N4: white matter
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
anatomy yr 1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
afferent fibres
carries impulses TOWARDS higher centres
sensory
efferent fibres
carries impulses AWAY from high centres
motor
towards spinal column
decussate
cross in midline
ipsilateral
input/out to or from same side
contralateral
input to/from opposite sides
nerve
a bundle of neurons that form a bigger structure that carries nerve impulses usually in the PNS (outside spinal cord)
tract
a bunch of axons travelling together within CNS (spinal cord or brain)
common function for either sensory or motor
3 types of white fibers
association
commissural
projection
association fibers location
within the same hemisphere; horizontal
function of association fibers
connect gyri and lobes on the same side of the brain
commissural fibers location
between left and right hemispheres; side to side
function of commissural fibers
share info across hemispheres
projection fibres location
lies btw basal ganglia and thalamus
projection fibers function
motor (efferent) /sensory (afferent) communication
long association fibers function
responsible for high order processing (memory, language)
travels from lobe to lobe
examples of long association
cingulum
superior longitudinal fasciculus
inferior longitudinal fasciculus
short association fibers function
connect gyrus to one next it (adjacent)
location of long association fibers
deeper within white matter
short association fibers function
short, curved (u-shaped)
connect adjacent gyri
sensory-motor
location of short association fibers
beneath cerebral cortex
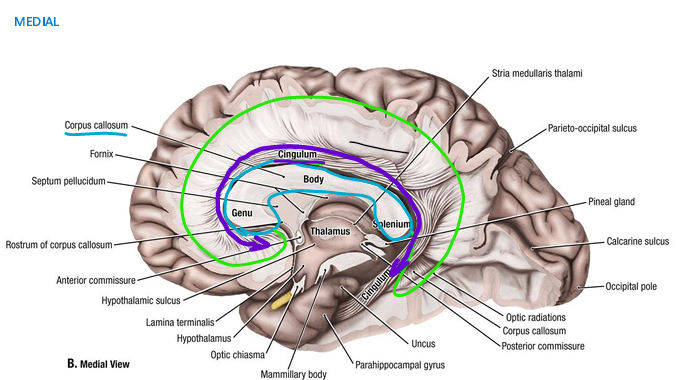
