chem exam 2 - unit 5 nomenclature
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
elements and molecular elements
diatomic molecules
molecular compounds
covalent compounds
ionic compounds (charged particles, cations, and anions)
type-1 binary ionic compounds
type-2 binary ionic compounds
polyatomic ionic compounds
acids
binary acids
oxy acids
nomenclature
a system or a process to assign very specific and particular scientific names to the chemical compounds according to its structure, properties
nomenclature rules allow chemists all over the world to use the same __ when referring to compounds
terminology
why do we need nomenclature?
to avoid any overlapping and confusion
helps with assigning proper classification
name rules for an element with a single atom?
keeps the name indicated in the periodic table (can possibly add the word atom)
name rules for an element that has two of the same kind of atoms
keeps the same name as in the periodic table with the added word molecular (to show that it is a molecule)
ex: molecular bromine, molecular iodine
how many elements are naturally occuring?
92
how many elements are synthetic, artificial, or created in labs through nuclear reactions?
26
what atoms are molecular compounds made up of?
nonmetal + nonmetal
neutral molecules (no charge)
they share electrons to form molecular bonds
what atoms are ionic compounds made up of?
metal + nonmetal
how to name molecular compounds
write the name of the first atom that appears in the chemical formula
add a prefix (di-, tri-, etc.) to indicate the number of atoms of the element in the compound
write the second atom’s name and alter it to add the suffix -ide to the root
add a prefix (di-,tri-, etc.) to indicate the number of atoms of the element in the compound
ex: P2O5 and CH4 —> DiPhosporous pentoxide Carbon tetra hydride
prefixes and subscripts:
1 mono-
2 di-
3 tri-
4 tetra-
5 penta-
6 hexa-
7 hepta-
8 octa-
9 nona-
10 deca-
element names used for the 2nd element in a covalent compound
hydrogen → hydride
carbon → carbide
nitrogen → nitride
oxygen → oxide
phosphorus → phosphide
sulphur → sulphide
fluorine → fluoride
chlorine → chloride
iodine → iodide
naming molecular compounds (Two nonmetals)
write the name of the first element and add the prefix if needed
write the second atom’s name and convert it using the suffix -ide
add prefix if needed to it
ex: CO2 is carbon dioxide
the number of atoms in the chemical formula indicated by a subscript
ex: N2O4, NO, NO3, N2O5)
NO: nitrogen oxide
NO3: nitrogen trioxide
N2O5: dinitrogen pentoxide
Type-1 ionic compounds are made from which groups in the periodic table?
group-1A, 2A, and 3A
Type-2 ionic compounds are made from which groups in the periodic table?
transition metals
nonmetals
how are ionic bonds formed?
by transfer of electrons between the atoms
ionic compounds are __ particles
charged
type-1 binary ionic compounds are formed when?
when group-1A, 2A, and 3A metals combine with non-metals
rules for naming type-1 binary ionic compounds
start by naming the atoms that appears first in the formula (always a metal) by using their name in the periodic table
name the second atom (always a nonmetal) and change it by adding the suffix -ide to its root
NOTE: prefixes are NOT used when naming ionic compounds (ONLY used with covalent compounds)
EX: MgBr2 → Magnesium Bromide
converting chemical name to chemical formula with type-1 binary ionic compounds:
identify the metal and nonmetal
find the charges on both the atoms using the periodic table
crisscross the numbers (ignore signs)
use them as subscripts
simplify if needed (if they have a common factor)
ex: Magnesium Chloride
step 1: Mg,Cl
step 2: charges
Mg = +2
Cl = -1
Step 3: criss cross
Mg+2 Cl-1 → Mg1Cl2
ex: Aluminum Fluoride
Al = +3
F = -1
crisscross → Al1F3 → AlF3
ex: Calcium Oxide
Ca = +2
O = -2
crisscross → Ca2O2 → Ca2O2 → simplify → CaO
Type-2 ionic compounds are indicated with the __ __ in the compound’s name
Roman numerals
these indicate the element’s positive charge
Polyatomic Ionic Compounds
consist of more than one type of atom
atoms in a polyatomic ion are usually covalently bonded to one another, so they stay together as a single charged unit
ex: NO3- = nitrate
rules for naming polyatomic ionic compound
the cation is written first in the name, and the anion is written second
if formula has 2+ of the same polyatomic ion, put the ion in parentheses, with the number outside of it
identify the cation (positive ion) first
if it is a metal with a fixed charge (like Na+, Ca2+) just use its name
if it is a transition metal, determine its charge and write it as a Roman numeral
identify the anion (negative ion)
if it is a polyatomic ion (N³-), use its ion name (like nitrate, sulfate, etc.)
do NOT change the ending to -ide if it is polyatomic
ex: Ca(NO₃)₂
Ca²+ = calcium
NO₃⁻ = nitrate
name = calcium nitrate
ex: Fe(NO₃)₃
Fe = Iron (a transition metal)
NO₃⁻ = Nitrate (charge = –1)
There are 3 NO₃⁻, so total negative charge = –3
That means Fe must be +3 to balance.
