Anatomy 2 Heart and blood vessels
1/140
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
141 Terms
Blood vessels that carry blood toward the heart are called
veins
Deoxygenated blood travels from the heart to the lungs via the Blank______ circuit.
pulmonary
What is the function of the systemic circuit?
The systemic circuit carries oxygenated blood from the heart to the rest of the body.
Which side of the heart?
Supplies blood to the systemic circulation to deliver oxygen to tissues
left side
Which side of the heart?
Supplies blood to the lungs for exchange of respiratory gases
right side
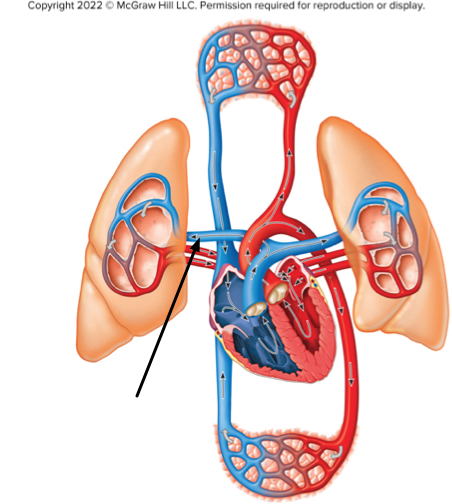
The structure at the tip of the arrow contains
deoxygenated blood of the pulmonary circuit
By definition, which blood vessels carry blood away from the heart?
Arteries
The heart is located in the Blank______ and is Blank______ to the diaphragm.
mediastinum; superior
Deoxygenated blood travels from the heart to the lungs (where it is loaded with oxygen) through the circuit.
pulmonary
The covering that encloses the heart is called the
pericardium
The pulmonary circuit receives blood from the Blank______ of the heart and the systemic circuit receives blood from the Blank______ of the heart.
right side; left side
Which statement accurately describes the fibrous pericardium?
It is the outer portion of the pericardial sac composed of tough connective tissue.
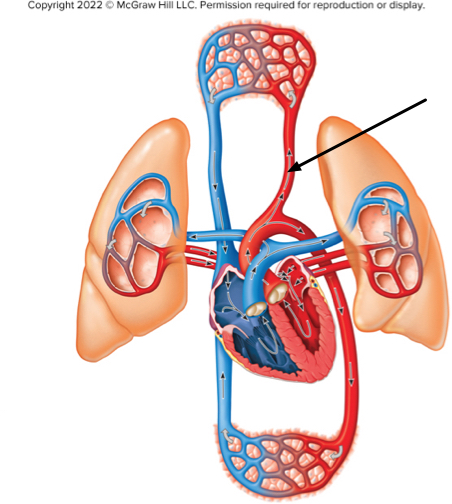
What type of blood is at the location indicated by the arrow?
oxygenated blood of the systemic circuit
The heart surface is covered by the innermost layer of the serous membrane, known as the____ pericardium, or the
visceral
The heart is housed within the mediastinum and rests ___, a muscle.
diaphragmWhat is the pulmonary circuit?
The circuit which carries oxygen-poor blood to the lungs
Which describes the parietal pericardium?
The outermost serous membrane
What is the pericardium?
The covering that encloses the heart
What is the space between the visceral and parietal pericardium called?
