Diseases of external nose and nasal vestibule
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
Cellulitis. The nasal skin can be invaded by Streptococcus or Staphylococcus bacteria, resulting in redness, swelling, and tenderness of the nose. Occasionally, this condition arises as an extension of infection from the nasal vestibule.
Treatment:
Systemic antibacterials
Hot fomentation
Analgesics
Cellulitis
Acute infection of the hair follicle of nasal vestibule
Furuncle or boil
Staphylococcus aureus
Most common organism causing boil
Nose picking
Plucking the nasal vibrissae
pulling out nasal hair
Predisposing factor of furuncle
Very painful
Fever, malaise,
Headache
Swelling of the cheeks
Swelling and redness of the conjunctiva
signs:
Hard, tender, red nodule present over nasal vestibule
Pyrexia
Swelling of face
Tenderness along the course of facial vein, Edema and chemosis of conjunctiva, proptosis, papilloedema and restricted eye movements in later cases
Clinical feature of furuncle
Never squeeze or premature incision
Warm fomentation
Antibiotics;flucoxacillin, cloxacillin mupirocin oinment
analgesucs
abscess-incision and drainage
In case of cavernous sinus thrombophlebiits-iv antibiotics
treat underlying cause
Management of furuncle
Frequent trauma to the nose by dirty fingers
Immunocompromised state
DIabetes
Recurrent furunculosis causes
Facial cellulitis
Upper lid abscess
Septal abscess
Cavernous sinus thrombophlebitis
Vestibular stenosis
Complications of furuncle
Diffuse dermatitis of the nasal vestibule caused due to nasal discharge as a resul of rhinitis, sinusitis, nasal allergy coupled with the trauma of hankerchief.
causative organism -staphylococcus aureus
Vestibulitis
Acute Form: Redness, swelling, and crusting.
Chronic Form: Induration, painful fissures, and crusting.
Form of vestibulitis
Cleaning with hydrogen peroxide
Application of antibiotic-steroid ointment
Cauterization of chronic fissures with silver nitrate
Treatment of vestibulitis
Dermoid cyst
Encephalocele or Meningoencephalocele
GLioma
Congenital tumors of the nose include
2 types-
a. Simple dermoid
b. Dermoid associated with a snius-pit or sinus seen in the midline of the dorsum of the nose and hair is seen protruding from the sinus.
Sinus track has intracranial connection hence meningitis may occur if infection travels along this route
Dermoid cyst
Herniation of the brain tissue with the meninges along the congenital bony defect.
Meningoencephalocele
Orbital followed by frontal
most common location of meningoencephalocele
Nasofrontal
Nasoehtmoidal
Nasoorbital
Types of meningoencephalocele
Nipped off portion of the encephalocele during embryonic development.
Glioma
Extranasal
Intranasal
Both extranasal and intranasal
Types of glioma
Rhinophyma
Most common benign tumor of the external nose
Papilloma
Rhinophyma, Haemangioma, Pigmented naevus, Seborrheic keratosis, Neurofibroma, Sweat gland tumor
Benign tumors of the nose
Rhinophyma
most common benign tumor of the external nose is
Inverted papilloma
Most common benign tumor of the nasal cavity is
Hypertrophy of the sebaceous lads at the tip of the nose in
Long standing cases of acne rosaceas
Rhinophyma cause
Bulking down the tumor using sharp knife or Co2 laser
Excision of tumor and regrafting of the epithelium.
Treatment of rhinophyma
Schneiderian or Rigertz tumor
Inverted paipilloma is also known as
Basal cell carcinoma
Squamous cell carcinoma
Melanoma
Malignant tumors of the nose
Basal cell carcinoma-least dangerous
Most common malignant tumor of external nose
Squamous cell carcinoma
MOst common malignant tumor of nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses
Early lesions respond to radiotherapy. Advanced cases require wide surgical excision and lymph node dissection.
