Unit 1 Flashcards AP Biology
1/51
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
Covalent bond
Sharing of electrons by two atoms
Forms molecules and compounds
Single bonds, double bonds, triple bonds, etc …
Nonpolar covalent bond
A type of bond where electrons are shared equally between the two atoms
Polar covalent bond
A type of bond where electrons are not shared equally between two atoms
Ionic bond
The attraction between oppositely charged atoms, where one atom steals electrons from another * Forms compounds and salts * NaCl (sodium chloride) * LiF (lithium fluoride)
Cation
Positively charged ion
Anion
Negatively charged ion
Cohesion
Two of the same molecules forming hydrogen bonds with each other.
Responsible for surface tension by allowing liquids to resist forces
Adhesion
Two different molecules forming hydrogen bonds with each other.
Allows water to cling to cell walls
Capillary action
The upward movement of water due to the forces of cohesion, adhesion, and surface tension
Adhesion > Cohesion
Temperature control
H₂O resists changes in temperature through hydrogen bonds.
Heat must be absorbed to break bonds, but heat is released when bonds form
Evaporative Cooling
Responsible for:
Moderating the Earth’s climate
Stabilizing temperatures in lakes and ponds
Preventing terrestrial organisms from overheating
Preventing leaves from becoming too warm
Floating Ice
Through water solidifying and becoming less dense / expanding:
Allows marine life to survive under the sheets of ice
Organic Chemistry
The study of compounds with covalently bonded carbon
Organic compounds
Compounds that contain carbon and hydrogen
Hydrocarbon
Organic molecules consisting only of carbon and hydrogen
Framework/skeletons for more complex molecules
Varies in length, branching, double bond positions, and presence of rings.
Dehydration Synthesis Reaction
Bonds two monomers with the loss of water
-OH of one monomer bonds to the -H of another, forms H₂O, which is then released.
A + B → AB + H₂O
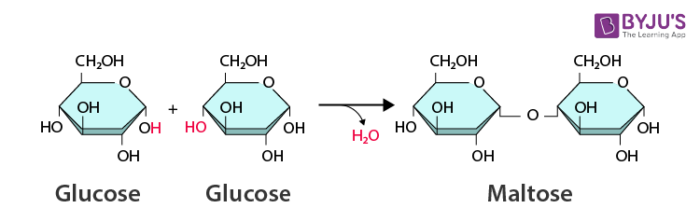
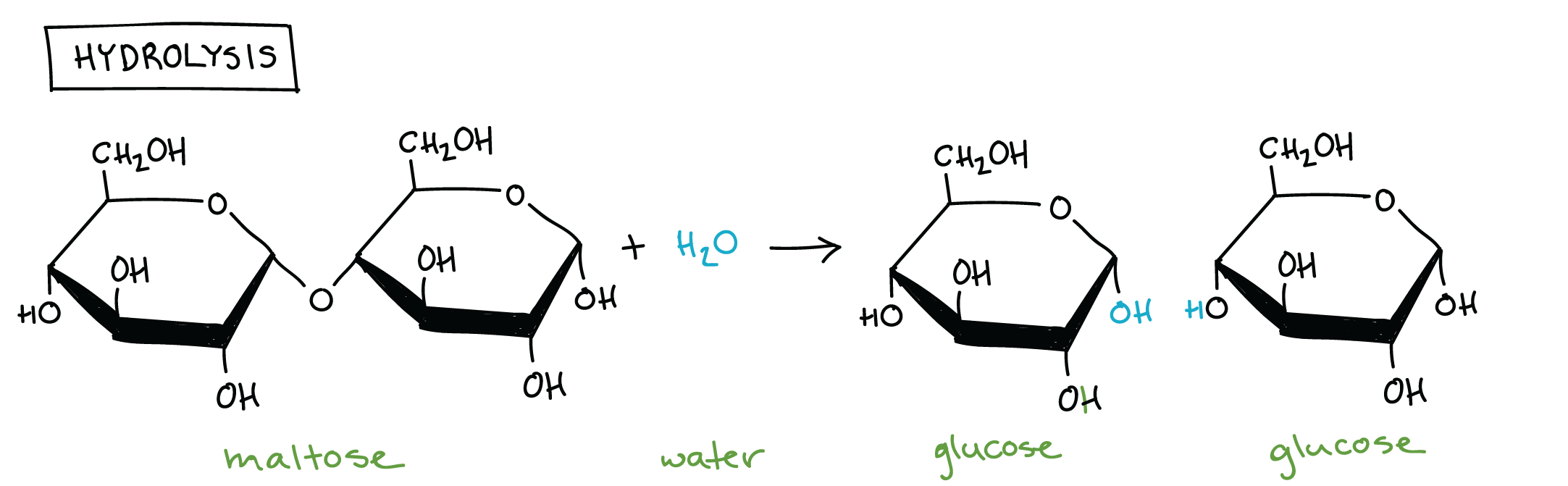
Hydrolysis
Breaks bonds by adding H₂O
-H of the H₂O bonds to one monomer and the remaining -OH attaches to the other monomer.
Covalent bonds are cleaved (broken).
