RNA Processing I (3)
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Where is the CTD of RNA Pol II?
On its large subunit
What sequence encodes that domain?
YSPTSPS: 52 repeats of this heptapeptide so it’s essential
Structure of the CTD
Extends out of RNA Pol II and has unique conformations or is entirely unstructured
Which phosphorylated AAs of YSPTSPS affect transcription?
The Serines at positions 2 and 5
What enzyme phosphorylates Ser5?
TF2H
When does RNA Pol II stall?
After 25-60 nt/ after the phosphorylation of Ser5
1st reason for stalling
Capping of the 5’ end of mRNA
Capping process
7-methylguanylate CAP added through a 5’-5’ triphosphate linkage= hard for exonucleases to cut
Advantages of CAP
Protection
Facilitated export
Recognition by translation factors
2nd reason for stalling
Methylation of 2’ hydroxyl of the first and (second: in vertebrates) nt
What enzyme phosphorylates Ser2?
CDK9
Other phosphorylated elements of stalled complex
DSIF and NELF
Effect of phosphorylation of DSIF
Clamp holds DNA down
Effect of phosphorylation of NELF
No stalling!
What proteins does P-Ser2 recruit?
Splicing factors
Polyadenylation factors
Export factors
Events of mRNA processing
5’ capping
Cleavage at poly(A) site
Polyadenylation (3’ poly A tail)
RNA splicing
CO-TRANSCRIPTIONAL
Splicing
Pre mRNA to mRNA
Process of splicing
Removal of introns bc they are not needed for translation: only regulatory elements
Hybridization experiments
Allow to visualize discrepancy between mRNA size and gene size
Loop outs indicated…
that the probe did not interact with the DNA introns
Conserved border sequences of introns (3)
Splice donor (GU)
Branch point (A)
Splice acceptor (AG)
Spliceosome
5 snRNPs
1 snRNP or small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particle
1 snRNA (U1,2,4,5,6) + 6-10 proteins
Splice donor snRNA
U1
Branch point snRNA
U2: the adenosine is not complementarily paired and bulges out!

Problem with U1
Limited homology with splice site (mutations)
Correction of problem
Introduction of a compensatory mutation in U1= proof that RNA:RNA paring is critical for spliceosome function
1st trans-esterification
2’ hydroxyl group of branch point attacks 5’ phosphate of the G residue of intron = lariat formation
2nd trans-esterification
3’ oxygen of exon attacks 5’ phosphate group of the exon = release of the lariat
How can a lariat be observed?
By using radio-labelled probes in vitro
How does the spliceosome assemble?
Sequentially: U1 and U2 first followed by U4, 5 and 6
The spliceosome becomes active when…
U1 and U4 snRNAs leave
Role of the debranching enzyme
Cuts and linearizes the intron
Do self-splicing introns also result in the formation of a lariat?
Yes in Group II introns but not in Group I introns
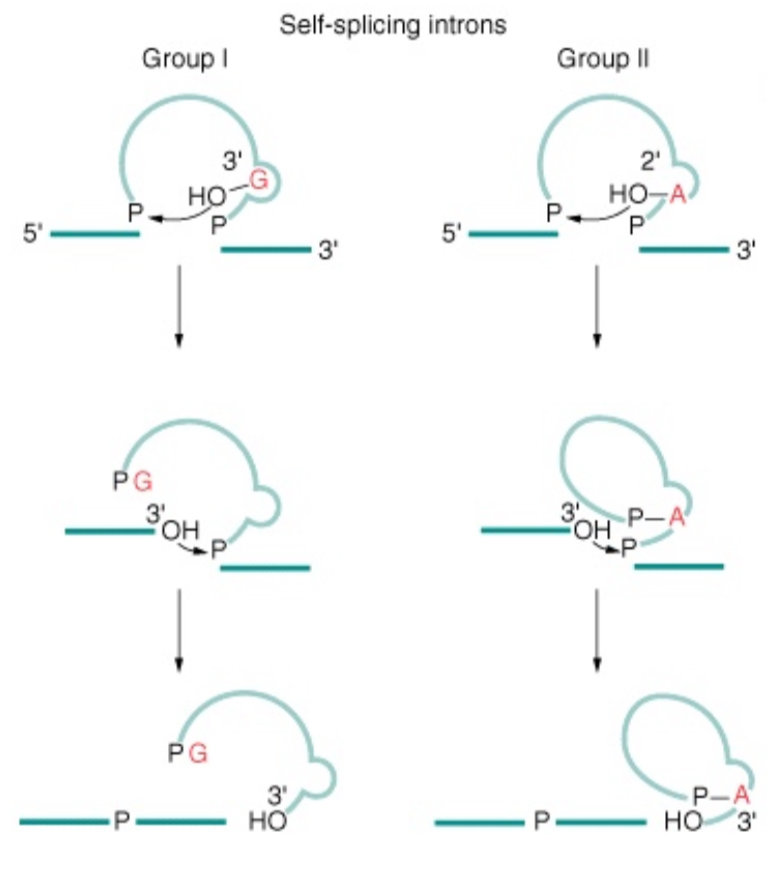
1% of human introns have…
A/CU…AC splice sites instead if GU…AG = need less snRNPs
Trans-splicing
Formation of mRNAs from 2 different pre-mRNAs