Options include cryosurgery, irradiation, or surgical excision with margins
Treatmen of scc and bcc
Saddle nose
Humped nose
Crooked nose
Deviated nose
Nasal deformities
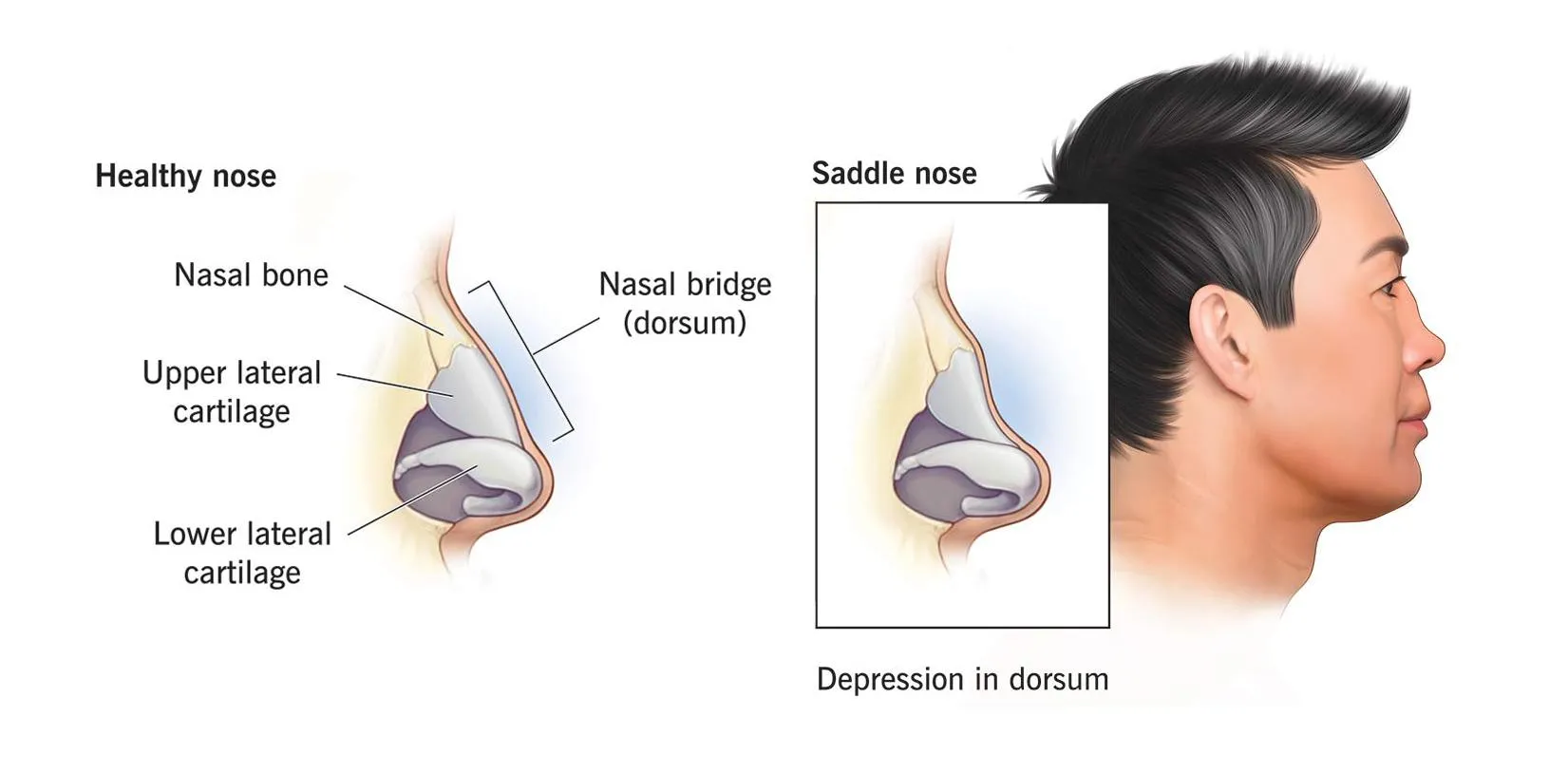
involves the dorsum of the nose. cartilage or bone or both
causes; HOT SALT
Haematoma, operative,trauma, syphilis, abscess,leprosy , tuberculosis
Correction-augmentation rhinoplasty
Saddle nose
Bony hump on the dorsum of nose
treatment-reduction rhinoplasty
Humped nose
Crooked nose-midline of the dorsum from the frontonasal angle to the tip of the nose is curved in a C or S shaped manner.corrective rhinoplasty is done
Deviated-midline is straight but it is deviated to one side
Crooked nose and deviated nose
Infestation of the nasal cavity by maggots. maggots are the larval form of the blue bottle fly( Chrysomyia).