AB + H₂O → A + B
Carbohydrates
Includes sugars and polymers of sugars; a major energy source for organisms
Carbonyl and hydroxyl groups
Composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen (CHO)
Monosaccharides
Simple sugars; monomers of carbohydrates
Composed of multiples of the unit CH₂O
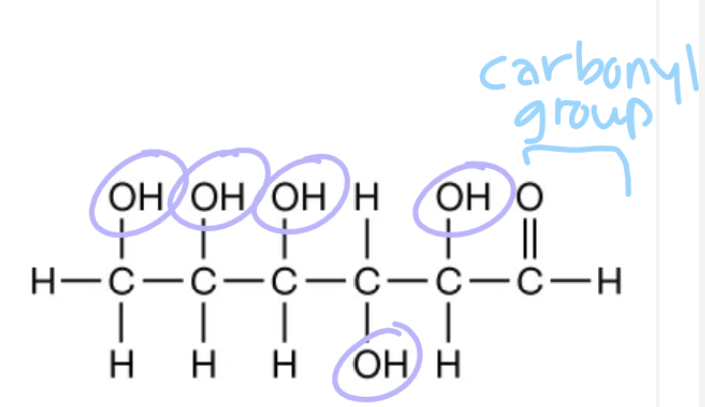
Glucose
Most common monosaccharides
Nutrients and fuels for cells
Used in cellular respiration
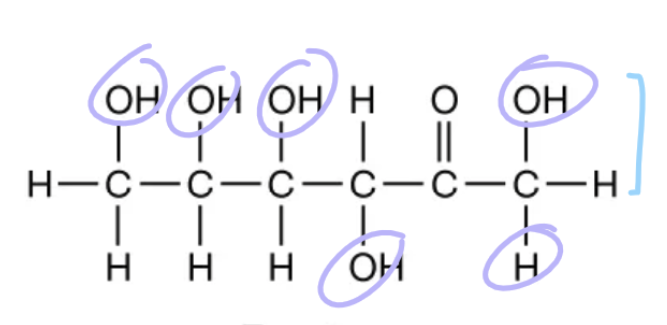
Fructose
“Fruit” sugar
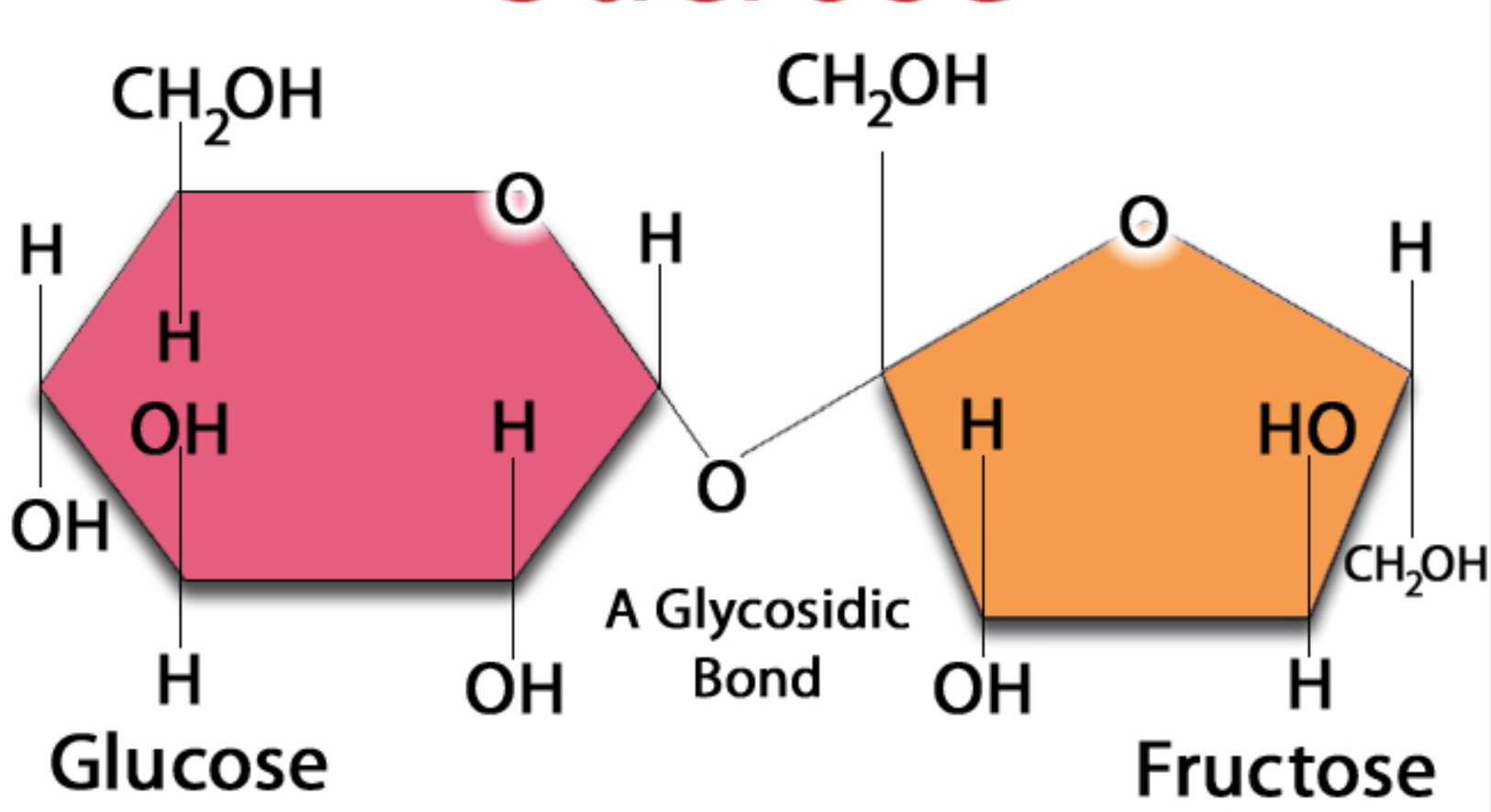
Sucrose
Most common disaccharide
Made up of glucose and fructose
Plants transfer carbs from roots to leaves in this form
