Chem H Sem 1 Final
1/271
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
272 Terms
units
the amount that a number is referring to
SI system
Mighty King Henry Died Unexpectedly Drinking Chocolate Milk Monday
derived units
units that combine base units through multiplication or division (Ex. volue, density)
volume
length x width x height
density
mass / volume (Ex. g/ml or kg/L)
measurements
using tools and having uncertainties; reported with certain digits and 1 uncertain digit
accuracy
how close measurements are to TRUE VALUE
precision
how closely individual measurements compare to EACH OTHER and how reproducible the measurements are
meniscus
the curve in narrow columns of liquid
percent error
(measured value - theoretical value) / theoretical value * 100
can be positive of negative; no absolute value
significant figures
digits you are certain of + one uncertain digit
Atlantic Pacific Rule
Decimal is Absent:
Atlantic rule & start with 1st non-zero unit
Decimal is Present:
use Pacific rule
sig fig add / substract
round the answer to the number with the least number of decimal places
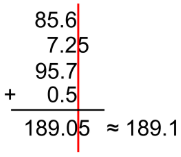
sig fig multiply / divide
round to the number with least number of sig figs

matter
anything that has mass and occupies space
solids
don’t move around, vibrate in place
liquids
flow freely; take shape of container
gases
molecules not attracted, colliding

physical change
rearranges molecules but doesn’t affect internal structure of individual molecules; no new chemicals formed
signs: changes in SIZE, SHAPE, STATE OF MATTER, texture
chemical change
forms new chemical substances, bonds between atoms broken and formed
signs: light emitted, HEAT generated, BUBBLES seen, odor, formation of new SUBSTANCES (precipitate), old substances changes COLOR / shape / mass
law of conservation of matter
states that matter is neither created / destroyed
elements
found on periodic table; can’t be separated into simpler substances with chemical changes
compounds
substances containing 2+ elements; can only be broken down w/ chemical processes
pure substances
made up of same type of atom, molecule, etc.
mixtures
2+ components PHYSICALLY combined; can be separated with physical means
homogenous mixture
evenly distributed physical mixture
heterogeneous mixture
not evenly distributed physical mixture
Democritus
______ proved that matter is made of tiny indivisible particles called atomos and can range in shape.
Dalton
_____ found the Law of Conservation of Matter, compounds, and found that ATOMS are tiny and invisible particles. Also discovered atoms of one element are the same
Thomson
______ discovered the ELECTRON, opposites attract, and protons and electrons even out
J. J. Thomson
Who discovered the Plum Pudding Model and cathode ray tube?
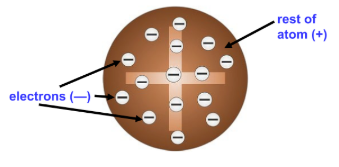
Plum Pudding Model
electrons stuck like pudding
What model is this?
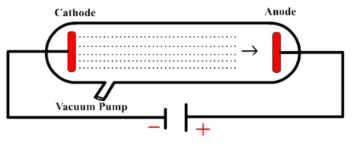
cathode ray tube experiment
electron rays bent toward positive plates and away from negative ones, finding the electron’s charge and proving that atoms are not indivisible
What model is this?
Rutherford
______ discovered the NUCLEUS and PROTONS in the center with electrons orbiting the nucleus
gold foil experiment
What model is this?
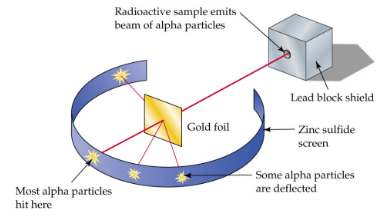
Ernest Rutherford
Who conducted the gold foil experiment?
most alpha particles (+) passed through the gold foil, showing that the atom is mostly empty space
some were deflected, meaning there is mass concentrated somewhere in the atom dense enough to deflect alpha particles
What did the gold foil experiment discover?
Bohr
______ discovered electrons lose energy in the light form with different layers and shells
Bohr model
light emission occurs when electron in excited atom drops from higher unstable energy to lower, stable one
exact energy difference released photon of light with specific frequency
What model is this?
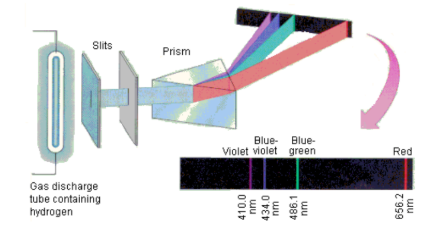
line spectra
specific “fingerprints” for each element since only specific energy jumps for electrons allowed
Chadwick
______ discovered the neutron
model of the atom
What model is this?
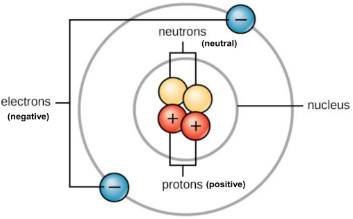
atomic number
# of protons in an element
neutral atoms
same number of protons and electrons
ions
same number of protons but different amount of electrons
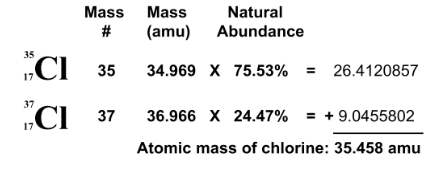
atomic mass
mass of protons + neutrons; 99.7% of mass is in the nucleus so electrons aren’t important (top number)
isotopes
elements with different numbers of neutrons (bottom number)
average atomic mass
multiply mass and natural abundance (%), add it together
characteristics of element
electromagnetic (EM) spectrum
all forms of electromagnetic radiation from increasing wavelength to decreasing
types of waves on EM spectrum
Radio
Microwave
Infrared
VISIBLE
Ultraviolet
X-ray
Gamma
wavelength
What does λ stand for?
electromagnetic radiation
how energy travels through space as a result of photons moving
photons
particles of light, differ from each other by the amount of energy they carry
frequency (v)
measured in cycles / second (Hertz)
number of waves / cycles that pass through a given point in one second
velocity (m/s)
3.00 × 10^8 (all electromagnetic waves) = λ * v
wave energy
diff wavelengths of EM radiation carry diff amounts of energy
formula for energy
Energy = h v (planck’s * frequency)
Planck’s constant (6.63 × 10-34 Js)
What does h stand for in E = hv?
What is the unit for Planck’s constant?
Joules
What is the unit for frequency?
Hertz
What is the unit for velocity?
m
What is the unit for energy?
same as Planck’s; Joules
continuous spectrum
light can be separated into constituent colors using a prism
line / emission spectra
specific dark / bright lines rather than a continuous spectrum of colors
Balmer Series
set of spectral lines for the hydrogen atom specifically in the visible + ultraviolet light region
results in emission of visible light, causing atomic line spectra
Aufbau principle
states that electron orbitals must be filled from the bottom up (lowest energy level first)
Pauli exclusion principle
each orbital in pairs must have them in opposite spins
Hund’s rule
all orbital levels must be filled singly before doubling up / pairing
noble gas configuration
uses the symbol of the preceding noble gas in brackets to represent the full electron core followed by remaining valence electrons
Ex. [Ne]3s2
excited electron configuration
breaks the Aufbau principle in case of overexciting
quantum mechanical model of the atom
eleectrons do not revolve around nucleus like planets w/ sun, but occupy regions called orbitals
orbitals
region in which electron is most likely to be found
electrostatic repulsion
states that like charges repel
nuclear force
an attractive force that acts between all nuclear particles (protons and neutrons) that are extremely close to each other
radioactive decay
when an unstable nucleus spontaneously disintegrates into something lighter but more stable, emitting particles and electromagnetic radiation
alpha decay
What type of decay emits 2 protons and 2 neutrons?
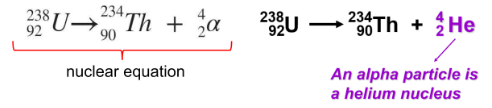
beta decay
What type of decay emits an electron?