Attracted by foul smelling discharge in- atrophic rhinitis, nasal syphilias and leprosy, purulent sinusitis, post radiotherapy carcinoma of maxilla.
Nasal myiasis(scholeiasis)
Formation of stones in the nasal cavity
Formed around the nucleus of a small exogenous foreign body, blood clot ot inspissated secretion by slow deposition of calcium and magnesium salts.
Rhinolith
UL obstruction with blood stained foul snelling discharge
Common repesentaiton of foreign body insertion especially in children is
Leakage of CSF from the nasal cavity which denotes the presence of fistulous connection between the subarachnoid space and nasal cavity.
CSF rhinorrhoea
Leakage of CSF into the nasal cavit but here the defect is present in the mastoid/ middle ear roof and CSF enters via the eustachian tube into the nasal cavity
Paradoxical CSF rhinorrhea
Traumatic (96%)
accidental(80%)-2%of head injuries
surgical (20%)-endoscopic sinus surgery, acoustic neuroma surgery,trans-sphenoidal hypophysectomy, surgery for meningocele
Non-traumatic\Normal ICP-congenital anomaly, focal atrophy, osteitis/osteomyelitis,idiopathic, cough/strain
High ICP-Tumor(85%), Hydrocephalus (15%)
Etiology of CSF rhinorrhea
From anterior cranial fossa-
cribriform plate, roof of ethmoidal air cells, frontal sinus
From middle and posterior cranial fossa- mastoid/middle ear and sphenoid sinus
Pathway of CSF rhinorrhea
1.Teapot sign/ Reservoir sign-watery nasal discharge increases on bending forward
2.Halo sign./ double target sign/ double ring sign-csf mixed with blood on filter paper/ pillow cover produces peripheral csf galo around the central blood
HAnkerchief sign-nasal discharge since containing mucin causes stiffening of the handkerchie. not so in csf
Signs seen in CSF rhinorrhea
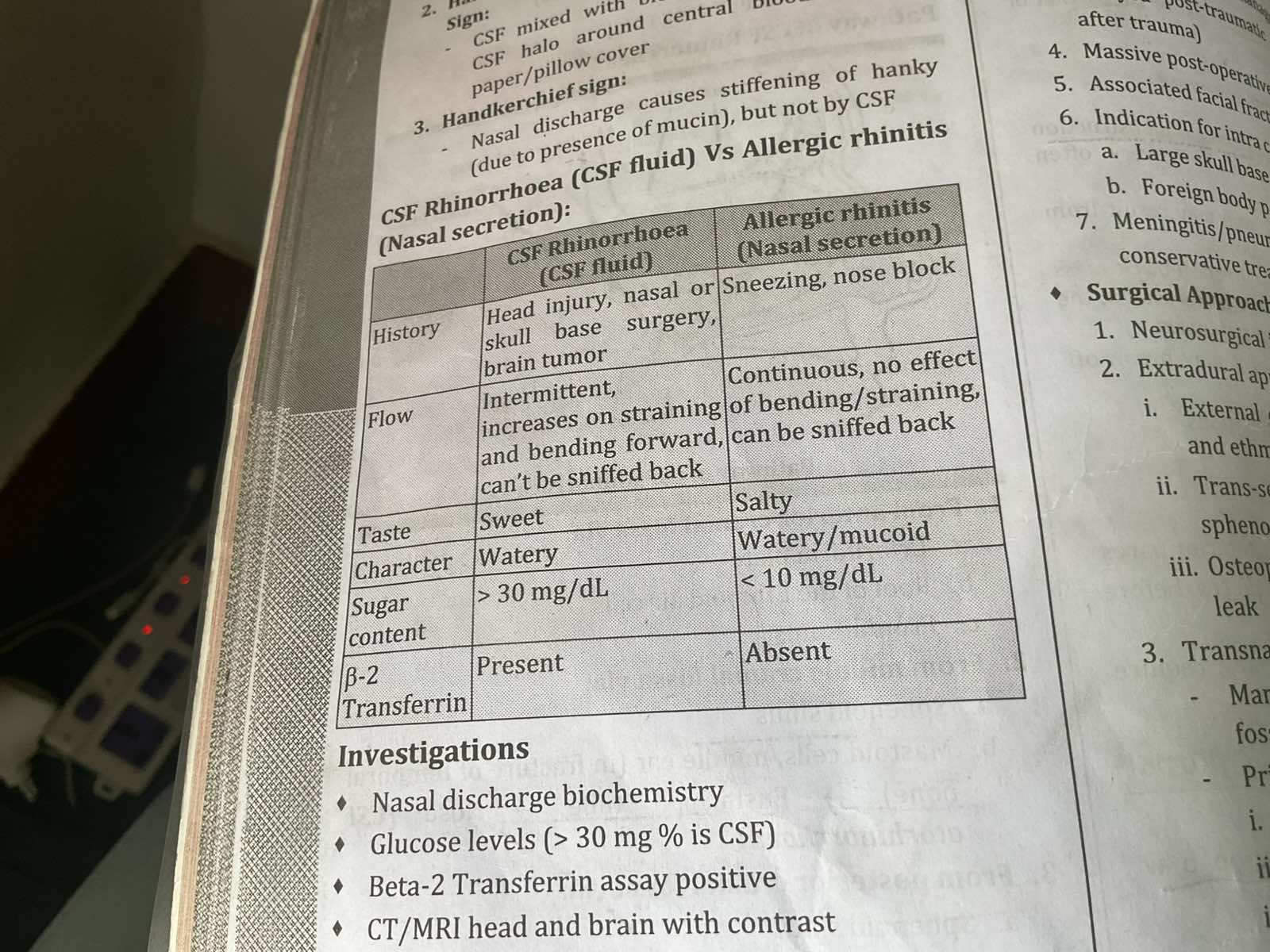
Difference between CSF rhinorrhea and Allergic rhinitis
COnservative treatment
Surgery-
NEurological intracranial approach
