Wiring Methods in Electrical Systems
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
86 Terms
What is open wiring on insulators?
An exposed wiring method using cleats, knobs, tubes, and flexible tubing for the protection and support of single insulated conductors run in or on buildings, permitted on systems of 600 volts or less.
Where is open wiring on insulators permitted?
In wet and dry locations, where subject to corrosive vapors, and for services.
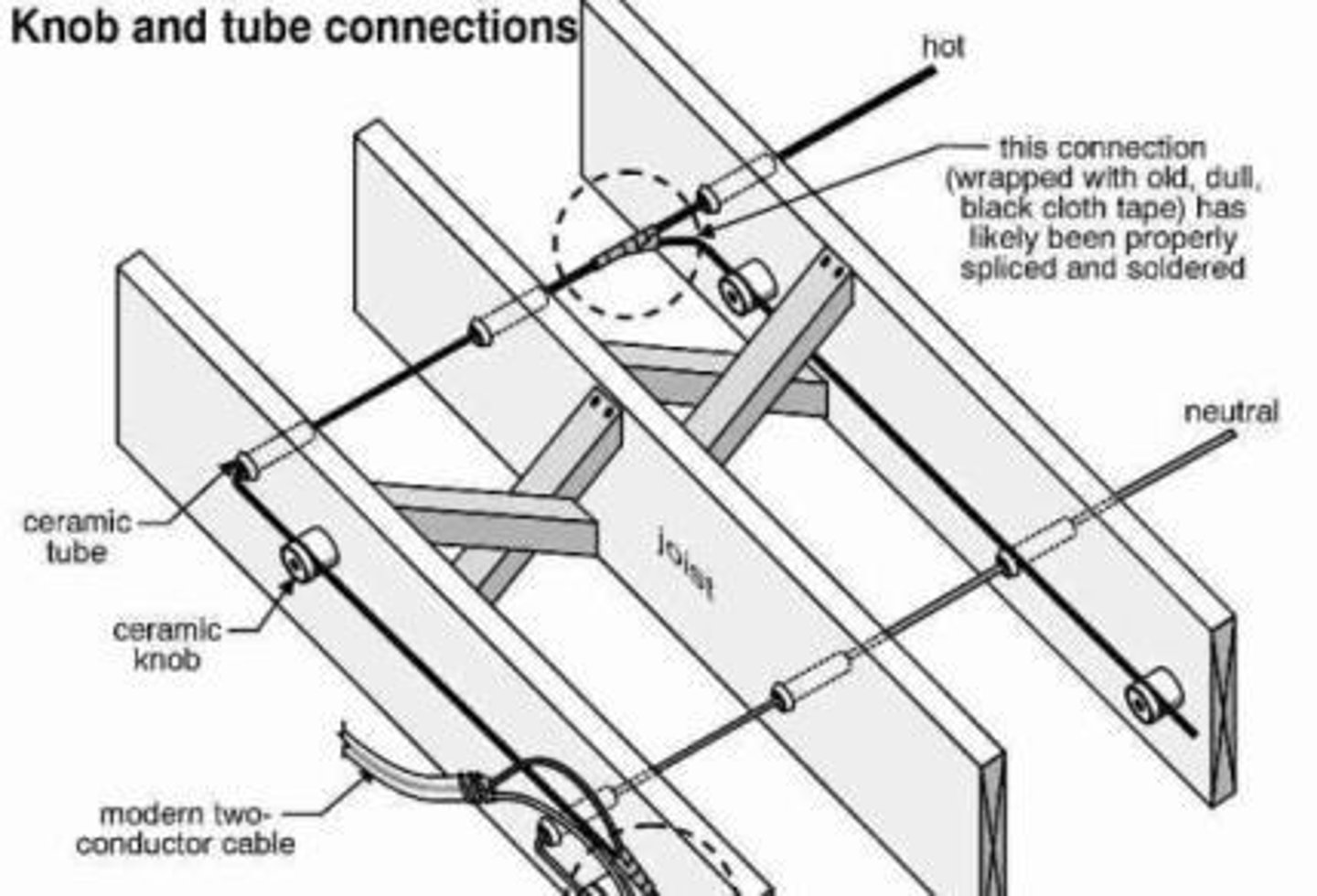
What is concealed knob-and-tube wiring?
