unit 1 brain structures // ap psych
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
created by jennalearyy on quizlet
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
hindbrain
controls basic biological structures; medulla, pons, cerebellum
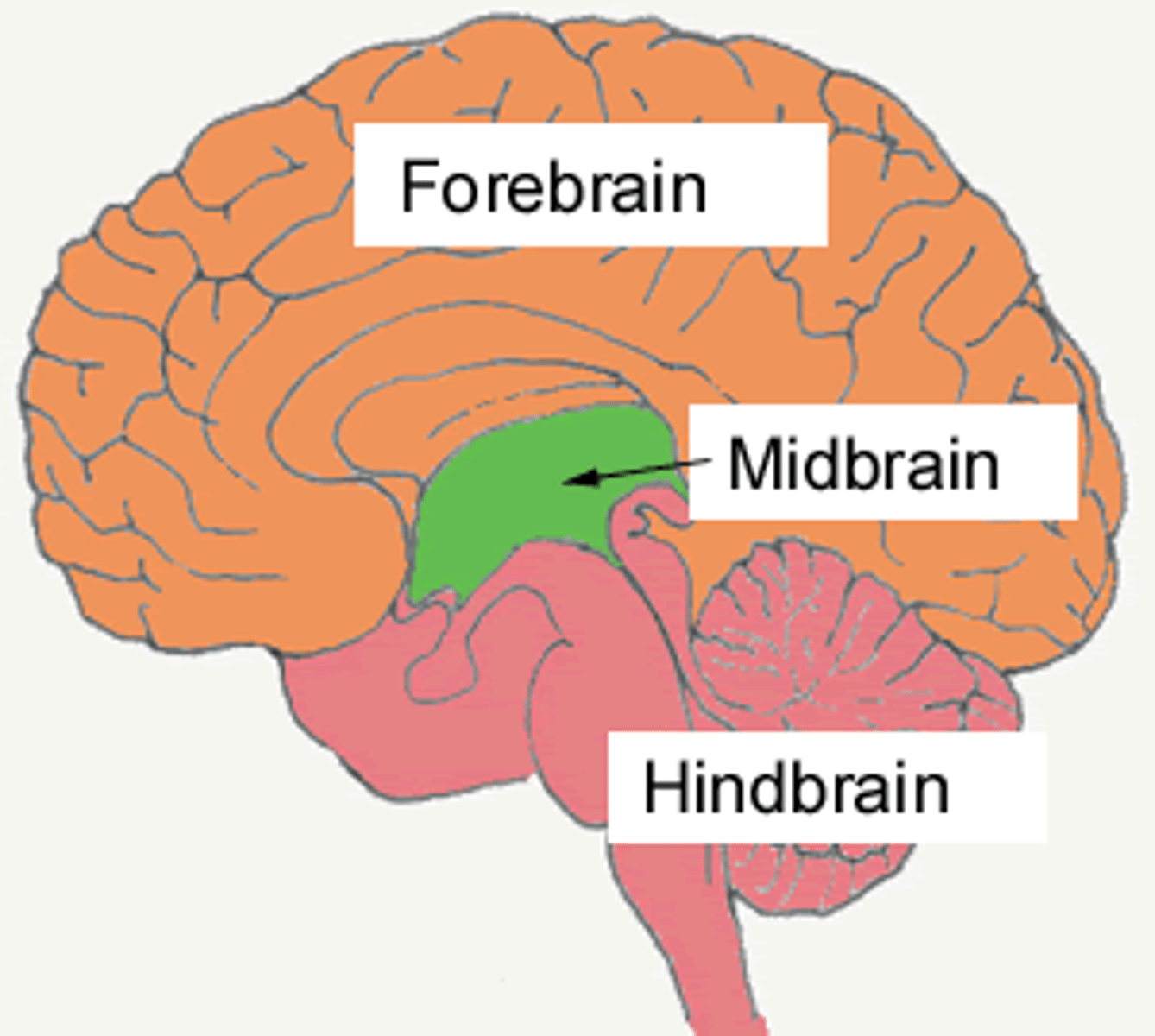
midbrain
controls simple movements with sensory info; reticular formation
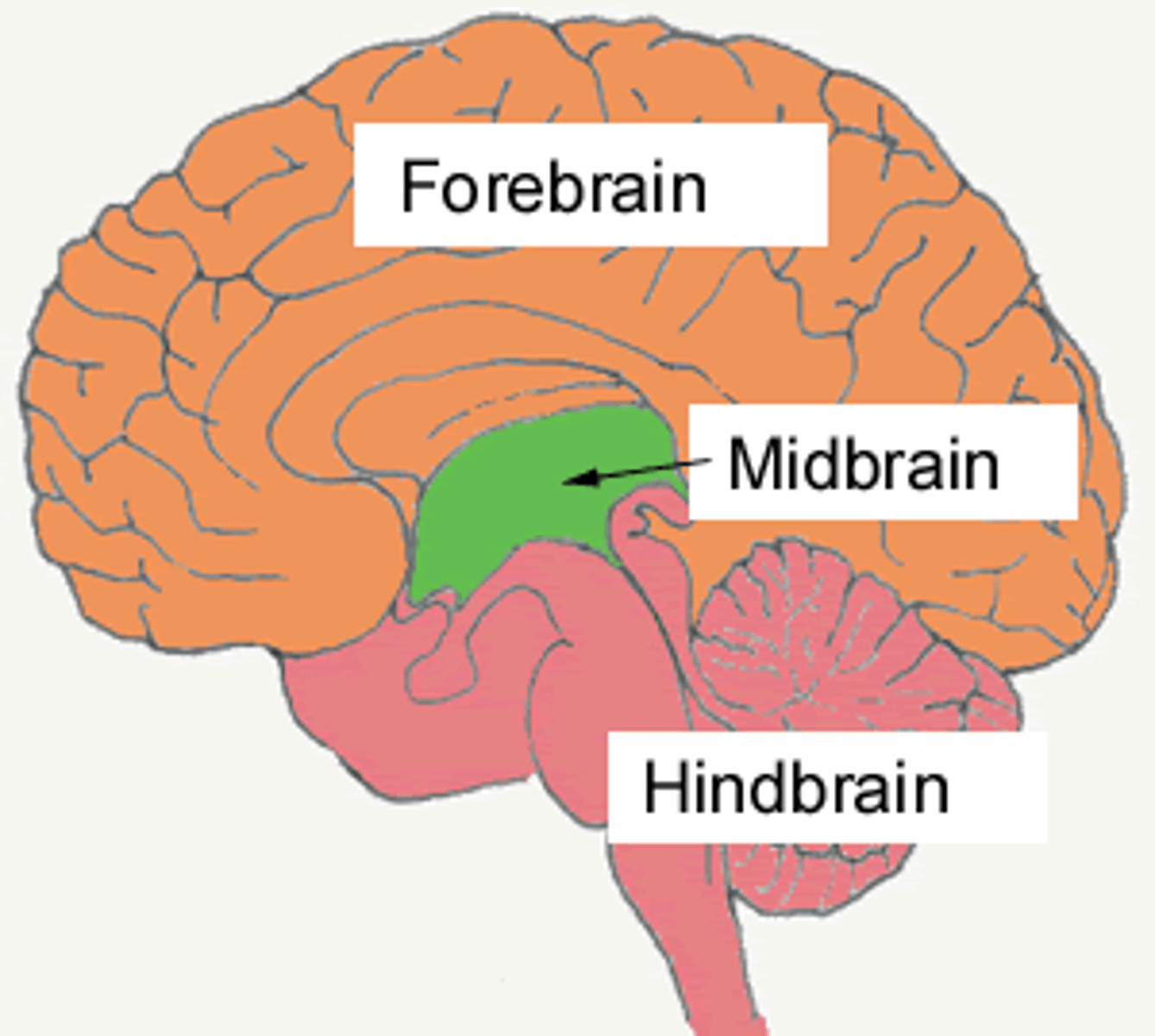
forebrain
most complicated region; thalamus, hypothalamus, limbic system, cerebral cortex
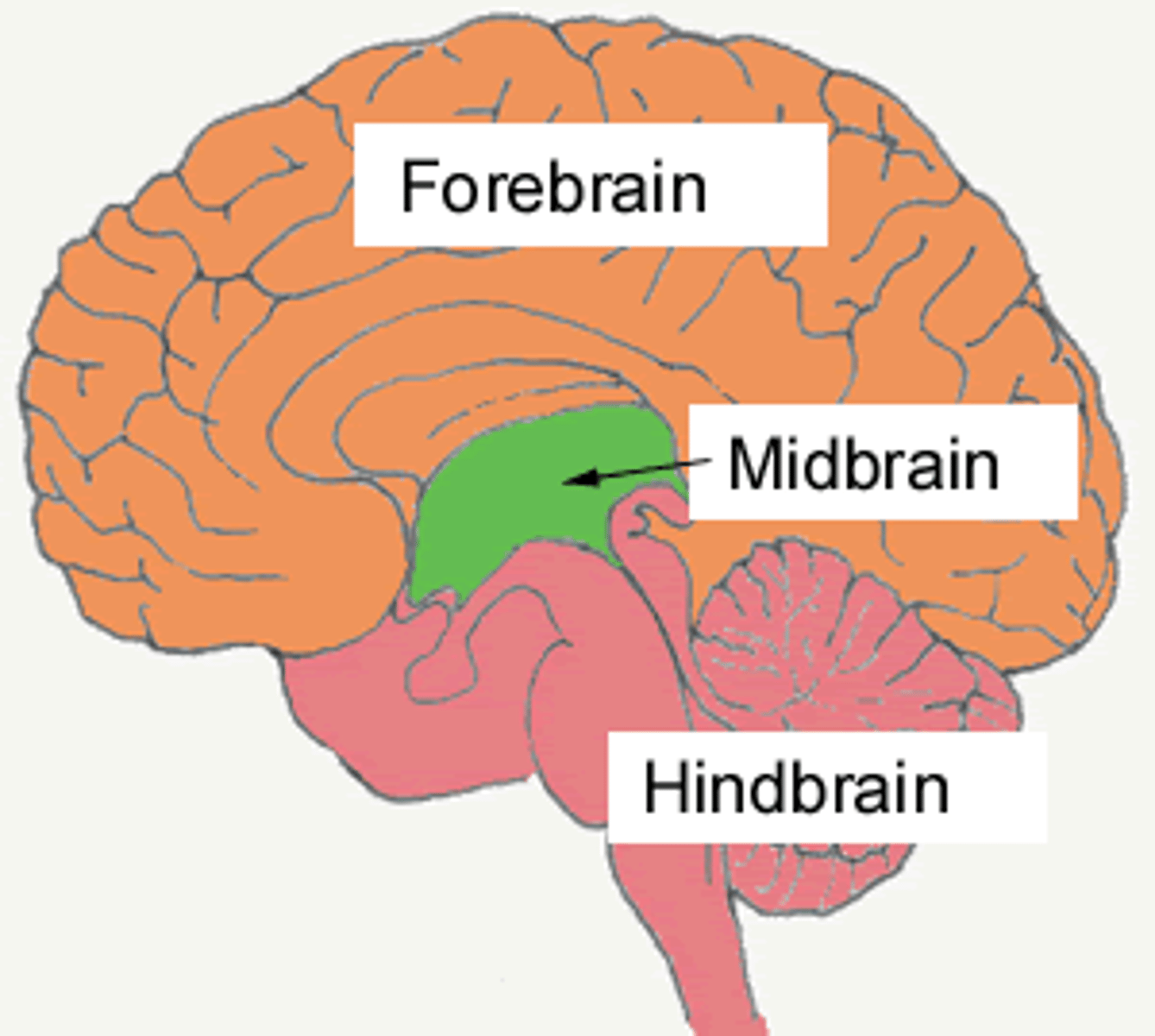
brain stem
shared stalk between creatures with complex brains; connects brain to spinal chord
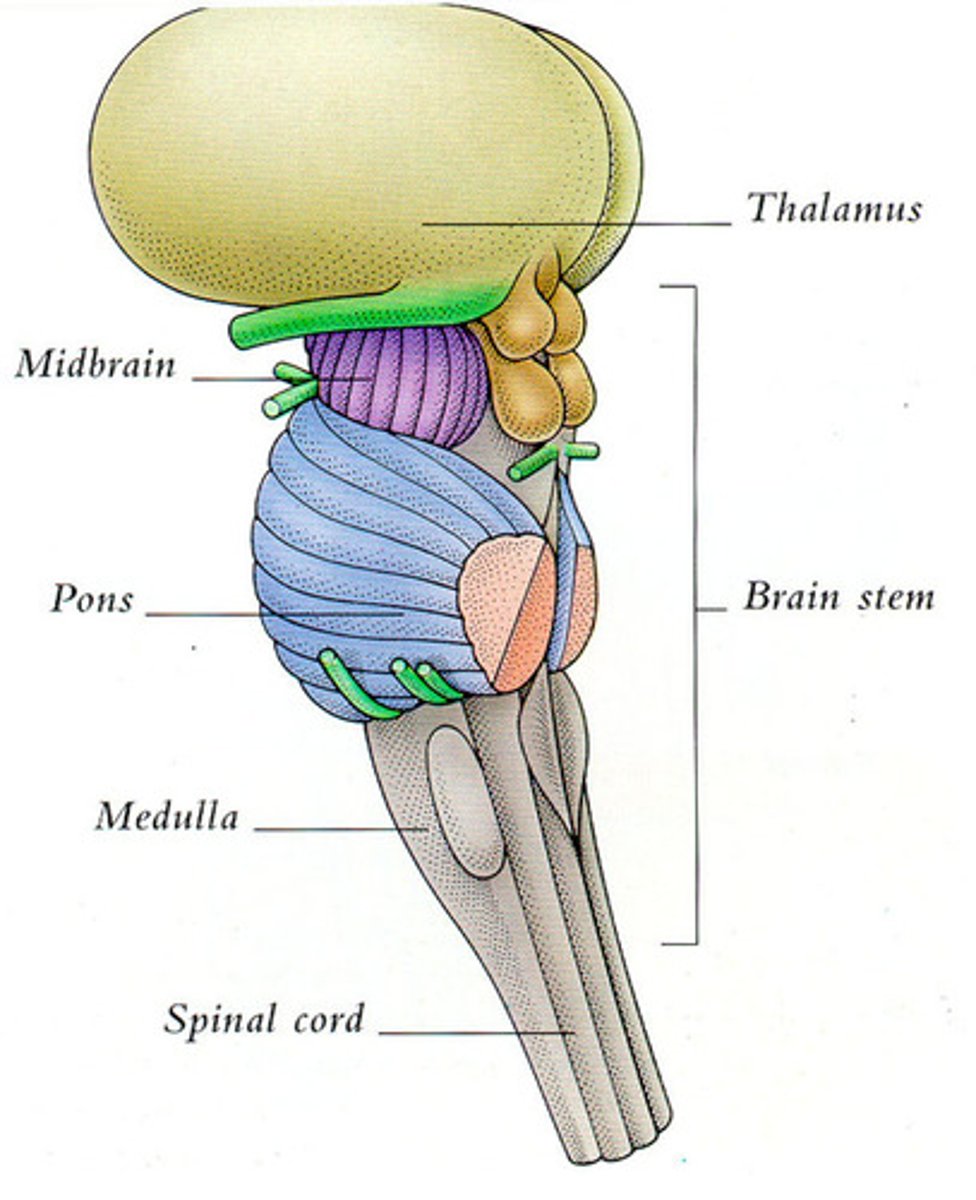
