Microbes-L10-Adaptive Immunity- Antibodies and Immunisation
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
what did Edward Jenner discover?
milkmen who were exposed to cowboy didn’t get smallpox- they’re exposed to something not as severe and were protected
what is important about a successful vaccination
we need to not only activate the innate system but the adaptive as it gives us memory!!
what makes up the adaptive immune system?
t cells
b cells- make the antibodies
what do vaccines need to do?
need to activate T and B cells
T helper cells- activate other immune cells including cytotoxic T cells
cytotoxic T cells- recognise and kill- CD8
specific antibodies- reocgnise and bind to antigenic epitopes- plasma cells make this
what is the innate immune system comprised of?
antigen presenting cells- such as dendritic cells and macrophages
antigen presenting cells express- PRR’s- pattern recognition receptors
PAMPs- pathogen associated molecular patterns- can be used in vaccines along with antigens!
difference between primary and secondary immune response
new virus- activates everything
infected again- reaction is bigger as you have memory bu won’t have ILLNESS! kills it straight away
what do vaccines do to your immune response?
induces a primary response- not very big but provides you with MEMORY
can prevent you from getting ill as you have a bigger response to the “real” bug
what is the adaptive immunity comprised of?
mediated by antigen presenting cells: dendritic cells(myeloid phagocytotic cells)
antigen is presenting in lymph node
T lymphocytes- CD4
B lymphocytes-Plasma cells
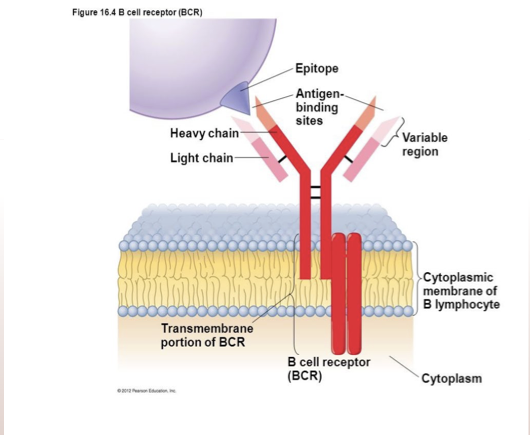
what is a B lymphocyte receptor consist of?
antigen binding subunit- binds to a viruses antigen- highly specific that triggers immune
2 heavy 2 light chains- variable regions to recognise many types
transmembrane region
signalling unit
what are B lymphocytes and plasma cells?
plasma cells differentiate from B lymphocytes
B lymphocytes express antigen specific B cell receptors- secrete antibodies
antigen specific B cells can becoming plasma cells which make antibodies and memory B cells
difference between B cells and antibodies?
same structure but B cells receptors are stuck to the membrane
when they shed- its an antibody
B cell responses to immunisation
primary: first infection
B cells become activated- produce antibodies- IgG and IgM
when infection clears-get long lived plasma cells in the bone marrow and memory B cells
what is an antigen, epitope and antibody
antigen- infectious agent and is specific
epitope- specific bit hat antibodies bind to
antibody- secreted by B cells and plasma and binds to antigen
5 classes of antibodies
IgG- main blood antibody- mother to baby- whopping cough vaccine given to make this
IgM- initial immune system defence
IgA- as monomers- respiratory infections- in the mucous
IgD- also prevention in respiratory tract infections
IgE- immunity to parasites
what do antibodies do?
neutralisation of pathogens or toxins- neutralise it.
toxin come in through endocytosis and antibodies bind to toxin
opsonisation
innate-macrophages phagocytose and degrade them
in adaptive- coats pathogen in antibody to make macrophage find it
complement action
reaction of all proteins
cause cell lysis ad cause opsoniation
rpomote pro inflammatory
cascade