Divisions of the Nervous System (11)
1/120
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
121 Terms
What structures make up the brain
2 cerebral hemispheres, diencephalon, brainstem, cerebellum
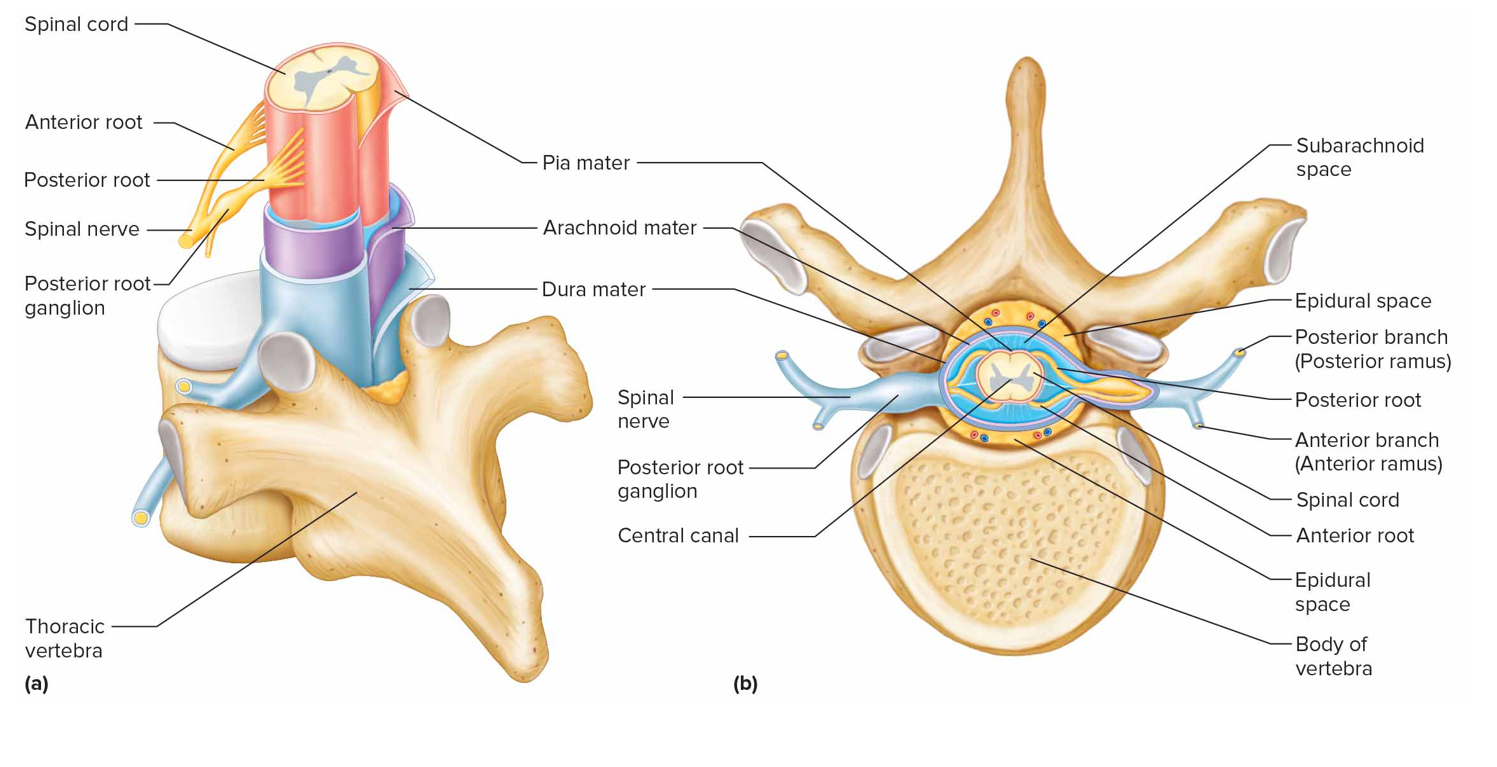
Meninges
Mems that lie btw bone + soft tissues of nervous sys to protect brain + spinal cord
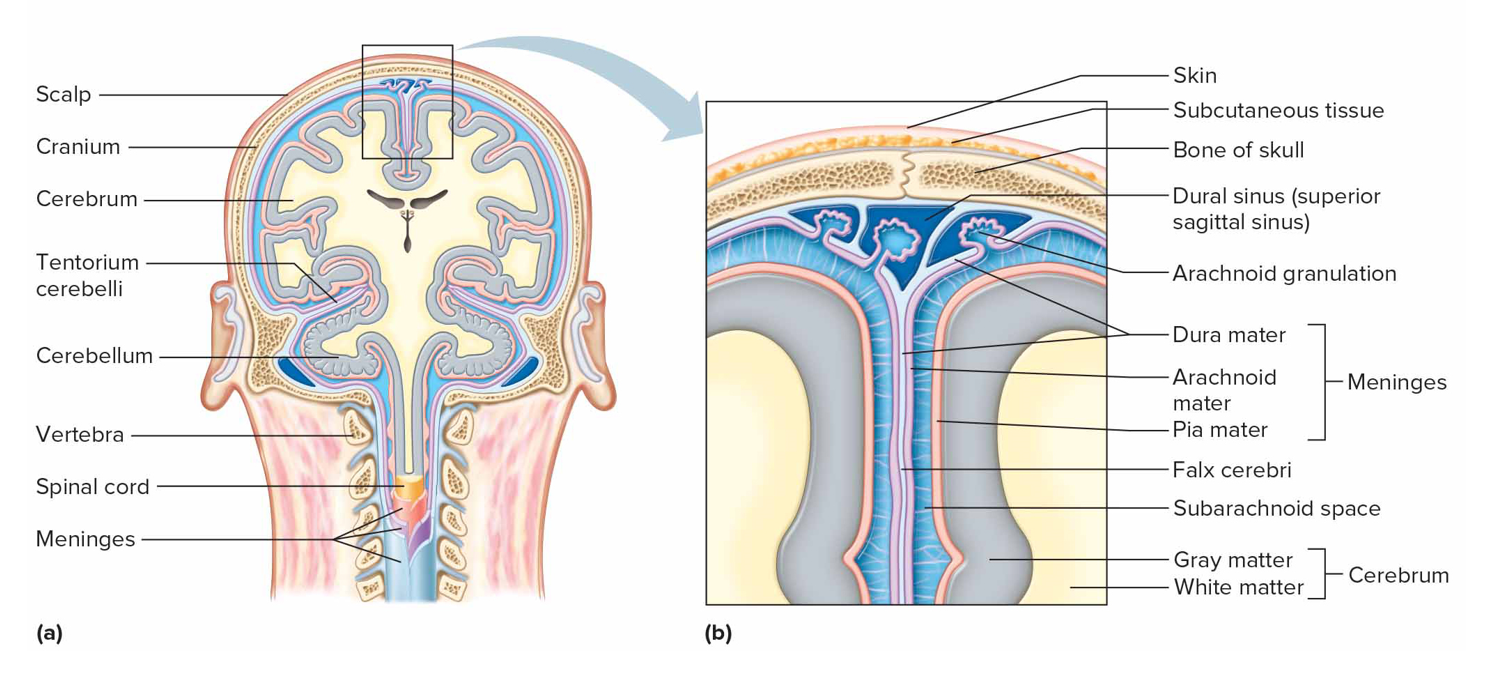
Dura mater characteristics
Outer layer of meninges made of dct; dural sinuses + epidural space
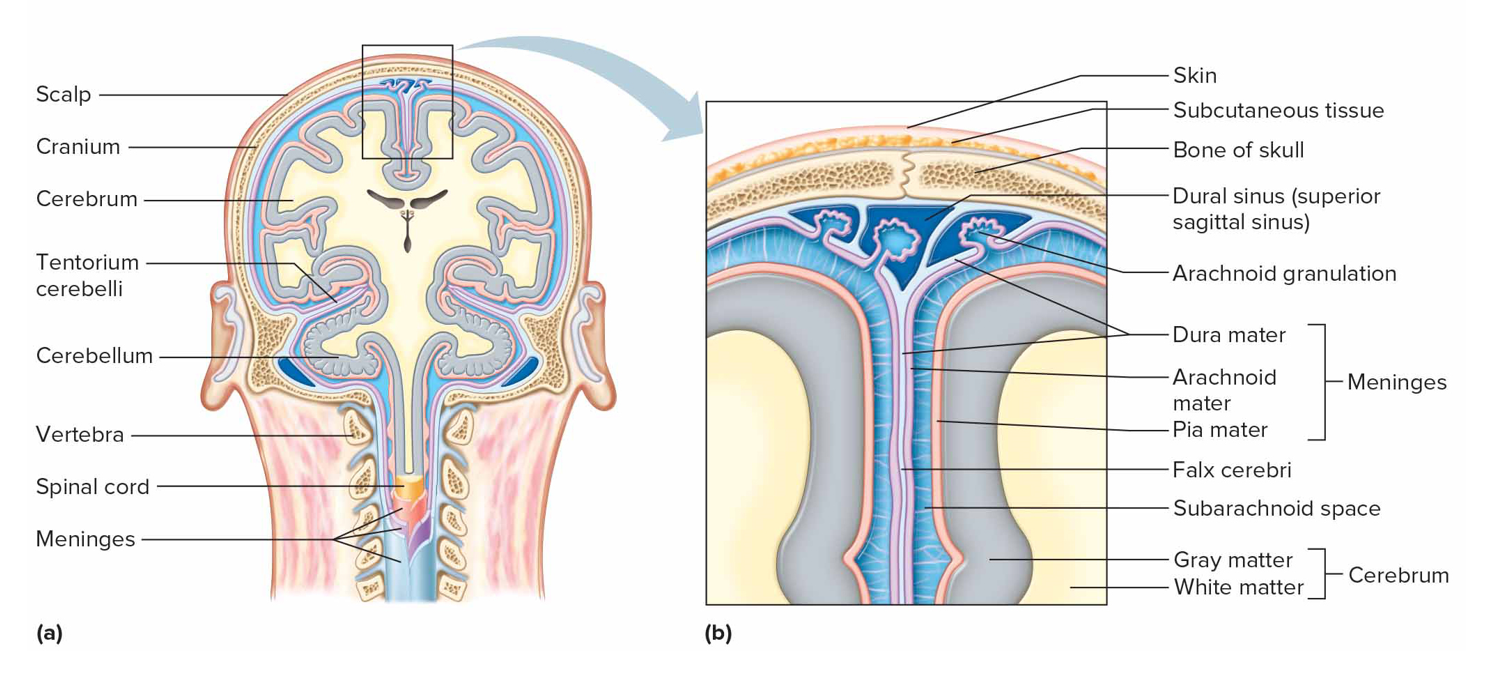
