Mark K Lectures
1/378
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
379 Terms
pH
7.35-7.45
PaCO2
35-45
HCO3
22-26
PaO2
80-100
02 sat
> 95%
acidosis
pH < 7.35
alkalosis
> 7.45
S/S of acidosis
if pH is low, everything is low except potassium
bradycardia, constipation, absent bowel sounds, flaccid, obtunded, lethargy, coma, hyporeflexia, bradypnea, low BP, hyperkalemia
acidosis nursing intervention
ventilate with ambu bag due to respiratory depression
S/S of alkalosis
if pH is high, everything is high except potassium
tachycardia, tachypnea, HTN, muscle cramps, tetany, paresthesia, irritability, seizures, hyperreflexia, borborygmi, spastic, diarrhea, hypokalemia
alkalosis nursing intervention
suctioning due to seizures
respiratory acidosis
underventilation
respiratory alkalosis
overventilation
metabolic acidosis
everything else
metabolic alkalosis
prolonged gastric suctioning or vomiting
ventilator
a machine designed to move breathable air into and out of the lungs, aids patients who are physically unable to breathe, or breathing insufficiently
high pressure alarm
triggered by increased resistance to air flowca
causes of high pressure alarm
kinks in tubing, condensed water in dependent tube, mucus plugs
appropriate order to address high pressure alarm in a mechanical ventilator
unkink
empty water out of tubing
turn pt, ask pt to cough or deep breathe
suction
low pressure alarm
triggered by decrease in resistance
causes of low pressure alarms
main tubing disconnection, O2 sensor disconnection
interventions for low pressure alarm
reconnect the tubing unless tube is on the floor, then call RT and bag pt
what is the number one psychological problem in any abuse situation?
denialis commonly the number one psychological problem in any abuse situation, as it prevents the acknowledgment of the abuse and the need for help.
how to respond to patients in denial
confront them by pointing out the difference in what they say and what they do; don’t attack the person; good answer has “I”, bad answer has “you”
stages of loss and grief
denial, anger, bargaining, depression, acceptance
one place where denial is okay, provide support
dependency
when they get the significant other to do things or make decisions for them; the abuser is dependent
co-dependency
when the significant other derives self-esteem for doing things or making decisions for the abuser; the significant other is co-dependent
how to treat dependency/codependency
-dependent pts are abusers; confront them
-co-dependent pts have self-esteem issues; teach pts how to set limits and enforce them
-agree in advance on what requests are allowed, then enforce
-teach significant other to say no
-work on self-esteem on the co-dependent person
manipulation