Pericardial cavity
The outermost layer of the sac surrounding the heart is composed of tough connective tissue. What is this layer called?
Fibrous pericardium
The outermost layer of the heart wall, called the____is composed of a serous membrane overlying adipose tissue and coronary vessels.
epicardium
Which layer of the pericardium directly covers the heart?
The visceral pericardium
The heart is located in the _____ and is _____ to the diaphragm.
mediastinum; superior
What is the myocardium?
The middle layer of heart tissue composed mostly of cardiac muscle
The____pericardium covers the inner surface of the fibrous pericardium.
parietal
What is the pericardial cavity?
The space between the visceral and parietal pericardium
Which of the following best describes the endocardium?
The inner lining of the heart
What is the outermost layer of heart wall called?
Epicardium
The heart is composed of___hollow chambers.
4
What is the visceral pericardium?
The serous membrane attached directly to the surface of the heart
The auricles are flap-like projection off of the___and serve to increase their blood volume.
atria
Blood from the superior and inferior vena cavae and the coronary sinus flow into the
right atrium
The tricuspid valve is located
between the right atrium and right ventricle
Contraction of the right ventricle leads to what action?
Closing of the tricuspid valve
How does the tricuspid valve close?
The contraction of the right ventricle forces blood against the cusps, which closes the valve.
The wall of the left ventricle is thicker than the wall of the right ventricle. Why?
The left ventricle has to pump blood farther.
Which valve is found between the right ventricle and the pulmonary trunk?
The pulmonary valve
Where does the blood that enters the left atrium come from?
The pulmonary veins
What chamber of the heart pumps blood into the pulmonary trunk?
The right ventricle
The left ___ receives blood from the four pulmonary___
atrium, veins
