Compana Lab LE2
1/254
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
255 Terms
Frontal (coronal) plane
separates the front and back of the body
Transverse (horizontal) plane
separates the upper and lower halves of the body
Midsagittal plane
divides the body equally into left and right
Parasagittal plane
divides the body into unequal left and right halves
Oblique plane
- any plane that is not perfectly sagittal, frontal, or transverse
- a combination of two or all three cardinal planes
Anterior/Ventral
At or near the front of the body
Posterior/Dorsal
At or near the back of the body
Superior/Cranial
Above, Toward the head
Inferior/Caudal
Below, Toward the tail/feet
Medial
Toward central line
Lateral
Away from the central line
Proximal
Closer to where a bone or body part is attached to the body
Distal
Farther away from where a bone or body part is attached to the body
Abduction
Movement away from the body
Adduction
Movement toward the body
Extension
Increasing the angle of a joint
Flexion
Decreasing the angle of a joint
Inversion
sole of your foot turns inward toward the midline of the body
Eversion
sole of your foot turns outward away from the body’s midline
Medial rotation
rotational movement towards the midline
Lateral rotation
rotating movement away from the midline
Elevation
movement in a superior direction (upwards)
Depression
movement in an inferior direction (downwards)
Protraction
a movement that results in a portion of the body being moved forward
Retraction
a movement that results in the protracted portion of the body back to its original position
Supination
Rotation of the forearm outwards, causing the palm to face upwards
Pronation
Rotation of the forearm inwards, causing the palm to face downwards
Skeletal System
▪ body's central framework
Bones, Cartilage, Ligaments, Tendons
What is included/components of the skeletal system?
20%
How many percent of the human’s body weight does the skeletal system accountable for?
300
How many bones does a human baby have at birth?
206
How many bones does a human adult have?
Long Bones, Short Bones, Flat Bones, Sesamoid Bones, Irregular Bones
What are the 5 classification of Bones?
True
True or False:
A bone is a living tissue.
False
True or False:
Bones cannot regenerate.
Axial and Appendicular Skeleton
What are the two divisions of the skeletal system?
Axial Skeleton
to provide support and protection for the brain , and the organs in the ventral body cavity , the spinal cord
skull, ossicles of the middle ear, hyoid bone of the throat, vertebral column, and the thoracic cage (ribcage)
Components of the Axial Skeleton
Skull, Vertebral Column, Rib Cage
What are the 3 Main Bone Groups of the Axial Skeleton?
Skull
▪ bone protective cavity for the brain
▪ consists of 22 bones
sutures
joins the junctions of the skull bones
Cranial bones (8), Facial bones (14), and auditory ossicles (6)
What are the 3 Categories of Skull Bones? Include how many bones per category.
Sphenoid (1), Temporal (2), Ethmoid (1), Parietal (2), Occipital (1), Frontal Bone (1).
What are the 6 categories of cranial bones? Include the number of bones per category.
Fontanelle
spots on an infant's head where the bony plates that make up the skull have not yet come together
Maxilla (2), Mandible (1), Inferior Nasal Concha (2), Nasal (2), Vomer (1), Lacrimal (2), Zygomatic (2), Palatine (2)
What are the 8 cateogries of Facial Bones? Include the number of bones per category.
Auditory Ossicles
the three tiny bones in the middle ear, the smallest bones in the human body
Foramen magnum
▪ large opening at the base of the skull
▪ located in the occipital bone, which is at the back and base of the skull
▪ passageway for the spinal cord to connect to the brain
Malleus (2), Incus (2), Stapes (2)
What are the three categories of the Auditory Ossicles? Include the number of bones.
Vertebral column
▪ surrounds and protects the spinal cord
▪ supports the head
Strength and Flexibility
What is the benefit of having an arched curvature for the vertebral column?
Cervical Vertebrae (C1-C7), Thoracic Vertebrae (Th1-Th12), Lumbar vertebrae (L1-L5), Sacrum, Coccyx
What are the parts of the vertebral column? Include the number of bones.
Neck
Where are the cervical vertebrae located?
Upper and mid-back
Where are the thoracic vertebrae located?
Lower back
Where are the Lumbar Vertebrae located?
Small and light
Describe the size of the cervical vertebrae.
Medium
Describe the size of the thoracic vertebrae.
Large and heavy
Describe the size of the lumbar vertebrae.
Small body, larger foramen
Describe the shape of the cervical vertebrae
Larger body, smaller foramen
Describe the shape of the thoracic vertebrae.