A wiring method using knobs, tubes, and flexible nonmetallic tubing for the protection and support of single insulated conductors concealed in hollow spaces of walls and ceilings.
What are the prohibitions for using Type AC cable?
1. In theaters and similar locations 2. In motion picture studios 3. In hazardous locations 4. Exposed to corrosive fumes or vapors 5. On cranes or hoists 6. In storage battery rooms 7. In hoistways or elevators 8. In commercial garages.
What is Type AC cable?
A fabricated assembly of insulated conductors in a flexible metal enclosure, also known as BX Cable.
What applications are permitted for Type MC cable?
Type MC cable is permitted in various locations including indoors and outdoors, in cable trays, in any raceway, and for direct burial where identified for such use.
What is the construction of Type MC cable?
A factory assembly of one or more conductors, each individually insulated and enclosed in a metallic sheath of interlocking metal tape, or a smooth or corrugated metallic tube.
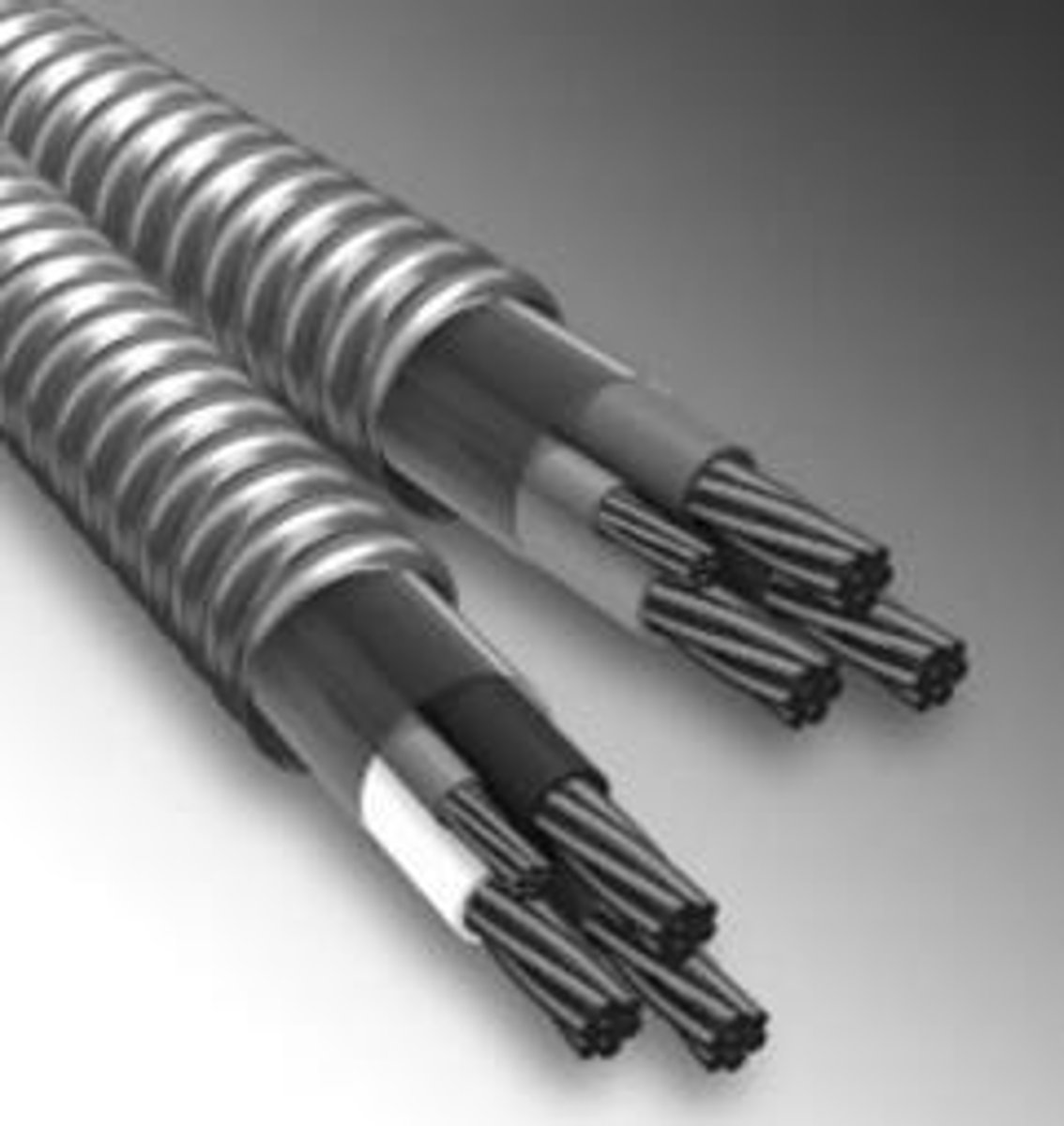

What locations should Type MC cable not be used?