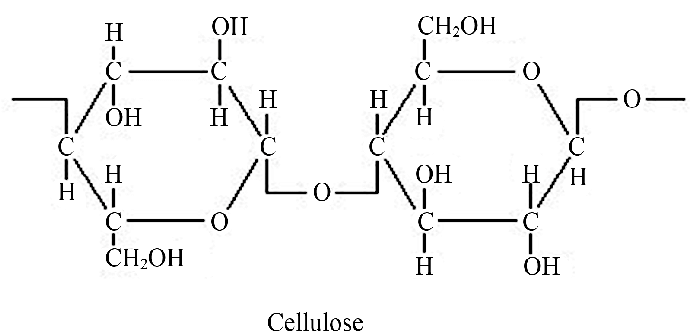
Cellulose
Polymer of glucose
Tough substance that forms cell walls
Lipid
Diverse group of molecules; generally won’t dissolve in water; does not include true polymers
Generally small in size
Nonpolar-hydrophobic
Fats
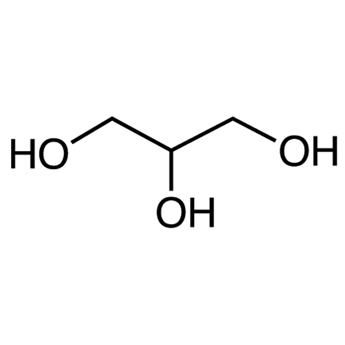
Lipids - Composed of glycerol (1) and fatty acids (3)
Glyercol
Classified as an alcohol (hydroxyl groups)
Fatty acids
Long carbon chains with a carboxyl group at one end
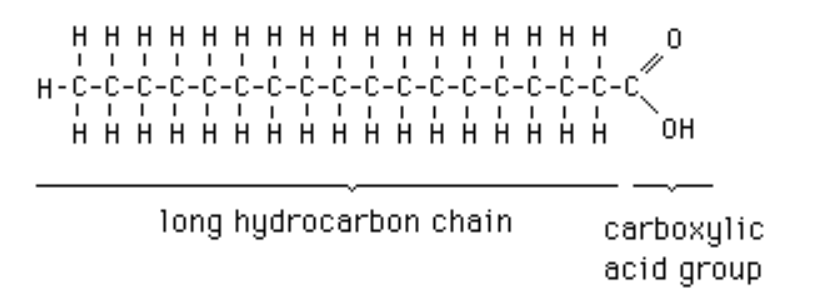
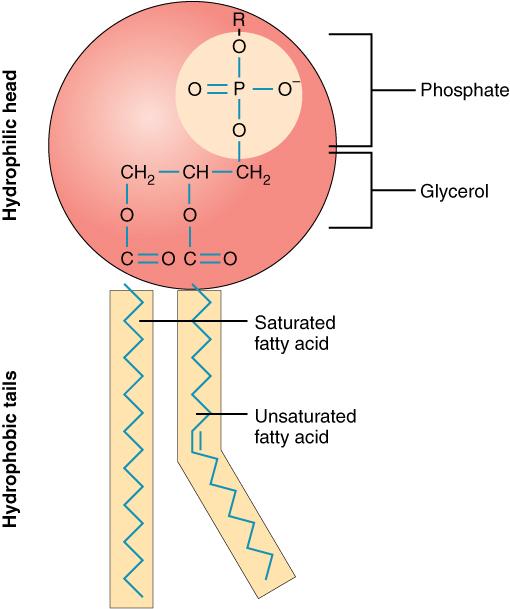
Saturated fatty acid
Type of fatty acid; No double bonds between carbons in the carbon chain; contains more hydrogen (saturated w/ hydrogen)
