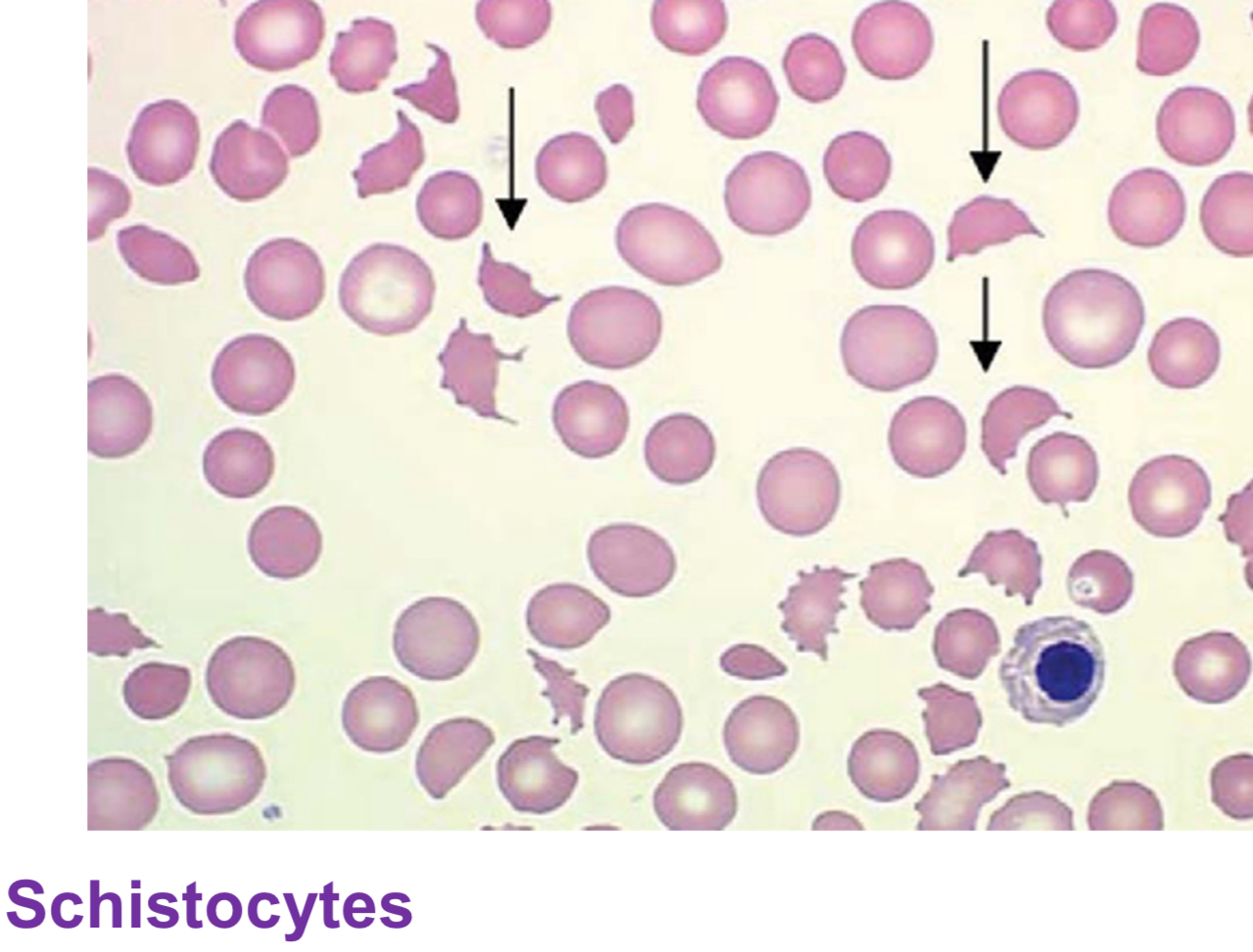
what RBC morphology is associated with multiple myeloma
rouleaux (stack of coins/ partially adhering to each other)
What is left shift and how is it determined?