Where exposed to destructive corrosive conditions, such as direct burial in the earth, in concrete, or where exposed to cinder fills, strong chlorides, caustic alkalis, or vapors of chlorine or hydrochloric acids.
What is the maximum voltage for open wiring on insulators?
600 volts, nominal or less.
In what locations can Type AC cable be embedded?
In dry locations and embedded in plaster finish on brick or other masonry, except in damp or wet locations.
What is the purpose of using cleats, knobs, and tubes in open wiring?
To provide protection and support for single insulated conductors.
What is the significance of Article 3.2 of PEC 2000, Part 1, Vol. 1?
It outlines the regulations for open wiring on insulators.
What is the significance of Article 3.24 of PEC 2000, Part 1, Vol. 1?
It specifies the prohibitions for using Type AC cable.
What is the significance of Article 3.34 of PEC 2000, Part 1, Vol. 1?
It details the regulations for Type MC cable and its applications.
What are the applications of armored cable (Type AC)?
Services, feeders, and branch circuits; power, lighting, control, and signal circuits; indoors and outdoors; exposed or concealed.
What is the alternative name for Type AC cable?
BX Cable.
What conditions allow Type MC cable to be used in wet locations?
When the metallic sheathing is impervious to moisture or a moisture-impervious jacket is provided.
What is a key feature of Type AC cable regarding installation?
It can be used in cable trays and is suitable for direct burial where identified.
What is the primary use of concealed knob-and-tube wiring?
To conceal single insulated conductors in hollow spaces of walls and ceilings.
What additional provisions are needed for concealed knob-and-tube wiring?
For extensions of existing installations or elsewhere by special permission.
What is the flexibility characteristic of Type AC cable?
It is a flexible metal enclosure that allows for various installation methods.
What is a key requirement for Type MC cable in corrosive environments?
The metallic sheath must be suitable for the conditions or protected by material suitable for the conditions.
What is Type MI cable and where is it permitted?
Type MI (Mineral-Insulated, Metal-Sheathed Cable) is a factory assembly of one or more conductors insulated with a highly-compressed refractory mineral and enclosed in a liquidtight and gastight continuous copper or alloy steel sheath. It is permitted in multifamily dwellings, cable trays, and other structures.
What are the restrictions for using Types NM, NMC, and NMS cables?
Types NM, NMC, and NMS cables shall not be used in multifamily dwellings exceeding three floors, as service entrance in commercial garages with hazardous locations, places of assembly, motion picture studios, storage battery rooms, hoistways, embedded in concrete, or in any hazardous locations.
Describe Type SNM cable and its characteristics.
Type SNM (Shielded Nonmetallic-Sheathed Cable) is a factory assembly of two or more insulated conductors in a moisture-resistant, flame-resistant nonmetallic material core, covered with overlapping spiral metal tape and wire shield, and jacketed with an extruded nonmetallic material resistant to moisture, flame, oil, corrosion, fungal growth, and sunlight.
What is the purpose of Service Entrance Cable (Types SE and USE)?
Service Entrance Cable (Types SE and USE) is used for services, feeders, and branch circuits, suitable for power, lighting, and signal circuits in dry, wet, or continuously moist locations, indoors and outdoors, exposed or concealed.
Where can Type NM and NMC cables be used?
Type NM (Nonmetallic-Sheathed Cable) and Type NMC cables are permitted for use in one and two-family dwellings.
What are the characteristics of Type USE cables?
Type USE cables are used for service laterals and can emerge above ground at terminations in meter bases or other enclosures where protected. They can also be utilized as branch circuit connectors or feeders.