location of cingulum
runs within the cingulate gyrus, arching around the corpus callosum
location and pathway of superior longitudinal fasciculus
connects frontal, parietal, occipital lobes within the same hemisphere
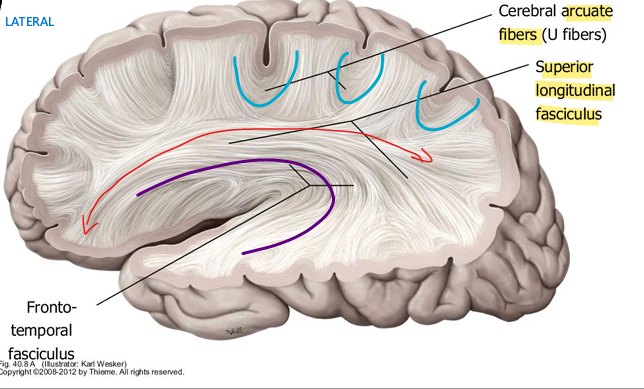
location and pathway of interior longitudinal fasciculus
runs from occipital lobe to anterior temporal lobe, beneath lateral sulcus
pathway of cingulum
association fibers under the gyri which connects to frontal, parietal and temporal lobes of the same hemisphere
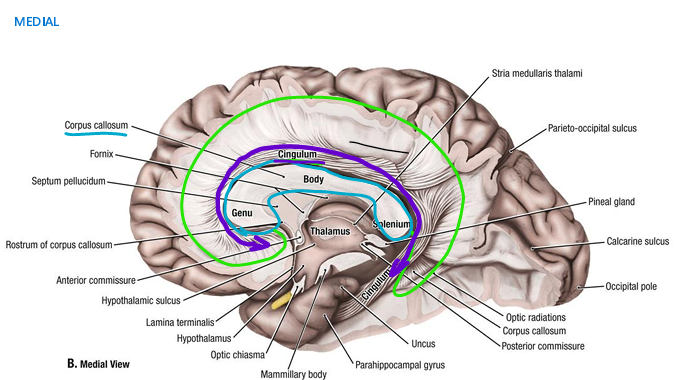
difference btw cingulum and cingulate
cingulate: superior to corpus callosum
grey matter
cingulum: white matter
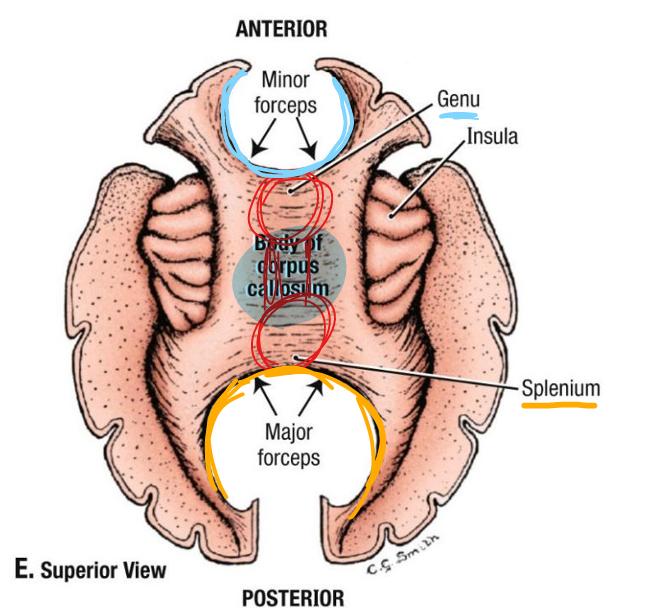
genu of corpus callosum
anterior curved aspect
connects frontal lobes
body of corpus callosum
middle portion
connects frontal and parietal lobes
splenium
posterior aspect; connects occipital lobes
forceps minor
extends laterally from genu to reach most anterior aspect of frontal lobe
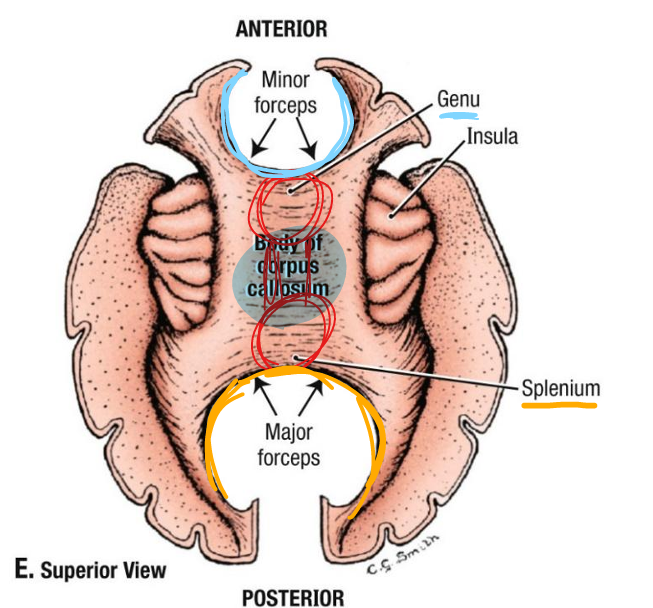
forceps major
extends laterally reach most posterior occipital lobe
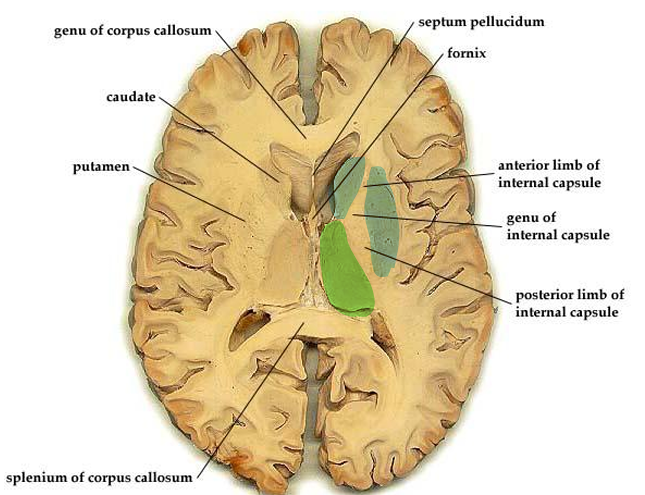
internal capsule location
middle of brain
boomerang shaped
positioned btw basal ganglia and thalamus
type of matter for pyramids
white matter
location of pyramids
medulla oblogonta
sends motor signals from cortex to spinal cord to brainstem
location of corona radiata
beneath the cerebral cortex and above the internal capsule
foot/leg location
medial aspect of cerebrum
torso location
superior cerebrum
arm/hand location
supero-lateral cerebrum
face location
lateral, just above lateral fissure