Extradural approach-Anterior ethmoidectomy for cribriform plate and ethmoid area
trans septal sphenoidal approach for sphenoid
Osteoplastic flap approach for frontal leak
Transnasal endoscopic approach
Treatment for CSF rhinorrhea
Persistence of bucconasal membrane
Choanal atresia
CHARGE Syndrome
Coloboma/cranial nerve defects
Hear defects(ASD)
Atresia of choana
Retarded growth
GEnitourinary anomaly
Ear defects
Choanal atresia is associated with
DNE with 2.7mm scope-atretic plate is seen
Flexible nasopharyngoscopy-atretic plate is seen
Rhinogram(choanogram)-dye instilled in nasal cavity collects in the choanal level
CT scan-posterior choanae<0.34cm or posterior vomer>0.55cm
Investigations
Emergency-Endoracheal intubation/tracheostomy
Mc Govern’s feeding nipple
Definitive-perforation of atretic plate
transnasal-for membranous and thin bony atresia
transpalatal-for thick bony atresia
Excision+mitomycin c
Tretament
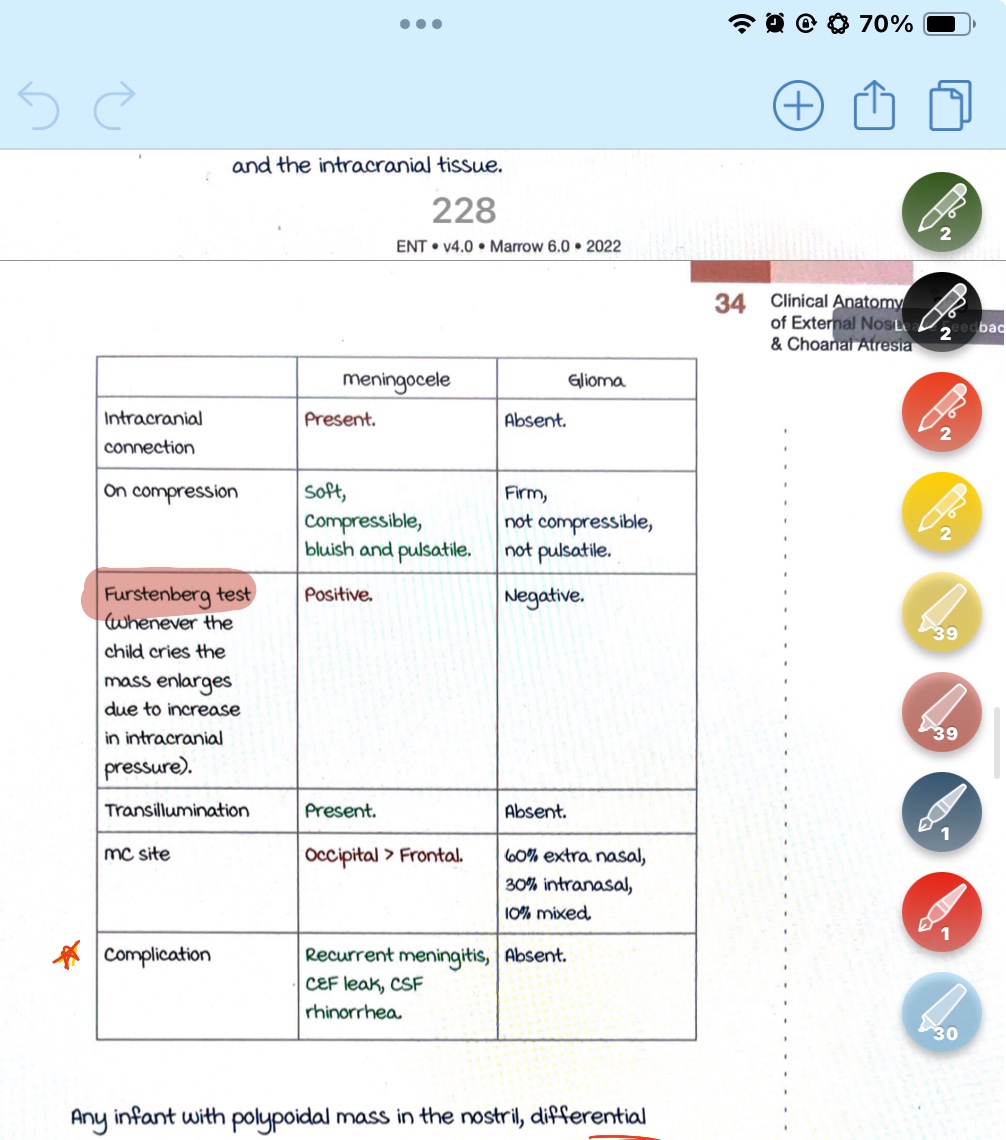
Meningitis vs glioma