medulla oblongata
heart rate, breathing, and blood pressure
pons
sleep-wake cycle and facial expressions
thalamus
receives info and sends it to appropriate areas of the forebrain; sensory switchboard but NOT SMELL
reticular formation
distributed throughout brainstem; arousal, consciousness, movement, and sensation
cerebellum
fine motor skills and body movements
limbic system
hypothalamus, amygdala, hippocampus; emotional center
hypothalamus
eating, drinking, body temperature, and emotion
amygdala
memory and emotion, particularly fear and aggression
hippocampus
process explicit memories for storage
cerebral cortex
made up of fissures and gray matter, divided into eight lobes, four in each hemisphere (occipital, parietal, temporal, and frontal)
fissures
brain wrinkles; increase surface area of brain
gray matter
densely packed neurons
association areas
any areas not dealing with senses or muscles
occipital lobe
visual cortex; visual input from eyes
parietal lobe
sensory cortex; incoming touch sensations
temporal lobe
auditory cortex; sound coming from ears AND wernicke's area
wernicke's area
left temporal lobe; language comprehension
frontal lobe
motor cortex; muscle movements AND prefrontal cortex; judgement and critical thinking AND broca's area
broca's area
frontal lobe; speech production
contralateral control
left brain controls right body and vise versa
corpus callosum
attaches 2 hemispheres of cerebral cortex
split brain patient
removed corpus callosum to relieve epilepsy
sperry experiment
cut through corpus callosum in attempt to relieve epilepsy
peripheral nervous system
the sensory and motor neurons that connect the central nervous system to the rest of the body
somatic nervous system
voluntary muscle movements; efferent/motor neurons
autonomic nervous system
automatic bodily functions; afferent/sensory neurons
sympathetic nervous system
part of autonomic; dealing with stressful events
parasympathetic nervous system
part of autonomic; automatic calming body after stress
