BB Overview of ABO Blood group
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
ABO Blood Group System
➢ Most important of all
blood groups
➢ Blood group system in
which individuals already have antibodies in their serum
to antigens that are absent from their red blood cells
(RBCs)
lysis
Presence of antibodies results to __________ of RBCs once ABO is
incompatible
hemolytic
transfusion reactions
ABO ➢ Remains as the predominant cause of death for________________
genes of three separate loci
ABO Principles
The formation of ABH antigens results from
interaction of____________
GLUCOTRANSFERASE
ABO Principles
Responsible for the production of____________________that add sugars to a basic precursor substance
α – 2 – L – fucosyltransferase
H GENE AND ANTIGENE GLYCOSYLTRANSFERASE
L – fucose
H GENE AND ANTIGENE IMMUNODOMINANT SUGAR
α – 3 – N –
acetylgalactosaminyransferase
A GENE AND ANTIGENE GLYCOSYLTRANSFERASE
N–acetyl–D–
galactosamine
A GENE AND ANTIGENE IMMONODOMINANT SUGAR
α – 3-D - galactosyltransferase
B GENE AND ANTIGENE GLYCOSYLTRANSFERASE
D –galactose
B GENE AND ANTIGEN IMMUNODOMINANT
SUGAR
Type-2-precursor chain
ABO Precursor
Bombay phenotype
hh Precursor structure unchanges
N-acetyl galactosaminyl and galactosyl transferases
A AND B GENES GLYCOSYLTRANSFERASE
N-Acetyl galactosamine and galactose
A AND B ANTIGEN IMMUNODOMINANT SUGAR
FORWARD TYPING
ABO TESTING
➢ Using known sources of commercial antisera (anti-A,
anti-B)
➢ Detects antigens on an individual’s RBCs
Blood Group O
Interpretation of Blood Group
Patient RBCs with Anti-A: 0
Patient RBC’s with Anti B: 0
Blood Group A
Interpretation of Blood Group
Patient RBCs with Anti-A: 4+
Patient RBC’s with Anti B: 0
Blood Group B
Interpretation of Blood Group
Patient RBCs with Anti-A: 0
Patient RBC’s with Anti B: 4+
Blood Group AB
Interpretation of Blood Group
Patient RBCs with Anti-A: 4+
Patient RBC’s with Anti B: 4+
agglutination
A positive antigen-antibody reaction is usually
demonstrated by______________
Anti-A Reagent
Type of Reagent

Anti-B Reagent
Type of Reagent
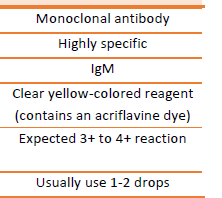
Monoclonal Antibody
• Contains antibody from a single type of B cell, clonally
expanded
• Preferred in testing
• Highly specific
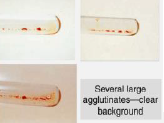
4+
Agglutination Grading

3+
Agglutination Grading
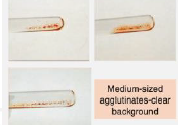
2+
Agglutination Grading
W+ to 1+
Agglutination Grading
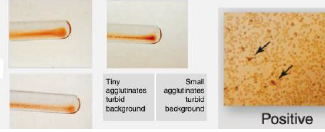
0
Agglutination Grading
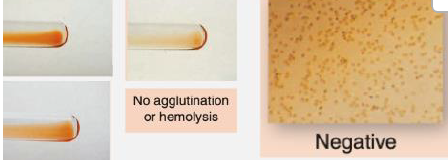
REVERSE TYPING
ABO TESTING
➢ Using known reagent RBCs (A and B cells)
➢ Detects ABO antibodies in the patient’s serum
Gloves
5 mL test tubes
Anti-sera
Centrifuge
Calibrated Plastic Pipette
Buffered NSS
Markers
Biohazard Container
Blood Samples
Materials/Reagents