Acute Inflammation GPPE
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Inflammation
Initial tissue reaction to wide range of injurious agents (Protective action)
Complex reaction in tissues that consists mainly of responses of blood vessels and leukocytes
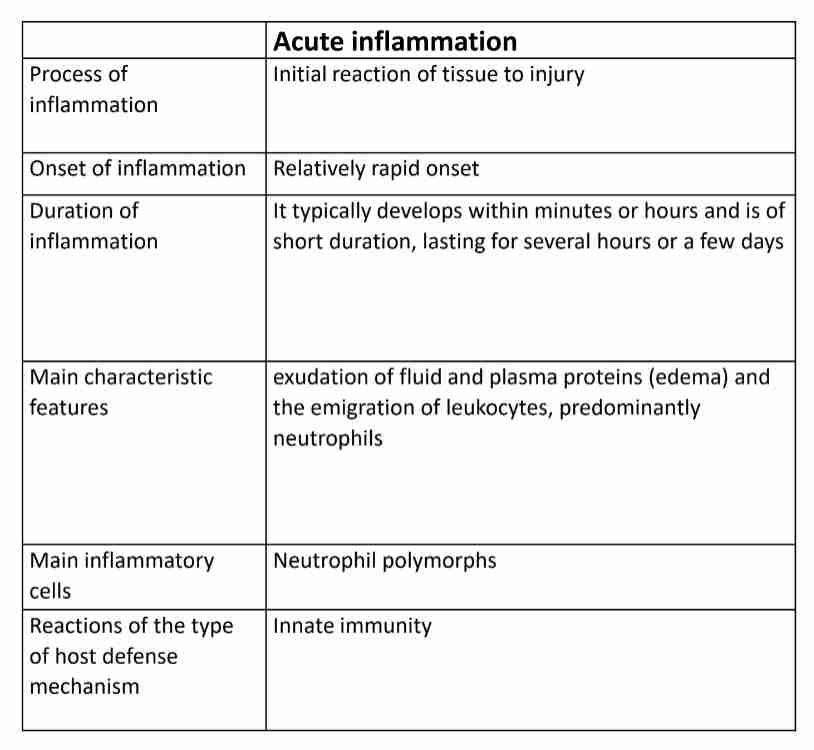
Type of inflammation
Acute : Rapid, short duration
Exudation of fluid and plasma proteins (edema)
Emigration of leukocytes, mostly neutrophils
Chronic : Slow, long duration
Proliferation of blood vessels, fibrosis and tissue destruction
Lymphocytes and macrophages
Causes of inflammation
Infection : pyogenic bacteria & viruses
Physical injury : trauma, burn & ionizing radiation
Chemical injury : corrosives, acids & alkalis
Immunologic injury
Tissue necrosis (dead cells): myocardial infarction - inflammatory changes occur in viable tissue adjacent to necrotic tissue
Cardinal signs of acute inflammation
Calor : heat caused by increased blood flow
Rubor : redness due to dilatation of vessels
Tumor : swelling due to an extravascular accumulation of fluid