when the abuser gets the significant other to do things or make interests that are not in the best interests of the significant other; the nature of the act is dangerous and harmful to the significant other
wernicke and korsakoff
-wernicke is an encephalopathy
-korsakoff is a psychosis
-they tend to go together
-psychosis induced by vitamin B1, thiamine deficiency
-the patient loses touch with reality due to vitamin B1 deficiency
S/S of wernicke/korsakoff
amnesia and confabulation
how to deal with a patient w/ wernicke & korsakoff
-redirect the pt to something they can do
characteristics of wernicke & korsakoff syndrome
preventable
arrestable (stop it from getting worse)
irreversible (70%) ~ will kill brain cells
antabuse and revia (disulfiram)
antabuse: alcohol deterrent, revia: antidote
aversion therapy: a type of behavior therapy designed to make a patient give up an undesirable habit by causing them to associate it with an unpleasant effect (works better in theory than in reality)
antabuse/revia onset and duration
takes 2 weeks to start working and lasts for 2 weeks
antabuse/revia pt teaching
-teach pt to avoid all forms of ETOH, not doing so may lead to symptoms of n/v or even death
-mouth wash, cologne, perfume, aftershave, elixir, most OTC liquid medicine, insect repellant, hand sanitizer, vanilla extract (NOT red wine vinaigrette)
upper drugs
caffeine, cocaine, PCP/LSD (psychedelics/hallucinogenics), methamphetamines, adderall
downer drugs
anything that is not an upper
upper overdose/withdrawal
overdose: things go up (euphoria, seizures, restlessness, irritability, hyperreflexia, tachycardia, increased bowels (borborygmi), diarrhea)
withdrawal: opposite
downer overdose/withdrawal
overdose: things go down (lethargic, respiratory depression/arrest, constipated, etc)
withdrawal: opposite
drug abuse in newborn
always assume intoxication, not withdrawal, in a newborn less than 24 hours after birth; more than 24 hours after birth, you can assume the newborn is in withdrawal
alcohol withdrawal syndrome
-occurs 24 hours after the person stops drinking
-non life threatening to self and others
-nursing care plan:
regular diet
semiprivate room anywhere on unit
pt is up ad lib
no restraints
delirium tremens
-occurs in less than 20% of AWS, 72 hours after drinking
-life-threatening to self and others
-nursing care plan
NPO or clear liquid diet
private room, near nursing station
restricted bed rest
restraints (vest or 2-point lockers)
aminoglycosides
“a mean old mycin”, used to treat serious, resistant, life-threatening, gram negative infections; unsafe at toxic levels; does NOT include mycins with “thro” in them; administer q8 hours
aminoglycoside toxic effects
ototoxicity: monitor hearing, balance, tinnitus (CN8 toxicity)
nephrotoxicity: monitor creatinine (24-hour Cr clearance better than serum Cr)
why are aminoglycosides only given IV/IM
