Contractility, Preload, and Afterload
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
LO: 1. Define cardiac output, stroke volume, and heart rate. 2. Explain contractility and how it is controlled. 3. Explain preload and what determines it. 4. Explain afterload and what determines it.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
___________ = stroke volume × heart rate
cardiac output = stroke volume × heart rate
___________ is the volume of blood expelled from the heart during one heartbeat and is expressed in milliliters. (The average__________ is 70 mL in a typical male, while a similarly sized female has a 20% lower stroke volume).
Stroke volume is the volume of blood expelled from the heart during one heartbeat and is expressed in milliliters. (The average stroke volume is 70 mL in a typical male, while a similarly sized female has a 20% lower stroke volume).
An increase in the calcium available will _______contractility and stroke volume
An increase in the calcium available will increase contractility and stroke volume
If the stroke volume falls without changes in blood volume or blood pressure, it can be inferred that the contractility has __________
If the stroke volume falls without changes in blood volume or blood pressure, it can be inferred that the contractility has declined
_________, which used to treat heart failure, is an inotrope. This drug increases contractility by increasing intracellular calcium.
Digoxin, which used to treat heart failure, is an inotrope. This drug increases contractility by increasing intracellular calcium.
The SNS increases intracellular calcium and contractility, also termed an ___________ effect.
The SNS increases intracellular calcium and contractility, also termed an inotropic effect.
The degree of ventricular stretching at the end of diastole is referred to as _________.
The degree of ventricular stretching at the end of diastole is referred to as preload.
How do we estimate preload?
End-diastolic volume (EDV) or the end-diastolic pressure (EDP) (because they incorporates the stretch of a sarcomere/sarcomere length)
High preload __________ the stroke volume, which, in turn, _________ cardiac output
High preload increases the stroke volume, which, in turn, increases cardiac output
What relationship is represented by the Frank-Starling law?
The relationship between preload and stroke volume
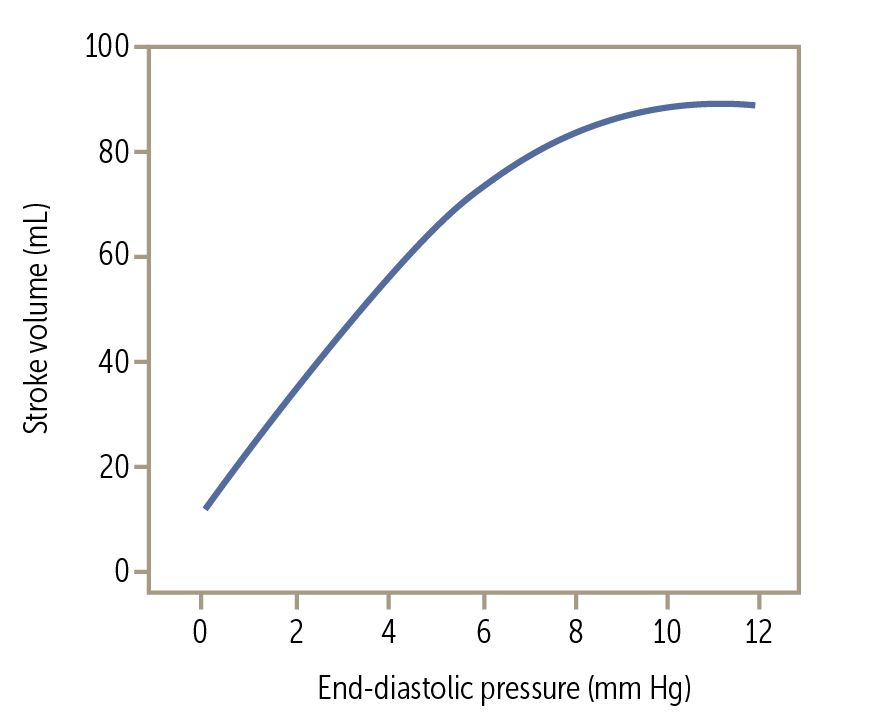
What factors increase preload (name 3)?
Increase in total blood volume
Increase in venous pressure
Decrease in intrathoracic pressure
How will a blood transfusion affect the stroke volume?
A blood transfusion will increase stroke volume. (A blood transfusion will increase the blood volume, which will increase venous return to the heart. The increase in venous return to the heart will increase end-diastolic volume. The larger diastolic volume will increase the preload and consequently the stroke volume.)
When you take a deep breath, the____________ drops, more venous blood returns to the heart, and preload increases.
When you take a deep breath, the intrathoracic pressure drops, more venous blood returns to the heart, and preload increases.
Afterload is mostly determined by the total resistance in the circulation, termed the ________________, which can be estimated in most cases by the arterial blood pressure
Afterload is mostly determined by the total resistance in the circulation, termed the systemic vascular resistance (SVR), which can be estimated in most cases by the arterial blood pressure
How would an increase in afterload affect the stroke volume?
It would cause a decrease in stroke volume
Sympathetic nerve stimulation or ____________________ can constrict the smooth muscle that surrounds these small vessels and thus increase SVR
Sympathetic nerve stimulation or circulating hormones (eg, vasopressin) can constrict the smooth muscle that surrounds these small vessels and thus increase SVR
The valve disease aortic stenosis will also ___________ afterload. As people age, their aortic valves may become calcified and narrowed. This creates resistance to blood exiting the heart during systole, increasing the afterload. Aortic stenosis will therefore reduce stroke volume and cardiac output, and patients may become dizzy or even pass out (syncope).
The valve disease aortic stenosis will also increase afterload. As people age, their aortic valves may become calcified and narrowed. This creates resistance to blood exiting the heart during systole, increasing the afterload. Aortic stenosis will therefore reduce stroke volume and cardiac output, and patients may become dizzy or even pass out (syncope).