What chamber of the heart pushes blood into the aorta?
left ventricle
Blood from the right ventricle flows to the_____ ______which then splits into two arteries (left and right) that lead into the lungs.
pulmonary, trunk
Which heart chamber receives blood that is low in oxygen?
The right atrium
The left ventricular contraction forces blood into the____a large artery.
Aorta
A blood cell is traveling in the inferior vena cava and approaches the heart. Rank the following structures in the order in which the cell encounters them, starting with the first one at the top.
1. Right atrium
2. Right ventricle
3. Lungs
4. Left atrium
5. Left ventricle
What is the name of the main vessels that supply the heart tissue with blood?
Coronary arteries
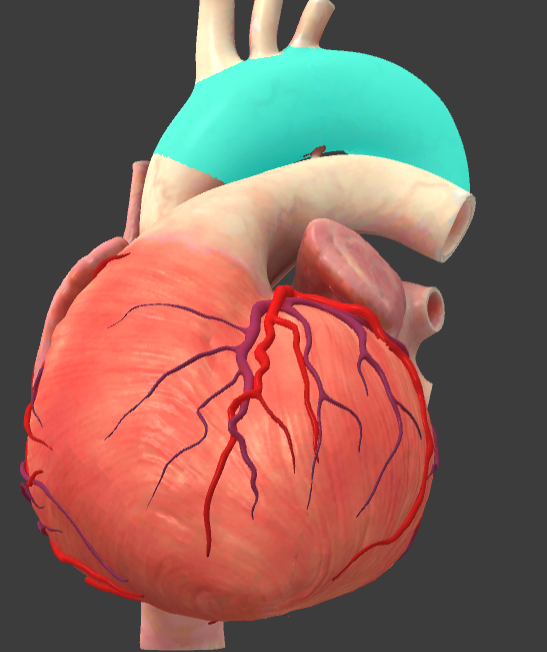
Arch of aorta
Brachiocephalic trunk
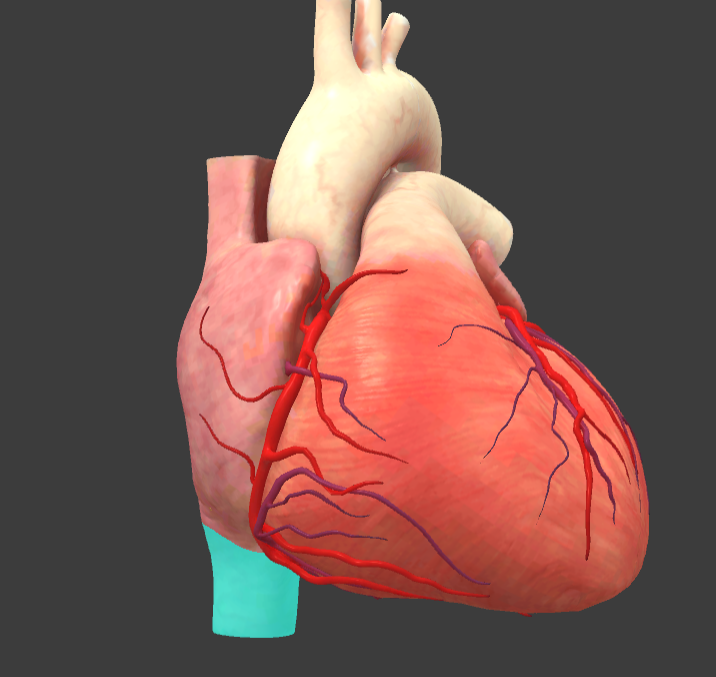
Inferior vena cava
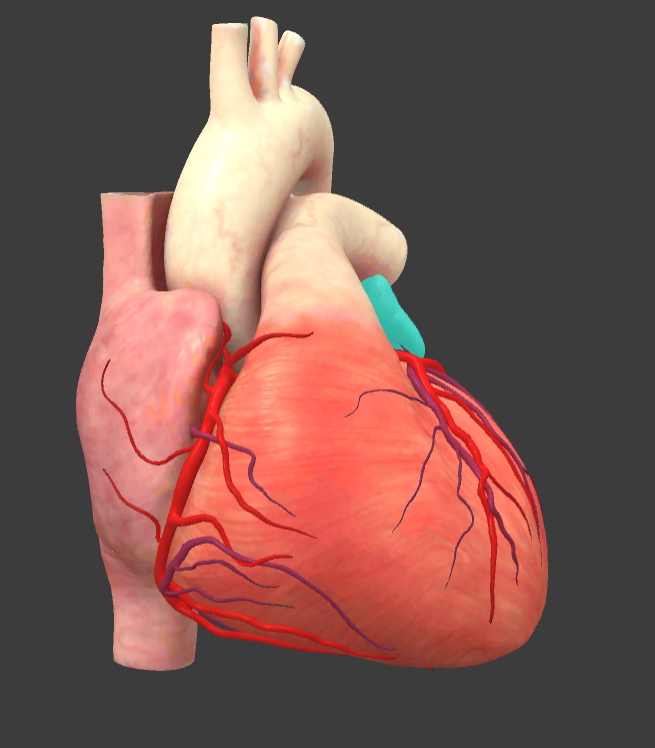
Left auricle
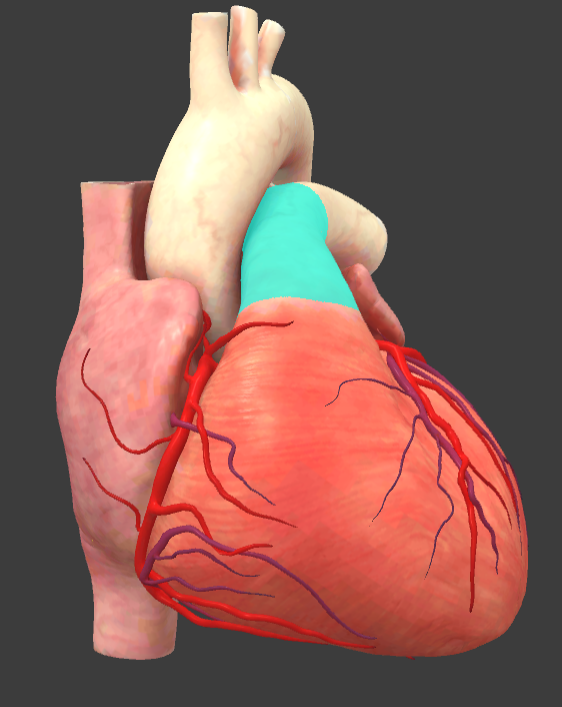
Pulmonary trunk
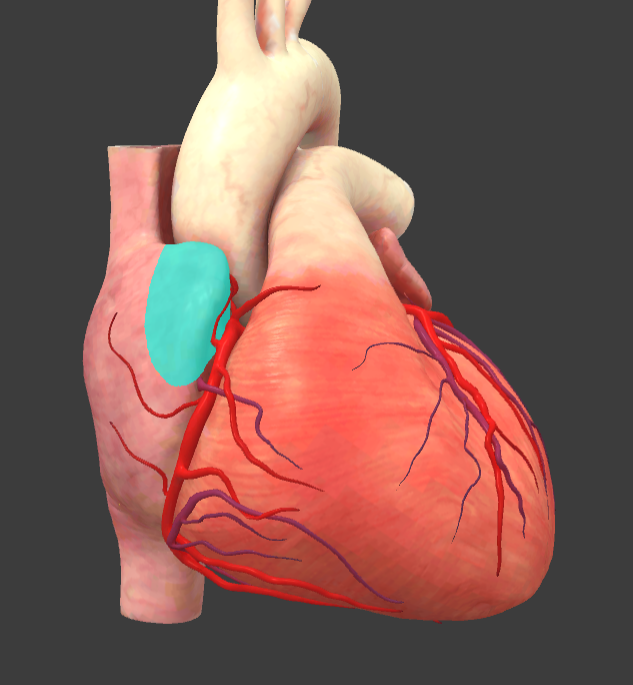
Right auricle
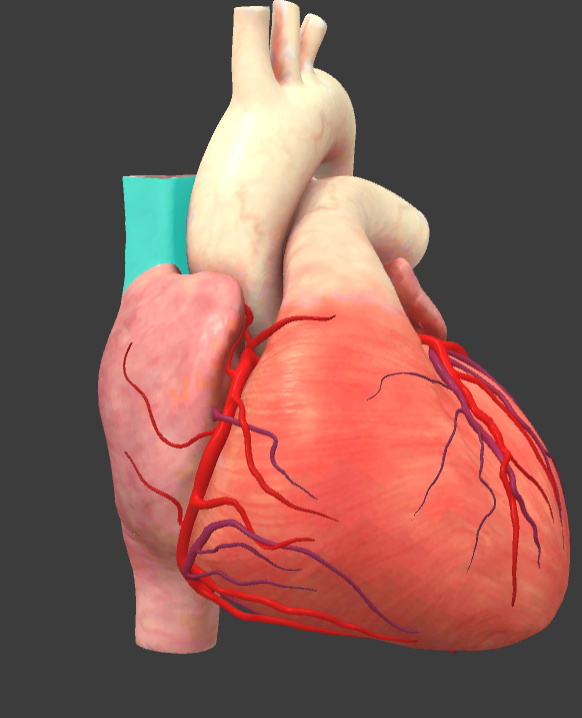
Superior vena cava
Aortic valve
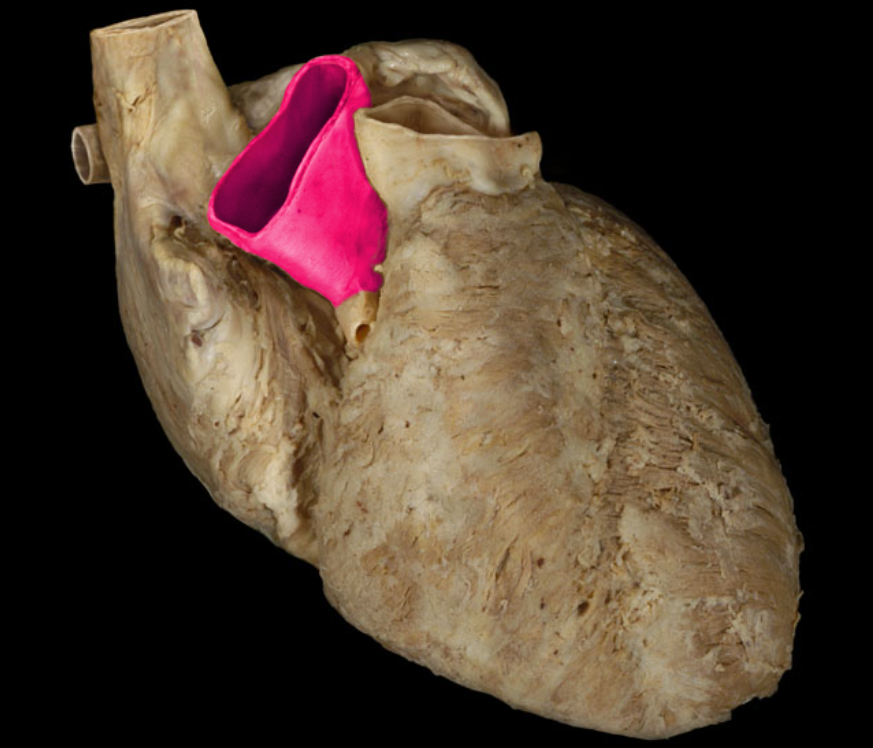
Ascending aorta
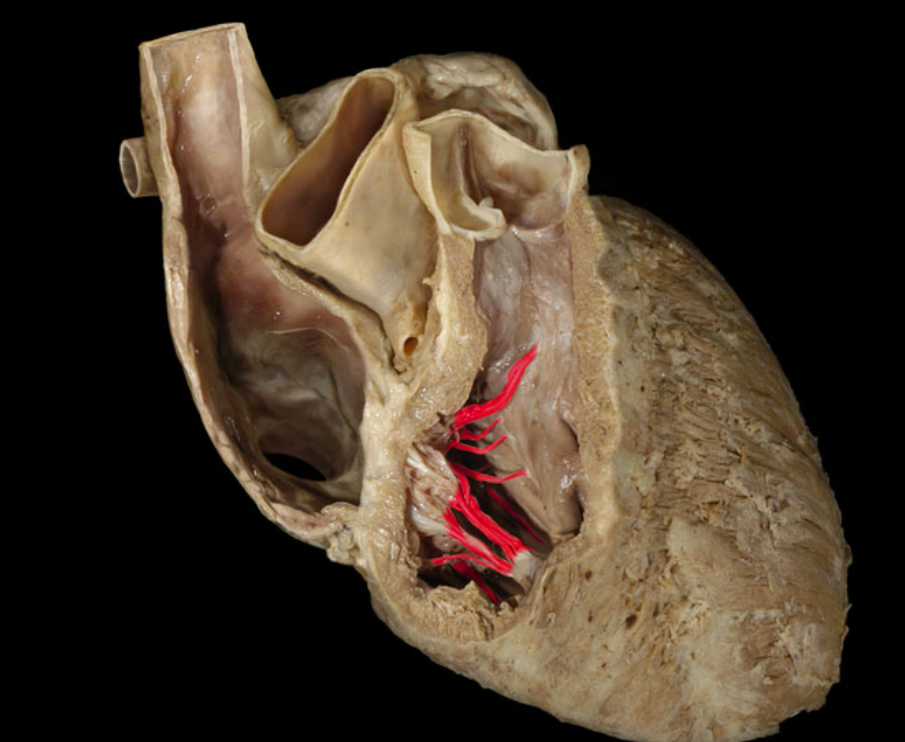
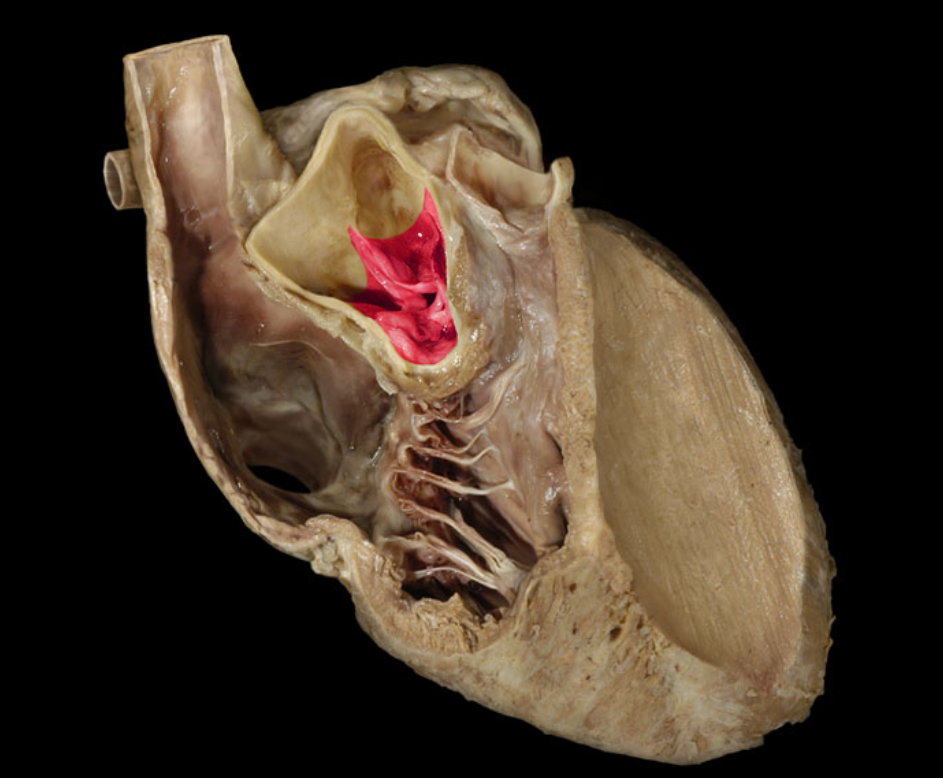
Chordae tendineae
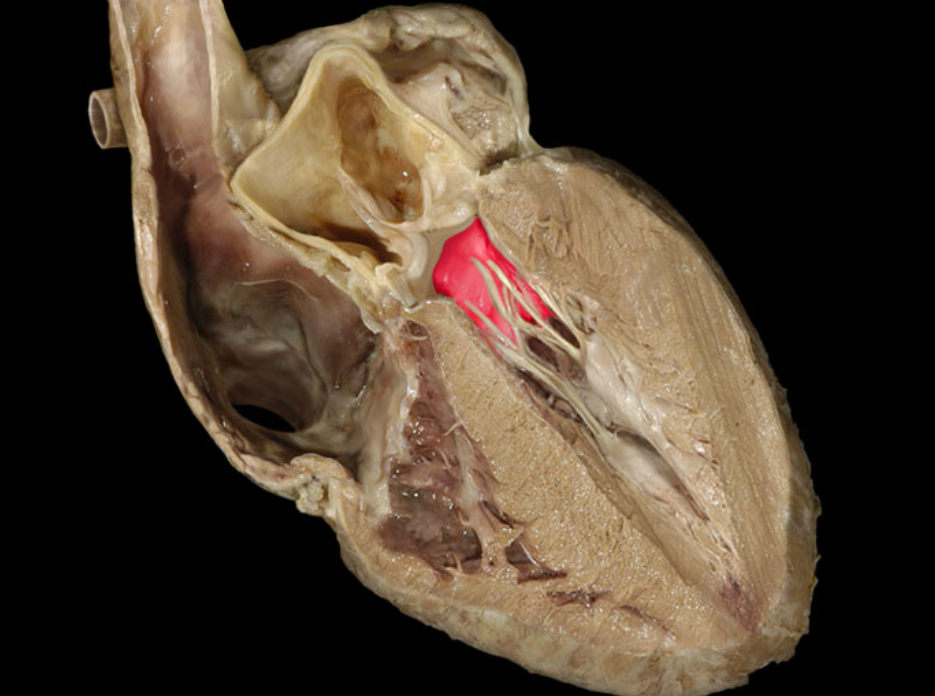
Left atrioventricular valve
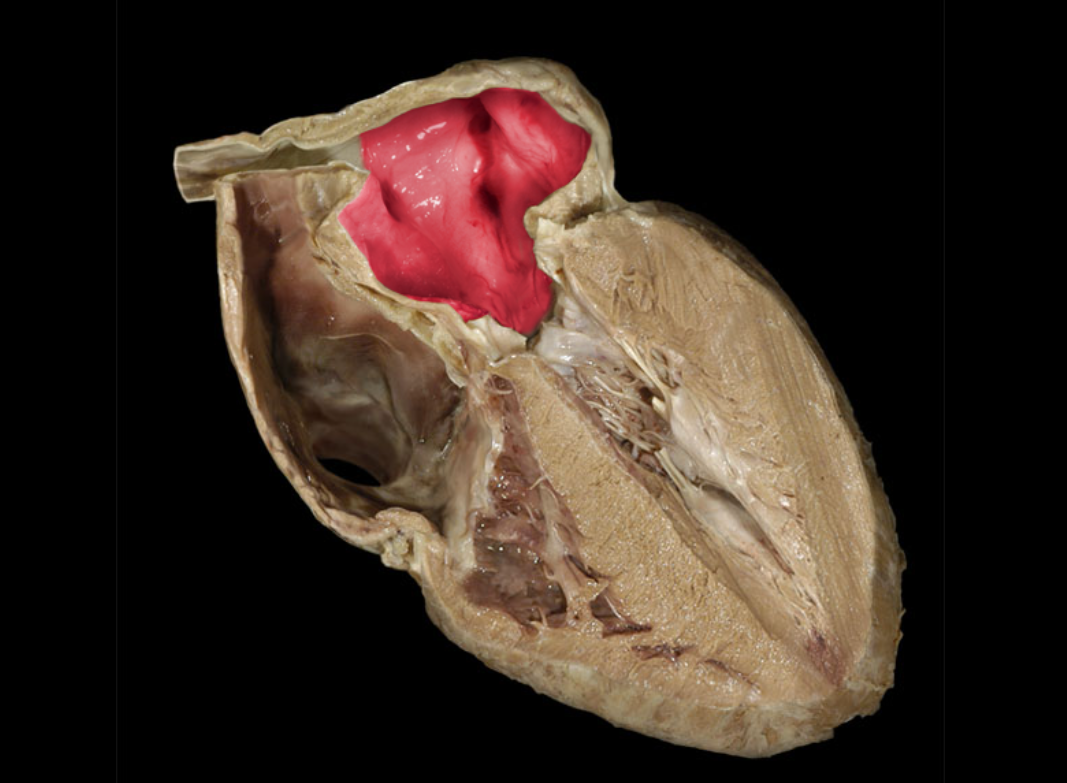
Left atrium
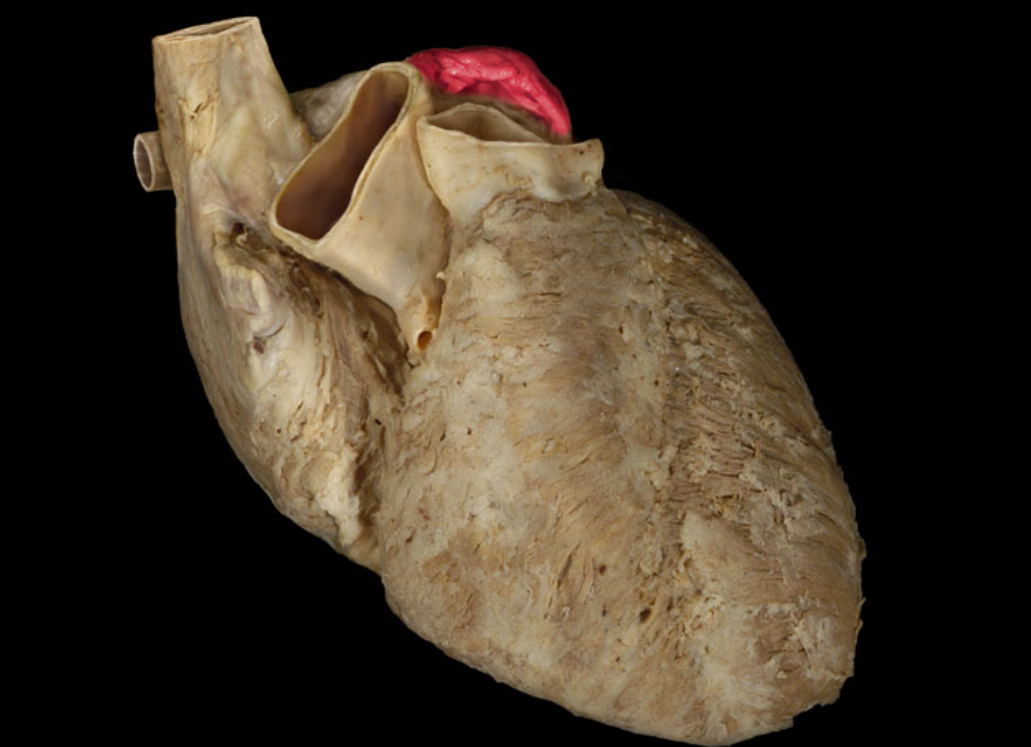
Left auricle
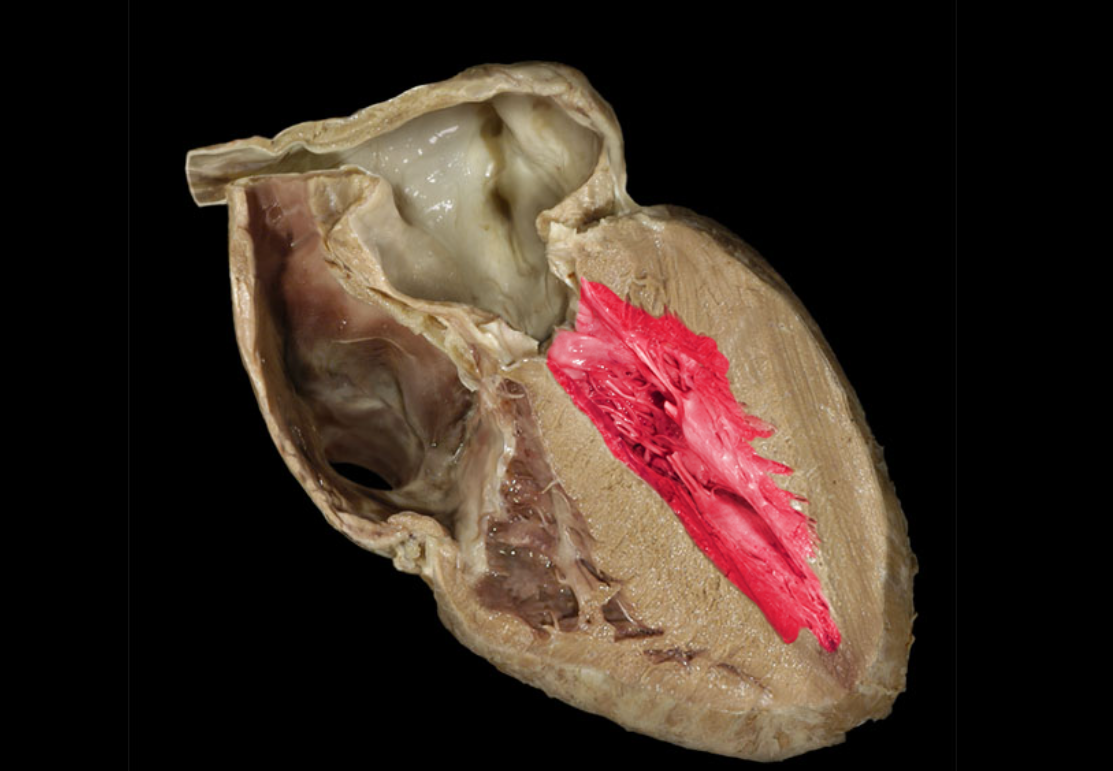
Left ventricle
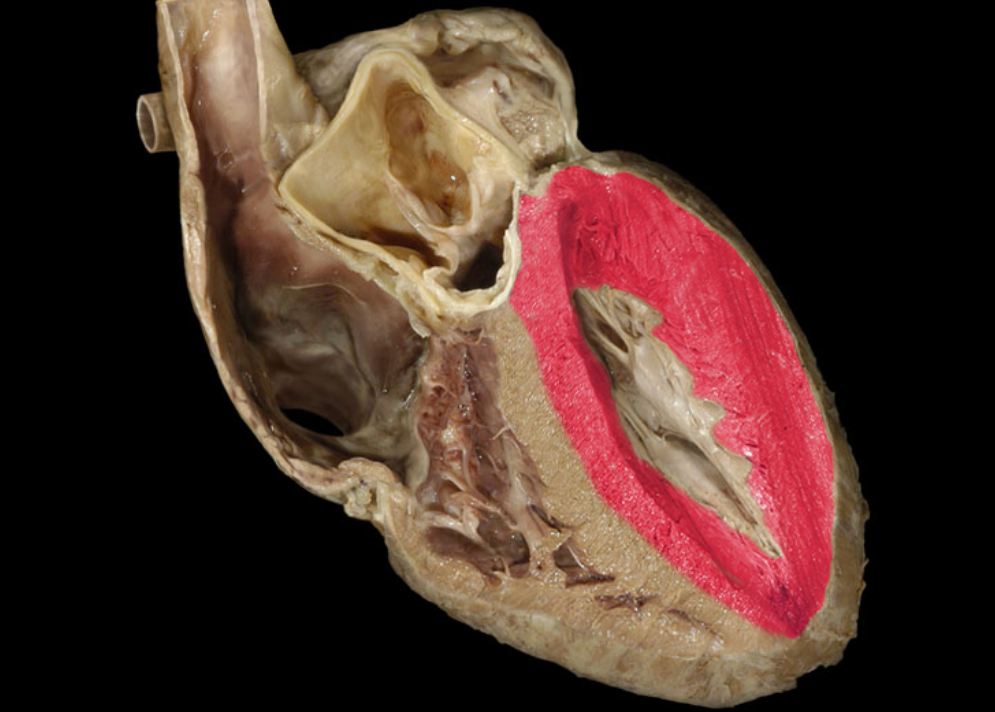
Myocardium of left ventricle
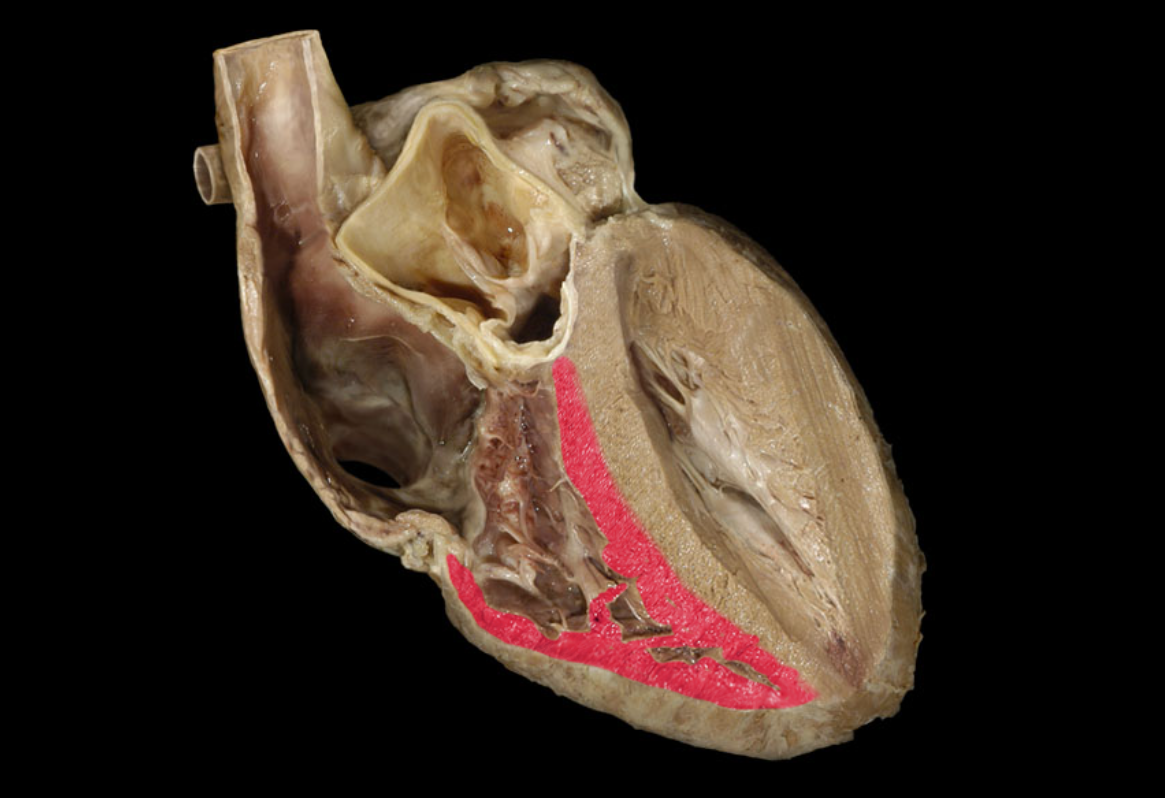
Myocardium of right ventricle
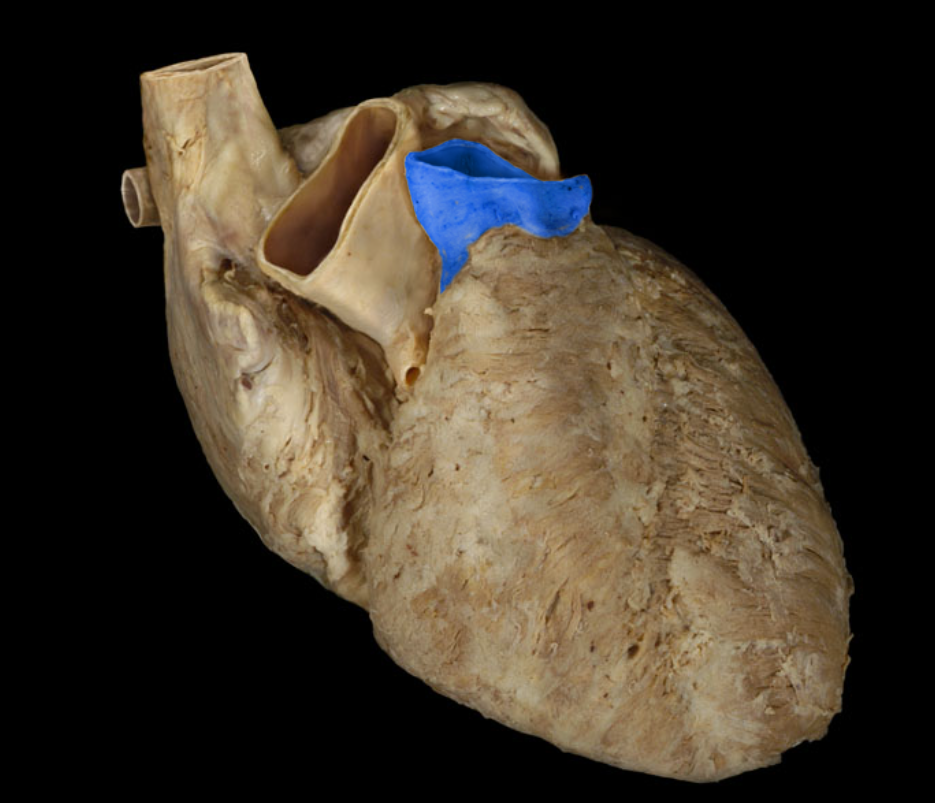
Pulmonary trunk
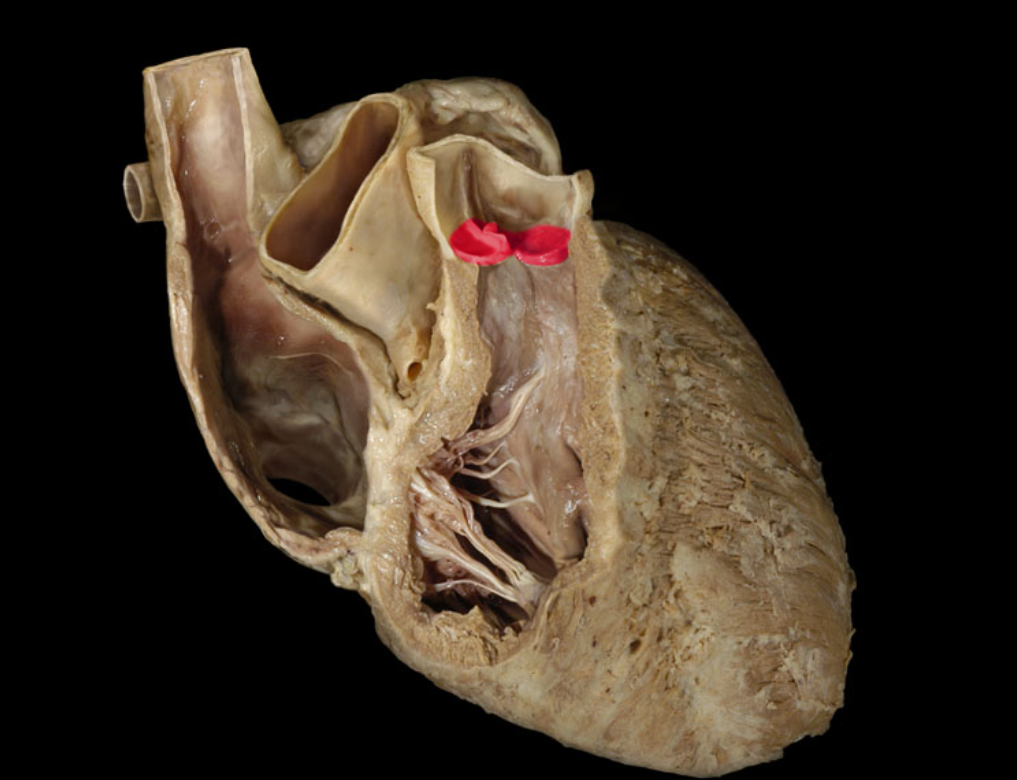
Pulmonary valve
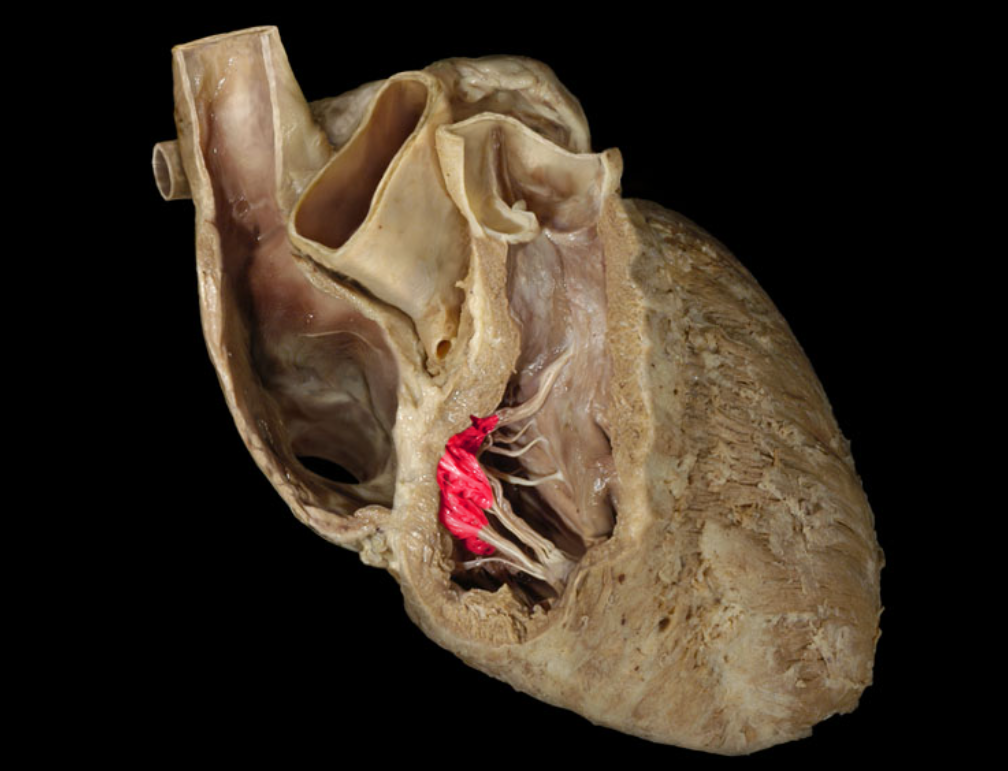
Right atrioventricular valve
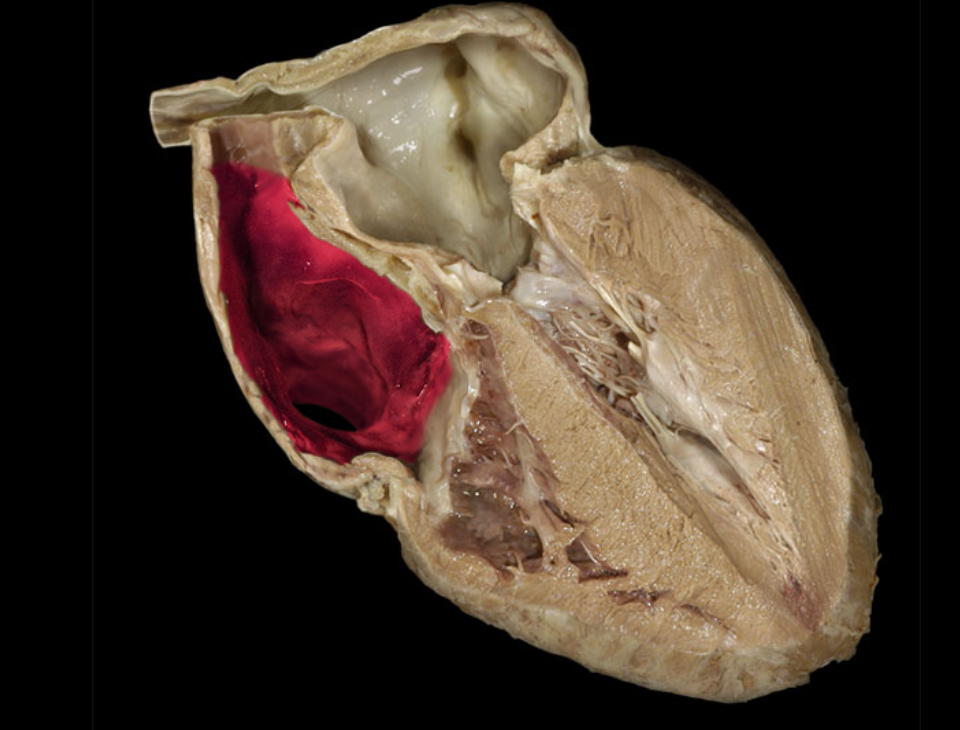
Right atrium
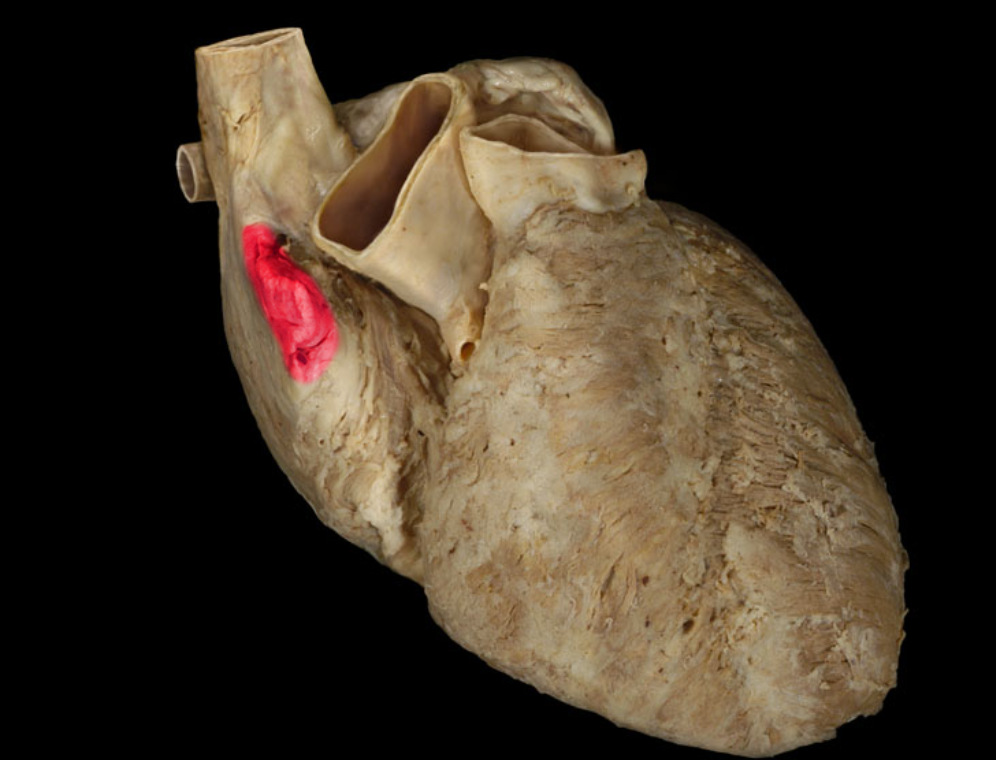
Right auricle
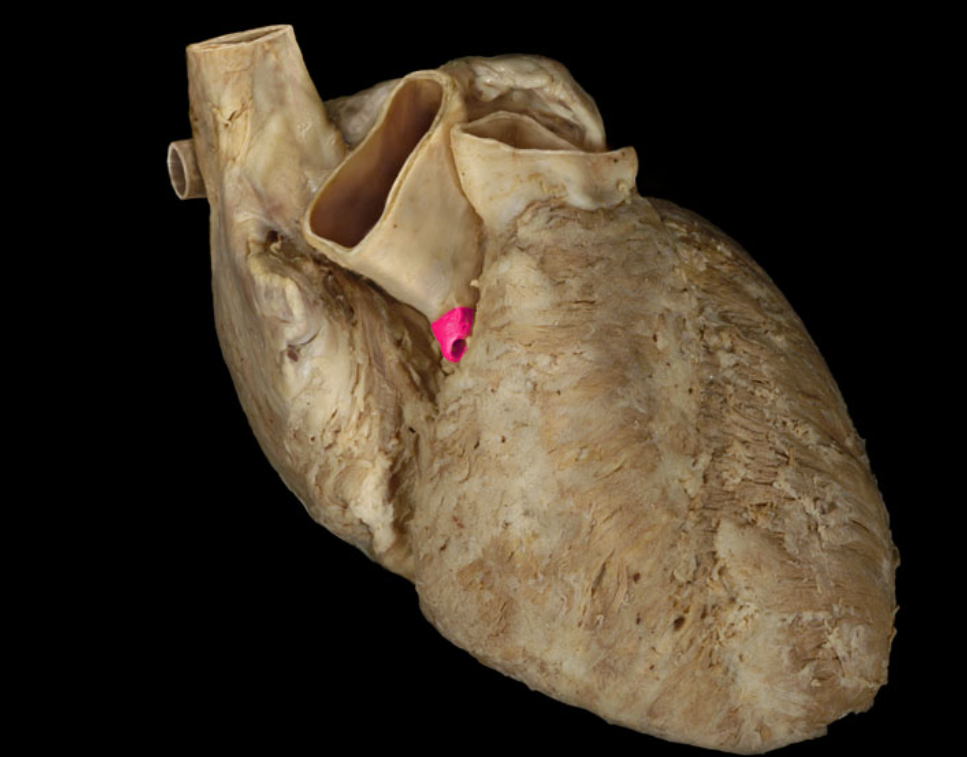
Right coronary a.