Arachnoid mater characteristics
Middle web-like layer of meninges containing cerebrospinal fluid in subarachnoid space
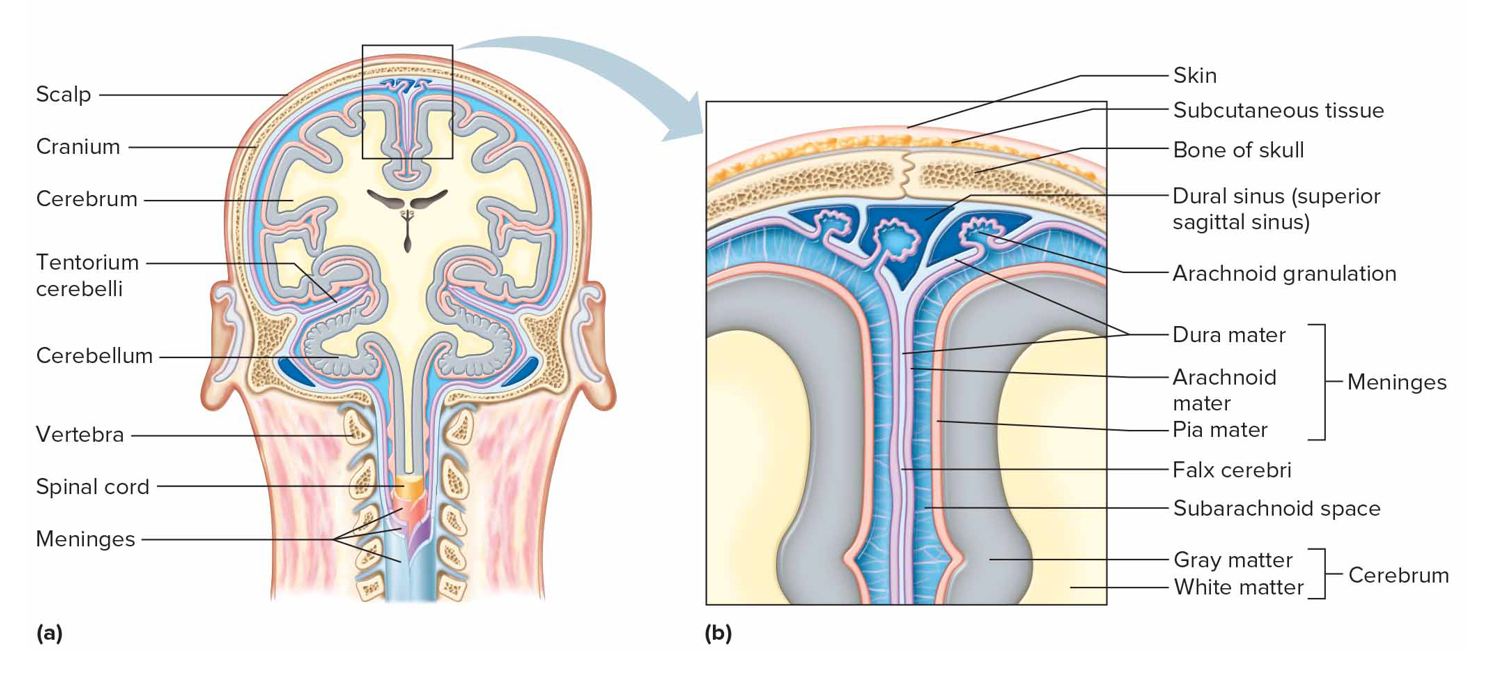
Pia mater characteristics
Inner layer of meninges, attached to brain + sc surface, containing bvs + nerves; nourishes CNS
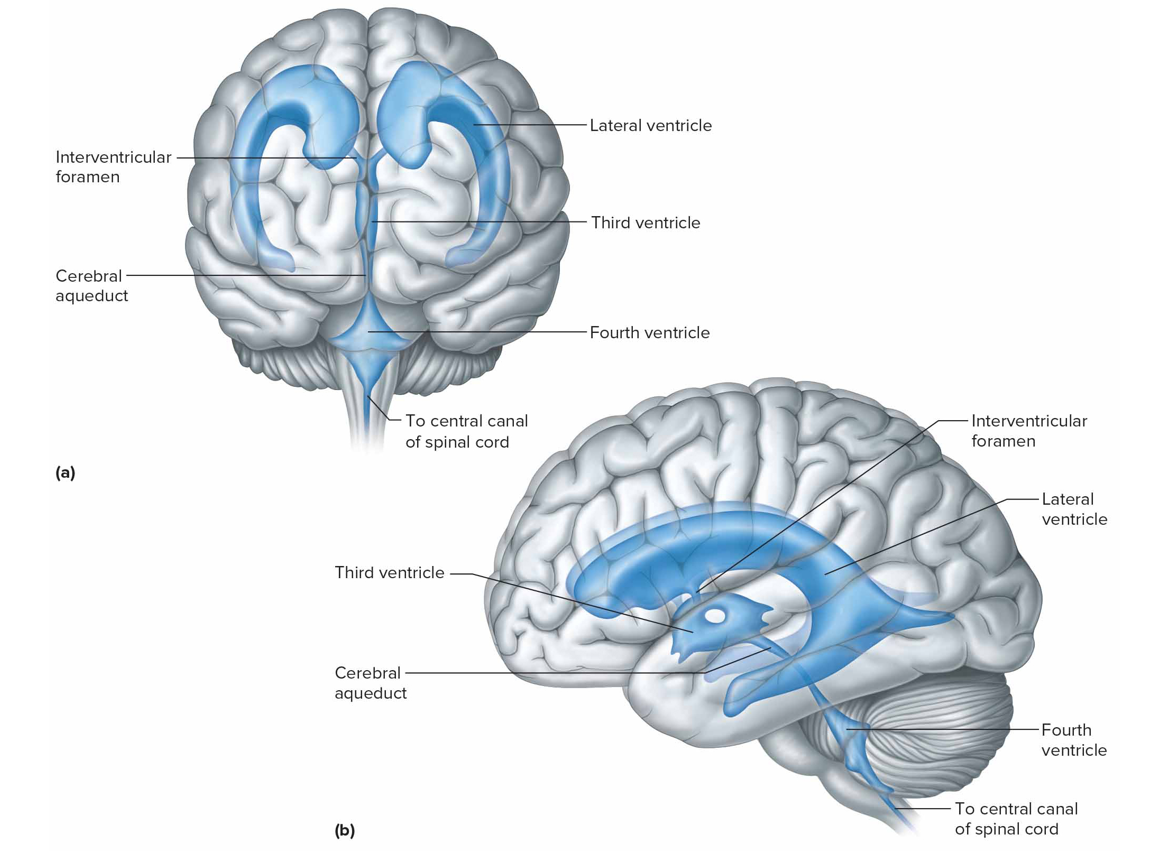
What connects the third ventricle to the lateral
Interventricular foramina
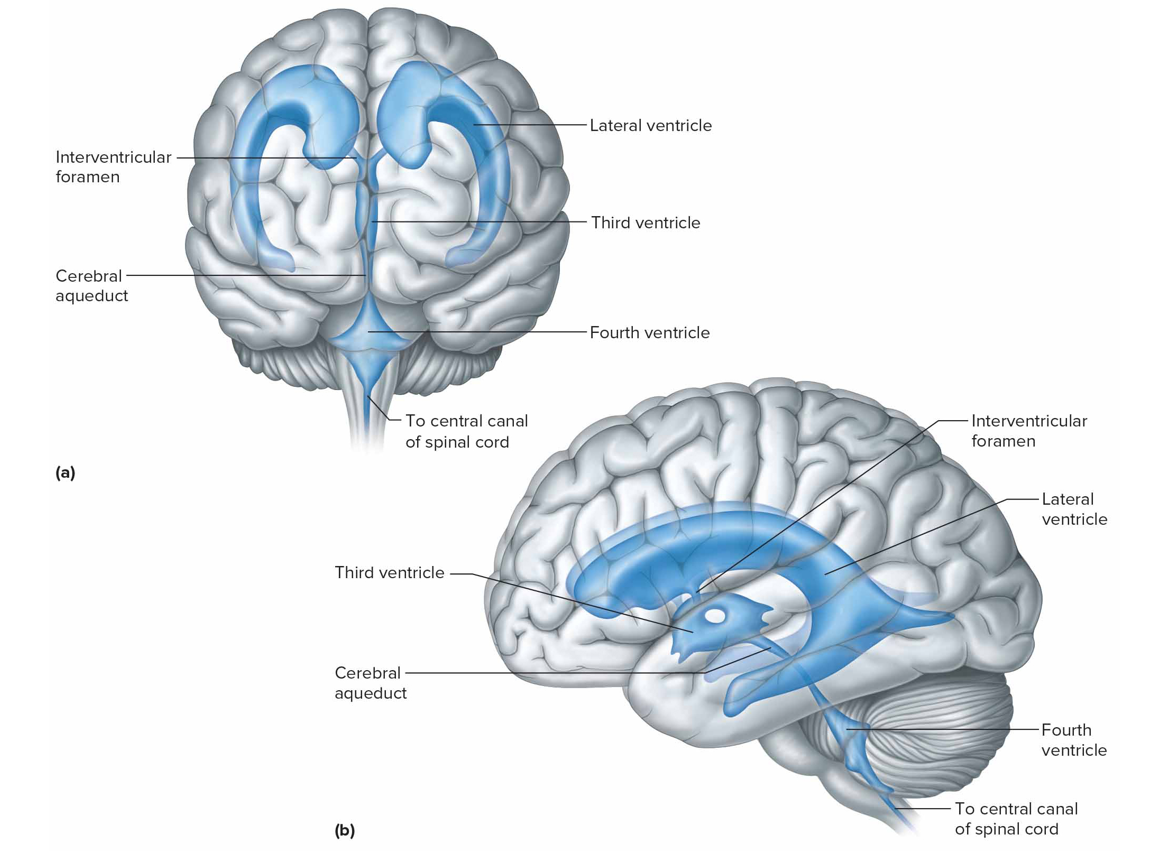
What connects the third ventricle and fourth ventricles