Dolor : pain due to increase pressure exerted by accumulation of interstitial fluid & to mediators
Functio laesa : loss of function
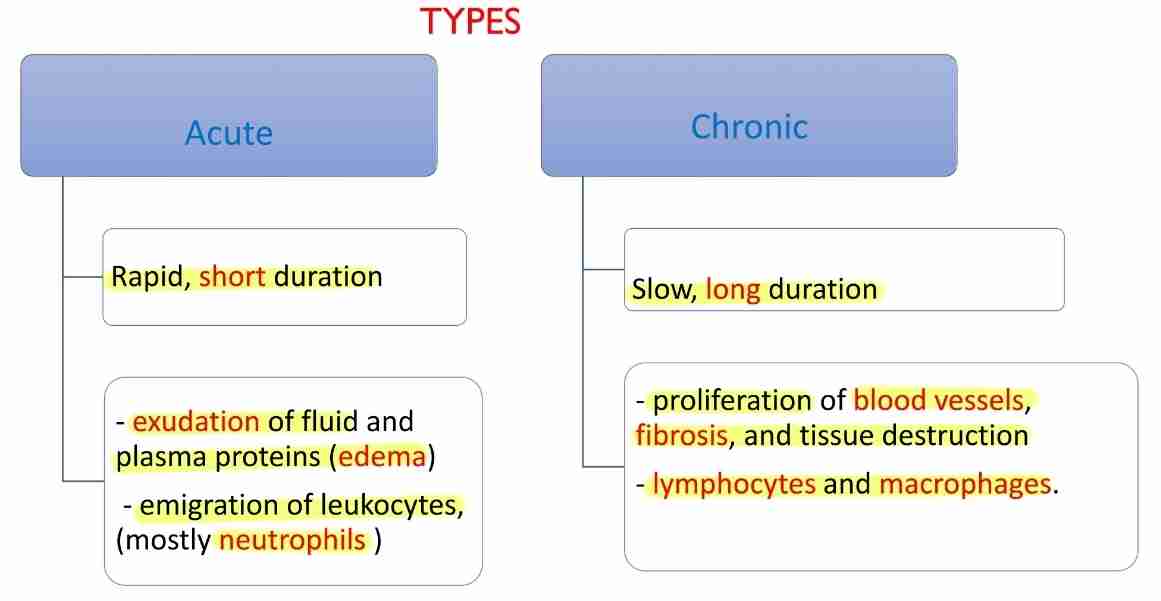
Vascular response in acute inflammation
Vasodilation : widening blood vessels
Change in flow of blood
Permeability of vessels
Lymphatic vessel response : lymphatic vessels undergo pronounced enlargement in inflamed tissue and display increased leakiness, indicating reduced functionality
Changes in blood flow & caliber
First involves arteriole and then leads to opening of new capillaries beds in area
Increased blood flow
Heat and redness (erythema) at site of inflammation
Mediators: histamine, prostaglandin and nitric oxide (NO), on vascular smooth muscle
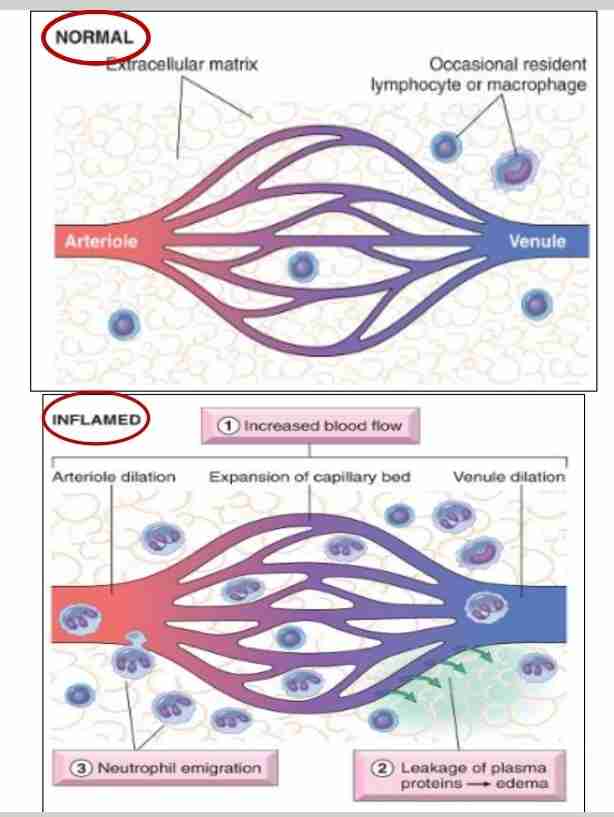
Increased vascular permeability (vascular leakage)
Leading to escape of protein-rich exudate into extravascular tissue, causing edema
Mechanism
Contraction of endothelial cells resulting in increased interendothelial spaces