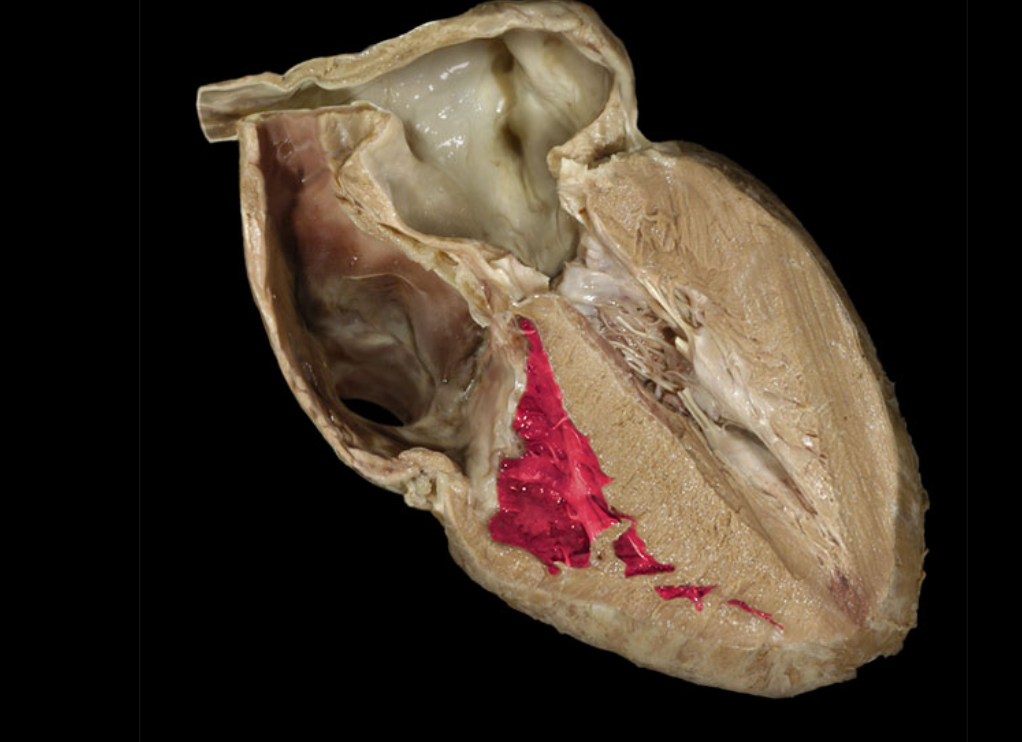
Right ventricle
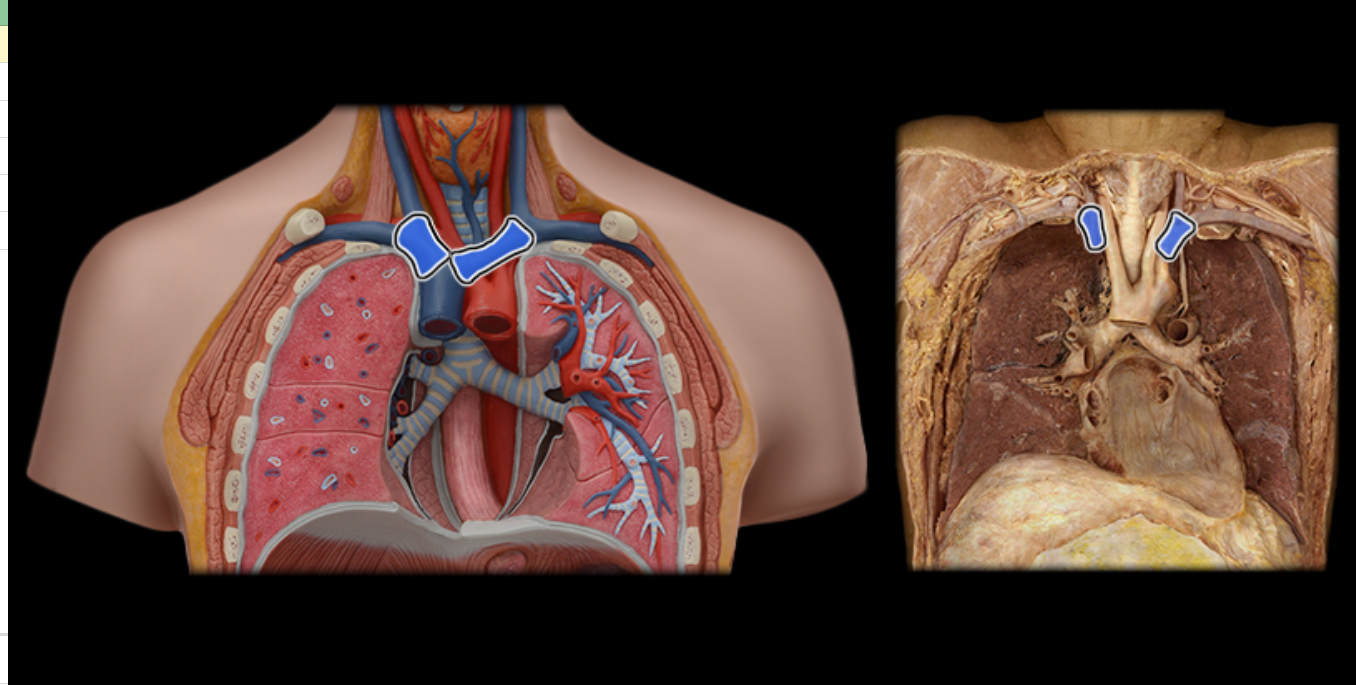
Brachiocephalic v.
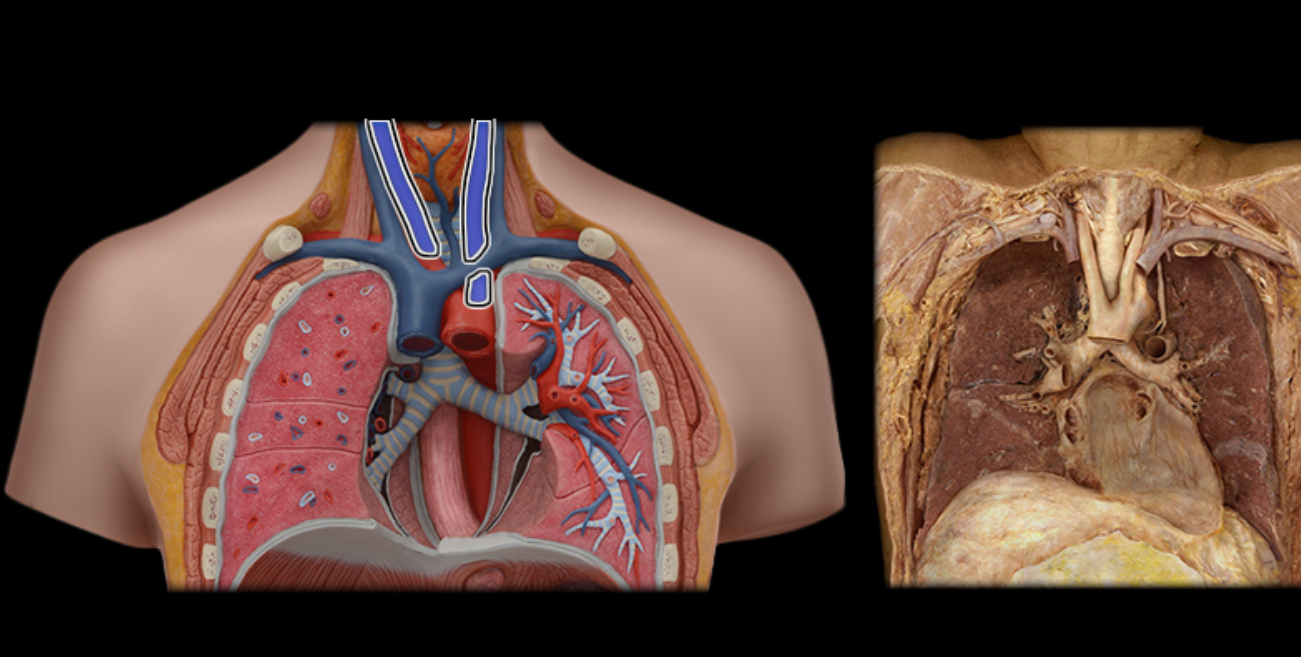
Common carotid a.
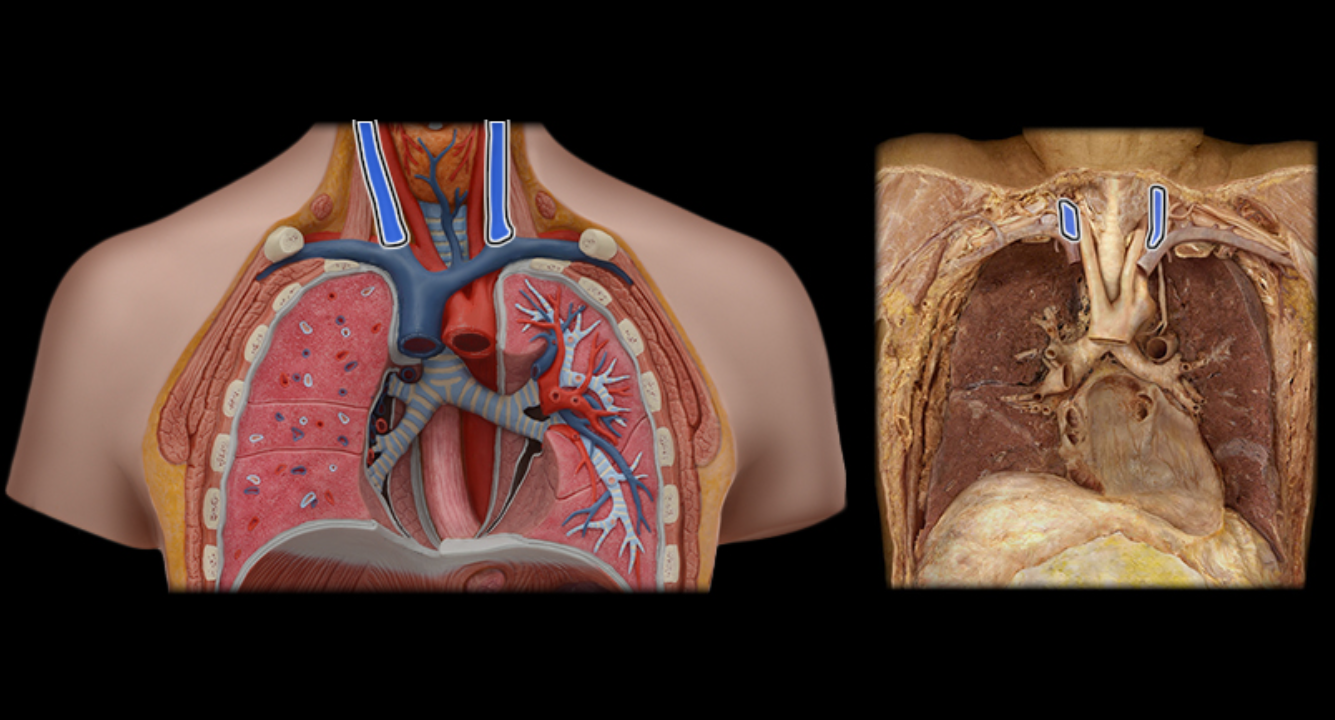
Internal jugular v.
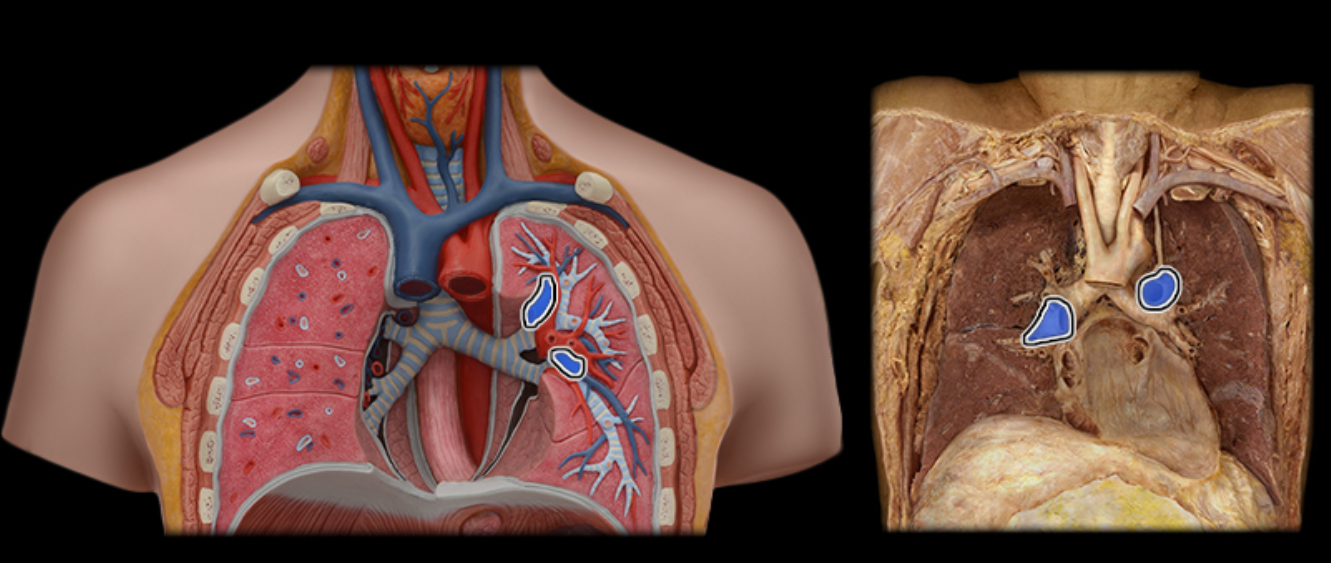
Pulmonary a.
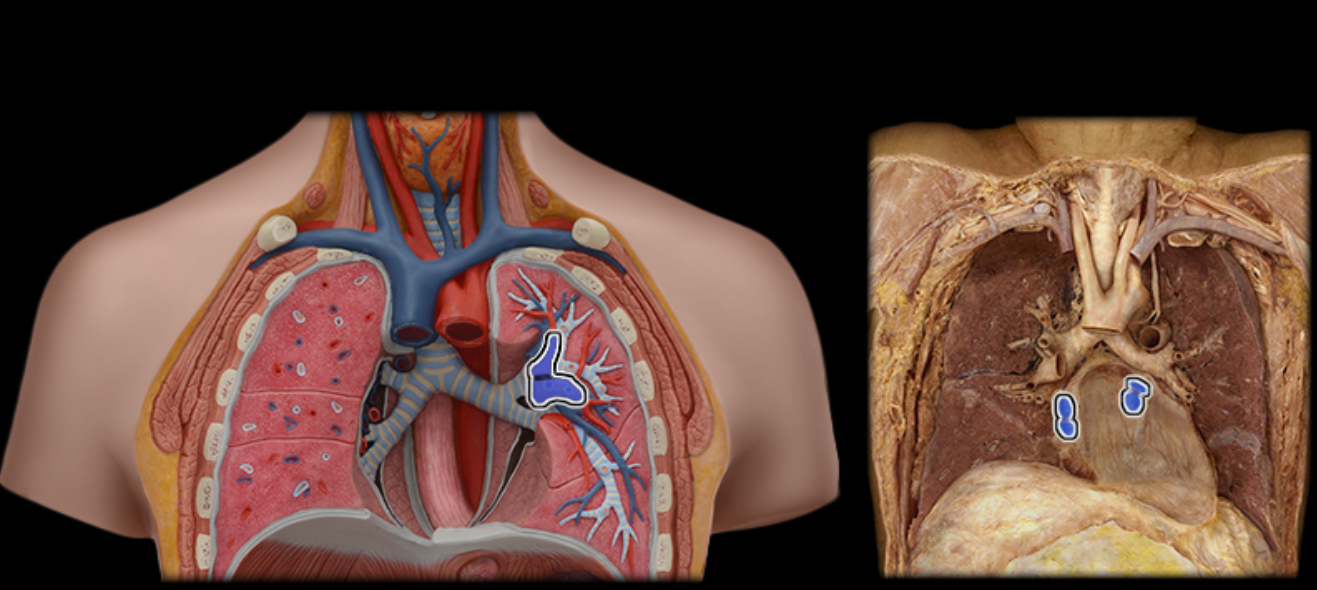
Pulmonary vv.