Largest body, small foramen
Describe the shape of the lumbar vertebrae.
Short and bifid (split)
Describe the spinous process of the cervical vertebrae.
Longer and pointed
Describe the spinous process of the thoracic vertebrae.
Thick and broad
Describe the spinous process of the lumbar vertebrae.
Supports the head, allows neck movement
What is the function of the cervical vertebrae?
Protects the heart and lungs, supports the ribs
What is the function of the thoracic vertebrae?
Supports body weight, allows bending
What is the function of the lumbar vertebrae?
Atlas Vertebrae
First cervical vertebrae, allows the yes motion of the head.
Axis Vertebrae
Second cervical vertebrae, allows the no motion of the head.
Scoliosis
an abnormal lateral (side-to-side) curvature of the spine.
Kyphosis
exaggerated forward curvature of the spine, leading to a hunched or rounded back.
Ribcage
encloses and protects the organs of the thoracic cavity, including the heart and lungs
12 pairs of ribs with costal cartilages, sternum
What are the parts of the rib cage?
True ribs, false ribs, floating ribs
What are the three types of rib cages?
True ribs
▪ first seven bones
▪ connected directly to the sternum
False ribs
▪ next five pairs of bones
▪ attached to the lowest true rib (7th bone) by cartilage
Floating ribs
▪ not connected to anything in the front
▪ smaller than both the true ribs and the false ribs
Appendicular skeleton
▪ comprised of the upper and lower extremities, which include the shoulder girdle and pelvis
▪ consisting of the bones that support the appendages
▪ there are 126 bones
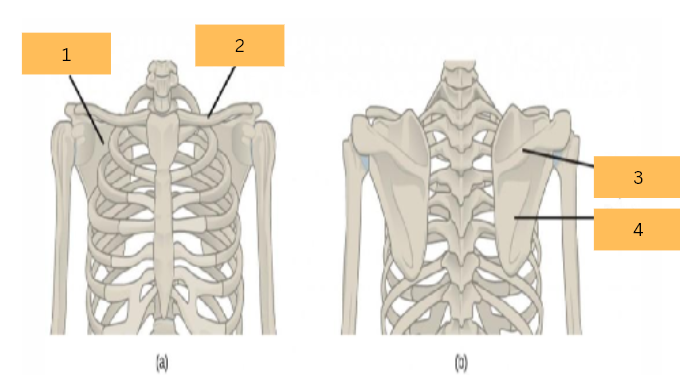
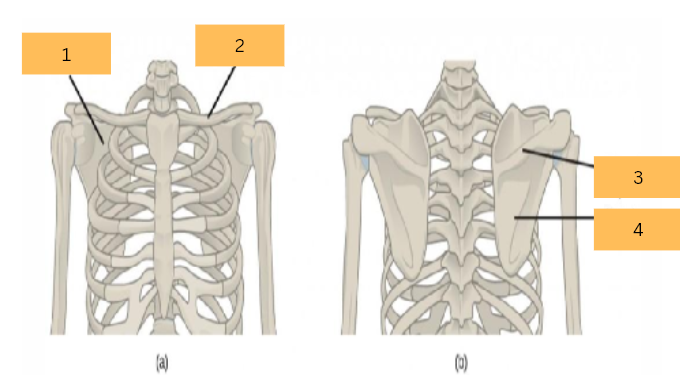
Scapula
What is the name of 1?
Pectoral girdle, Upper Limb, Pelvic Girdle, Lower Limb
What are the 4 Main Bone Groups of the Appendicular Skeleton?
Pectoral girdle
▪ provide the points of attachment of the upper limbs to the axial skeleton
▪ consists of the clavicle (or collarbone) in the anterior, and the scapula (or shoulder blades) in the posterior
Upper limb
▪ humerus of the upper arm
▪ radius and ulna of the forearm
▪ eight bones of the carpus
▪ five bones of the metacarpus
▪ 14 bones of the phalanges
Pelvic Girdle
▪ attaches to the lower limbs of the axial skeleton
▪ bears the weight of the body
Ischium, Ilium, Pubis
What are the 3 hip bones?
Lower limb
▪ consists of the thigh, the leg, and the foot
▪ thicker and stronger than the bones of the upper limbs
Clavicle
What is the name of 2?