Cerebral aqueduct
What is CSF secreted by
Choroid plexuses: special capillaries of pia mater covered by epend, absorbed by arachnoid granulations after exchanging substances
Volume of CSF
140 mL
Concussion
A mild traumatic brain injury from one-time injury
Chronic traumatic encephalopathy
Mild repetitive TBI from many small injuries over time; symptoms begin years later + have long-lasting effects on memory + behavior
Blast-related brain injury
Severe TBI from explosions in combats; leads to cognitive decline years after injury
What keeps CFS pressure constant + how to relieve pressure
Continuous secretion + reabsorption; insertion of drain into subarachnoid space
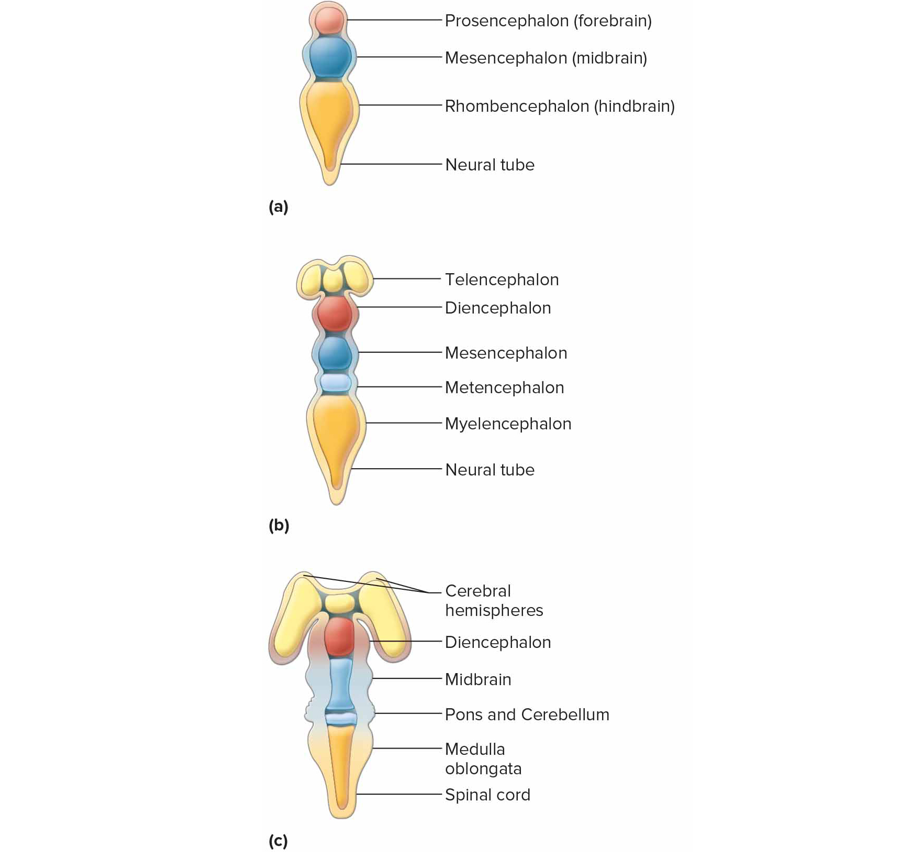
What does the brain form from
3 vesicles (cavities)
Forebrain (prosencephalon) → telencephalon, diencephalon → cerebrum, basal nuclei, diencephalon
Midbrain (mesencephalon)
Hindbrain (rhombencephalon) → metencephalon, myelencephalon → cerebellum, pons, medulla oblongata

Cerebrum
Largest part of brain halfed by falx cerebri