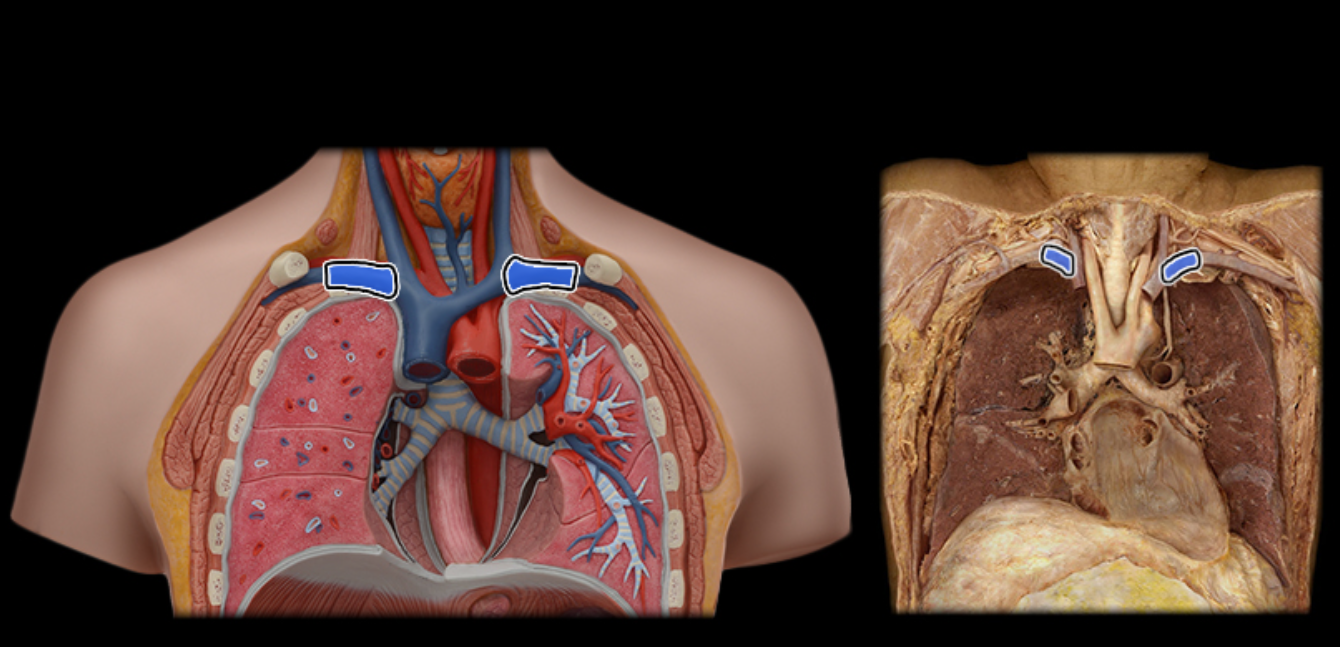
Subclavian v.
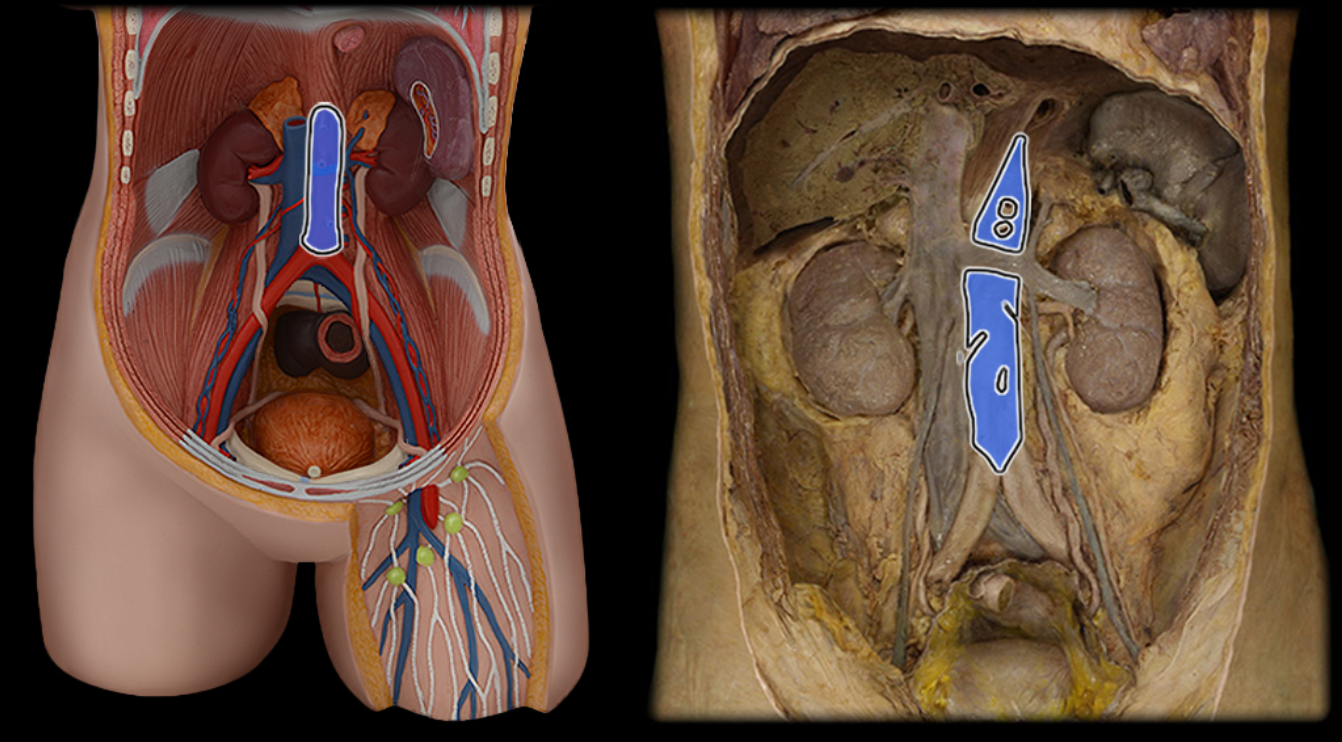
Abdominal aorta
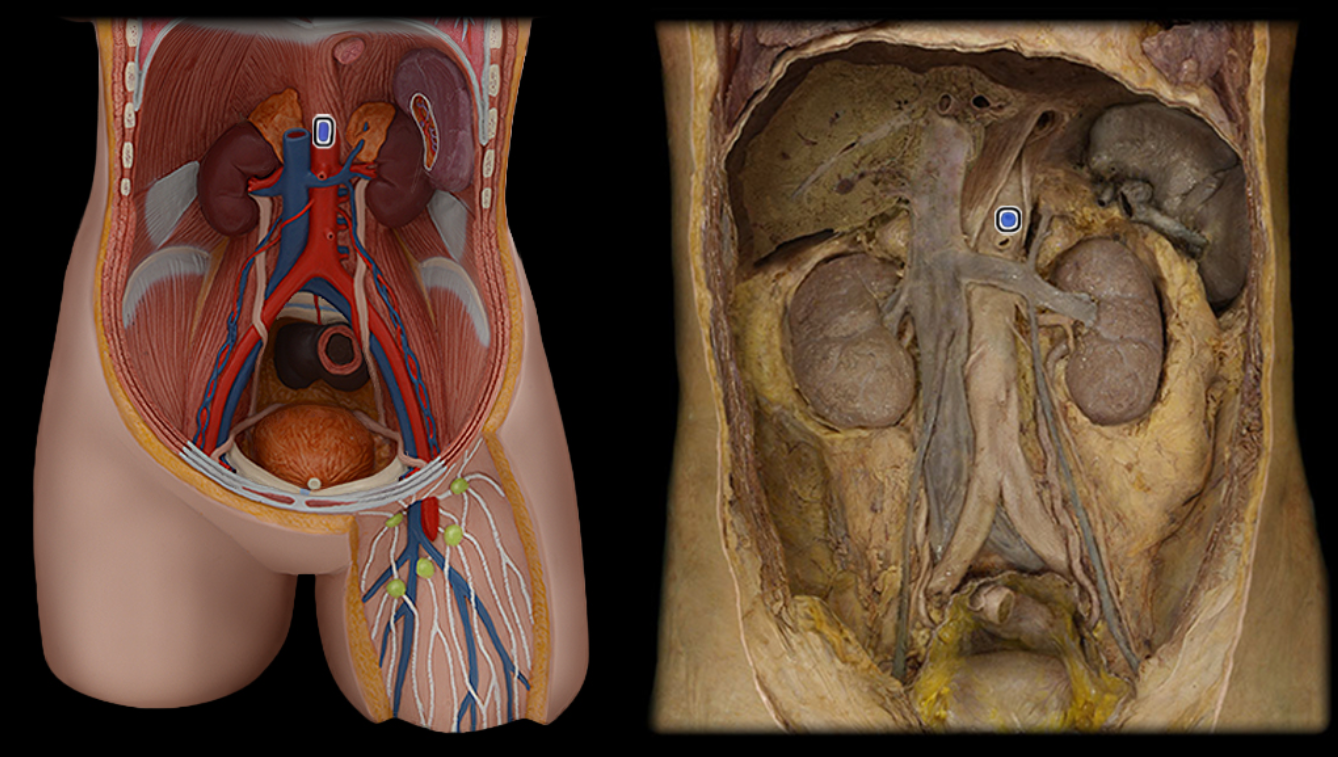
Celiac a.
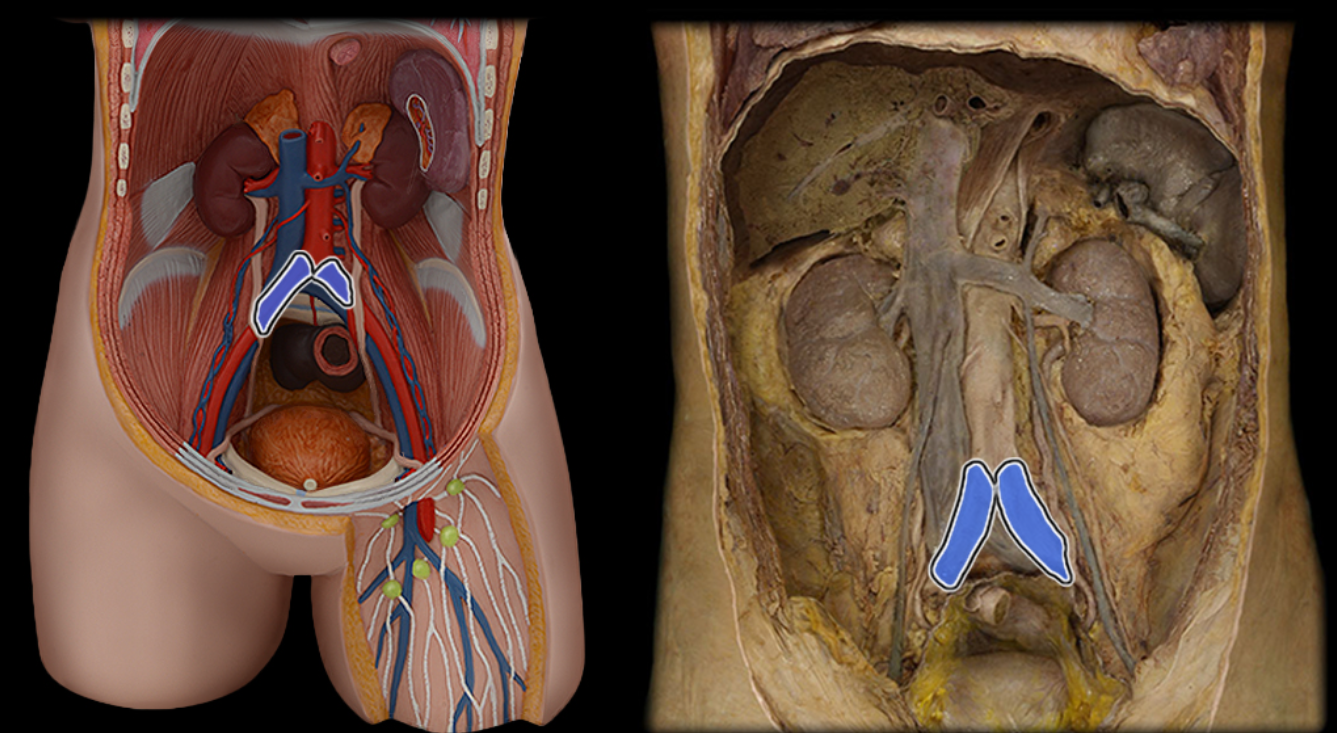
Common iliac a.
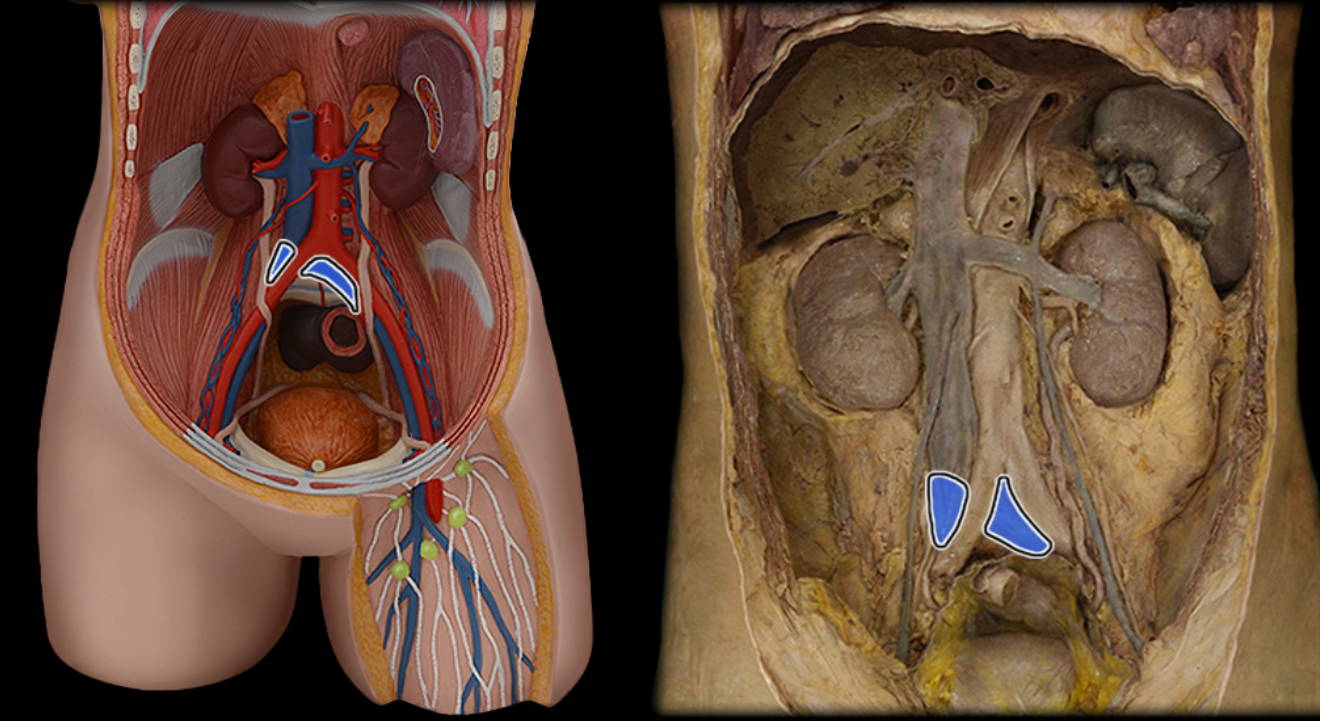
Common iliac v.
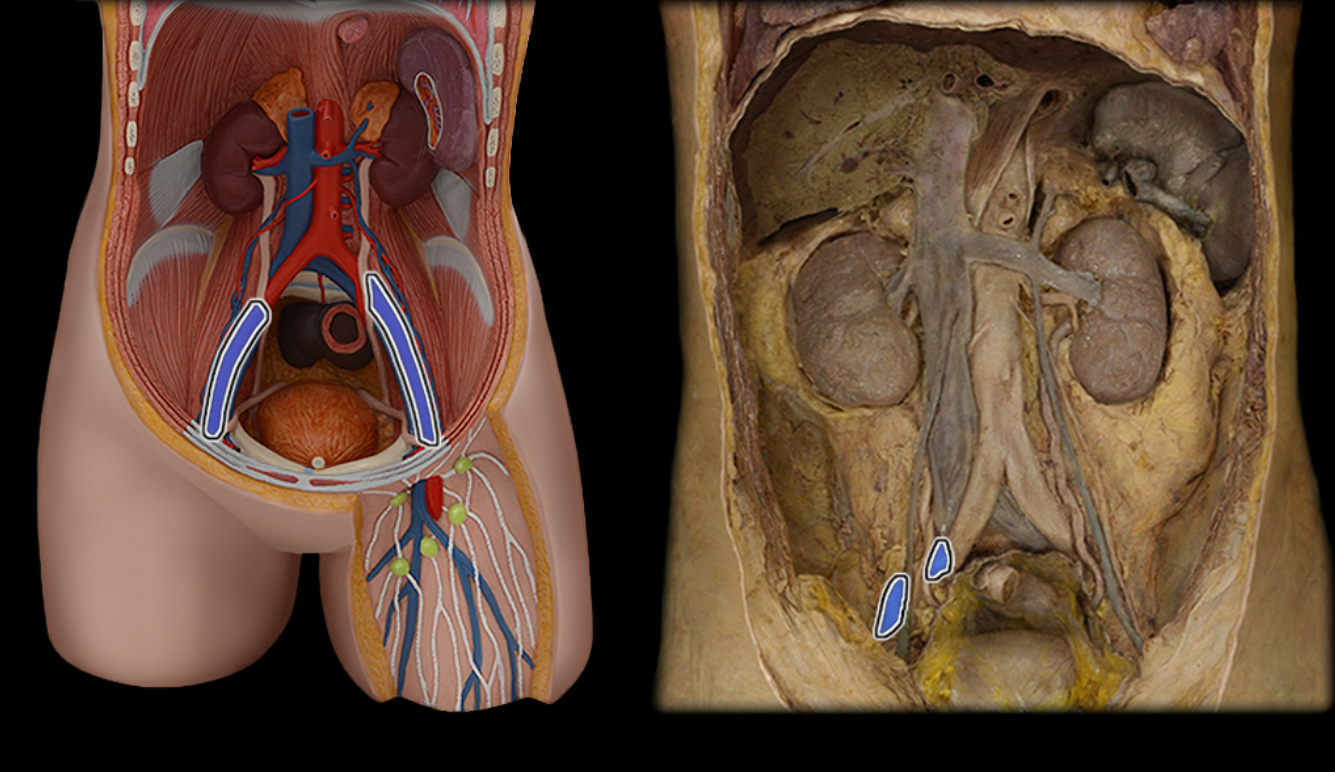
External iliac a.