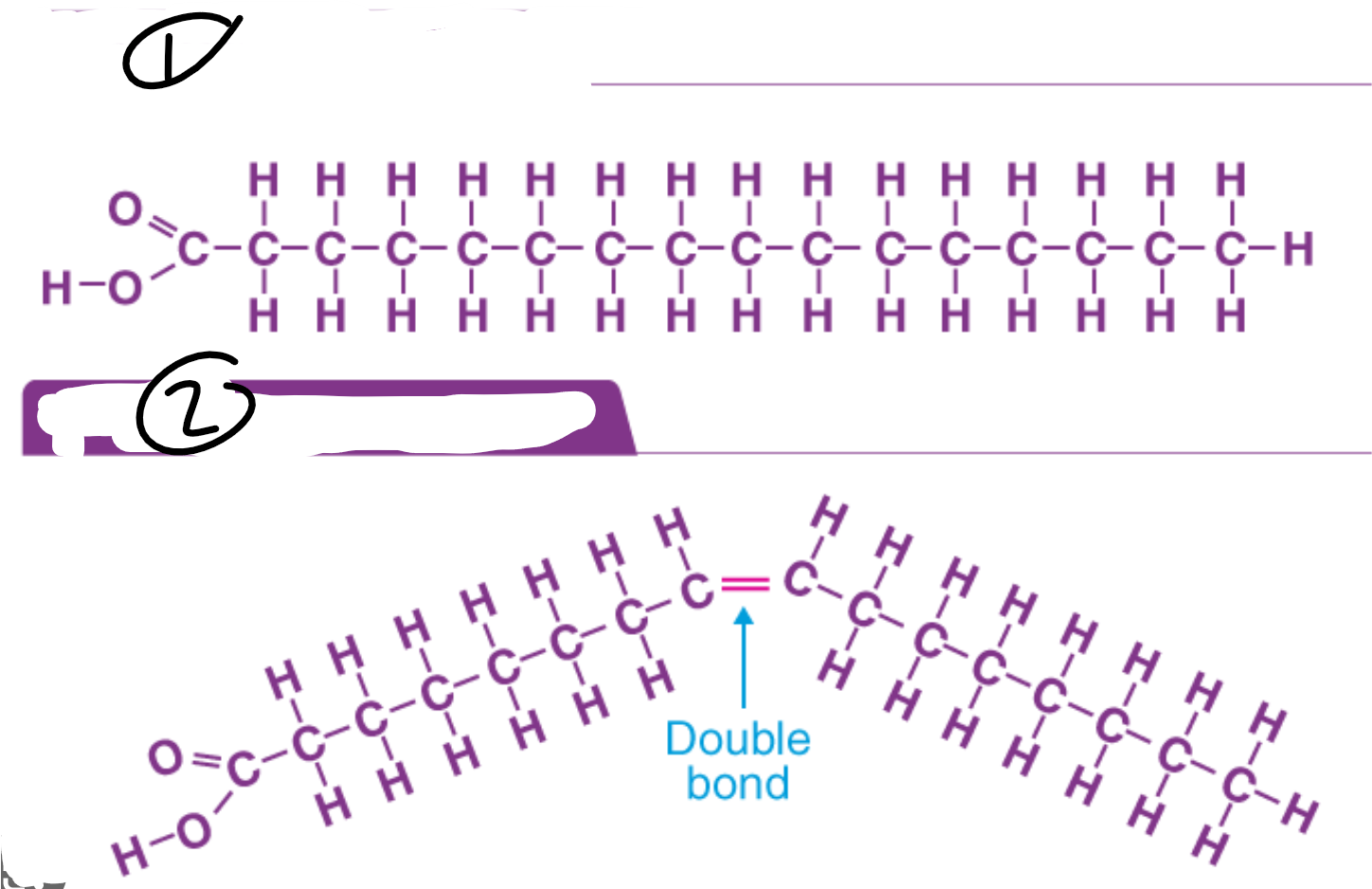
Unsaturated fatty acid
Fatty acid that contains one or more double carbon bonds, leaving less room for hydrogen molecules
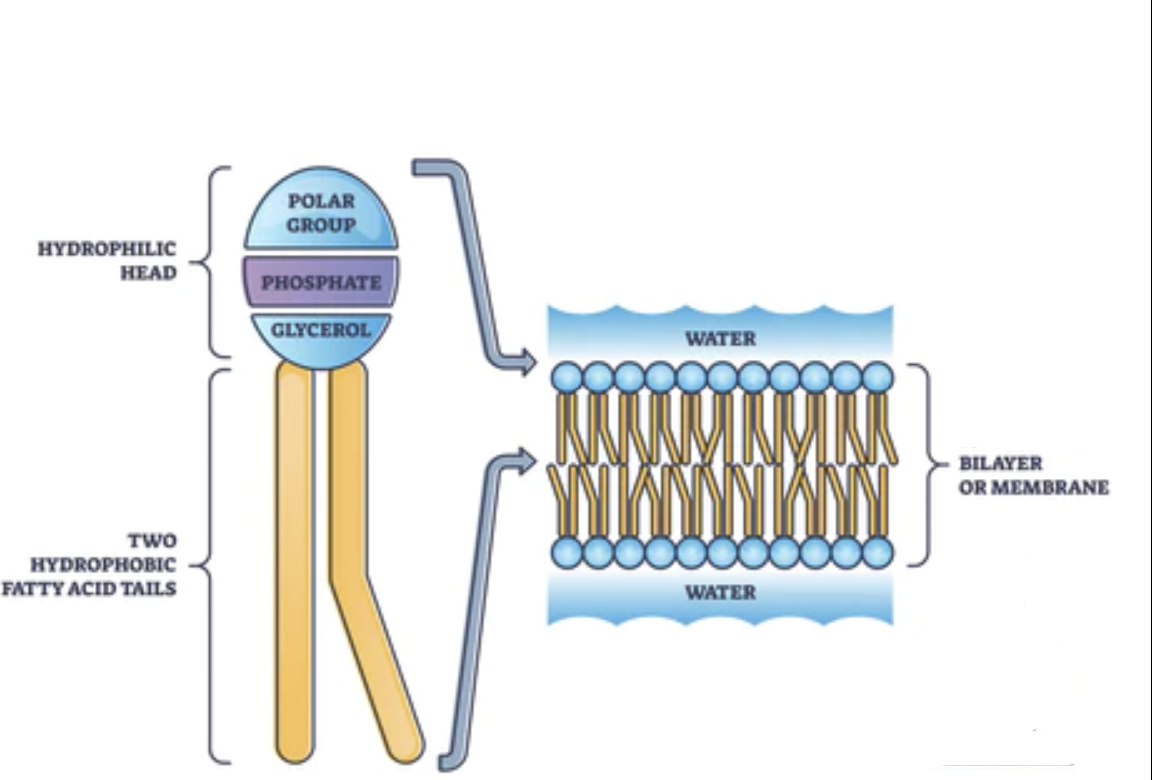
Phospholipids
Major components of cell membranes
Two fatty acids - glycerol - phosphate
Assembled as a bilayer in H₂O
Tails are hydrophobic
Head is hydrophillic
Steroids
Lipids that have four fused rings
Unique groups attached to the ring determine the type of steroid
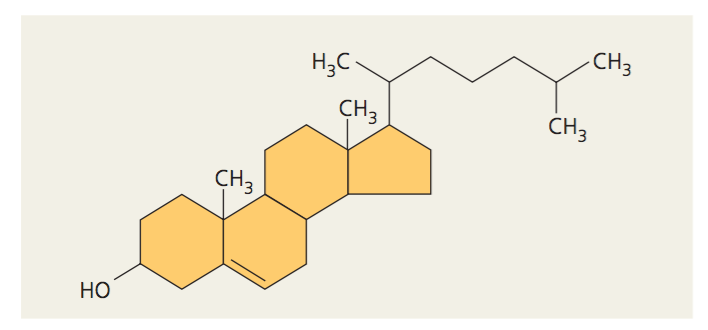
Lipid
Moving and storing energy
Absorbing vitamins
Making hormones
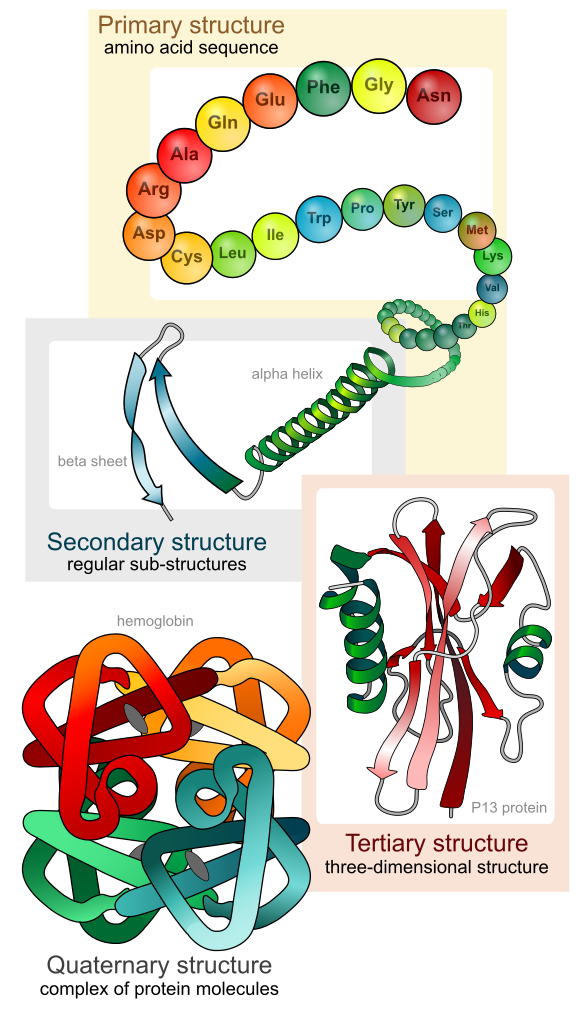
Protein