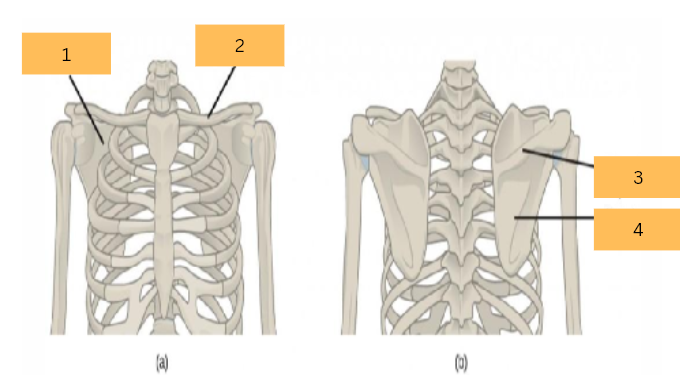
Spine of Scapule
What do you call 3?
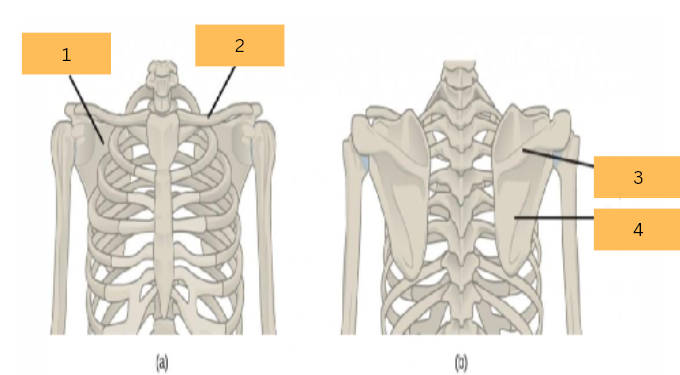
Scapula
What do you call 4?
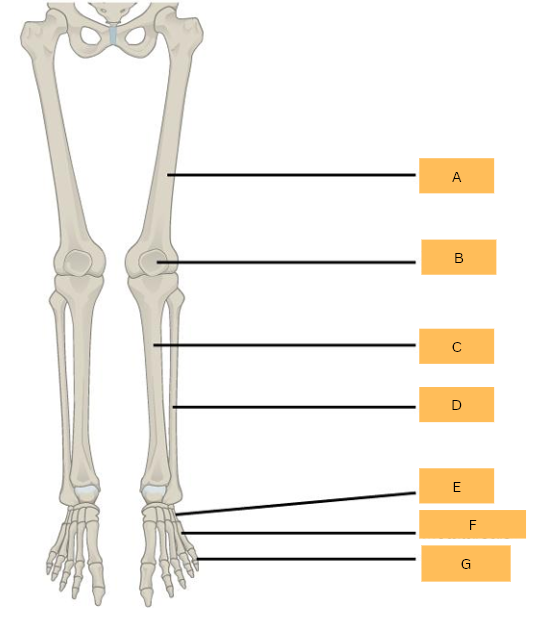
Humerus
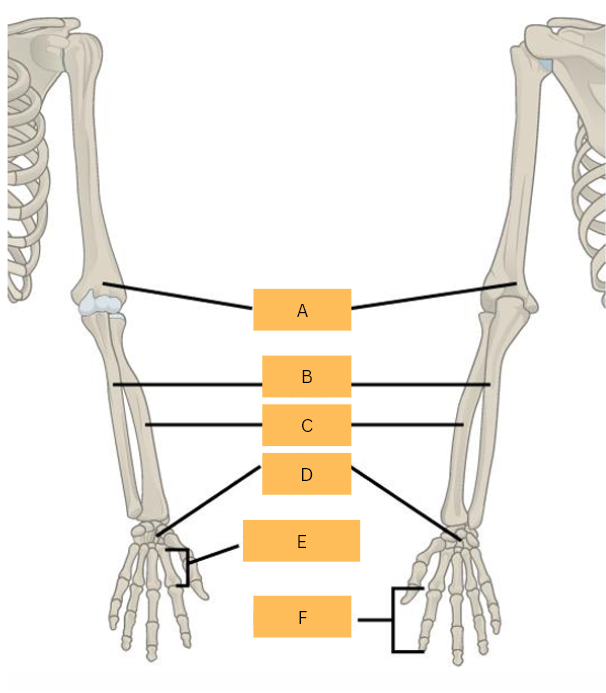
What is A?