What are the permitted uses for Type UF cables?
Type UF (Underground Feeder and Branch Circuit Cables) are approved for power, lighting, control, and signal circuits, in cable trays, raceways, or supported by messenger wire in outdoor locations.
What are the restrictions for installing Type TC cables?
Type TC cables cannot be installed where exposed to physical damage, as open cables on brackets or cleats, exposed to direct sunlight unless sunlight-resistant, or directly buried.
What is a Flat Cable Assembly (Type FC)?
Type FC is an assembly of parallel conductors formed integrally with an insulating material web, specially designed for field installation in metal surface raceway.
Describe Flat Conductor Cable (Type FCC).
Type FCC cable consists of three or more flat copper conductors placed edge-to-edge, separated and enclosed within an insulating material.
What are the size requirements for Underground feeder and branch circuit cables?
Underground feeder and branch circuit cables (Type UF) must be in sizes 2.0 mm² copper and 3.5 mm² aluminum or copper-clad aluminum through 100 mm².
What are the covering requirements for Type UF cables?
The overall covering of Type UF cables must be flame-retardant, moisture-resistant, fungus-resistant, corrosion-resistant, and suitable for direct burial in the earth.
What is the main function of Type MI cable?
Type MI cable is primarily used for applications requiring high resistance to heat and corrosive environments.
In what situations should Type MI not be used?
Type MI should not be used where exposed to destructive corrosive conditions unless protected by suitable sheath materials.
What is the significance of moisture resistance in cable types?
Moisture resistance is crucial for preventing electrical failures and ensuring safety in environments where cables may be exposed to water or humidity.
What does the term 'hazardous locations' refer to in cable installation?
Hazardous locations refer to areas where flammable gases, vapors, or dust may be present, requiring special cable types to prevent ignition.
What is the importance of flame resistance in electrical cables?
Flame resistance is important to prevent the spread of fire in the event of a short circuit or electrical failure.
What is the role of shielding in Type SNM cables?
The shielding in Type SNM cables protects against electromagnetic interference and enhances safety by preventing exposure to electrical fields.
How does Type FCC differ from standard round cables?
Type FCC consists of flat conductors which allow for more efficient installation in tight spaces compared to standard round cables.
What is the purpose of overlapping spiral metal tape in Type SNM cables?
The overlapping spiral metal tape in Type SNM cables provides additional shielding and protection against physical damage.
What are the benefits of using nonmetallic materials in cable sheathing?
Nonmetallic materials in cable sheathing provide resistance to moisture, flame, oil, corrosion, and fungal growth, enhancing durability and safety.
What is the primary use of Service Entrance Cable?
The primary use of Service Entrance Cable is to connect the utility supply to the electrical system of a building.
What are the permitted uses of Type UF cables?
Type UF cables can be used underground, including direct burial, as feeder or branch circuit cables with overcurrent protection of the rated ampacity, and for interior wiring in wet, dry, or corrosive locations.
What are the restrictions on using Type UF cables?
Type UF cables shall not be used as service entrance cables, in commercial garages, theaters, motion picture studios, storage battery rooms, hoistways, or hazardous (classified) locations.
What is Type TC cable used for?
Type TC is a Power and Control Tray Cable.
What is Type FCC cable permitted for?
Type FCC is permitted as a branch circuit conductor for general purpose, appliance branch circuits, and individual branch circuits on continuous floor surfaces made of concrete, ceramic, or wood.
Where is Type FCC cable not permitted?
Type FCC shall not be permitted in outdoor areas, wet areas, where subject to corrosive vapors, or in hazardous (classified) locations.
What are nonmetallic extensions?
Nonmetallic extensions are factory assemblies of two or more insulated conductors, with or without a grounding conductor, under a nonmetallic sheath, approved for installation in cable trays, raceways, or supported by messenger wire.
What are the restrictions on using nonmetallic extensions?
Nonmetallic extensions are restricted from use in aerial cables, unfinished areas, where voltage exceeds 250 volts for surface extensions and 300 volts for aerial cables, and in areas with corrosive vapors.
