AP HUG Chapter 9 Agriculture
Origination’s of Hunter-Gathering has multiple hearths from over 10,000 years ago:
-Fertile Crescent (Middle East near modern day Iraq)
-Southwest Asia
-Sub-Saharan Africa
-Indus River Valley
-Mesoamerica
Subsistence and Commercial Agriculture-
Subsistence Agriculture - The production of plants and animals for self-sustainability
Subsistence Agriculture features:
-Habitat Loss
-Poor water quality (fertilizers and pesticides)
-Changes to natural landscapes (Increase in wetlands ie. rice paddies and rice fields)
-Increase diseases (Malaria)
-Increase in air pollution (Smoke from slash & burn ie. rice paddies)
-Mainly in LDC’s ( Developing Countries)
-Less machinery is used
-Ex. intensive farming
-Increase in food pressure
Commercial Agriculture - The production of plants and animals to sell in marketplace
Commercial Agriculture features:
-Mixed Crop and livestock farming
-Capital intensive (money driven)
-Crops differ depending on climate
-Mixed crops and livestock (for selling)
-Ranching
-Dairying (extensive form of agriculture)
-Large-scale grain production
-Mainly MDC’s ( Developed Countries)
-Poor air quality (spraying chemicals)
-Poor water quality (Runoff: Chemicals and soil erosion)
-Poor soil quality (Erosion, decreased nutrients, chemicals)
-Modified biodiversity (Mono-cropping & Destruction of natural landscapes)
-Water availability issues (Irrigation)
-Ex. extensive farming
*In developed countries, their leading source of protein is mean products while developing countries have a leading source of protein through cereal grains.
Commercial Agriculture products:
-Sugarcane
-Tobacco
-Corn
-Coffee
In more Mediterranean commercial farming:
-Grapes
-Olives
-Citrus fruits
-Apples
Subsistence Agricultural products:
-Wheat
-Corn
-Beans
-Grains
-Spices
-Rice
Von Thunen’s Model:
Agricultural land and relation to agricultural business can vary due to what the production item(s) are.
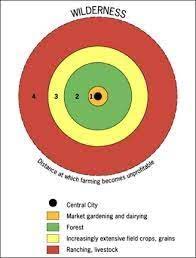
Ring 0 The central market.
Ring 1 is closer to the market having the highest land costs because of it’s proximity to the market which means less accessible land. It needs to be closer to the market because the plants such as fruit, vegetables, milk, fish, poultry, red meats spoil quickly so they need to be transported quickly.
Ring 2 is closer to the market because it relatively close to market meaning there’s less accessible land. It needs to be closer to market to transport heavier items (Wood or minerals) which makes for a greater transportation cost.
Ring 3 is further from the market making for more accessible land but longer travel time. The transportation is also relatively low since the products being transported (Wheat, corn, etc) are light weight so there is lower transportation costs.
Ring 4 is the furthest from the market due to the more accessible land used for their cattle ranching and animal farming businesses. This ring is the cheapest when it comes to labor and transportation because the animals can transport themselves to the market place.
Bid Rent Curve 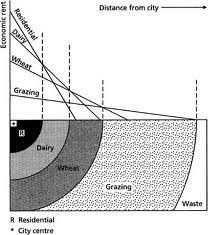
These models aren’t applicable today due to the fact that agriculture and landscapes including buildings have moved and developed to today, Von Thunen’s model is a model based off of fixed landscape and proximity between rural to urban areas.
Green Revolution:
Started in Mexico to increase wheat production and led to the creation of miracle seeds, new fertilizers, pesticides, GMOs, and the rapid diffusion of new technology
→ Global grain production increased by 45% from 1940 to 1990
→ Asia increased rice production by 66% by 1985
→ India can to supply its own wheat and rice by 1980s
It was able to increase the yield of crops and reduced hunger and famine, but world hunger isn’t eliminated because of social and transportation problems
Environmental Impacts:
- Pollution (water, soil, and air)
- Pesticides and chemicals
- Health concerns- chemicals
- Strain on water resources
- Conflict over water
- Irrigation systems
- Reroute water
- Lack of genetic diversity in seeds
- Increased vulnerability to disease and pests
- Increased fossil fuel consumption and pollution due to machines
Economic Impacts:
- Technology reduces the need for human labor = less jobs
- Higher level of crop failure due to less diversity = less income
- Higher-yielding crops are not farmable in drier climates (Africa)
- Increased economic inequality due to expensive $$ technologies and seeds
- LDCs and Periphery states impacted