9. Screening & Diagnostics
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
A ____ ________ test is an accepted test that is assumed to be able to determine the true disease state of a patient (often expensive or highly invasive)
gold standard
_____ _______ occurs when a test is positive for a disease, but no disease is present
false positive
_____ _________ occurs when a test is negative for a disease, but the disease is present
false negative
____ _________ can lead to unnecessary anxiety or unnecessary treatment
false positives
______ ________ can result in failure to detect early, increasing the health risks to the patient, and potentially others
false negatives
To determine which screening test should be used, we must first consider two properties of the test: ________ and ________
sensitivity
specificity
The ________ of a screening test is the conditional probability that the test is positive given the person actually has the disease
sensitivity
Sensitivity =
P(Test(+) | Disease(+))
High sensitivity for a test is (good or bad)?
good
If sensitivity is high, the false negative rate is ___
low
The probability of a false negative is:
FNR =
1 - sensitivity
1 - P(Test(+) | Disease(+))
P(Test(-) | Disease(+))
The ________ of a screening test is the conditional probability that the test is negative given the person does not have the disease
specificity
Specificity=
P(Test(-) | Disease(-))
High specificity for a test is _____
good
If specificity is high, the false positive rate is ___
low
The probability of a false positive is:
FNR =
1 - specificity
1 - P(Test(-) | Disease(-))
P(Test(+) | Disease(-))
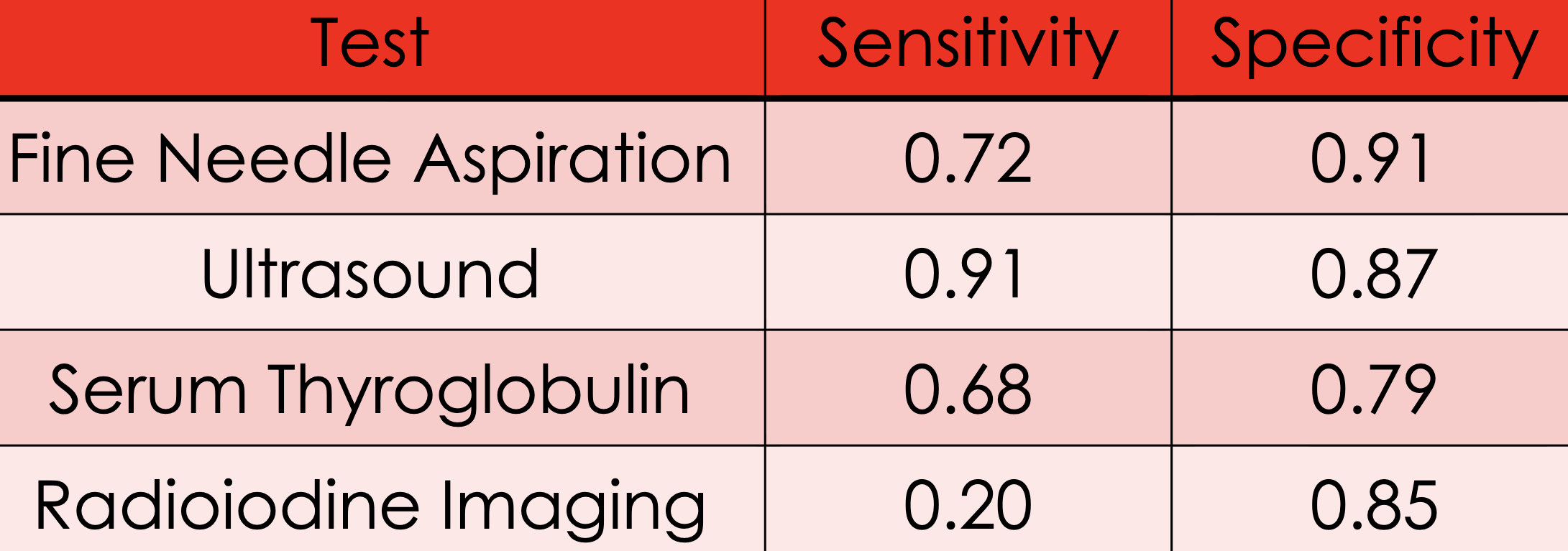
If we wish to minimize the false negative rate, we should select __________
→ minimizes the chance that thyroid cancer is not detected, when in fact it is present
→ Cost: Higher FPR. . . more people who do not have cancer may test positive, causing them to be unnecessarily alarmed and may cause them to have unnecessary surgery
ultrasound
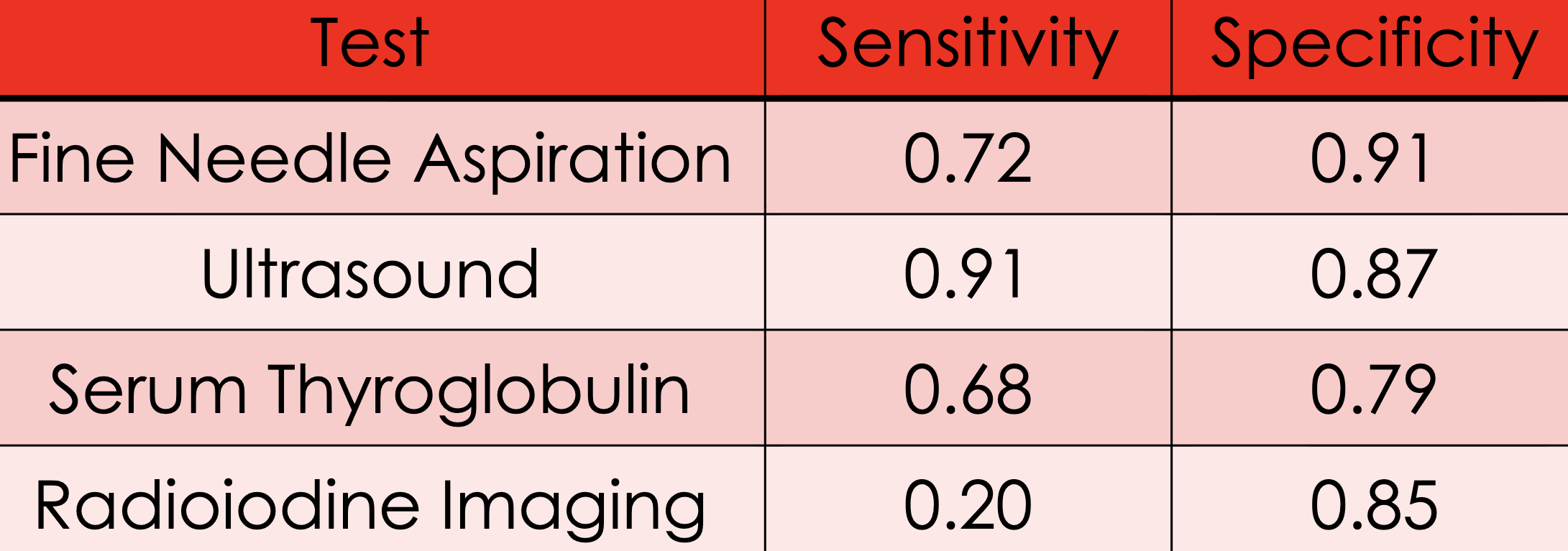
If we wish to minimize the false positive rate, we should select __________________
→ Minimizes the chance that thyroid cancer is diagnosed, when in fact it is not present
→ Cost: Higher FNR. . . more people who do have cancer may test negative, leading to lower chances of successful treatment
fine needle aspiration
While very useful, the sensitivity and specificity of a test still do not tell us:
→ If someone gets a positive result, what is the probability that they actually have the disease?
→ If someone gets a negative test result, what is the probability that actually are disease free?