Corpus callosum: connects cerebral hemispheres
Gyri: ridges/convolutions
Sulci: shallow grooves in surface
What is the cerebral cortex
Thin layer of gray matter which makes up outermost layer of all outer lobes; contains 75% of neuron cell bodies
What makes up most of cerebrum
White matter under cerebral cortex; contains myelinated axons that connect neuron cell bodies in cc to other portions
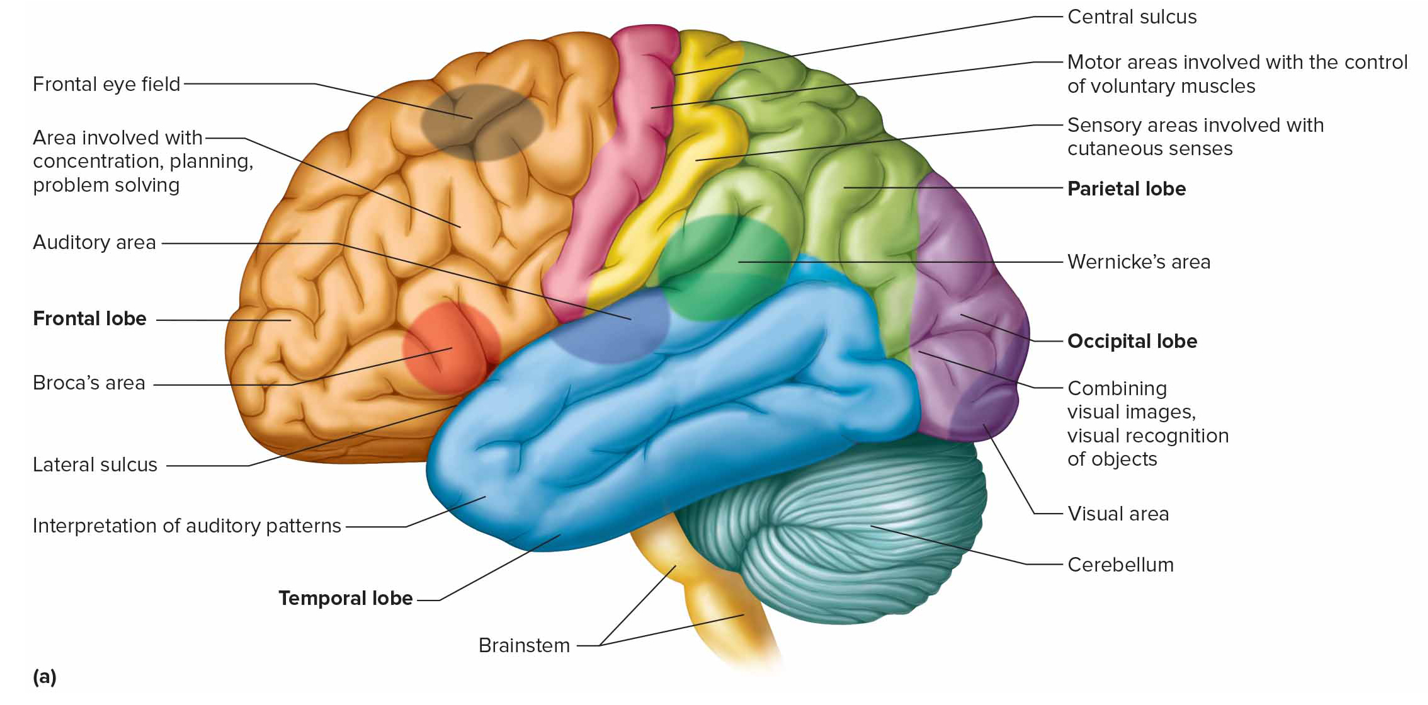
What functions is the cerebral cortex responsible for