Molecule consisting of polypeptides (polymers of amino acids) folded in a 3D space
Includes sulfur
Shape determines function
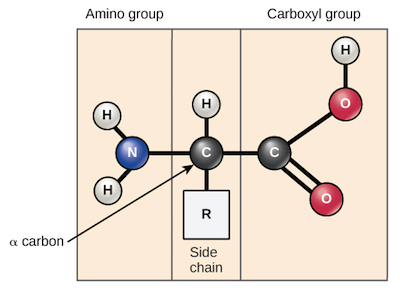
Amino acids
Molecules that have an amino group and a carboxyl group
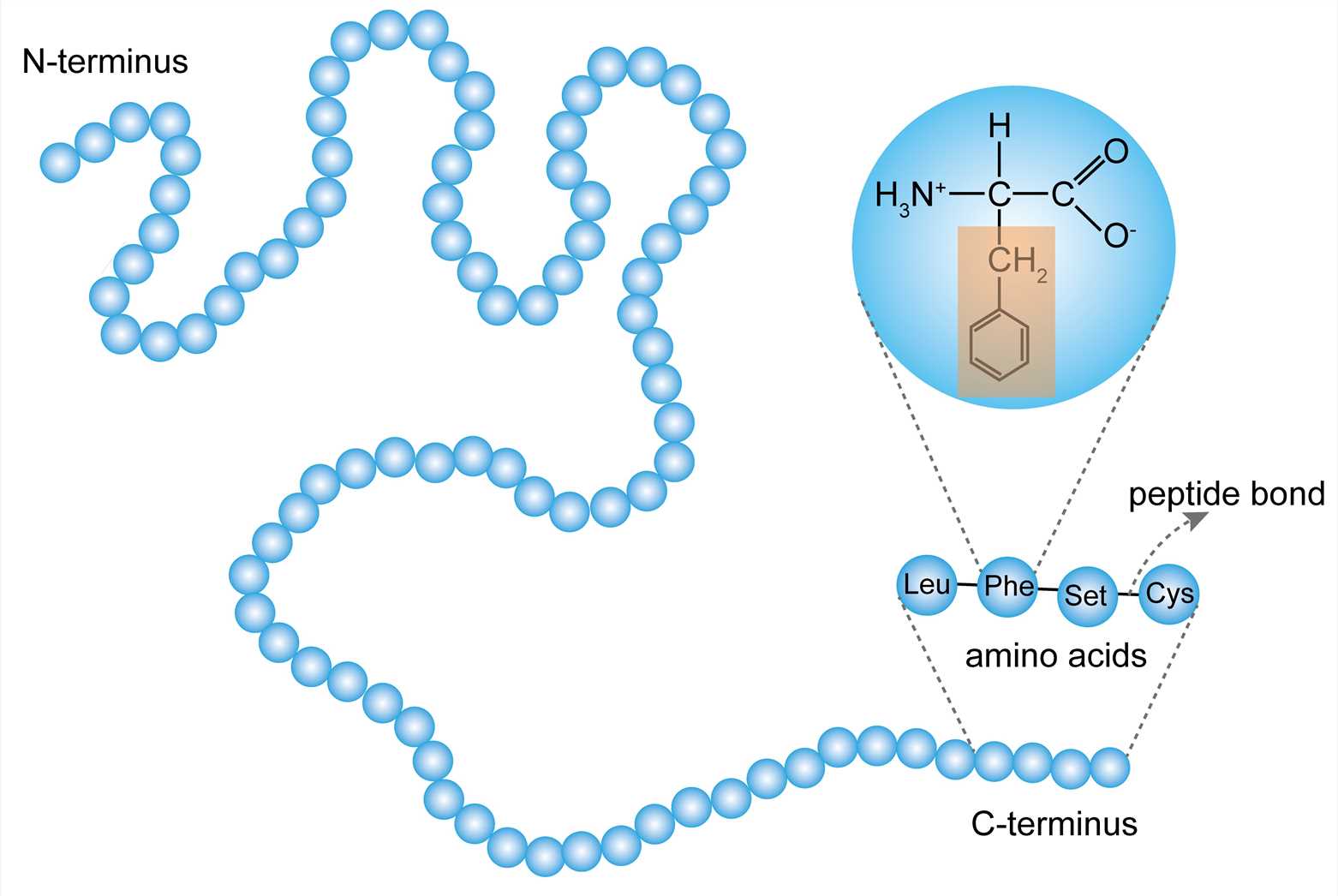
Polypeptides
Many amino acids linked by peptide bonds
Each has a unique sequence of amino acids and directionality
Each end is chemically unique (one end is a free amino group, N-terminus; one is a free carboxyl group, C-terminus)
Sequence of AAs determine shape (and shape determines functions)
Primary
Protein level
Linear chain of amino acids
Determined by genes