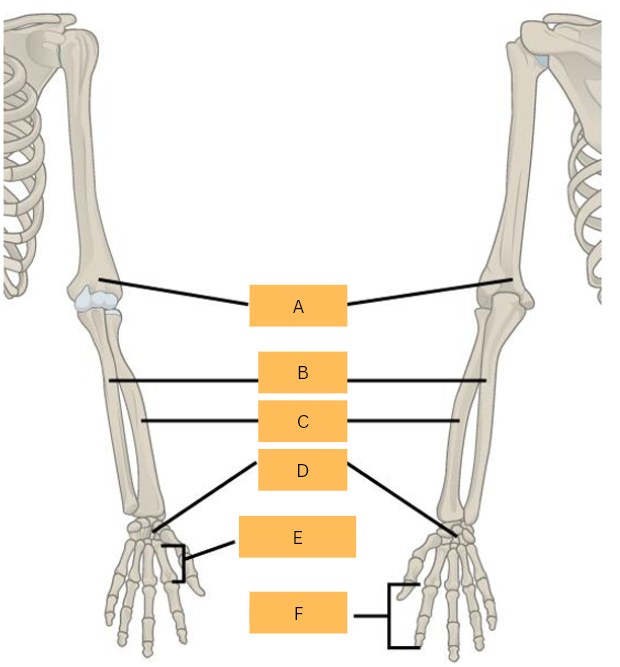
Ulna
What is B?
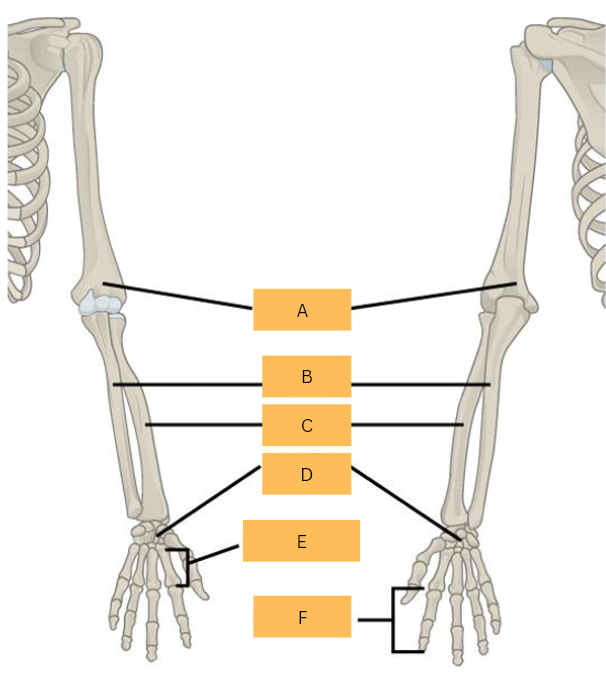
Radius
What is C?
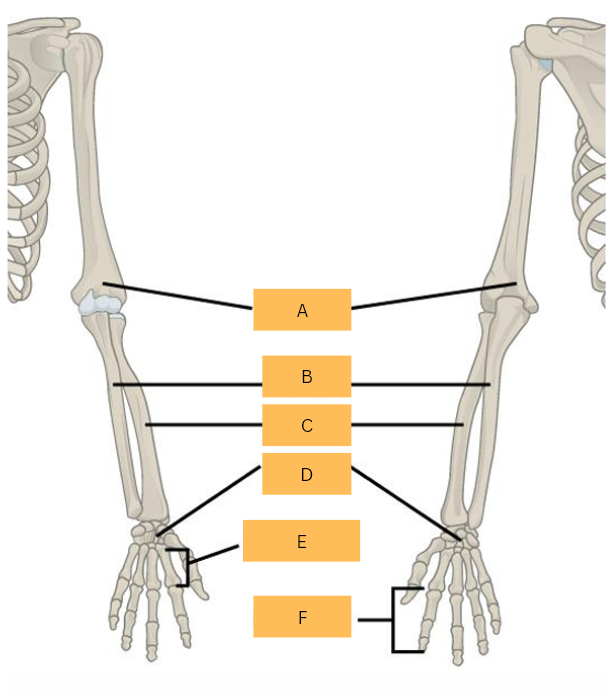
Carpals
What is D?