name: Iron(III) nitrate
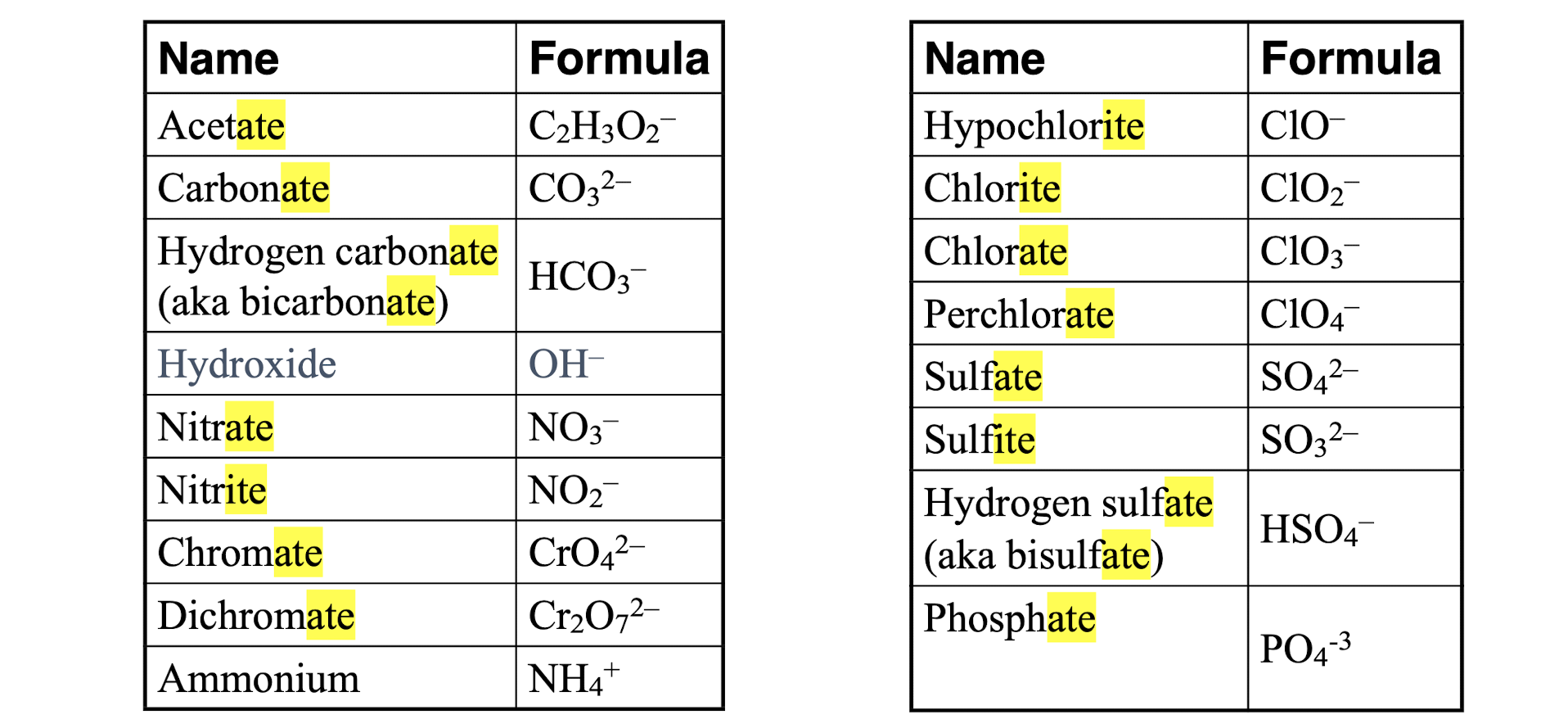
converting name to formula with polyatomic ionic compounds
steps:
write the symbols of cation and anion
determine charges of each ion
use crisscross method to balance charges
use parenthesis around poly ion if u need more than one of it
Ammonium phosphate
Ammonium = NH₄⁺
Phosphate = PO₄³⁻
Crisscross: NH₄⁺ (1) and PO₄³⁻ (3) → need 3 ammonium ions to balance 1 phosphate.
✅ Formula: (NH₄)₃PO₄
rule naming polyatomic ionic compounds
write the name of cation (no prefix)
write the name of anion from polyatomic chart (no prefix)
naming acids
if name or formula starts with hydrogen —> its an acid
acids are categorized into two groups:
binary acids: those containing only hydrogen and a nonmetal ex: HCI)
oxy-acids: those containing hydrogen, a nonmetal part includes oxygen ex: HNO3)
naming binary acids
composed of hydrogen and a nonmetal
(name format: hydro)+(base name of nonmetal + -ic)+acid
ex: HCI(aq) is hydrochloric acid
naming oxyacids
omit “hydrogen”
start with the root name of the anion
replace “-ate” with “-ic” , or “-ite” with “-ous”
add “Acid” at the end
ex: H2CO3 —> carbonic acid