Dictates secondary and tertiary forms
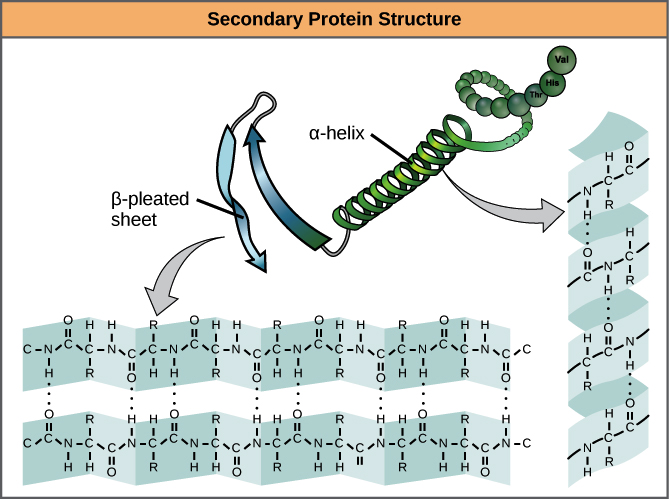
Secondary
Coils and folds due to hydrogen bonding within the polypeptide backbone
β pleated sheets - hydrogen bonds between chains lying side to side
α helix - hydrogen bonding between every 4th AA
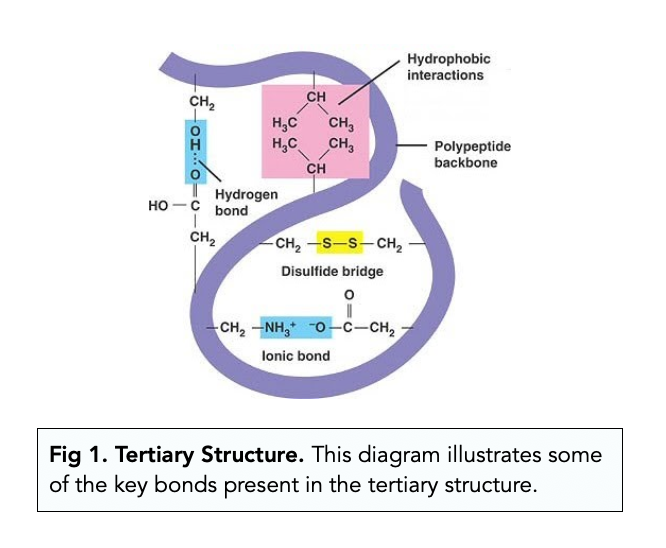
Tertiary
3D folding due to interactions between the side chains
Reinforced by hydrophobia interactions and disulfide bridges of the side chains
Covalent bond formed between sulfur atoms of the cysteine monomers
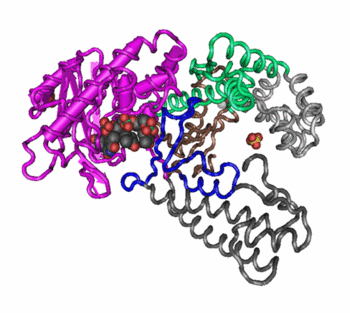
Quaternary
Association of two or more polypeptides
Found only in some polypeptides
Protein
Antibodies
Enzymes