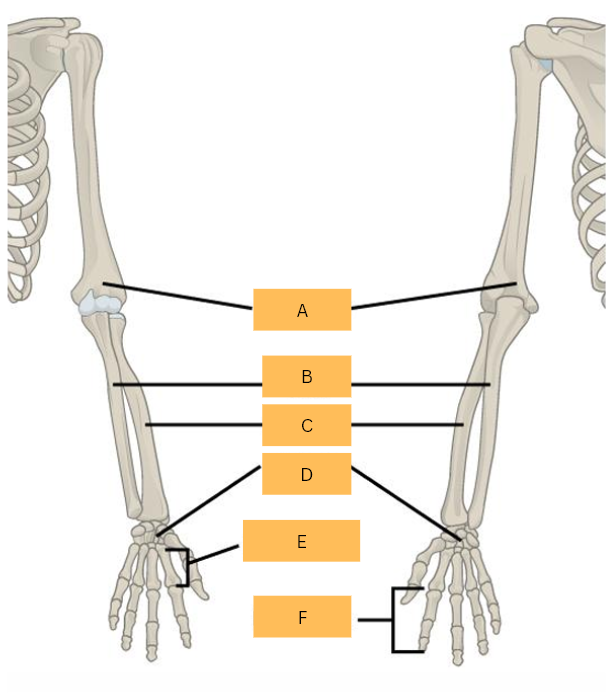
Metacarpals
What is E?
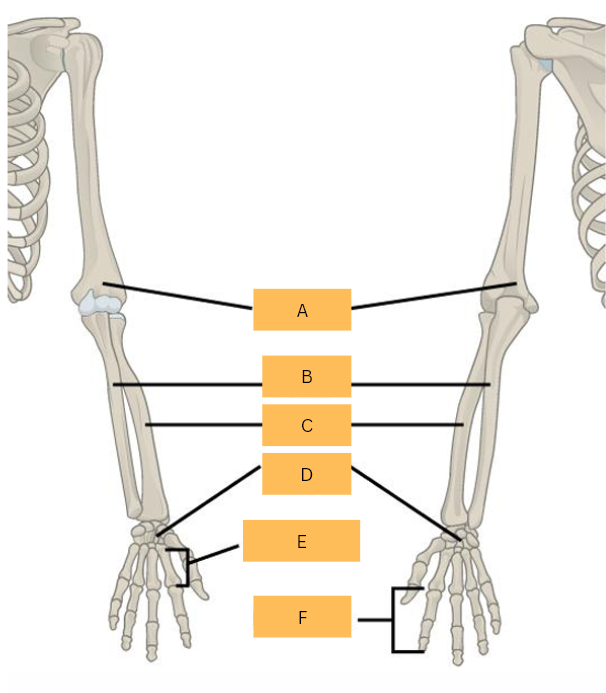
Phalanges
What is F?
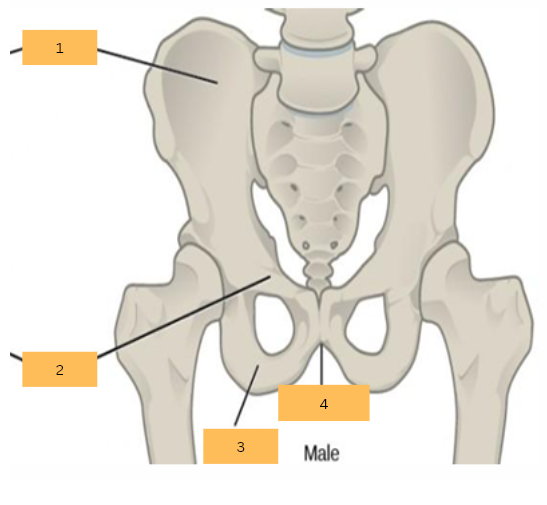
Ilium
What is 1?
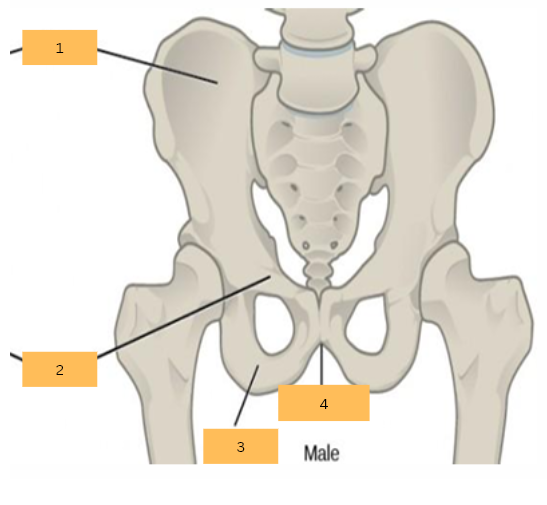
Pubis
What is 2?
