Week 7: Market Structures: Perfect Competition
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
perfectly competitive industry
an industry in which firms are price-takers
price-taking firm
a firm whose actions have no effect on the market price of the good or service it sells
Why does the agricultural industry reflect the perfectly competitive market model to a degree?
• Commodities such as tea, coffee, wheat, corn, soya beans, rape, barley, milk and so on are relatively homogeneous,
• are produced by many firms
• which are small in relation to the total market (which is global in some cases) and
• where firms are price takers.
• There are also relatively low barriers to entry.
The model can be used to analyse these markets, make predictions about how firms might behave and how far the market delivers both allocative and productive efficiency.
commodity (standardized product)
describes a good produced by different firms, but that consumers regard as the same good
free entry and exit
when new firms can easily enter into an industry and existing firms can easily leave that industry
sunk cost
a cost that has already been committed and cannot be recovered
productive efficiency
achieved when firms minimize the average cost of producing their goods
allocative efficiency
achieved when the goods and services produced are those most valued by society
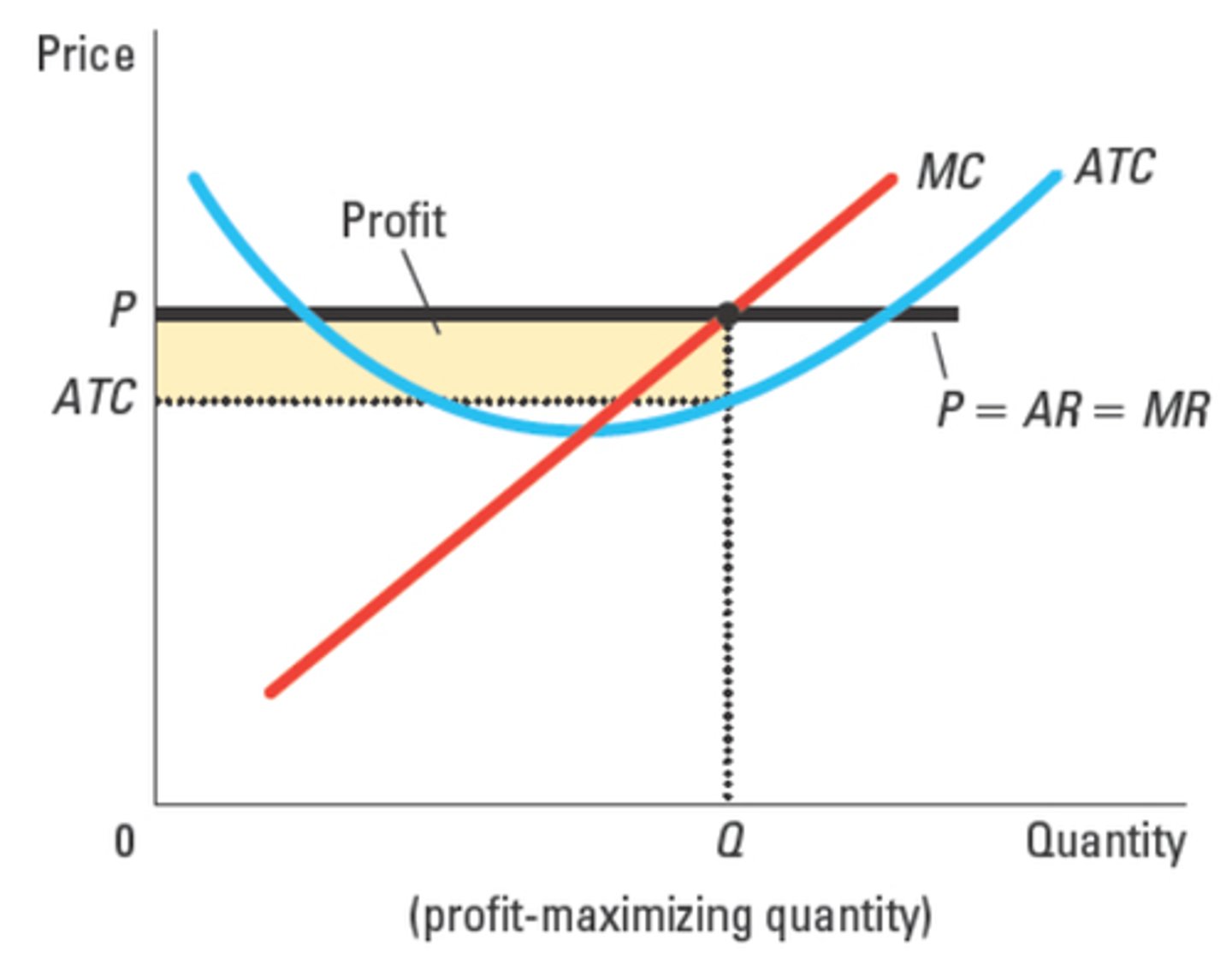
economic profit (supernormal profit)
a firm earning...