Interpreting impulses from sensory organs
Initiating voluntary movements
Storying info as memory
Retrieving stored info
Reasoning, seat of intelligence, personality
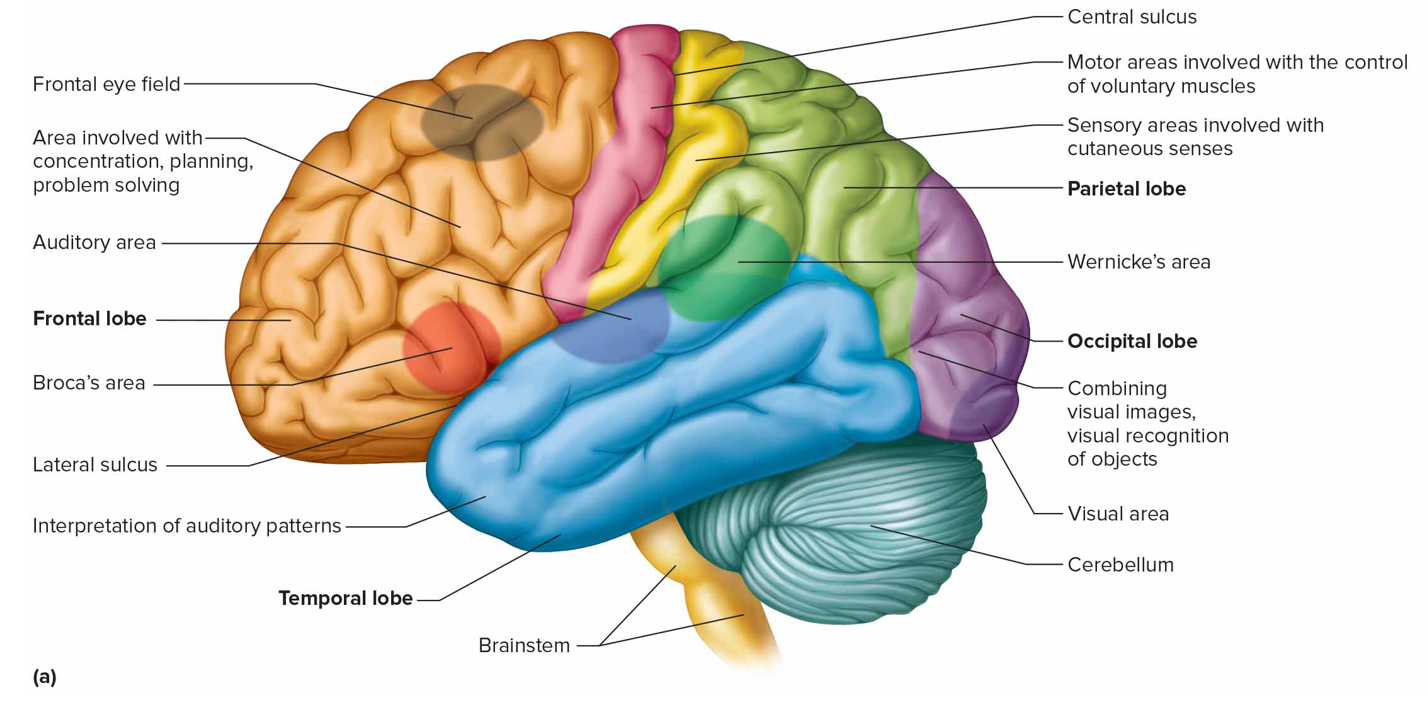
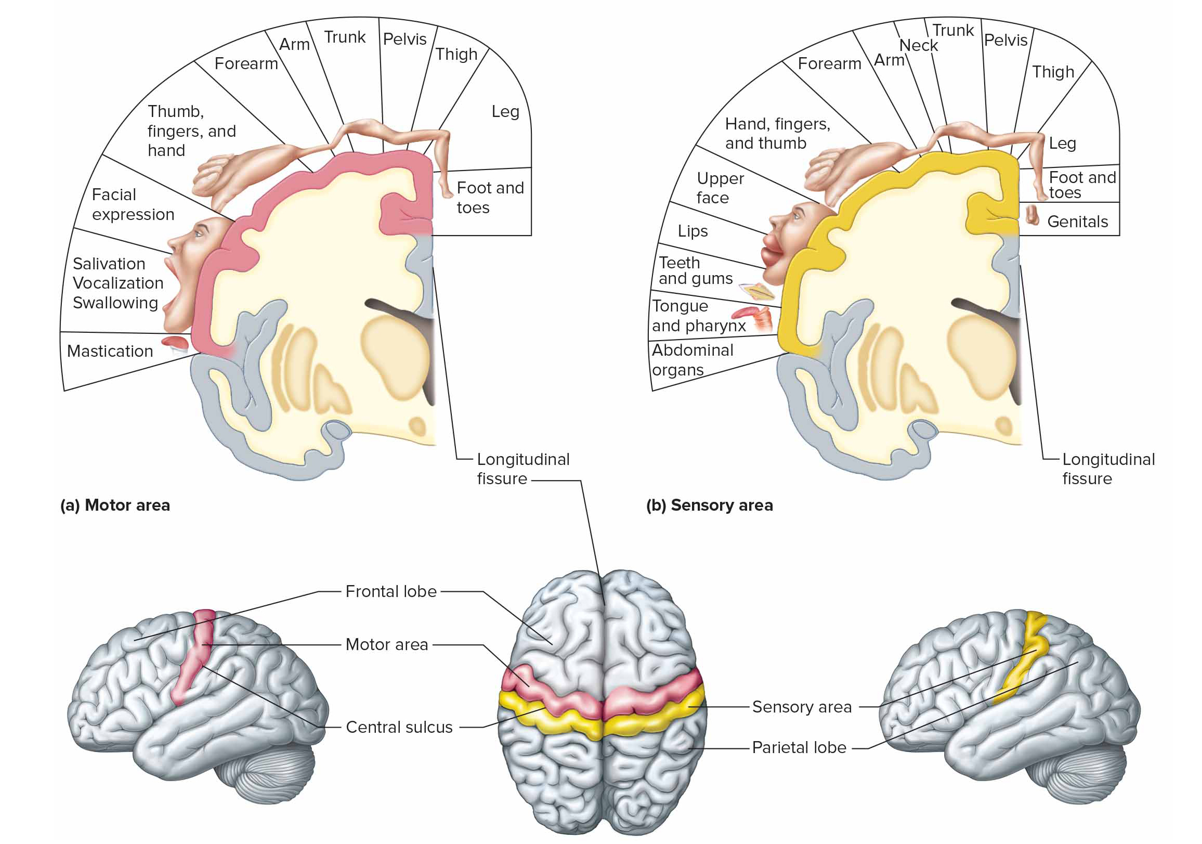
Where is the cutaneous sensory area + what is it responsible for (s)
Parietal lobe; interprets sensations on skin
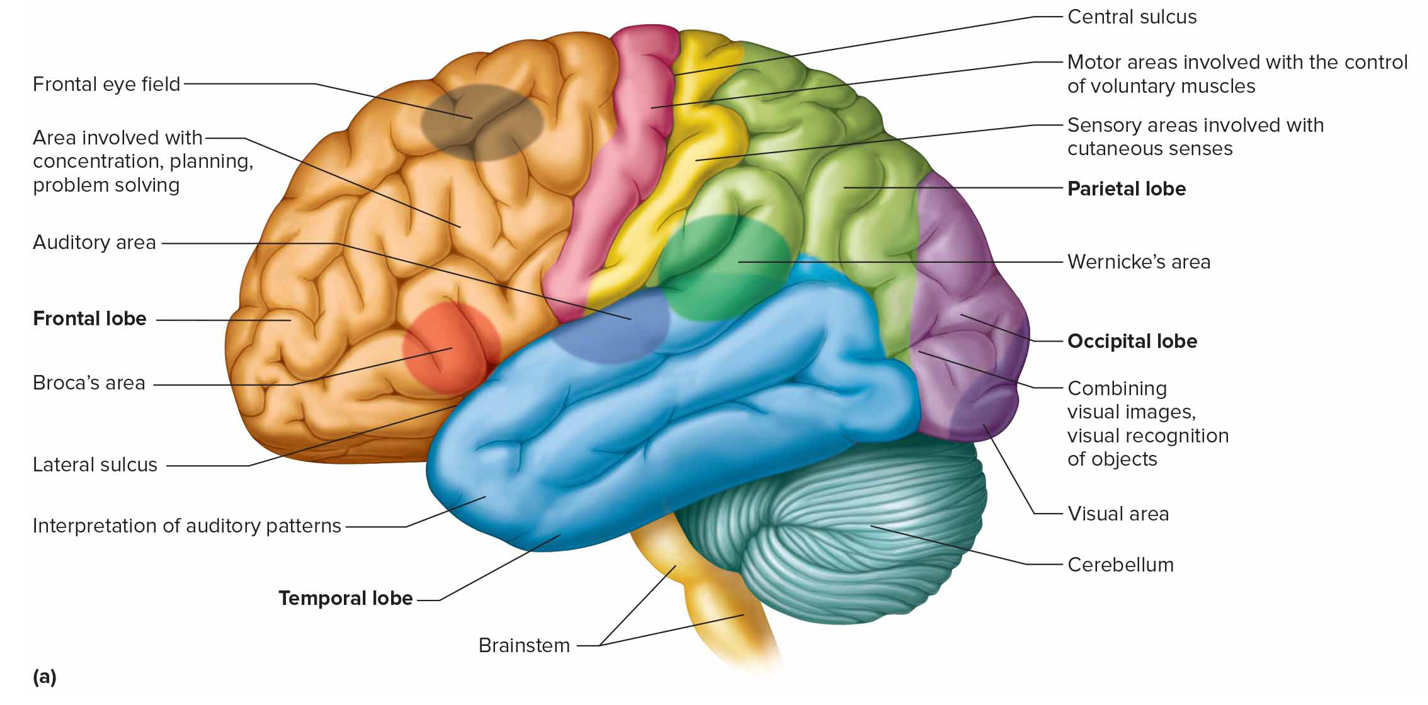
Where is the sensory speech (Wernicke’s) area + what is it responsible for (s)