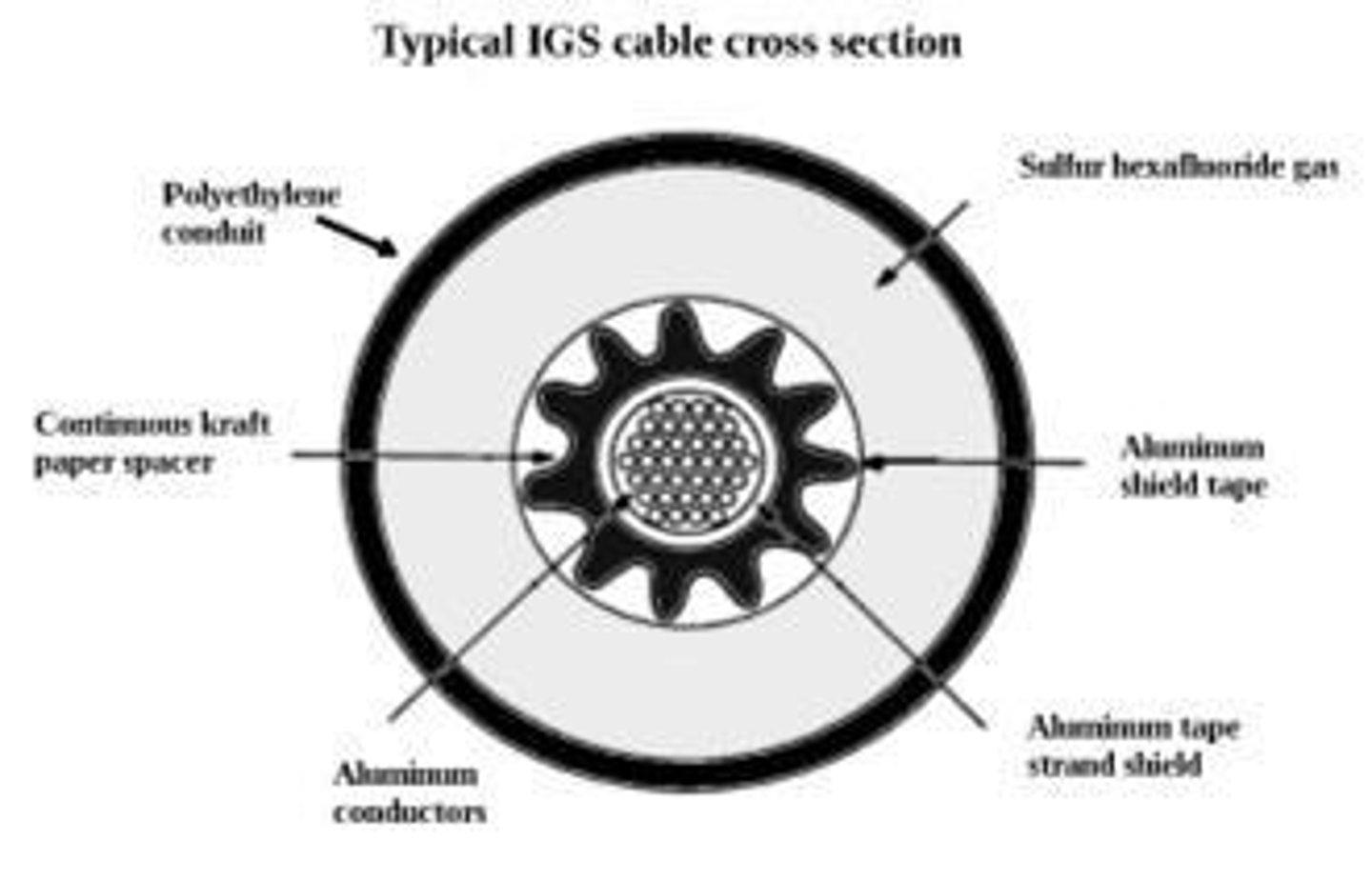
What is Type IGS cable?
Type IGS is a factory assembly of one or more individually insulated conductors enclosed in a loose-fit nonmetallic flexible conduit, rated at 0 - 600 volts.
Where can Type IGS cable be used?
Type IGS cable is permitted for use underground, including direct burial, as service entrance conductors, or as feeder or branch circuit conductors.
What are the restrictions on using Type IGS cable?
Type IGS cable shall not be used as interior wiring or be exposed in contact with buildings.