they are not absorbed through the GI tract, therefore would not have any effects
only two cases when aminoglycosides are given PO
hepatic encephalopathy (decrease ammonia production by E. coli) and pre-op bowel surgery (sterilizes bowel)
who can sterilize my bowel
Neo Kan (neomycin and kanamycin)
why are troughs and peaks drawn
a drug has a narrow therapeutic window or index, which means there is a small difference between what works and what kills
when are troughs drawn
30 minutes before next dose
sublingual med peak
5 to 10 minutes after drug is dissolved
IV med peak
15 to 30 minutes after drug is finished (bag empty)
IM peak
30 to 60 minutes
positive inotropy
increase cardiac contractile force → ventricles empty more completely → cardiac output improved
positive chronotropy
increased rate of impulse formation at SA node → accelerate heart rate
positive dromotropy
increase speed that impulses from SA node travel to AV node
negative inotropy
weaken/decrease force of myocardial contractionne
negative chronotropy
decrease rate of impulse formation at the SA node → decelerate heart rate
negative dromotropy
decrease speed that impulses from SA node travel to AV node
calcium channel blockers
negative inotropic, chromotropic, and dromotropic effects on the heart
when do you want to use CCBs
antihypertensive
antianginal drugs
antiatrial arrhythmia
CCB side effects
headache and hypotension
names of CCBs
anything that ends in “dipine”, verapamil, cardizem (diltiazem): given continuous IV drip
parameters to assess before administering CCBs
BP (hold is SBP < 100)
normal sinus rhythm
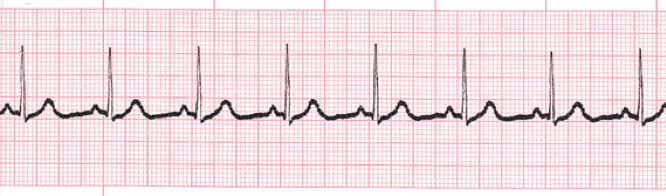
-there is a p wave, followed by a QRS, followed by a t wave for every complex
-peaks of the p wave is equally distant to the QRS and fall within 5 small boxes
ventricular fibrillation
-no pattern
-chaotic QRS complexes
![Ventricular Fibrillation: Causes & Treatment [ACLS Algorithm]](https://aclsonline.s3.amazonaws.com/live/cms/image/d3c64ab32f76459995598cdccb97eb8d/Ventricular-Fibrillation.png)
ventricular tachycardia
-sharp peaks with a pattern
-bizarre QRS complexes
asystole
-a flat line
-a lask of QRS complexes

atrial flutter

-P waves in the form of saw tooth wave
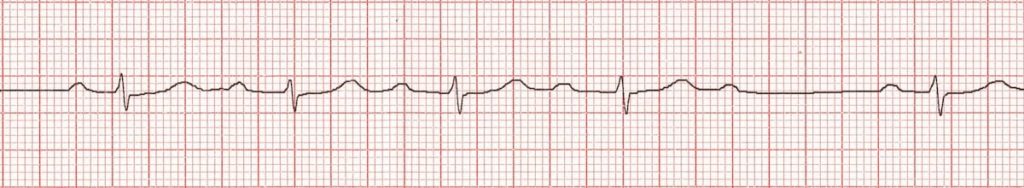
atrial fibrillation
-chaotic P wave patterns
1st degree AV block

-prolonged PR interval
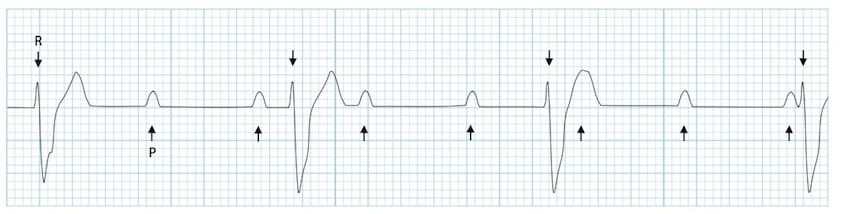
2nd degree AV block type 1
-progressive lengthening of PR interval until P wave is dropped
2nd degree AV block type 2
-p waves with missing QRS
3rd degree AV block
-no correlation between atria and ventricles
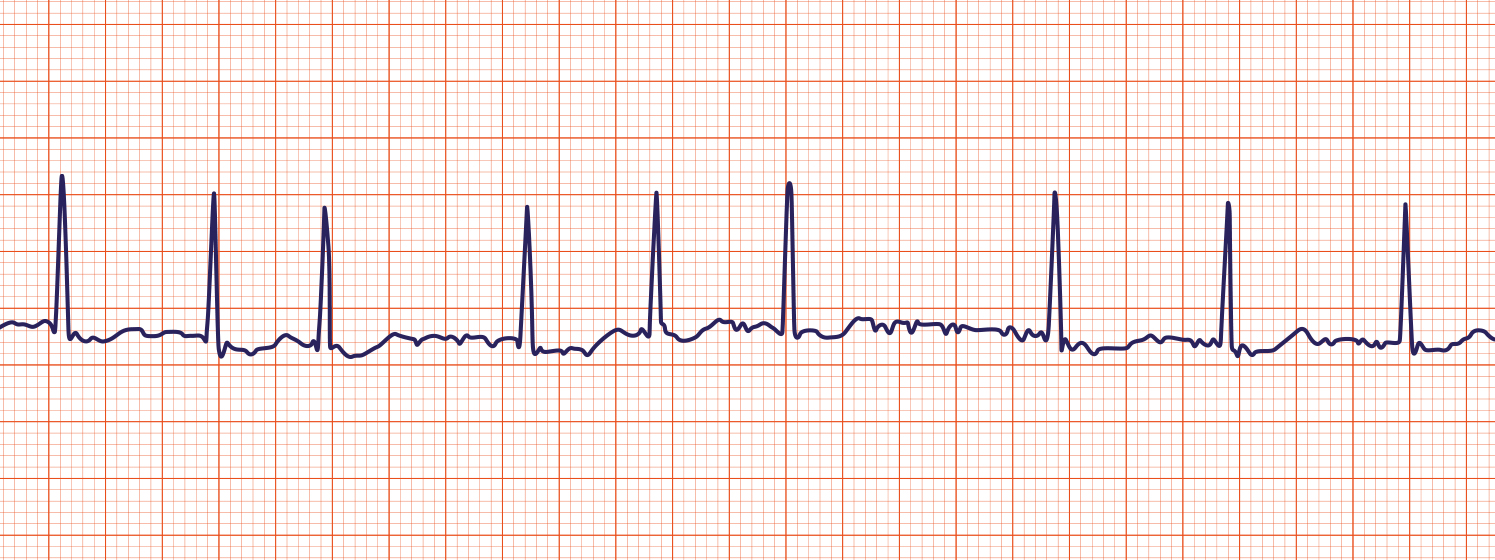
PVC
-periodic, wide, bizarre QRS complexes
-common after MI and is a low priority

QRS depolarization
ventricular
P wave
atrial
when should PVCs be elevated from low priority to moderate priority?