neutrophils present in blood are at a slightly earlier stage of maturation than usual. results in an increased number of band neutrophils (bandemia)
indicates acute bacterial infection
What is hemoglobin composed of?
spheroid protein composed of 4 global chains (1 pair of alpha or zeta chains, one pair of non alpha chains - delta, beta, epsilon, gamma) with 4 heme molecules that bind and transport 4 O2 molecules
What 3 parts are needed for hemoglobin synthesis to occur? what stage in erythropoesis does it occur?
dependent on: adequate iron delivery and supply, adequate synthesis of heme molecule, adequate globin chain synthesis
begins in the Rubricyte (polychromatophilic normoblast) stage of RBC maturation (right before nucleus ejection)
carboxyhemoglobin
hemoglobin - carbon monoxide complex
comprises very low concentration of normal hemoglobin
Elevated in CO poisoning → tissue hypoxia causes cherry red blood
methemoglobin
hemoglobin in which Fe2+ (ferrous iron) is oxidized to Fe3+ (ferric iron) resulting in molecule that’s unable to transport oxygen
pathophysiology of Hgb SS (defective hemoglobin molecule )
forms when polymers which damage RBC membrane resulting in the sickle cell shape when RBC is deoxygenated
sickle cells cannot travel through small capillaries resulting in vast-occlusion, tissue hypoxia, etc
thalassemia
blood disorder when body doesn’t make enough Hgb
difficult to diagnoses, best study is genetic testing
alpha thalassemia
lack of alpha chain production
beta thalassemia
reduced or absent beta chain production
elevation of Hb F may indicate, elevation of Hb A2 level confirms diagnosis
best test to evaluate HGB abnormalities
hemoglobin electrophoresis
purple tube - EDTA
Where is the majority of iron in the body?
hemoglobin contained in RBCs (70%)
How is iron transported? What are the storage forms?
transferrin transports iron
storage forms- ferritin (soluble form) and hemosiderin (insoluble form)
best test to evaluate iron body stores
serum ferritin level
What are the causes of Fe deficient anemia?
chronic blood loss (GI bleeding/heavy menstruation)
increased body iron usage (pregnancy, lactation)
inadequate dietary iron intake
decreased iron absorption (intestinal disorders, post-small bowel resection, vit c deficiency)
What will you see on iron study labs for IDA (iron deficient anemias)?
dec serum iron
inc TIBC
dec trans-ferrin
dec serum ferritin
dec or absent body iron stores
pathophysiology of sideroblastic anemia
defective incorporation of iron into heme molecule- iron insertion into porphyrin ring prevented
inherited- rare sex-linked disorder, or acquired- alcohol abuse, lead poisoning, drugs that inhibit B6
results in accumulation of iron in mitochondria of RBC precursors
dec iron available, dec hemolgobin and hematocrit
hemochromatosis
inherited autosomal recessive disorder which results in idiopathic increase of iron absorption in intestine
slow, chronic build up of iron, accumulates outside of RE cells causing injury to parenchymal cells
porphyria cutanea tarda
most common porphyria (enzyme defect in heme synthetic pathway)
sun exposed areas develop blisters (vampire)
heme intermediates accumulate in tissues
petechiae
small pinpoint intradermal hemorrhage; <2 mm diameter
represent extravasation of blood into skin
stays bright red until healed
purpura
group of petechiae; (2mm-1cm)
can be palpable or non-palpable
ecchymosis
intradermal hemorrhage(s), larger than purpura often referred to as “bruises”; greater than 1cm
turns yellow/green when healing
What is exposed during an injury to the bloodstream to start the coagulation process?
subendothelium
How does aspirin affect platelets?
prevents platelets from signaling each other by blocking receptor sites
results in platelet inactivation
reduces number of platelets that adhere to injury site
Which studies assess platelet function?
bleeding time
platelet count
platelet closure time
How do platelets and vonWillibrand factor interact?
reduction of platelet adhesion
Which factors are vitamin K dependent?
factor II- prothrombin
factor VII- stable factor
factor IX- Christmas factor
factor X- Stuart-prower factor
Which factor is the starting point of the common pathway?
factor X- Stuart-prower factor