gamma emission
What rays emit high energy EM radiation with no mass (occurs when alpha/beta has excess energy)?

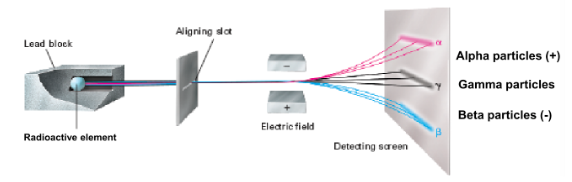
charges of alpha, gamma, and beta particles
What is being demonstrated in this picture?
half life
time required for ½ of the amount of unstable material to degrade into more stable material; pattern is the same but length is different per radioisotope
radiometric dating
process of determining the age of a substance from decay of radioactive elements in the substance
carbon dating
dates organic material up to ~60,000 years old; used on previously alive and relatively material
uranium dating
dates up to billions of years old; usually dates mineral / rocks
groups / families
columns in the periodic table
same amount of VALENCE electrons
periods
rows in the periodic table (your right hand goes left to right when you clock it perioddd)
same amount of electron SHELLS
highest energy electrons in periodic table labeled orbitals
What is being demonstrated?
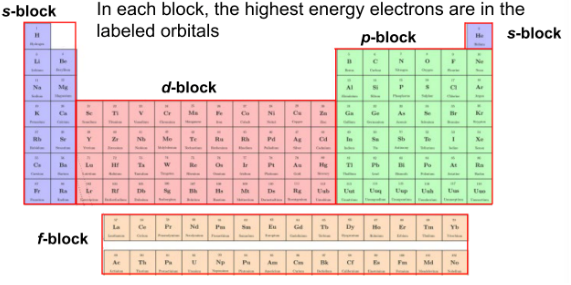
valence electrons
electrons in the outermost energy level
rule for reactivity and electron configurations
electrons with similar electron config have similar reactivities
alkali metals
Group 1; have a single valence electrons in s orbital
exists in nature in the form of ions with 1+ charge
highly reactive
good conductors of heat / electricity
alkaline earth metals
Group 2; have 2 valence electrons in an s orbital
2+ charge
more reactive than most (but not all) elements
good conductors
transition metals
Group 3 - 12; they’re kinda funny
exist in the d block
inner transition / rare earth metals
most have highest energy electrons in f orbitals
top = lanthanides; bottom = actinides (bottom is w/ uranium)
all lose electrons to form positively charged ions
all actinides radioactive
halogens
Group 17; short 1 valence electrons in a p orbital
1- charge
highly reactive
metallic character
how willing an element is to give an electron away
noble gases
Group 18; full s and p subshells
do not react with other elements
atomic radius
half the distance between 2 nuclei
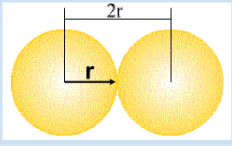
shielding
when electrons in lower energy levels prevent outer electrons from experiencing the full attractive force of protons
adding an electron to a higher energy level
_______________ increases atomic size.
decreases; # of protons increases attractive force, drawing outer electrons in
Across a period, atomic size ________