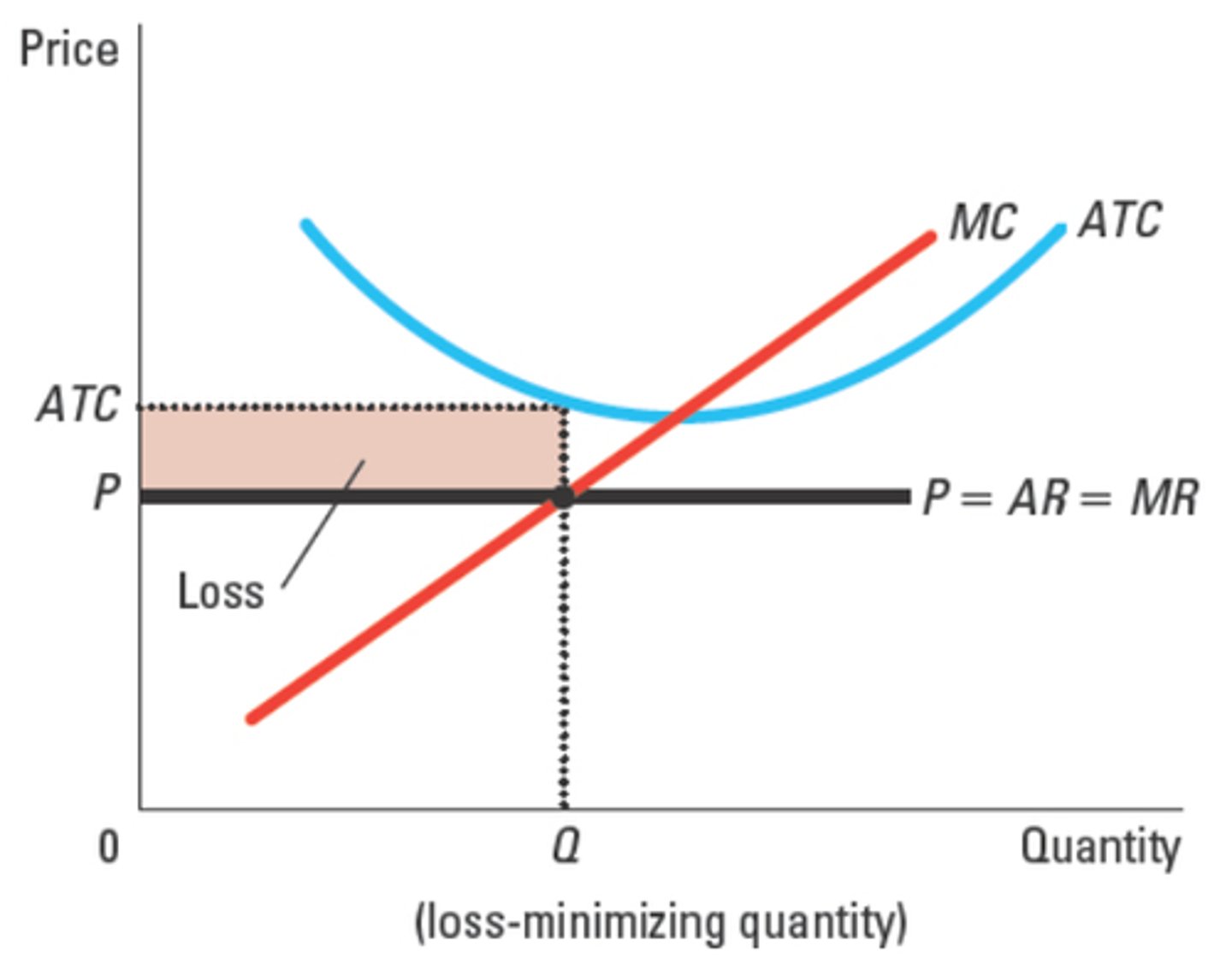
economic loss (subnormal profit)
a firm with...