-there are more than 6 PVCs in a minute
-more than 6 PVCs in a row
-R on T phenomenon (falls on a T wave)
lethal arrhythmias
-asystole
-v-fib
-potentially v-tach (check for pulse to determine CO)
treatment of ventricular arrhythmias
amiodarone (used to be lidocaine as well)
treatment of atrial arrhythmias (supraventricular)
-Adenocard (adenosine): push in less than 8 seconds, 20 mL of NS right after; asystole will occur for about 3 seconds
-Beta blockers (end in -olol)
-CCBs
-Digitalis (digoxin), Lanoxin
beta blockers
-negative inotropic, chronotropic, and dromotropic effects on the heart
-antihypertensive, antianginal, antiatrial arrhythmia
-side effects: headache, hypotension
treatment of v-fib
defibrillate
treatment for asystole
epinephrine and atropine
chest tubes
purpose is to reestablish negative pressure in the pleural space, which makes things stick so that the lung expands when the chest wall expands
-in a pneumothorax, chest tube removes air
-in a hemothorax, chest tube removes blood
-in a hemopneumothorax, chest tube removes blood and air
apical chest tube
on top, removes air
basilar chest tube
at base, removes blood
post trauma or postsurgical patient needs
-always assume trauma and surgery in unilateral unless otherwise specified
-no need for a chest tube with a pneumectomy
-chest tube will be used for lobectomy or wedge resection
closed chest drainage devices
Jackson-Pratt, emission, pneumovac, hemovac, etc
what happens if a closed chest drainage device is knocked over?
-ask the patient to take a deep breath and set the device back up
-not a medical emergency, no need to call the physician
if the water seal of the chest tube breaks:
-clamp the tube
-cut the tube away
-submerge the end of the tube under sterile water
-unclamp the tube if it was initially clamped
-this all must be done in 15 seconds or less
if a chest tube get pulled out:
-take and gloved hand and cover the opening
-take a sterile vaseline gauze and tape 3 sides
bubbling in the water seal chamber
-if it is intermittent, it is good (document it)
-if it is continuous, it is bad and indicates a break/leak in the system (find it and tape it)
bubbling in the suction control chamber
-if it is intermittent, suction pressure is too low (increase it at the wall until it is continuous)
-if it is continuous, it is good (document it)
rules for clamping tubes
-do not clamp a tube for more than 15 seconds without a physician’s order
-use rubber, double clamps (will not puncture tubing)
parent teaching for patients with TRouBLe congenital heart defects
-needs surgery now/soon to live
-has slowed/delayed growth and development (failure to thrive)
-has a shortened life expectancy
-parents will experience a lot of grief, financial, and emotional stress
-patient is likely to be discharged home on a cardiac monitor
-after birth, patient will be in the hospital for weeks
-pediatrician or pediatric nurse will likely refer patient to a pediatric cardiologist
what is a TRouBLe congenital heart defect?
-shunts blood from Right to Left
-Blue (cyanotic)
examples of TRouBLe:
-tetralogy of fallot
-truncus arteriosus
-transposition of the great vessels
-tricuspid atresia
-totally anomalous of pulmonary vasculature (TAPV)
-left ventricular hypoplastic syndrome
examples of no TRouBLe heart defects
-ventricular septal defect (VSD)
-patent ductus arteriosus (PDA)
-patent foramen ovale
-arterial septal defect
-pulmonic stenosis
what do all children with a congenital heart defect have? (TRouBLe or no TRouBLe)
a murmur (an echocardiogram needs to be done to find out cause of murmur)