Endothelial injury, resulting in endothelial cell necrosis and detachment
Leukocytes meditate vascular injury
Increased transport of fluid and proteins, called transcytosis, through endothelial cell
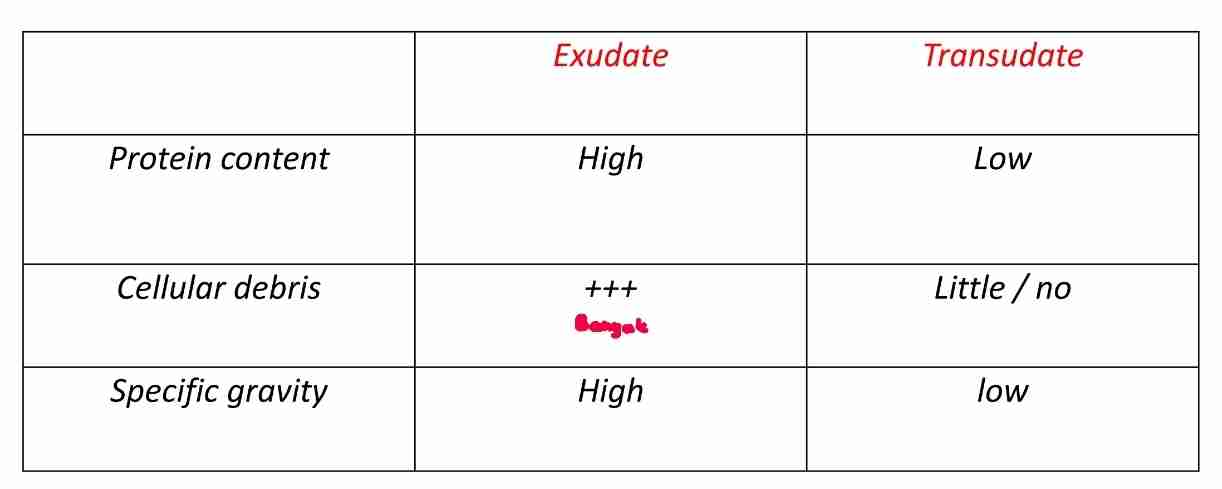
Vascular leakage
Exudation : escape of fluid, proteins, and blood cells from vascular system into interstitial tissue/body cavities
Transudate :
Fluid with low protein content (mostly albumin)
Little/no cellular material
Low specific gravity
Exudate :
Extravascular fluid that has high protein concentration
Due to increased vascular permeability
Cellular debris
High specific gravity
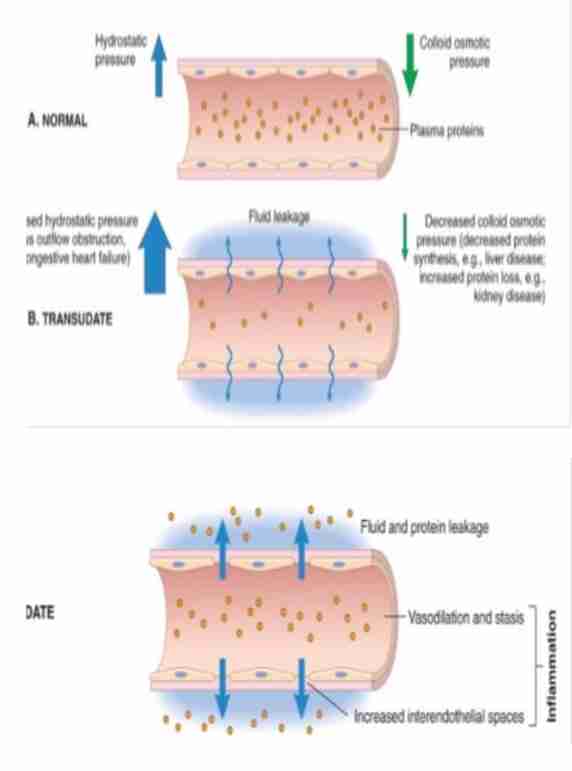
Cellular response in acute inflammation
Recruitment from blood into extravascular tissue
Recognition of microbes and necrotic tissues
Removal of offending agents (by WBC)
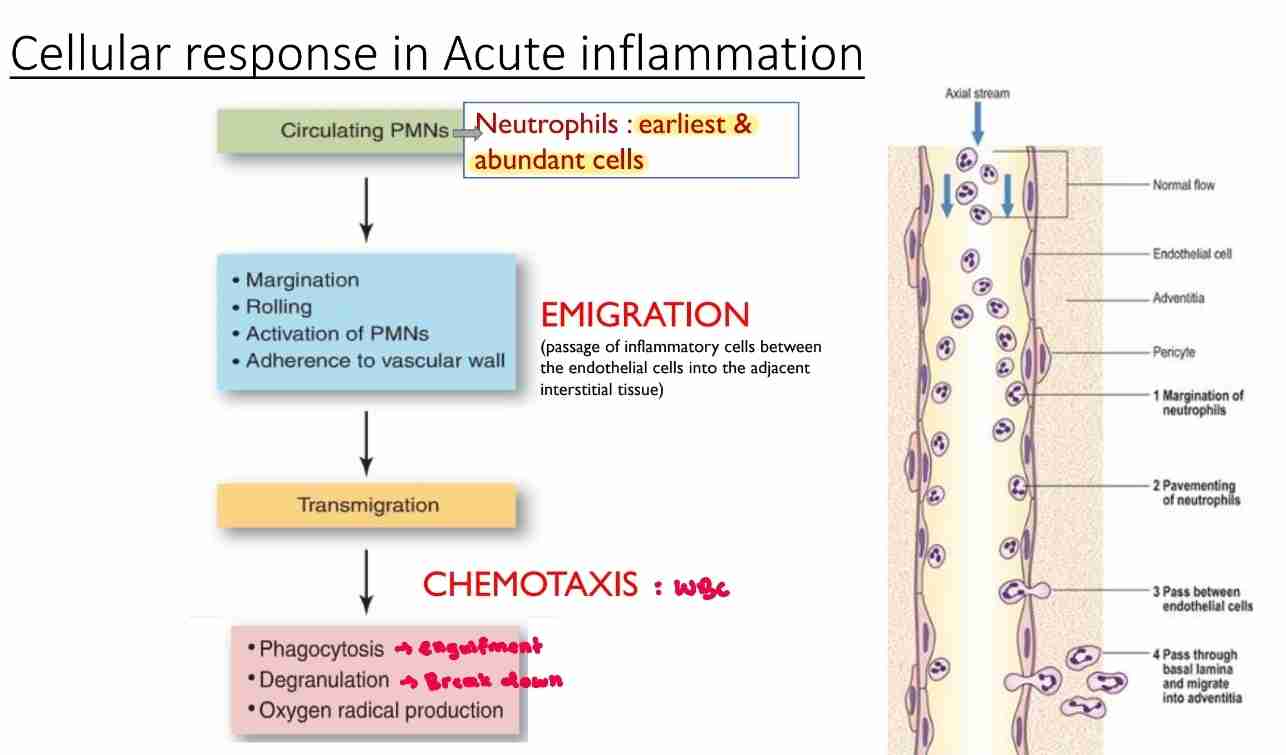
Emigration
Passage of inflammatory leukocytes between endothelial cells into adjacent interstitial tissue
Margination: leukocytes localize to outer margin of blood flow adjacent to vascular endothelium