What is Type MV cable?
Type MV is a medium voltage cable that is a single or multi-conductor solid dielectric cable rated at 2001 volts or higher.
Where can Type MV cables be used?
Type MV cables are permitted for use on power systems rated up to 35,000 volts, in wet or dry locations, in raceways, in cable trays, or directly buried in the earth.
What are the restrictions on using Type MV cables?
Type MV cables should not be used where there is a risk of exposure to direct sunlight.
What is a raceway?
A raceway is an enclosed channel designed expressly for holding wires, cables, or busbars with additional functions.
What is the purpose of messenger-supported wiring?
Messenger-supported wiring is used for supporting cables and conductors in various installations, but it cannot be used in hoistways or where subject to severe physical damage.
What is a nonmetallic extension assembly composed of?
A nonmetallic extension assembly consists of two insulated conductors within a nonmetallic jacket or an extruded thermoplastic covering.
What is the maximum voltage for nonmetallic surface extensions?
The maximum voltage for nonmetallic surface extensions is 250 volts.
What is the maximum voltage for aerial cables?
The maximum voltage for aerial cables is 300 volts.
What types of flooring are Type FCC cables permitted on?
Type FCC cables are permitted on continuous floor surfaces made of concrete, ceramic, wood, or similar materials.
What is the significance of overcurrent protection for Type UF cables?
Overcurrent protection is required for Type UF cables to ensure they operate within their rated ampacity when used as feeder or branch circuit cables.
What is the classification of nonmetallic extensions?
Nonmetallic extensions are classified as an assembly of insulated conductors under a nonmetallic sheath.
What is the purpose of Type TC cables?
Type TC cables are used for power and control applications.
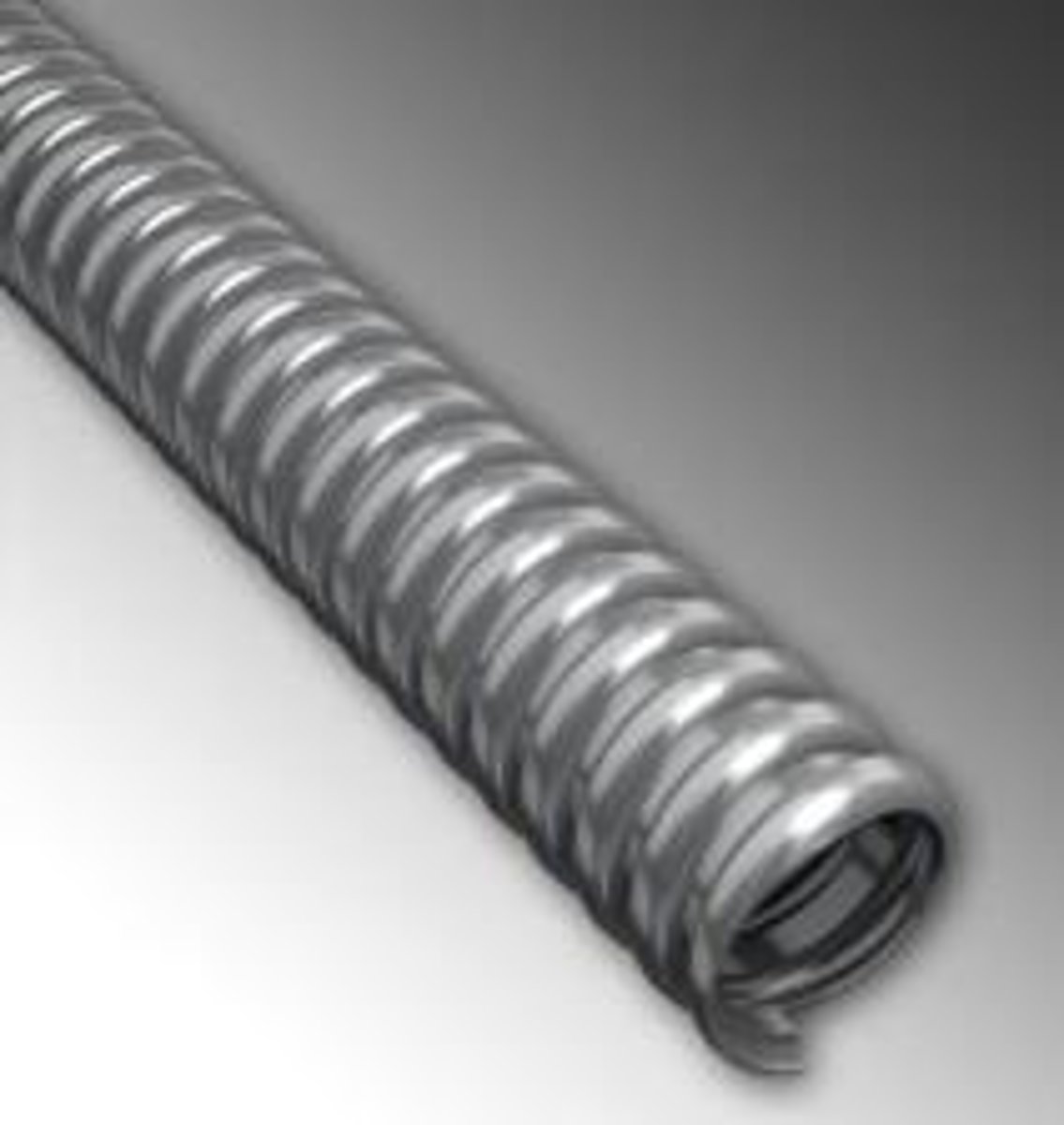
What is Intermediate Metal Conduit (IMC)?
A metal raceway of circular cross-section with integral or associated couplings, connectors, and fittings approved for the installation of electrical conductors.
What are the three methods of supporting insulated conductors using IMC?
1. A messenger with rings and saddles for conductor support. 2. A messenger with field-installed lashing material for conductor support. 3. Factory-assembled aerial cable.
What is Rigid Metal Conduit (RMC)?
A type of conduit with fittings approved for the installation of electric conductors.
What is Flexible Metallic Tubing (FMT) used for?