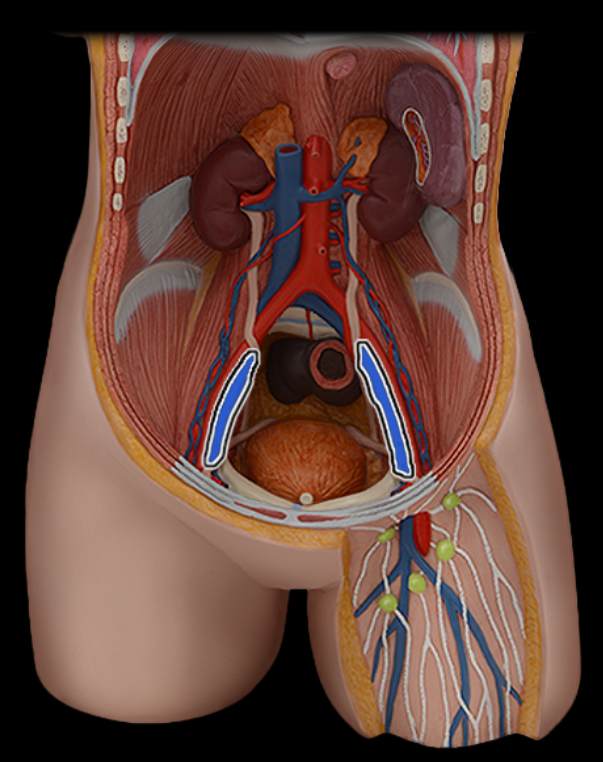
External iliac v.
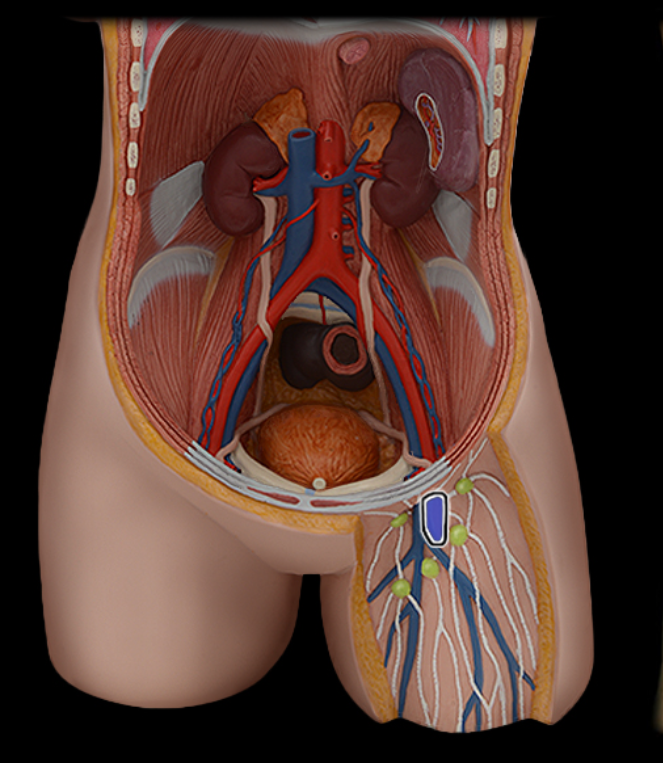
Femoral a.
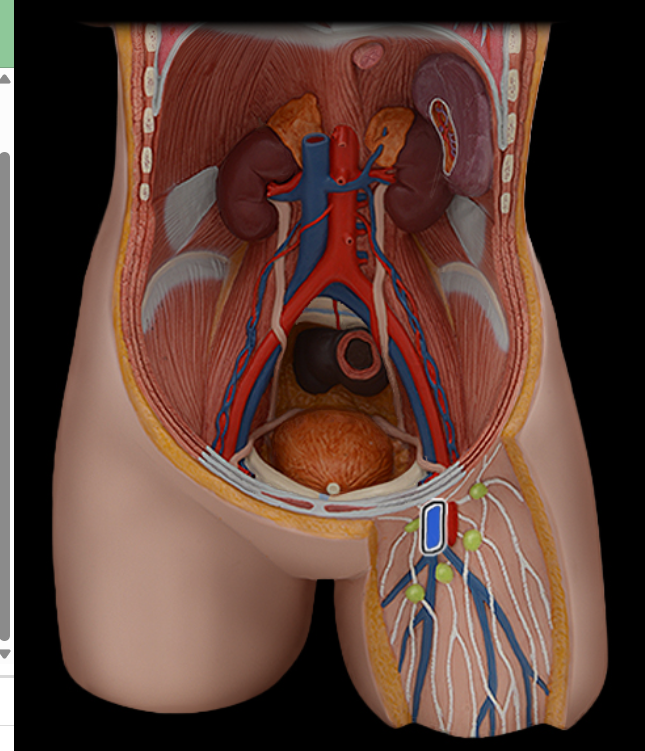
Femoral v.
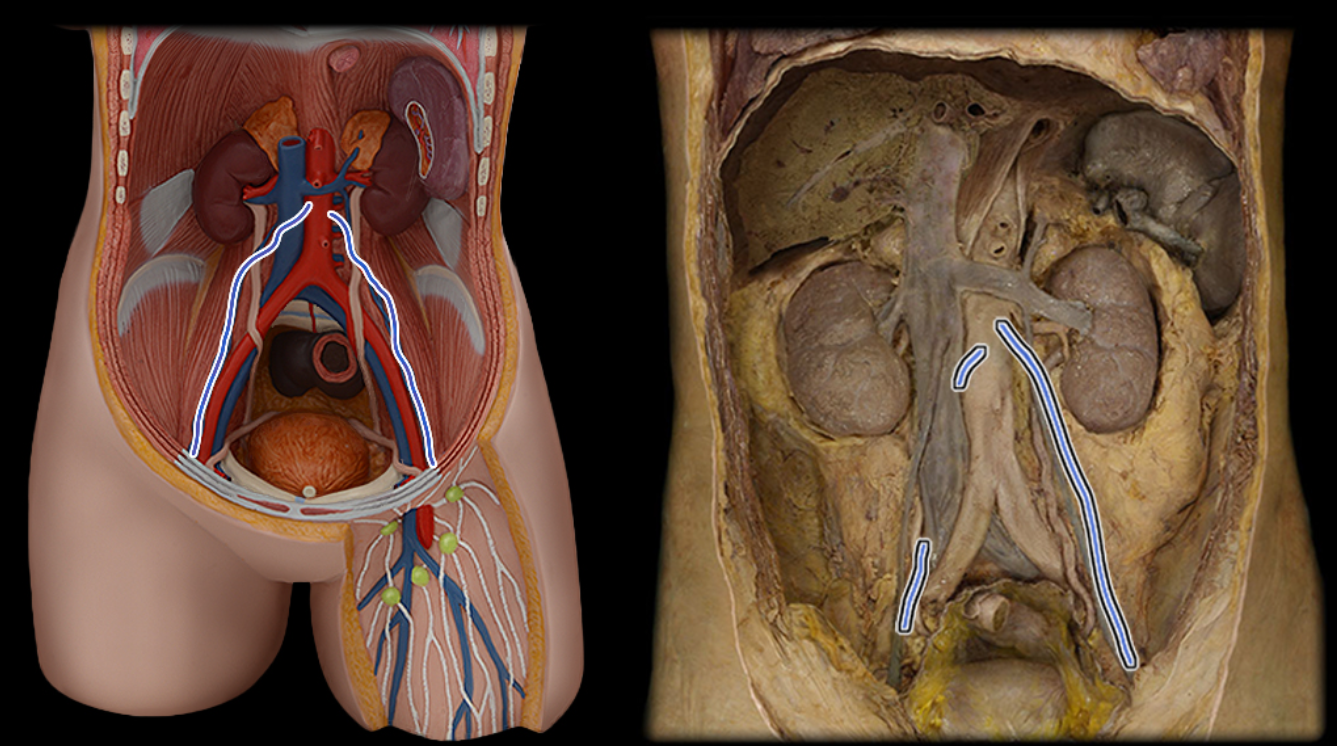
Gonadal a.
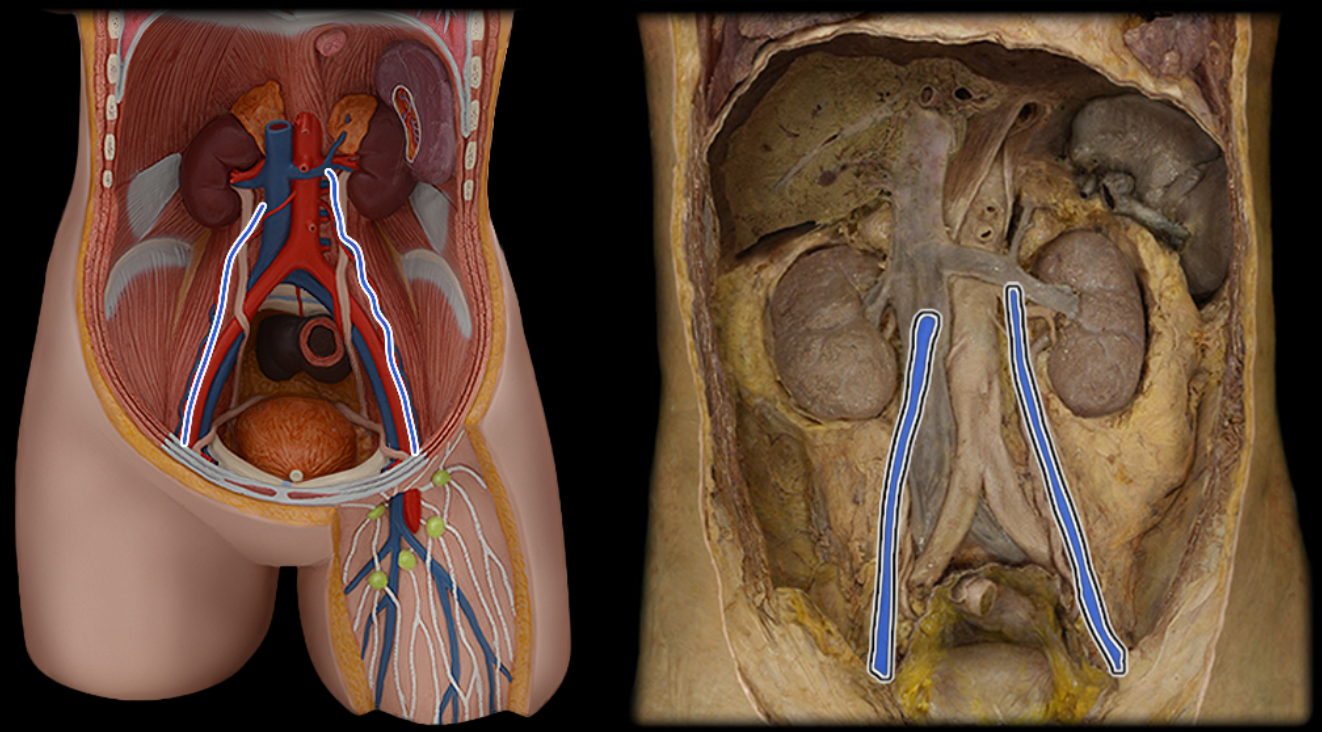
Gonadal v.
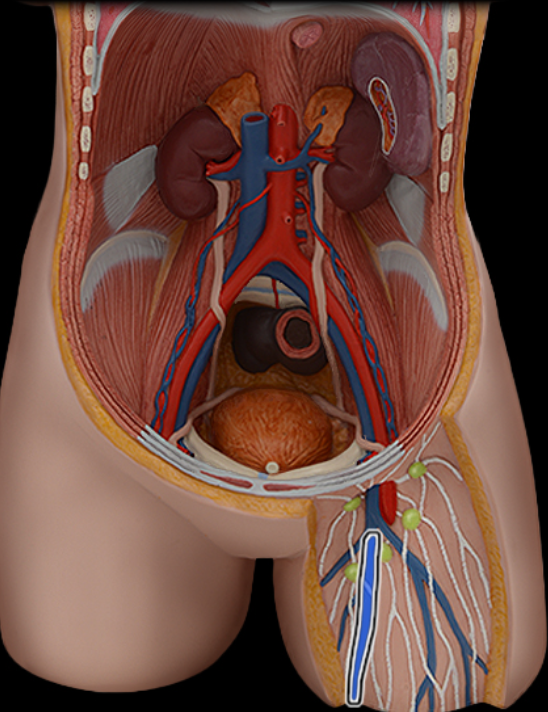
Great saphenous v.
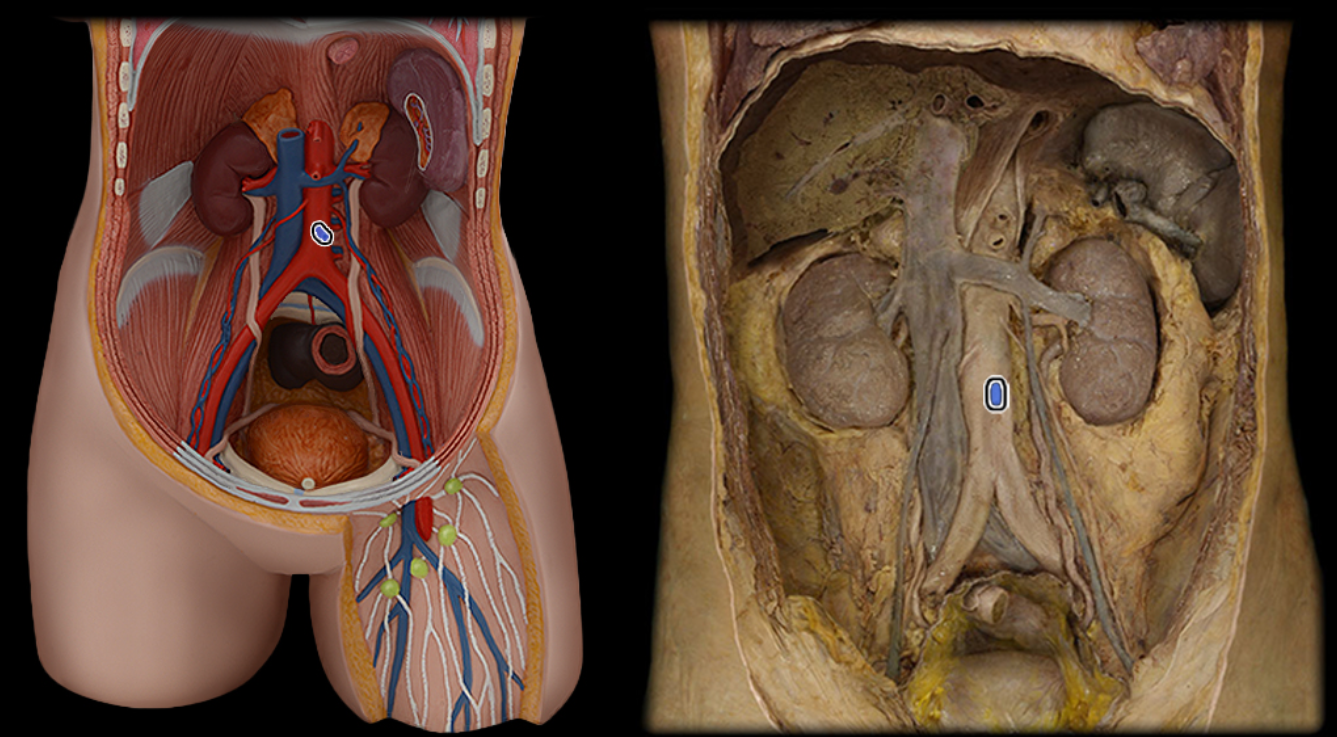
Inferior mesenteric a.
