Lecture 10 - Acid-base Catalysis
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Acid Catalysis
PROTONATE the molecule to make more electrophilic (acid is a proton DONOR)
Base Catalysis
DEPROTONATE water to make more nucleophilic (base is a proton ACCEPTOR)
Amino Acid Bases
Arginine, lysine, histidine, tyrosine, cysteine
Amino Acid Acids
Aspartic acid, glutamic acid, histidine
Importance of histidine in acid-base catalysis
Can act as BOTH acid and base catalyst
What amino acids can participate in acid-base catalysis?
Those with IONIZABLE side chains
Aspartate, glutamate, HISTIDINE, arginine, lysine, cysteine, tyrosine
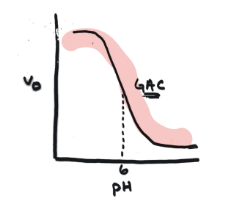
Graph of acid catalysis
Higher v0 at lower pH
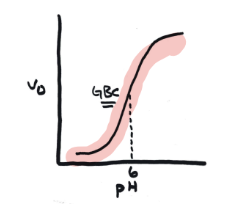
Graph of base catalysis
Higher v0 at higher pH
Protease Papain
Contains cysteine and histidine, which both act in catalysis
Cysteine - Base (deprotonated → protonated)
Histidine - Acid (protonated → deprotonated)
pH rate profile
Graph that represents ionization states of ALL species in the transition state
Papain unique feature
Cysteine and histidine are very close together, resulting in change in pKa
Histidine wants Cysteine’s proton, trying to pull it
pKa’s change…
Depending on environment (ex. proximity to other residues), altering acid-base behavior
Chymotrypsin
Endoprotease during digestion
Cleaves peptide bonds of bulky hydrophobic residues
Phe, Try, Tyr, Leu
Cleaves esters
SERINE PROTEASE
Is chymotrypsin an endoprotease or exoprotease?
ENDOprotease
What does chymotrypsin cleave?
Esters and bulky, hydrophobic residues
Examples of bulky, hydrophobic residues
Phenylalanine, Tryptophan, Tyrosine, Leucine
Chymotrypsin function
Intestinal digestion
What family does chymotrypsin belong to?
Serine proteases
Key players in chymotrypsin action
Serine - reactive nucleophile
Aspartic acid - electrostatic interaction, enhances nucleophilicity
Histidine - acid/base
Oxyanion hole - stabilizes transition
Specificity pocket - binds bulky hydrophobic residues
Kinetics of serine protease (chymotrypsin)
Burst and steady-state phases
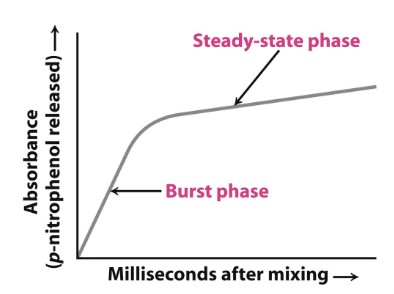
Burst phase
Beginning of chymotrypsin activity, acylation of chymotrypsin (all enzyme is free)
Steady-state phase
Slow phase, when enzyme is acylated and it takes longer for deacylation to occur
Serine proteases CANNOT function acylated
Size of burst =
Amount of enzyme available
more enzyme = larger burst
Steady-state is proportional to:
Concentration of [E]