Hormones
Provides structure and support
Transport/Storage
Nucleic acids
Made from nucleotides; DNA/RNA
Stores, transmits, and expresses hereditary information
A nitrogenous base, a five carbon sugar (pentose), and phosphate group(s)
Parts of a nucleotide
Nucleoside
A nitrogenous base and a five carbon sugar
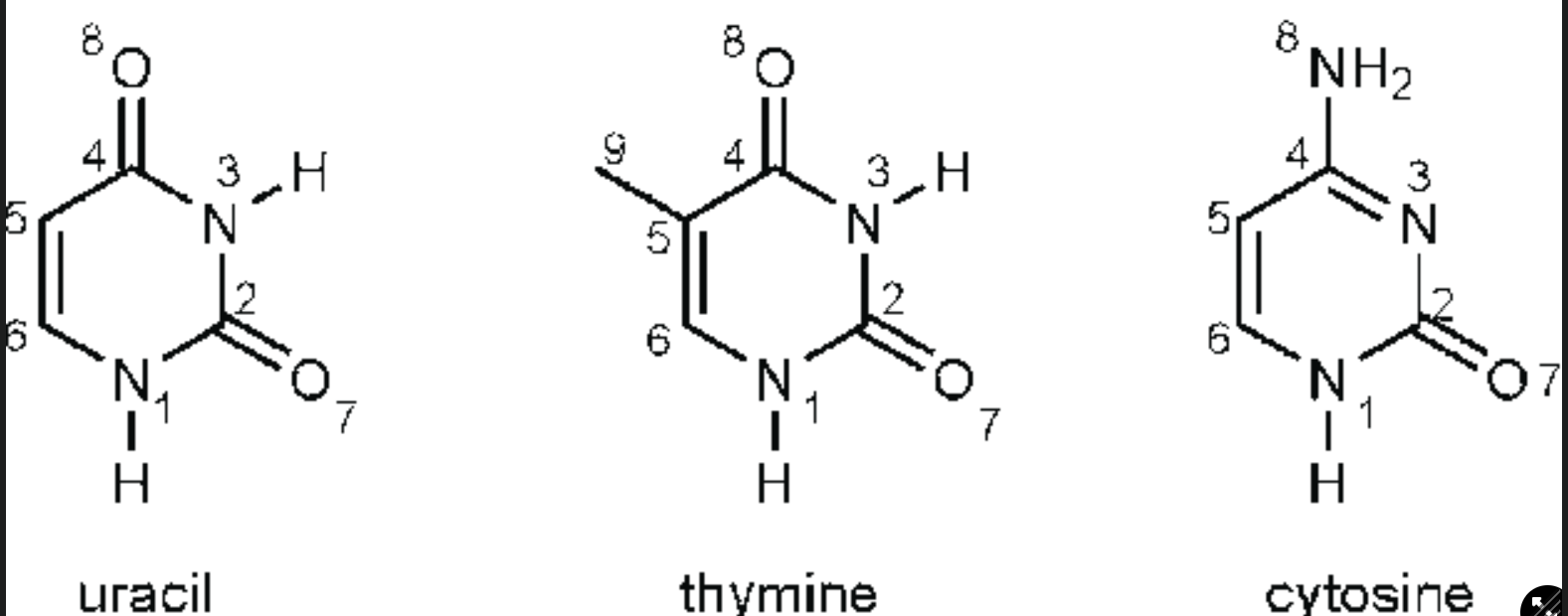
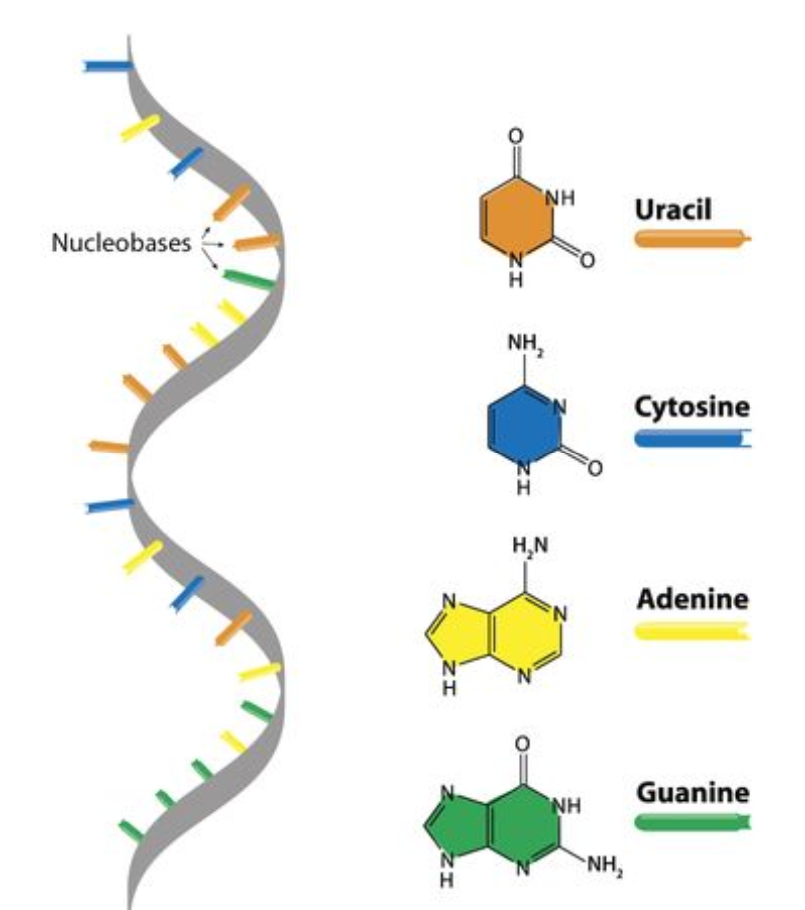
Pyrimidine and purine
Types of nitrogenous bases
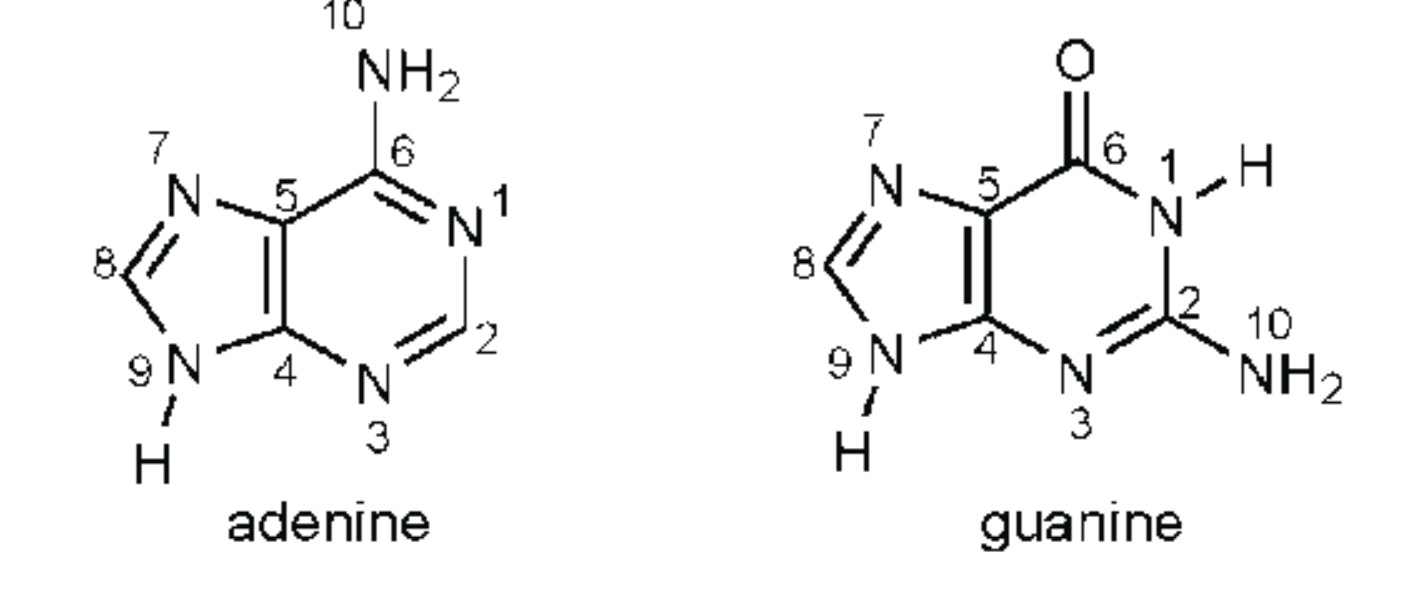
Purine
One ring with 6 atoms bonded to one ring with five atoms
Adenine, guanine
Pyrimidine
One ring with 6 atoms
Cytosine, thymine (only found in DNA), uracil (only found in RNA)