→ Predictive values converts the test result into the ____ probability of the event
real
_______ __________ ______ is the conditional probability that disease is present given the test is positive
positive predictive value (PPV or PV+)
PPV=
P(Disease(+) | Test(+))
_________ __________ ______ is the conditional probability that disease is absent given the test is negative
negative predictive value (NPV or PV-)
NPV=
NPV = P(Disease(-) | Test(-))
We desire tests with ____ predictive values
high
Predictive values are a ______ criterion for test selection than sensitivity and specificity since:
→ we don’t know a patients true disease status when they are screened, but,
→ we do know the result of the test
better
In practice,
Sensitivity and specificity ___ be estimated directly from data
can
Predictive values often _______ be estimated directly from data
cannot
The predictive values depend on what proportion of all positive tests can be expected to be true positives
→ this depends on three pieces of information:
1) _________ of the test
2) __________ of the test
3) the _____________ of the disease is in the population
sensitivity
specificity
prevelance
The ___________ of a disease is the proportion of a population who have the disease in a given time period
prevalence
The _________ of a disease is the probability that a randomly selected member of a population has the disease
prevalence
___________ is estimated from large-scale prospective epidemiological studies
prevelance
the sensitivity and specificity of the test are measures of overall _____ _______
But, because predictive values are dependent on the prevalence of the disease in the population, they can be thought of as measures of how well the test works in a particular population
test quality
Sometimes, it is possible to estimate the predictive values directly form a table
→ this can only be done when the data were generated from a ____ prospective study
large
Data generated from case-control studies yields _______ estimates of the prevalence of disease because the investigator chooses the number of cases and controls to include in the study
biased
Many screening tests are based on a clinical measurement that can assume a range of values…
→ That is, many medical tests produce _________ numerical data, not just two categories (+ or -)
continuous
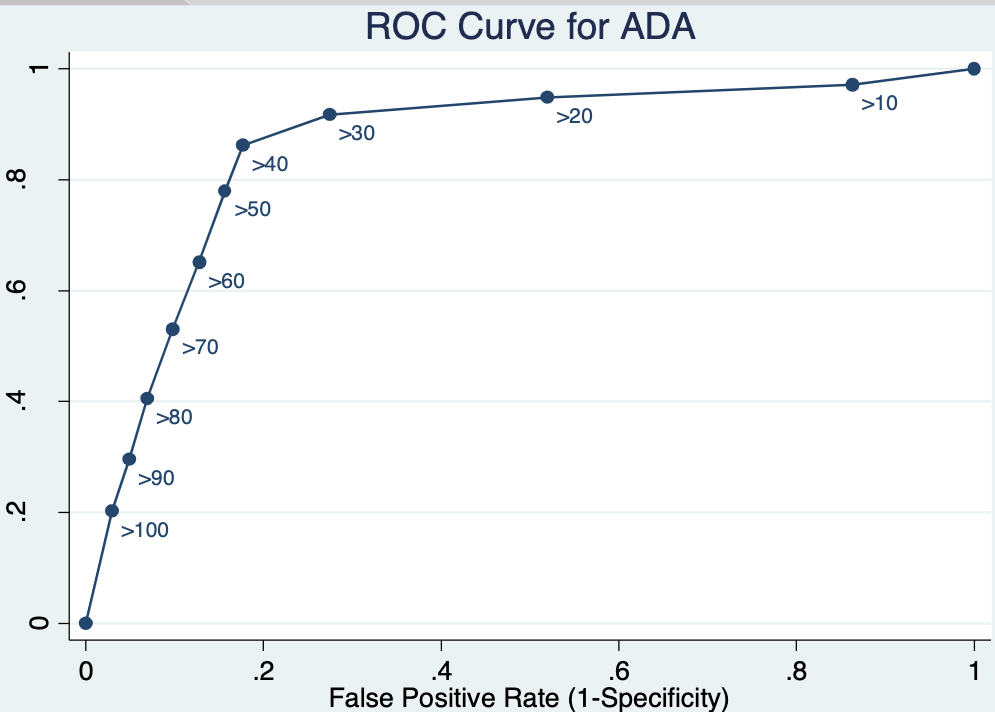
The __________ __________ _________ (ROC) curve is a plot of the sensitivity on the y-axis against (1 - specificity) on the x-axis
→ The distinct points on the curve represent different screening cutoff values used to designate a positive test
→ ROC curves provide a way to assess a test that produces continuous numerical data
Receiver Operating Characteristic
The quality of a screening test using a particular marker can be assessed by calculating the _____ _____ ___ ______ (AUC) of the ROC curve
area under the curve
The area under the ROC curve will generally lie between ___ and __
½ and 1
The closer the area is to 1, the ______ the marker for screening
better
Diagnostic tests with
AUC ≥ 0.9
is considered “__________”
excellent
Diagnostic tests with
0.8 ≤ AUC ≤ 0.9
is considered “_____”
good
Diagnostic tests with
0.7 ≤ AUC ≤ 0.8
is considered “____”
fair
Diagnostic tests with
AUC < 0.7
is considered “____”
poor
Where should we set the screening value for ADA?
→ If the cost of a false positive exceeds the cost of a false negative, then we want to have a more ______ test
specific
Where should we set the screening value for ADA?
→If the cost of a false negative exceeds the cost of a false positive, then we want to have a more ________ test
sensitive
If the costs of false positives and false negatives are equal, we choose the screening value so as to _________ sensitivity and specificity
equalize