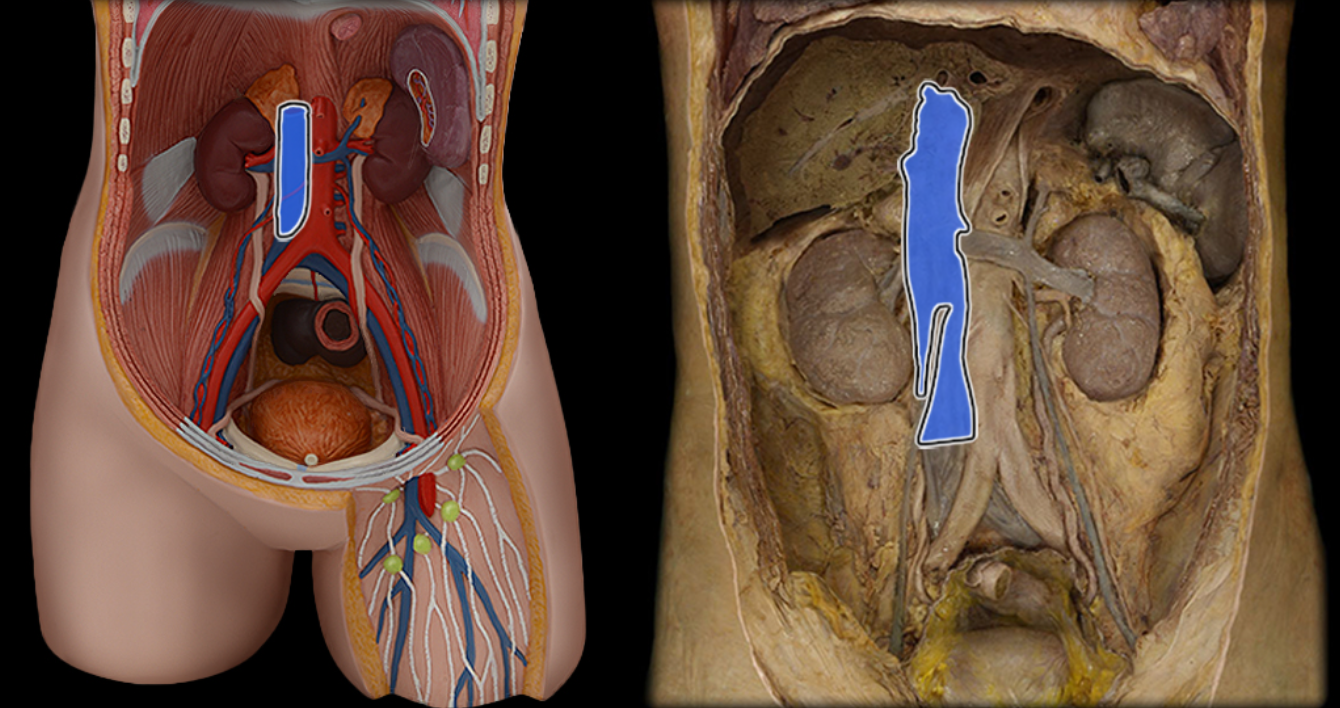
Inferior vena cava
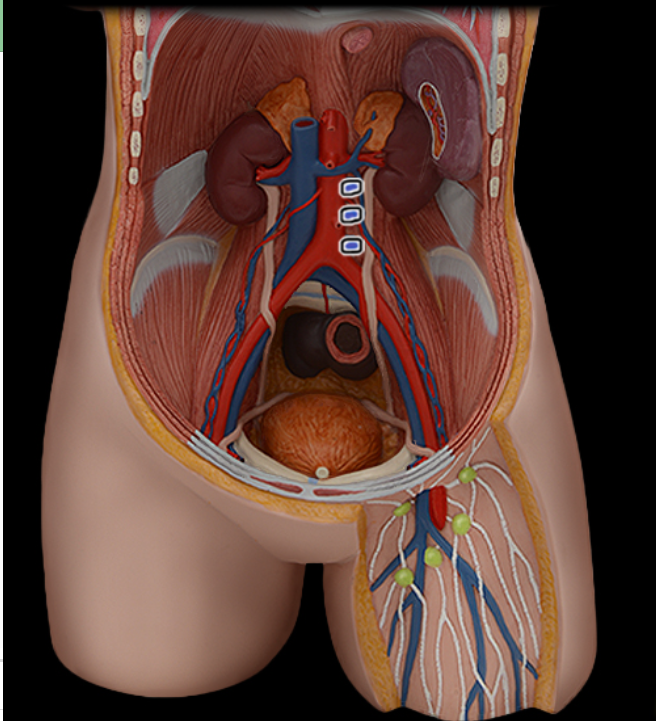
Lumbar a.
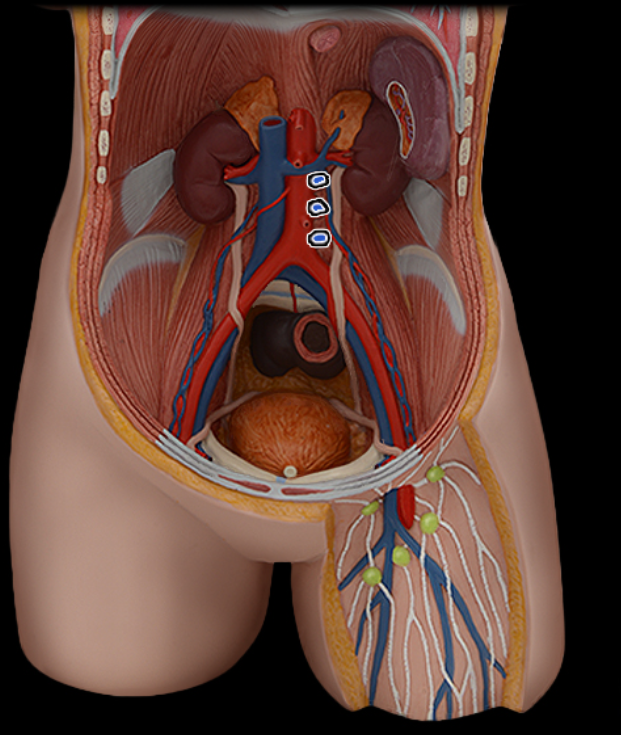
Lumbar v.
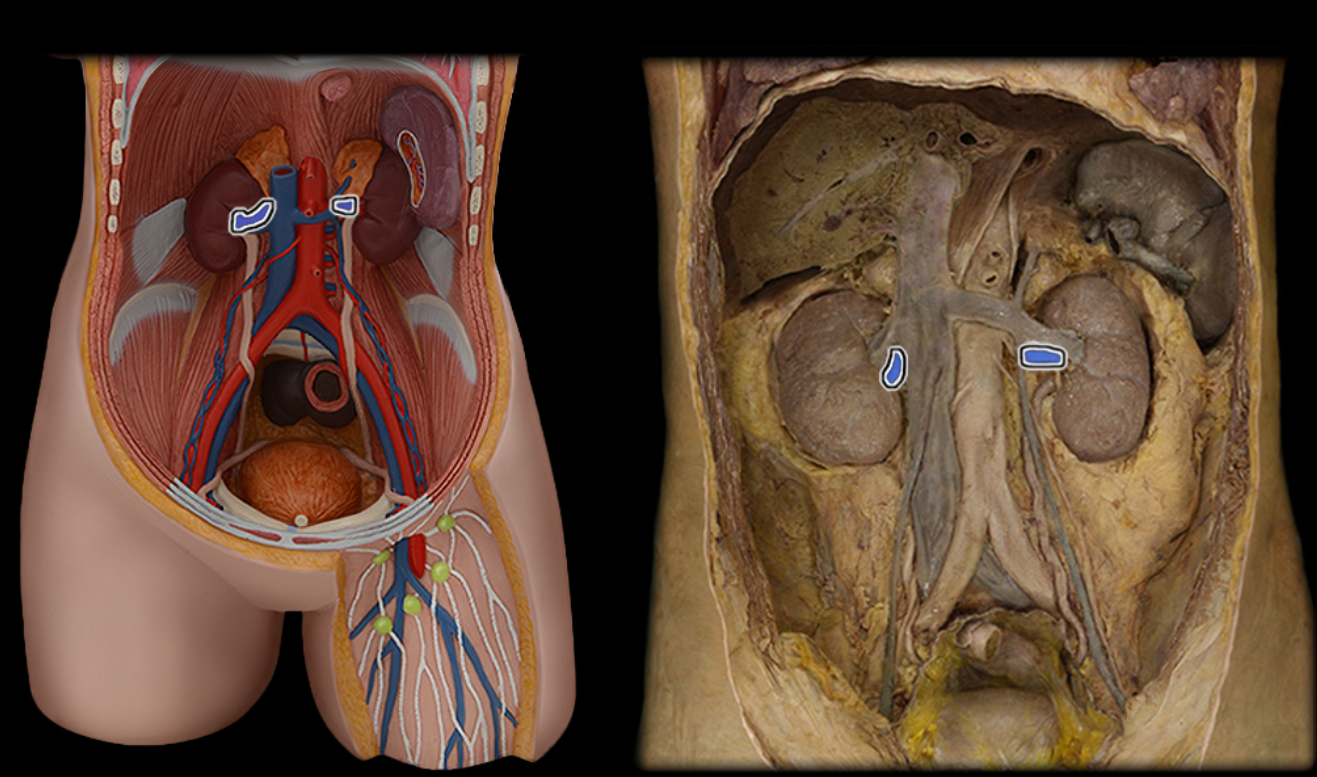
Renal a.
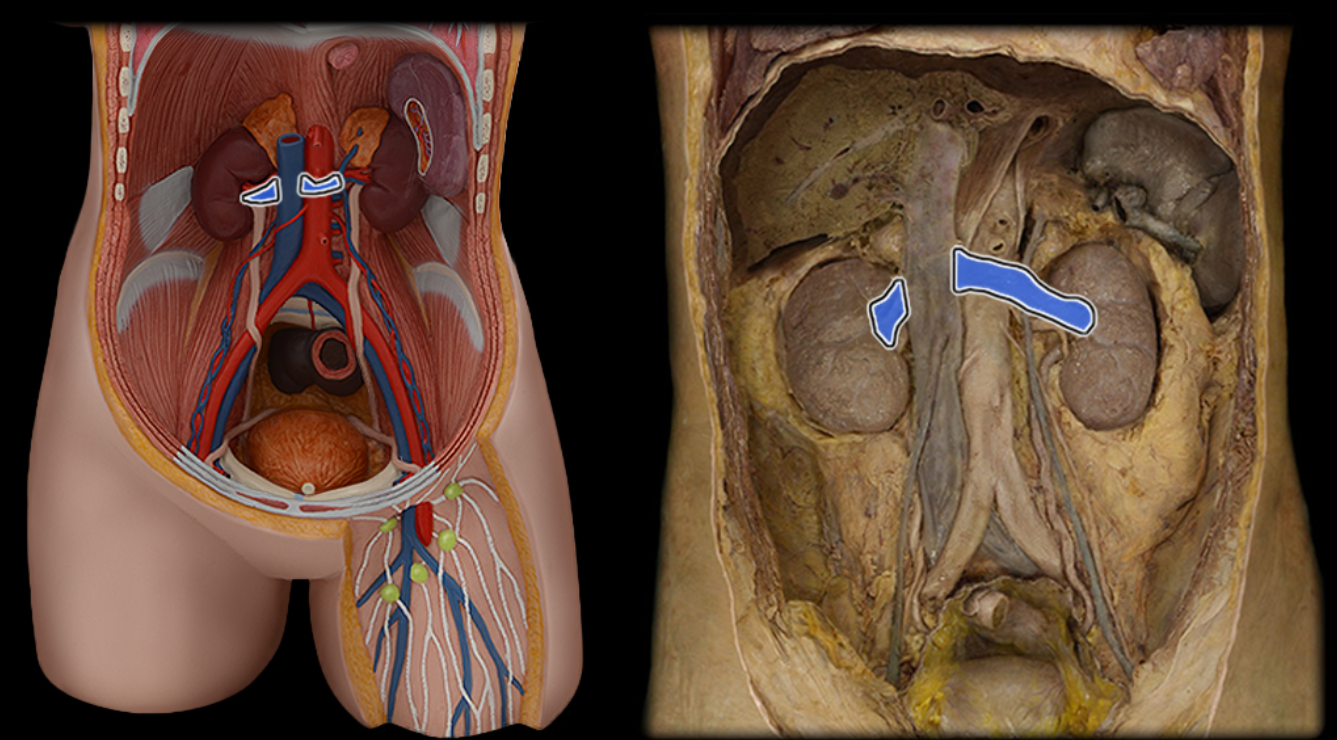
Renal v.
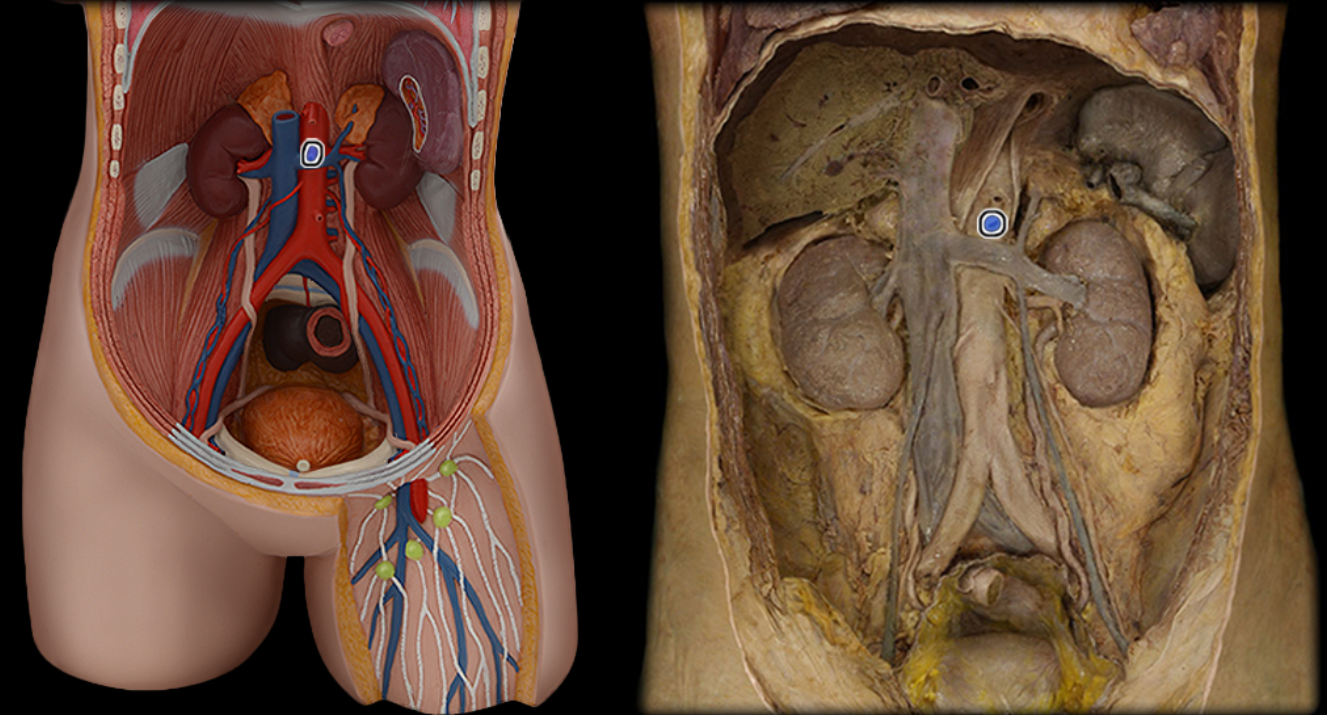
Superior mesenteric a.
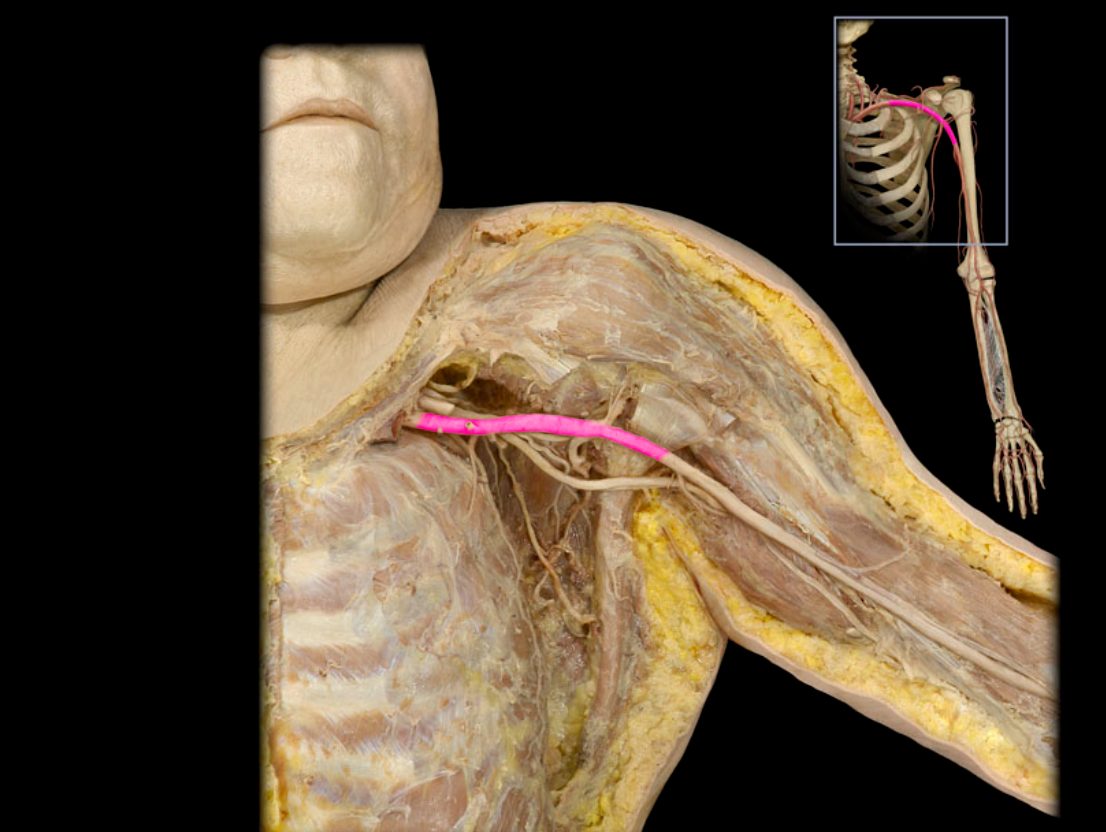
Axillary a.
