Chapter 6: Axial Skeleton
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
long bone
leverage
short bone
provide stability and support
sesamoid bone
protect tendons from compressive forces
irregular bone
protects internal organs
tendon and ligament attachment
periosteum
periosteum
vascularized bone membrane
medullary cavity
hollow cavity with yellow bone marrow
yellow bone marrow
contains fat
diaphysis bone type
compact bone
epiphysis bone type
spongy bone
epiphyseal line formation
cartilage hardens from osseous tissue
endosteum
medullary cavity membrane that produces bone growth and repair
flat bone example
cranial bones, scapulaw, sternum, ribs
long bone examples
humerus, ulna, radius, femur, tibia, fibula, metacarpals, phalanges
short bone examples
carpals and tarsals
irregular bones
vertebral column and facial ones
sesamoid bone examples
patellae
epiphyseal plate
where bone growth occurs
articular cartilage
reduces friction and acts as a shock absorber
articulation
where two bone surfaces join
projection
attachment point for tendons and ligaments
holes
allow blood vessels and nerves to enter bones
meatus
opening into a canal
tuberosity
rough surface
facet
flat surface
process
prominent feature
tubercle
small rounded process
fossa
enlongated basin
canal
passage in bone
sulcus
groove
protuberance
protruding
osteoblast
forms new bone tissue
osteoblast differentiation
osteocyte
osteocyte function
maintain the mineral concentration of matrix via enzymes
lacuna
space surrounding osteocytes
cells with no mitotic activity
osteocytes and osteoblasts
saccral bones
5
coccyx bones
4
osteogenic cell
only bone cells that divide, found in deep layers of the periosteum and marrow
canaliculi
osteocyte communication and receive nutrients
lamellae
concentric calcified matrix rings
haversian canal
center of osteon that contain lymph nodes, blood vessels, and nerves
Volkmann’s canal
perforating canals that extend to the periosteum
axis
C1 vertabrae
manubrium
first piece of sternum
xyphoid process
inferior tip of sternum
body
middle and biggest portion of sternum
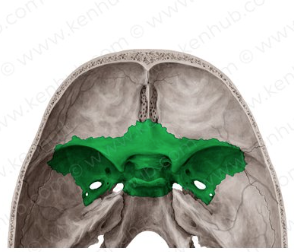
sphenoid bone
keystone of the cranial floor
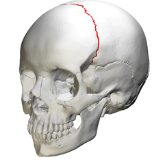
coronal suture
suture connecting parietal bone and frontal
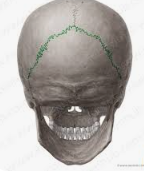
lamboid suture
parietal and occipital bone suture
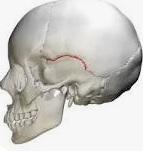
squamous suture
parietal and temporal suture
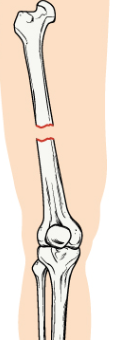
closed
bone breaks in two pieces
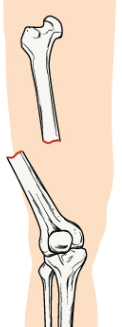
open
bone breaks in two and is sideways
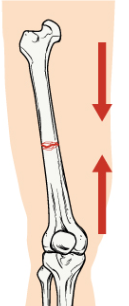
transverse
impact comes from both directions
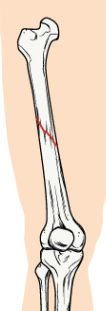
spiral
comminuted
bone breaks into several pieces
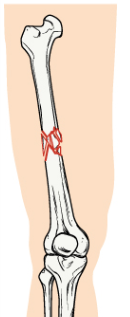
impacted
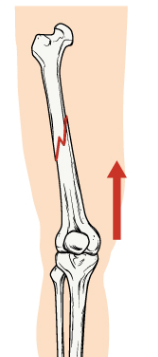
greenstick
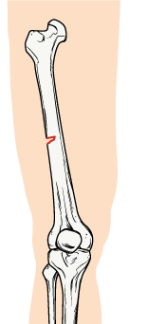
oblique
intramembranous ossification
forms skull flat bones, cranial bones, and clavicles
ossification center
clusters of mesenchymal cells
endochondral ossification
forms bones at the base of skull and long bones
appositonal growth
bone growth diameter wise