Temporal/parietal lobe left hemisphere; understanding + formulating language; Broca’s produce speech
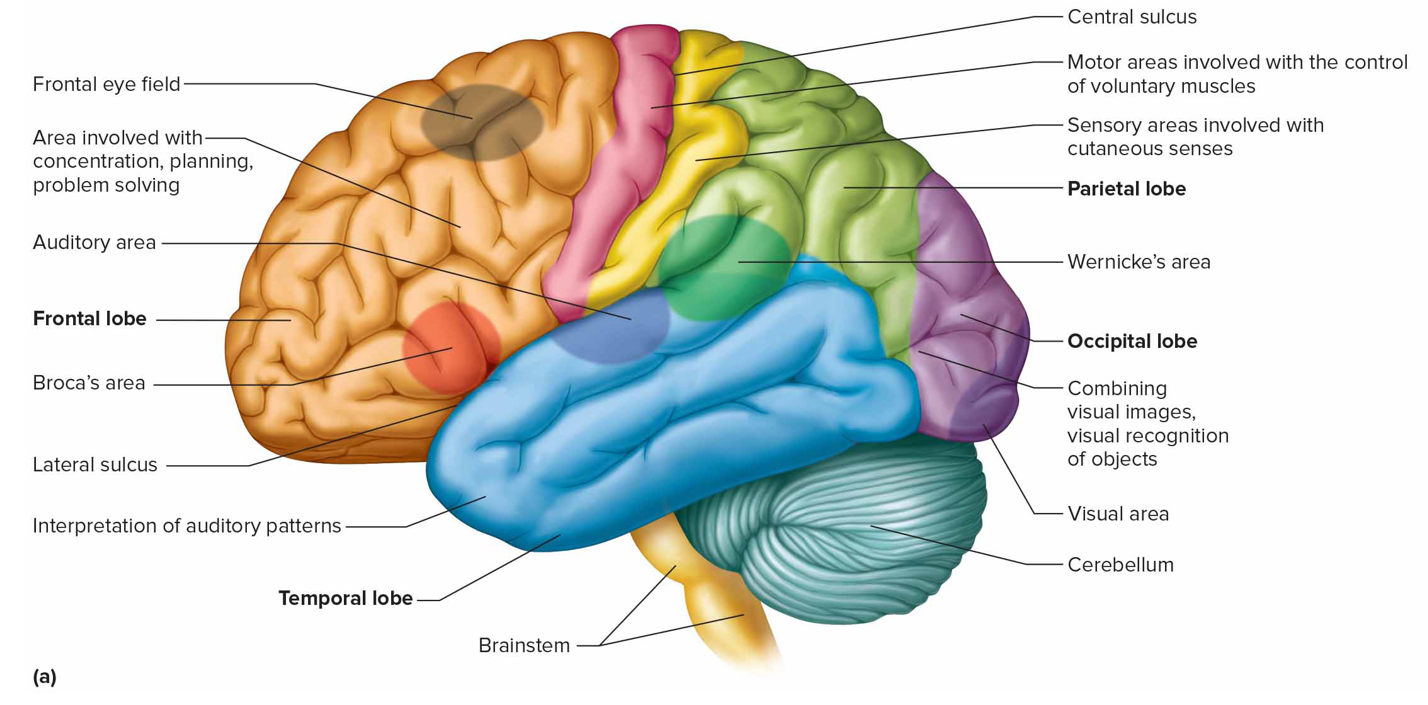
Where is the visual area + what is it responsible for (s)
Occipital lobe; interprets vision
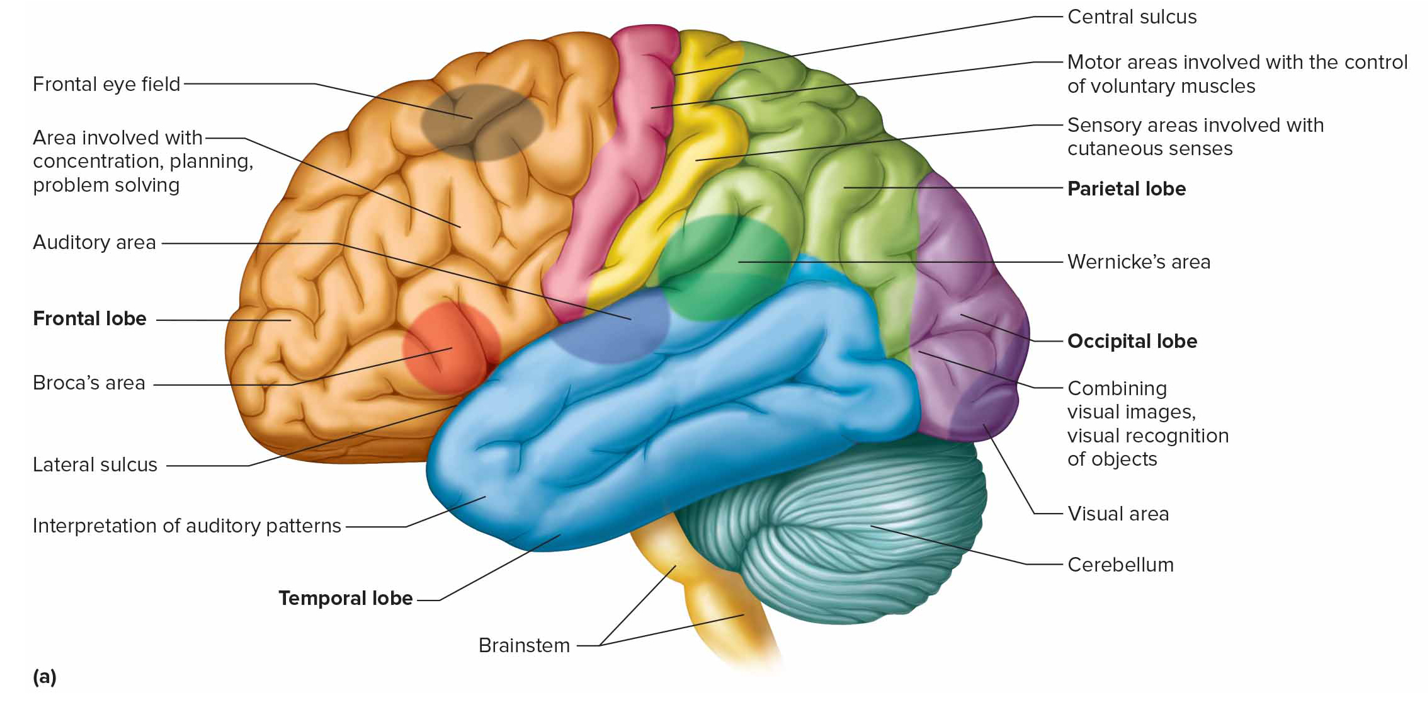
Where is the auditory area + what is it responsible for (s)
Temporal lobe; interprets hearing
Where is the sensory area for taste
Near base of central sulcus includes part of insula
Where is the sensory area for smell
Arises from centers deep within temporal lobes