Pavementing : leukocytes line endothelial surface
Rolling: mediated by actions of endothelial selection loosely binding to leukocytes, producing “rolling” movement of leukocytes along endothelial surface
Adhesion : leukocytes adhere to endothelial surface and mediated by interaction of integrins on leukocytes binding to immunoglobulin-family adhesion protein on endothelium
Transmigration
Movement of leukocytes across endothelium and mediated by platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule- I(PECAM-I) on both leukocytes and endothelium
Chemotaxis
Process which leukocytes are attracted to and move towards an injury
Mediated by diffusible chemical agents
Chemotactic factors for neutrophils:
Products from bacteria
C5a
Arachidonic acid metabolites (leukotriene B4(LTB4)
Phagocytosis
Ingestion of particular material like tissue debris, living/dead bacteria and other foreign cells by phagocytic cells
Recognition and attachment: particle to be ingested by leukocyte
Engulfment: with formation of phagocytic vacuole
Killing/degradation: ingested material
Most important phagocytic cells:
Neutrophils
Monocytes-macrophages
Inflammatory mediators
Causing blood vessels to dilate, which increase blood flow to affected area. Leads to redness and warmth
Increase permeability of blood vessels, allowing (WBC) to enter
Histamine
Prostaglandin
Nitric oxide (NO)
Protein
Peptides
Glycoprotein
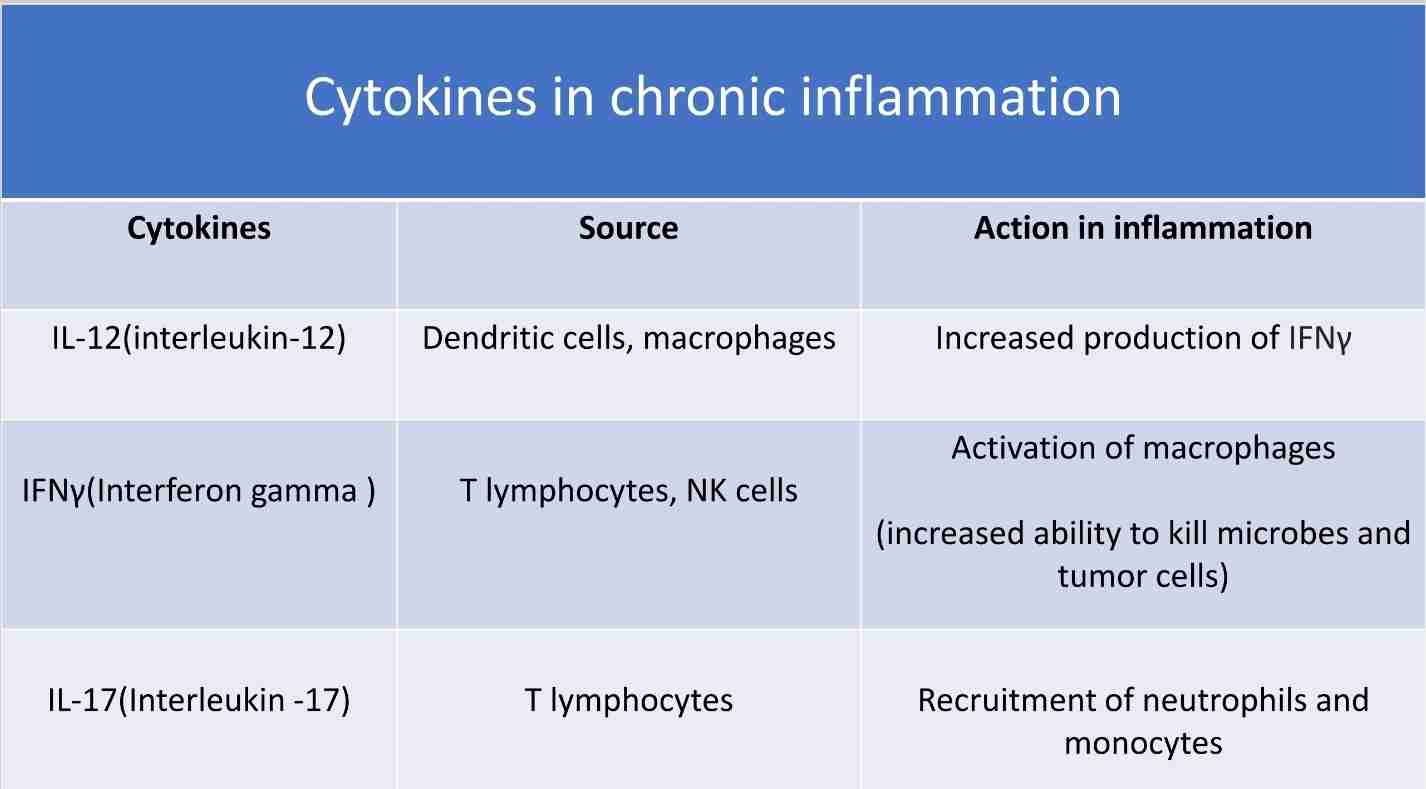
Cytokines
Protein produced by many cell types
Mostly activated lymphocytes, macrophages, endothelium, epithelium & connective cells at sites of tissue injury
Regulate inflammatory response, ranging from initial changes in vascular permeability to resolution and restoration of tissue integrity
Types of inflammatory cells
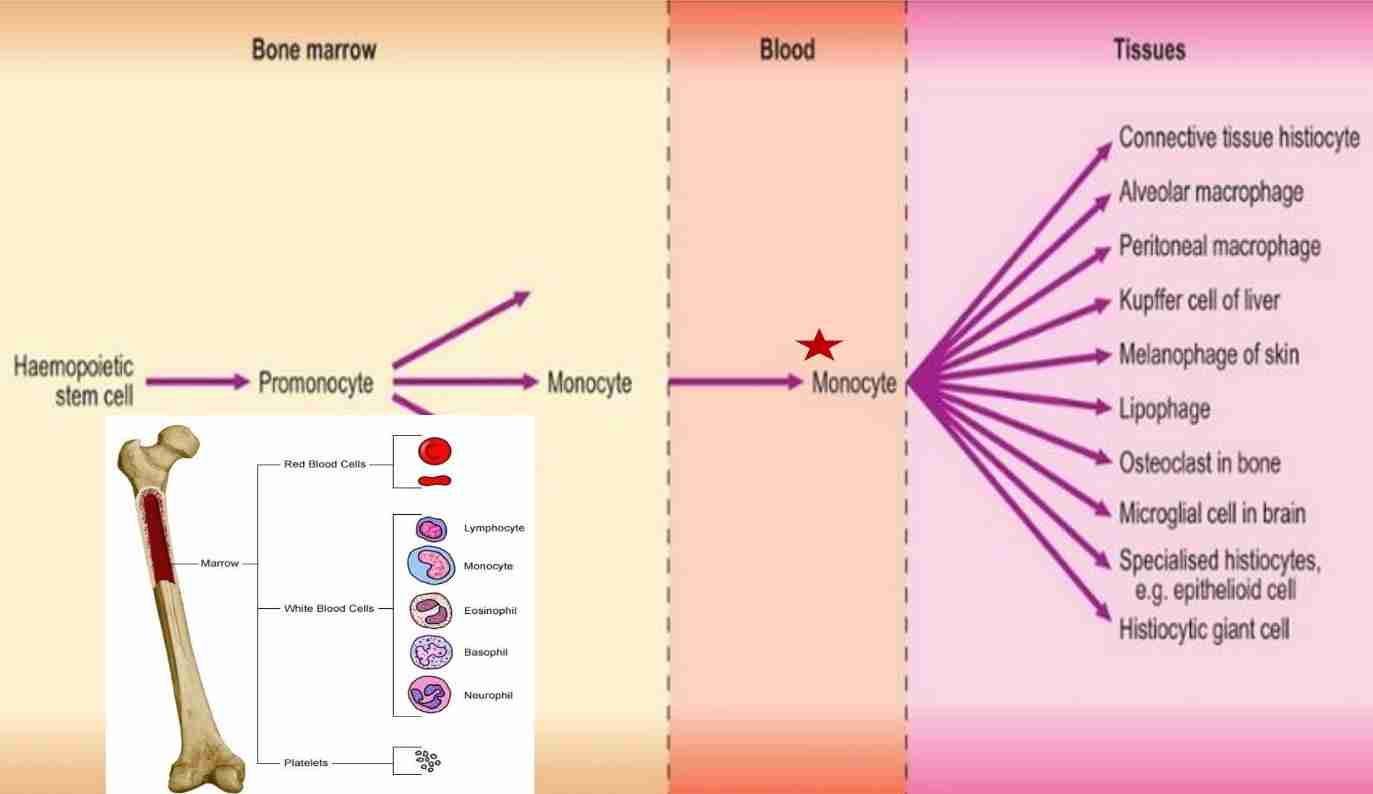
Monocytes
Macrophages in chronic inflammation
Products of activated macrophages serve to eliminate injurious agents; microbes & initiate process of repair
Other cell types: lymphocytes, plasma cells, eosinophils & mast cells