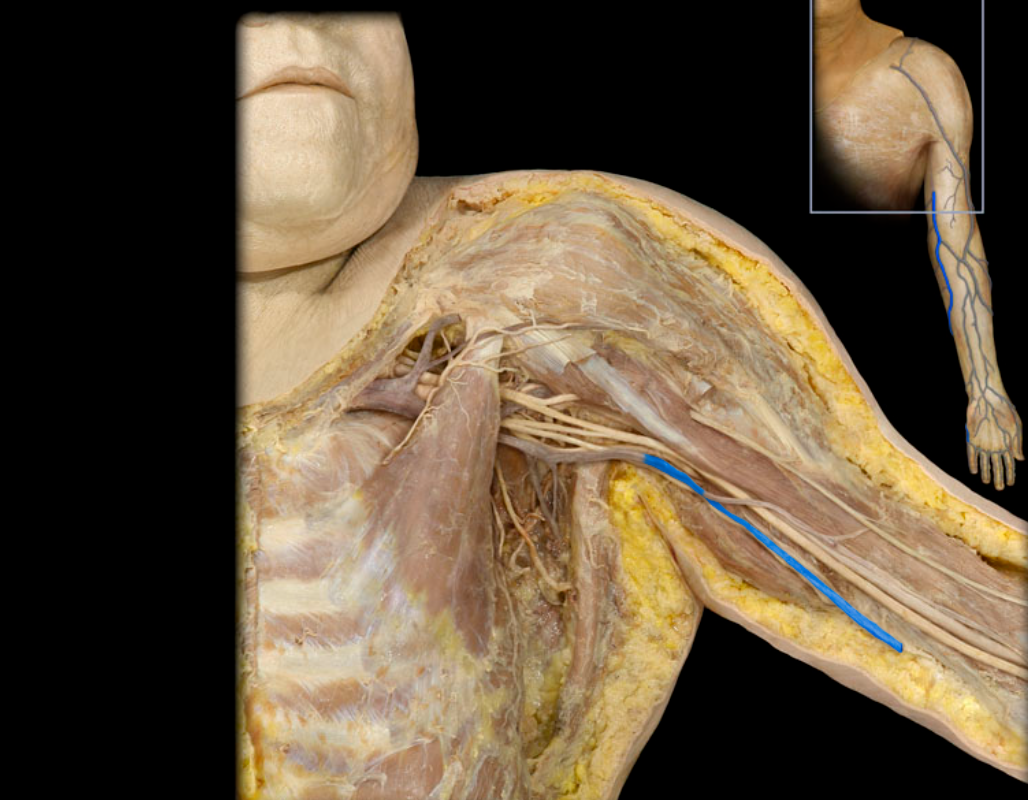
Basilic v.
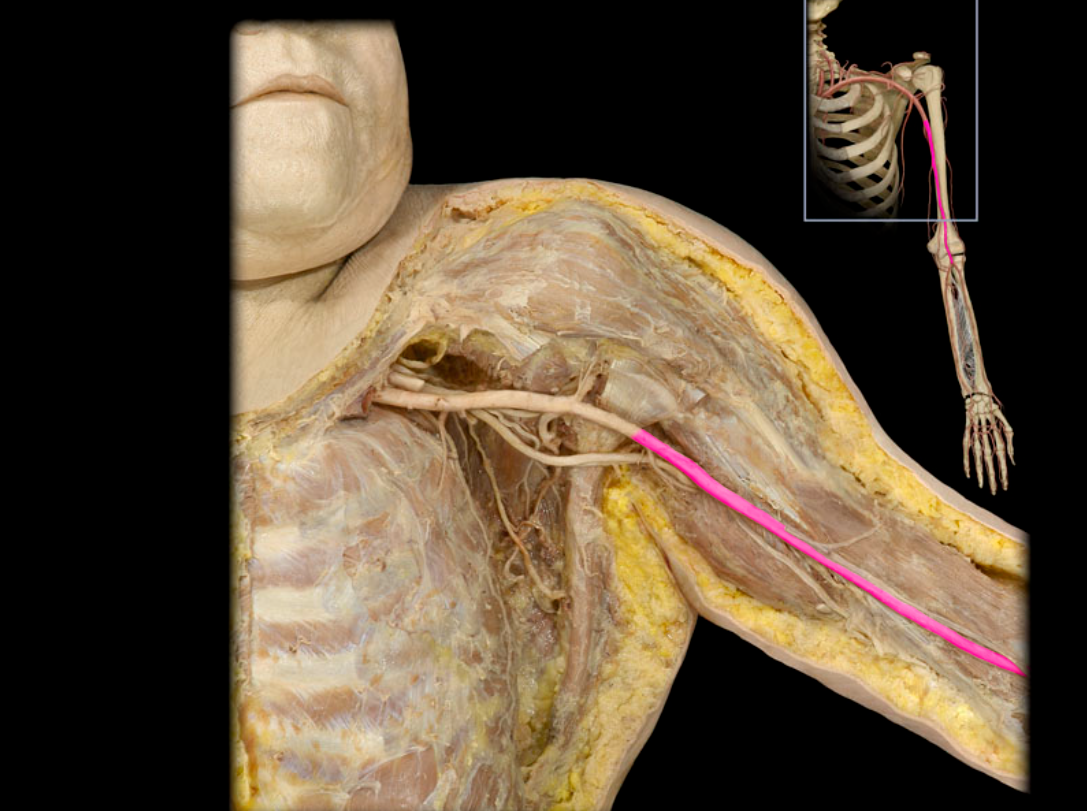
Brachial a.
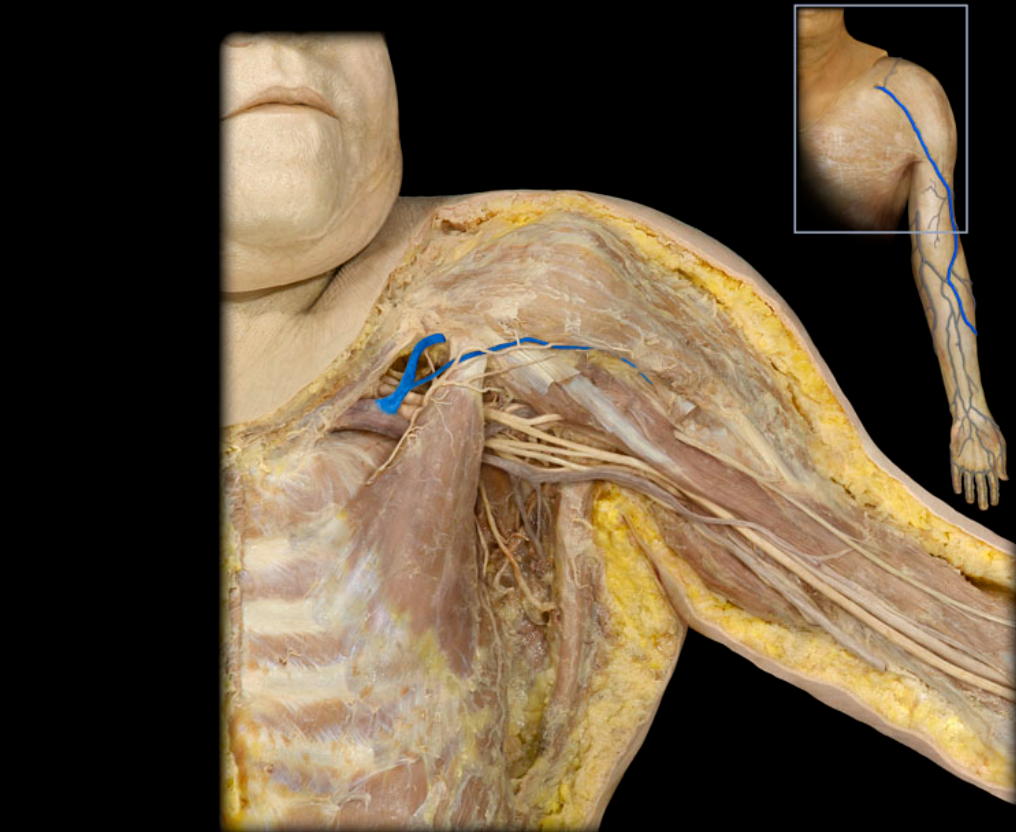
Cephalic v.
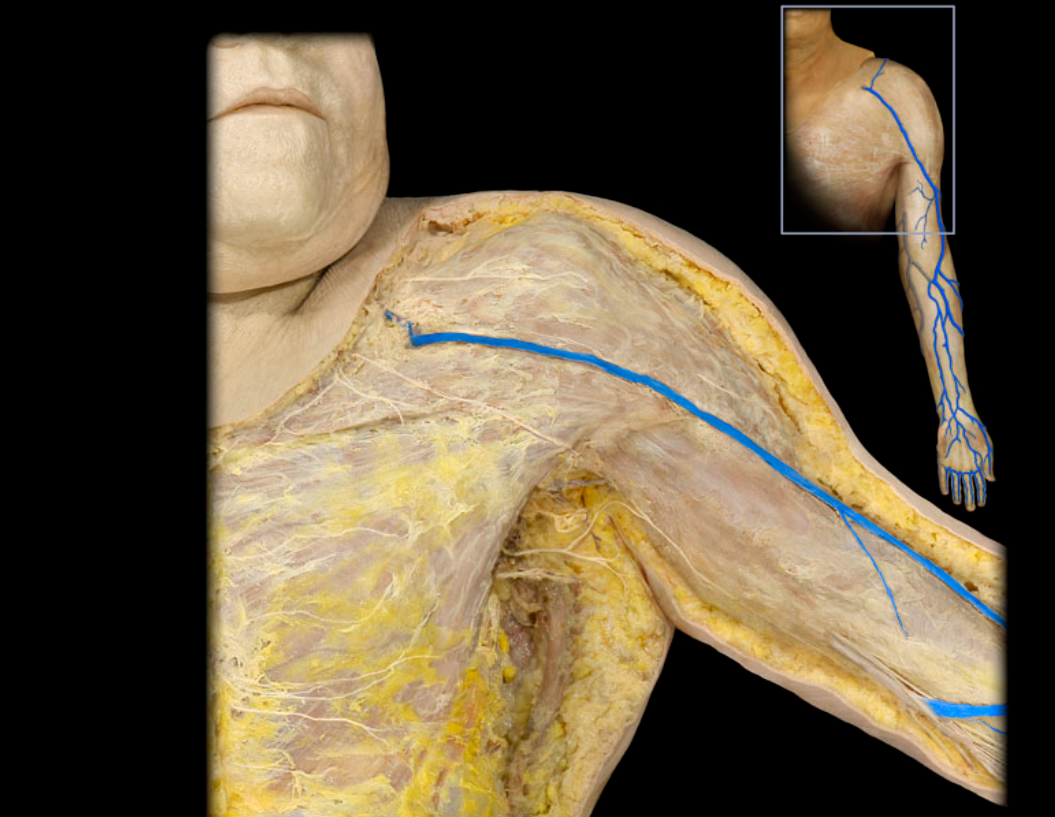
Cephalic v. and tributaries
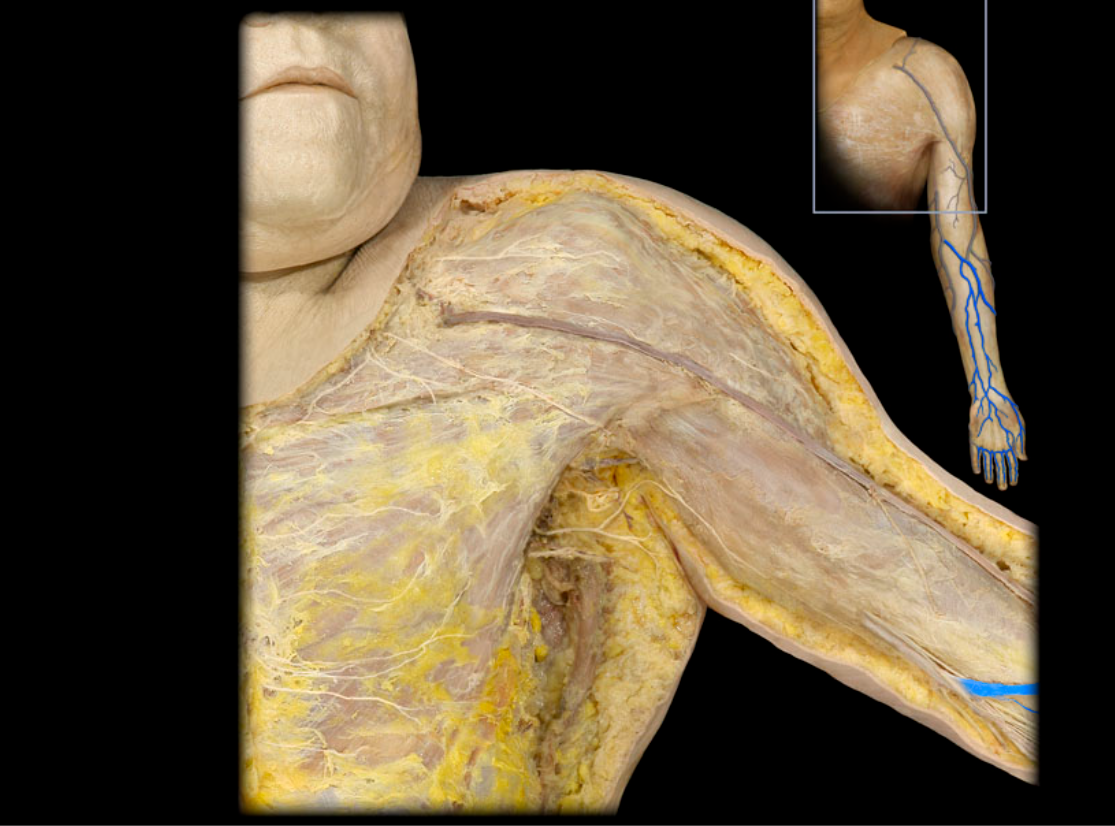
Median cubital v.
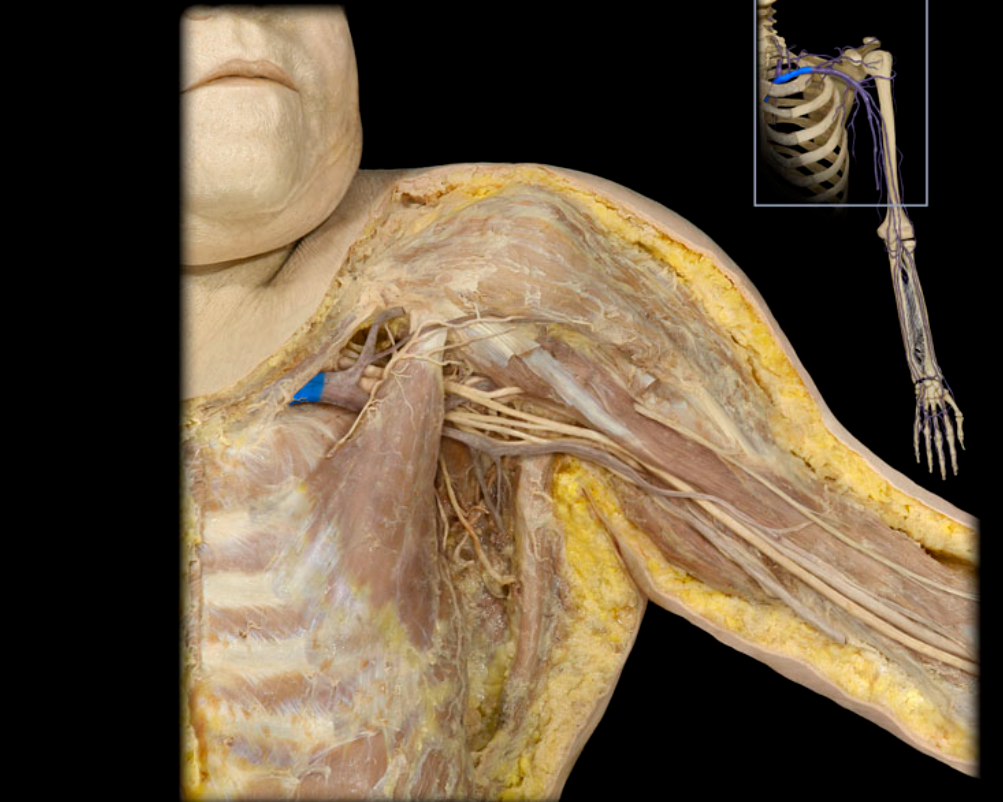
Subclavian v.