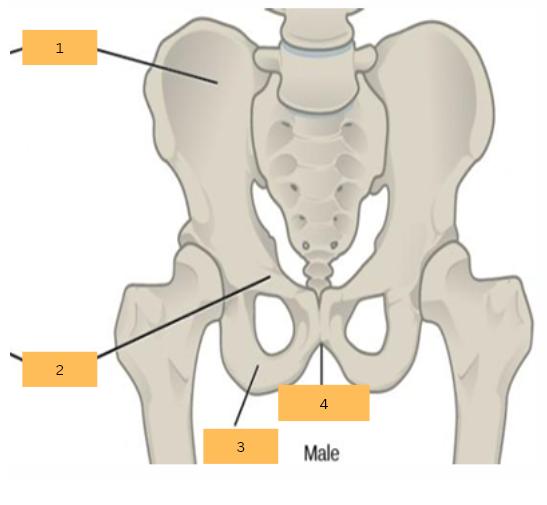
Ischium
What is 3?
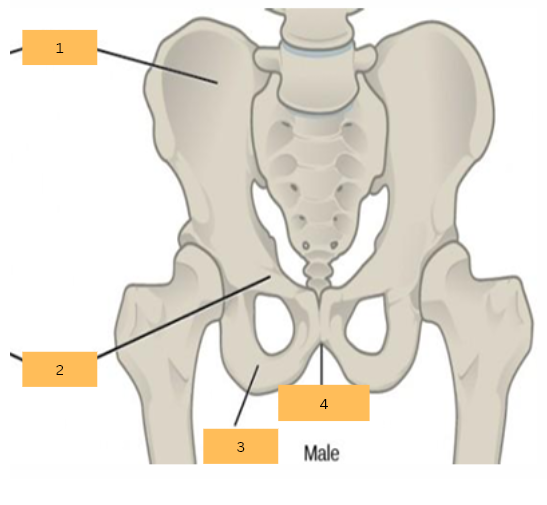
Pubic Arch
What is 4?
Femur
What is A?
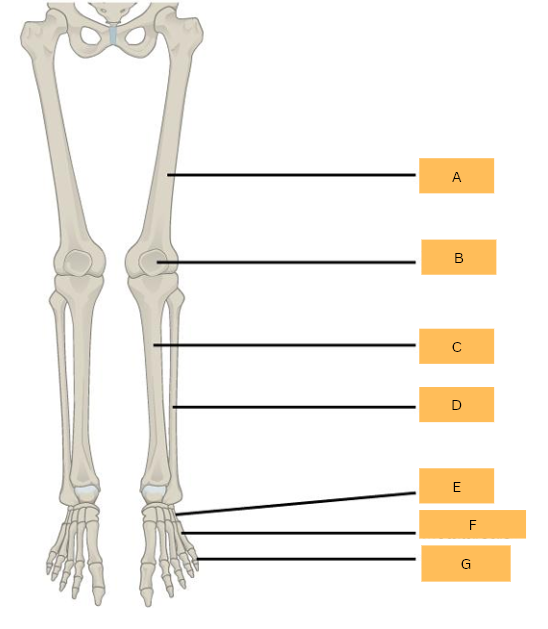
Patella
What is B?
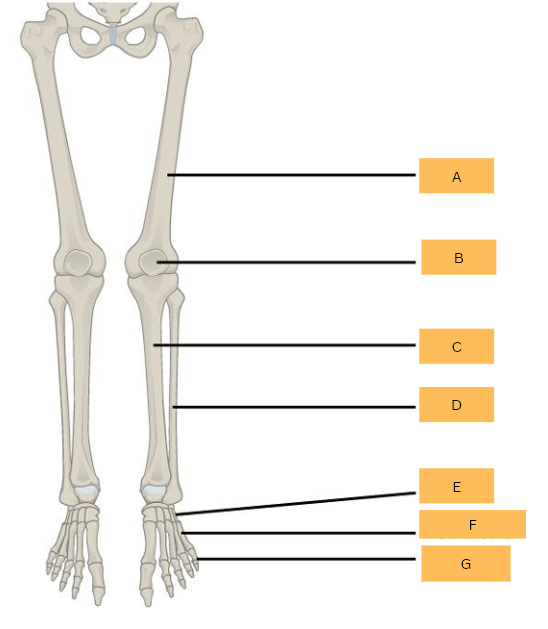
Tibia
What is C?