It is a non-rigid metal conduit into which conductors may be drawn, used in locations where wires or cables need to be pulled in or withdrawn.

Under what conditions can rigid metal conduits be used?
1. Protected by enamel. 2. In dry locations. 3. In accessible locations protected from physical damage. 4. For 1000 volts or more. 5. In branch circuits.
What is Electrical Metallic Tubing (EMT)?
A metal pipe into which electrical conductors may be drawn, with a thinner wall thickness than rigid metal conduit, used for both exposed and concealed work.
Where should Electrical Metallic Tubing (EMT) not be used?
1. Where it will be subject to severe physical damage. 2. Where protected from corrosion solely by enamel. 3. In hazardous locations.
What is Surface Metal Raceway (SMR)?
A raceway consisting of an assembly of metal backing and capping, permitted for use in dry locations.
What are the limitations of using Surface Metal Raceway (SMR)?
It should not be used where subject to severe physical damage.
What is Rigid Nonmetallic Conduit?
A type of conduit made of suitable nonmetallic material that is resistant to moisture and chemical atmosphere.
What is Liquidtight Flexible Metal Conduit?
A raceway of circular cross-section with an outer liquidtight, nonmetallic jacket over an inner flexible metal core.
Where should Liquidtight Flexible Metal Conduit not be used?
1. Where the voltage is 300 volts or more between conductors. 2. Where subject to corrosive vapors. 3. Where concealed.
What is a Busway?
A type of nonmetallic raceway not to be used in concealed areas or where subject to severe physical damage.
What is an Underfloor Raceway?
An approved, completely assembled metal troughing and fitting containing bare conductors intended for use as feeders.
What is a Cable Tray?
A unit assembly of sections and associated fittings forming a rigid structural system used to support cables.
What is a Cable Bus?
A raceway type suitable for use under floor, permitted beneath concrete or other flooring material.
What is a Cellular Floor Raceway?
An approved assembly of insulated conductors with fittings terminating in a completely enclosed ventilated metal housing.
What defines a cell in a Cellular Floor Raceway?
A single, enclosed tubular space in a cellular metal floor member.
What is a Multi-outlet Assembly?
A type of surface flush raceway designed to receive conductors and receptacles assembled in the field or factory.
What is the purpose of a surface flush raceway?
To allow insulated conductors to be readily drawn in and withdrawn, or laid in and removed.