zero economic profit (normal profit)
a firm at a minimum amount required to keep factors of production in their current use
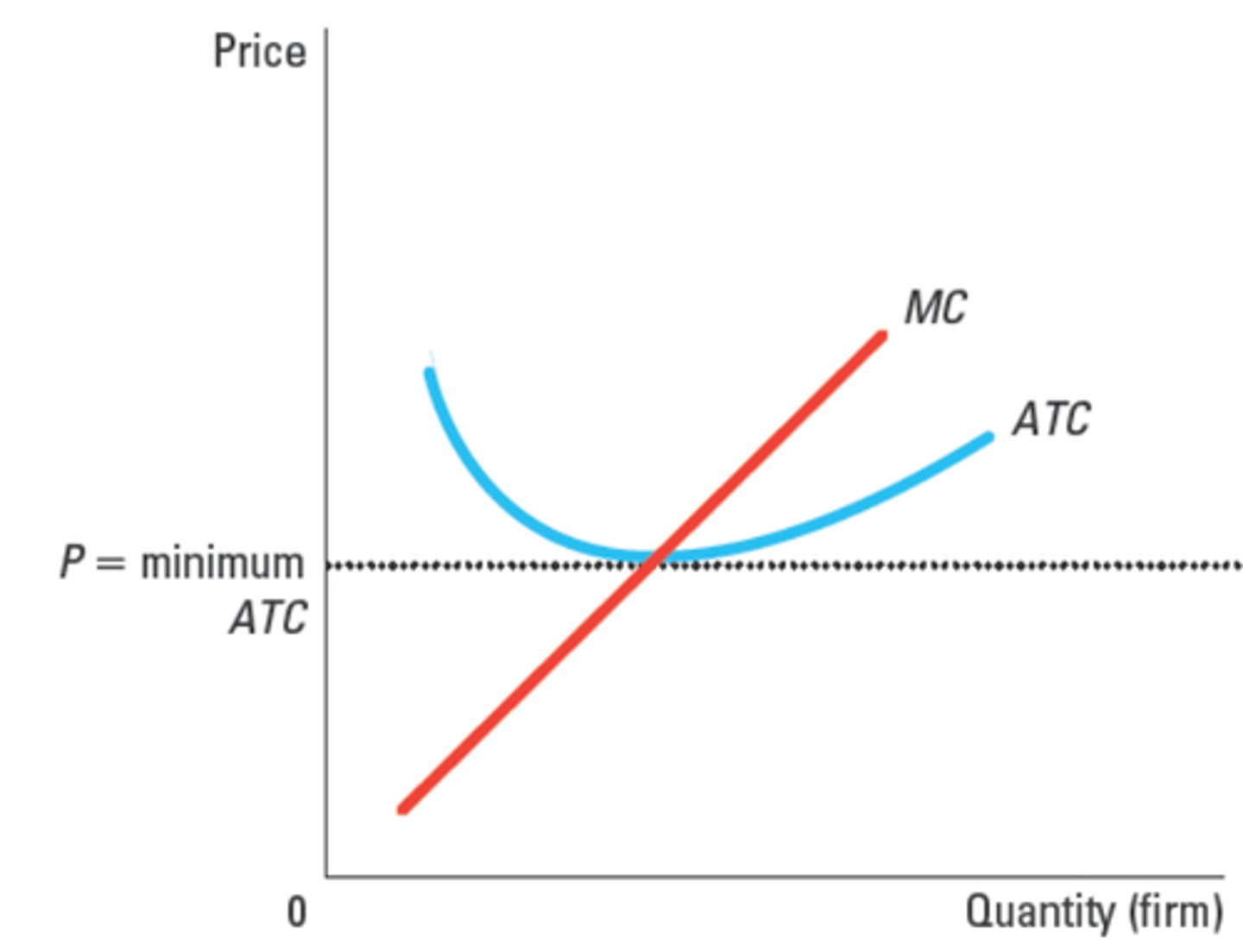
Why do competitive firms stay in business if they make zero profit?
When talking about zero economic profit, it is important to remember the distinction between economic profit and accounting profit. When economists talk of zero profit they are referring to economic profit.
In the zero profit equilibrium, the firm’s revenue must compensate the owners for the time and money that they expend to keep their business going.
profit formula
π = TR − TC
To measure profit in graphs, it needs to be rewritten as:
π = [(TR/Q) − (TC/Q)] × Q
π = (P − ATC) × Q
firm's exit criterion
if P < ATC
firm's enter criterion
if P > ATC