Lymphocytes
Most prominent inflammatory cells in many viral infection: influenza, mumps, rubella & bacterial infections like whooping cough & tuberculosis
Chronic inflammation
Plasma cell
Associated with antibody synthesis
Derived from B lymphocytes
Chronic inflammation
Local effects of inflammation
Heat
Redness
Sweeling
Pain
Loss of function
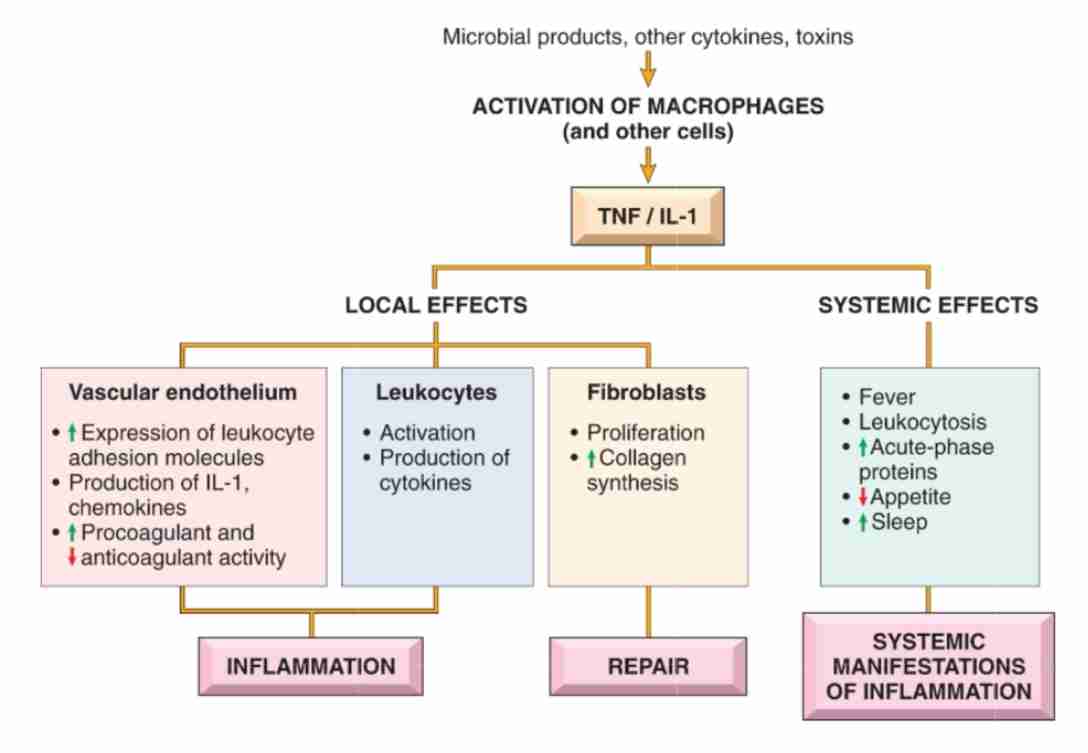
Systemic effect of inflammation
Changes are reaction to cytokines whose production is stimulated by bacterial products (LPS)
Fever
Sepsis
Leukocytosis
C-reactive protein (CRP)
Increased pulse and blood pressure
Anorexia
Malaise
Systemic effect
Production is stimulated by bacteria products (LPS)
Fever
Elevation of body temperature
Pyrogens act by stimulating prostaglandin synthesis in vascular & perivascular cells of hypothalamus
LPS stimulate leukocytes to release cytokines such as IL-I & TNF increase enzymes (cyclooxygenase) that convert AA into prostaglandin
Sepsis
Severe bacterial infection
Large amounts of organisms and LPS in blood stimulate production of several cytokines (TNF&IL-I): cause disseminated intravascular coagulation, cardiovascular failure & metabolic disturbance, which prescribed as septic shock
Leukocytosis
Increased number of WBC in blood
Accelerated release of cells from bone marrow, caused by cytokines (TNF&IL-L)
C-reactive protein ( CRP)
Plasma concentration: may increase several hundred-fold as part of responses to inflammatory stimuli
Fibrinogen
Serum amyloid A(SAA) protein
Outcomes of acute inflammation
Resolution of tissue structure and function often occurs if injurious agent is eliminated (tissue back to normal)
Tissue destruction & persistent acute inflammation
Abscess: localized collection of purulent exudate. Cavity filled pus (neutrophils, monocytes & liquefied cellular debris)
Ulcer : loss of surface epithelium (peptic ulcer, ulcers of skin)
Fistula : abnormal communication between 2 organs or between organ and surface
Scar : tissue destruction, with resultant distortion of structure
3.Conversion to chronic inflammation