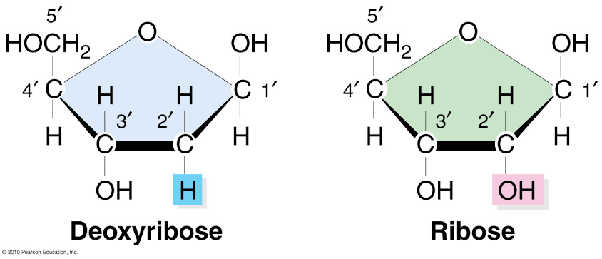
Five carbon sugar
A sugar is bonded to the base \n In DNA the sugar is deoxyribose. \n In RNA the sugar is ribose.
Phosphate group
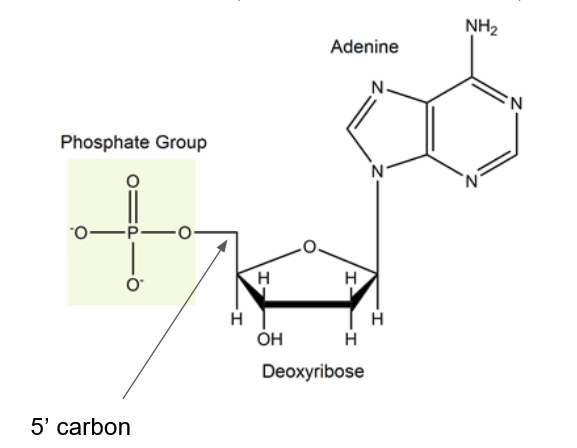
Polynucleotides
Phosphate groups that link adjacent nucleotides produce…
DNA
Consists of two polynucleotides
Forms the double helix
Strands are antiparallel (parallel but moving in opposite directions) and held by hydrogen bonds between bases
Cytosine - guanine; adenine - thymine
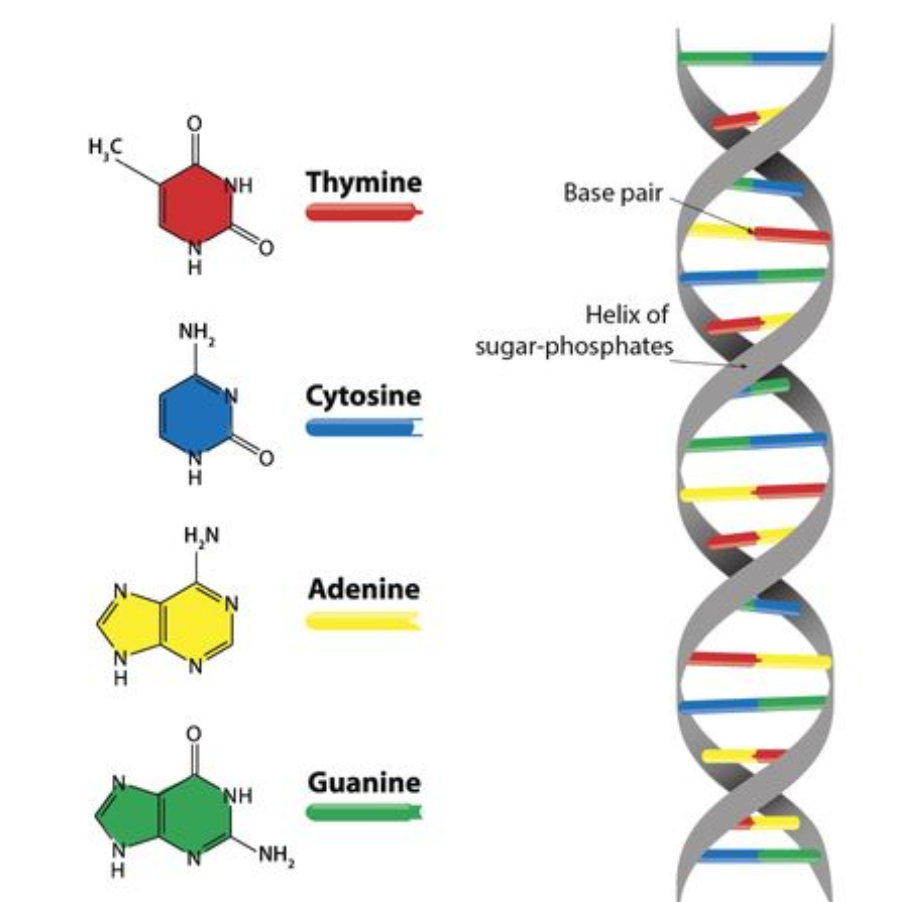
RNA
A single stranded polynucleotide
Varied in shape
Adenine - uracil; cytosine - guanine
glysodic link
two monopsaccardies