What are association areas
Regions not motor/sensory that interpret sensory experiences; provide memory, reasoning, verbalization, judgment, emotions
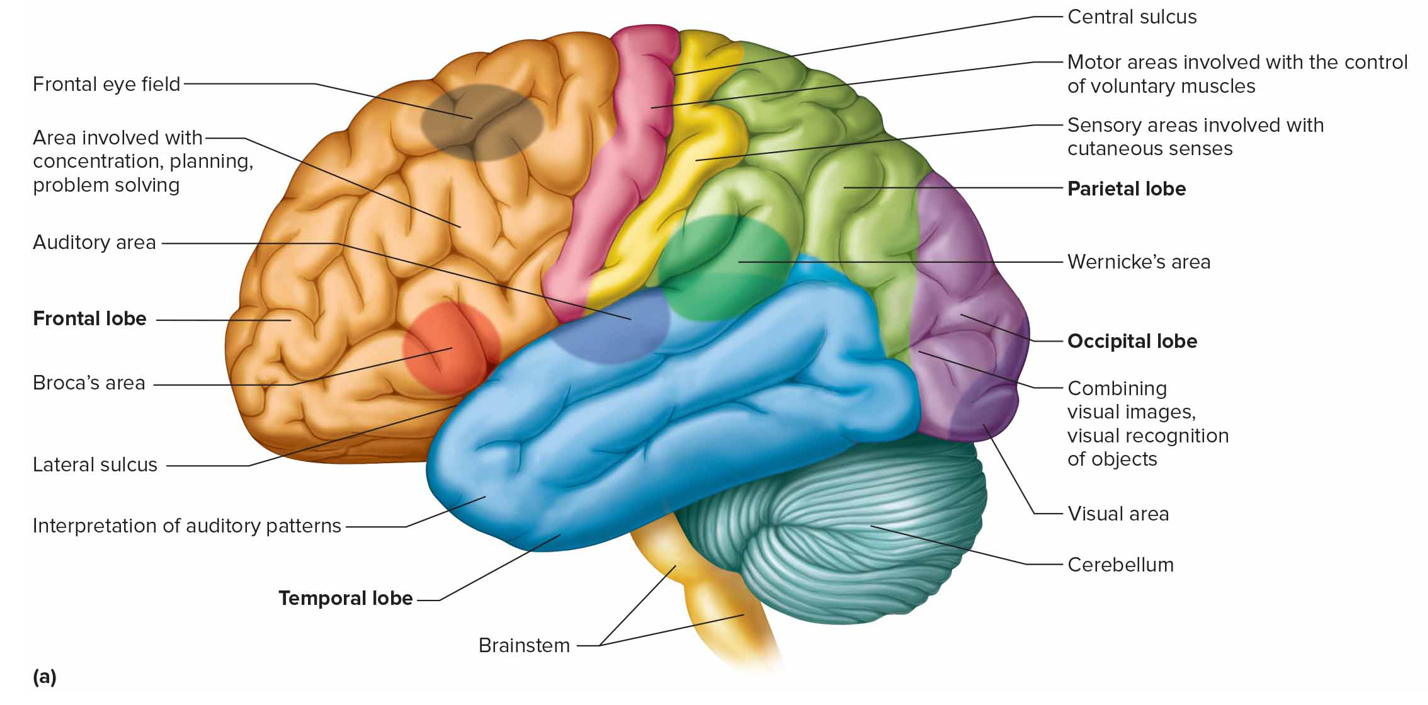
Frontal lobe association areas function
Concentrating, planning, emotional + judging behavior
Parietal lobe association areas function
Understanding speech, choosing words to express
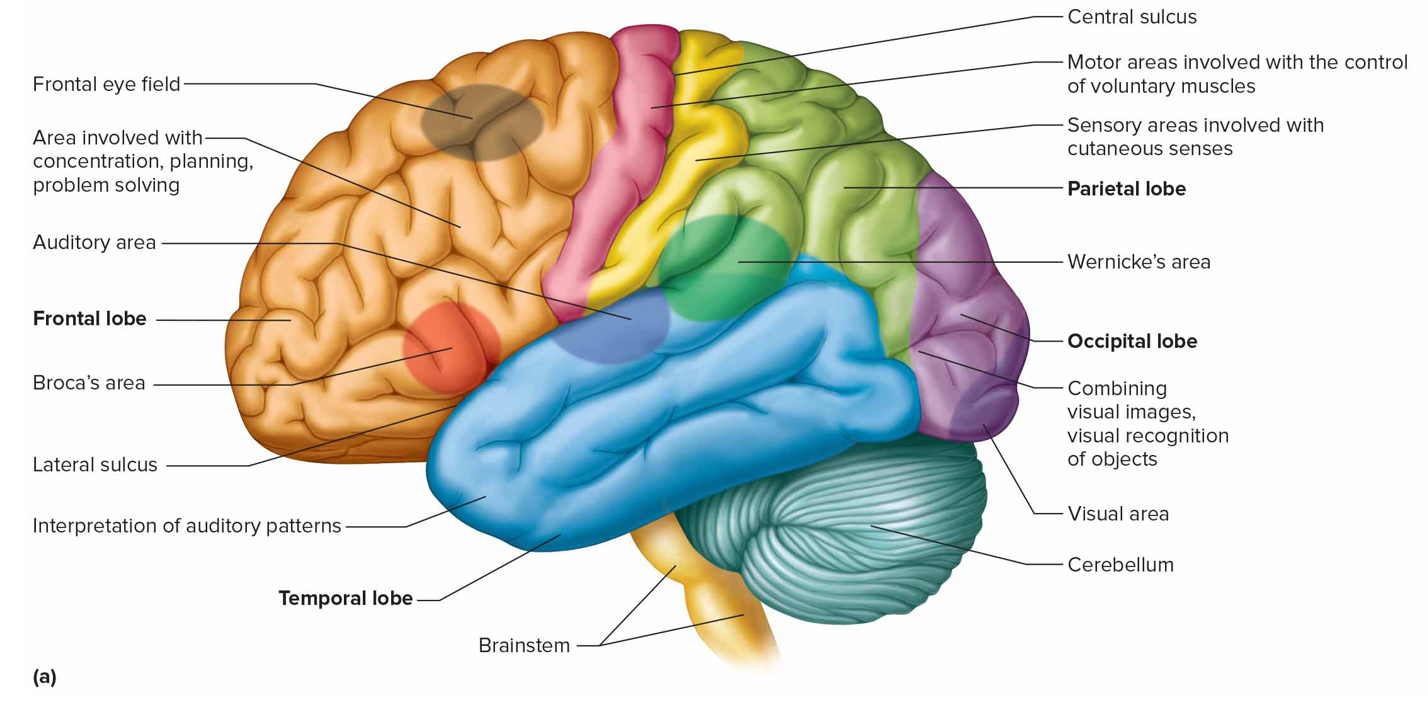
Temporal lobe association areas function
Interpret complex sensory exps, store memories
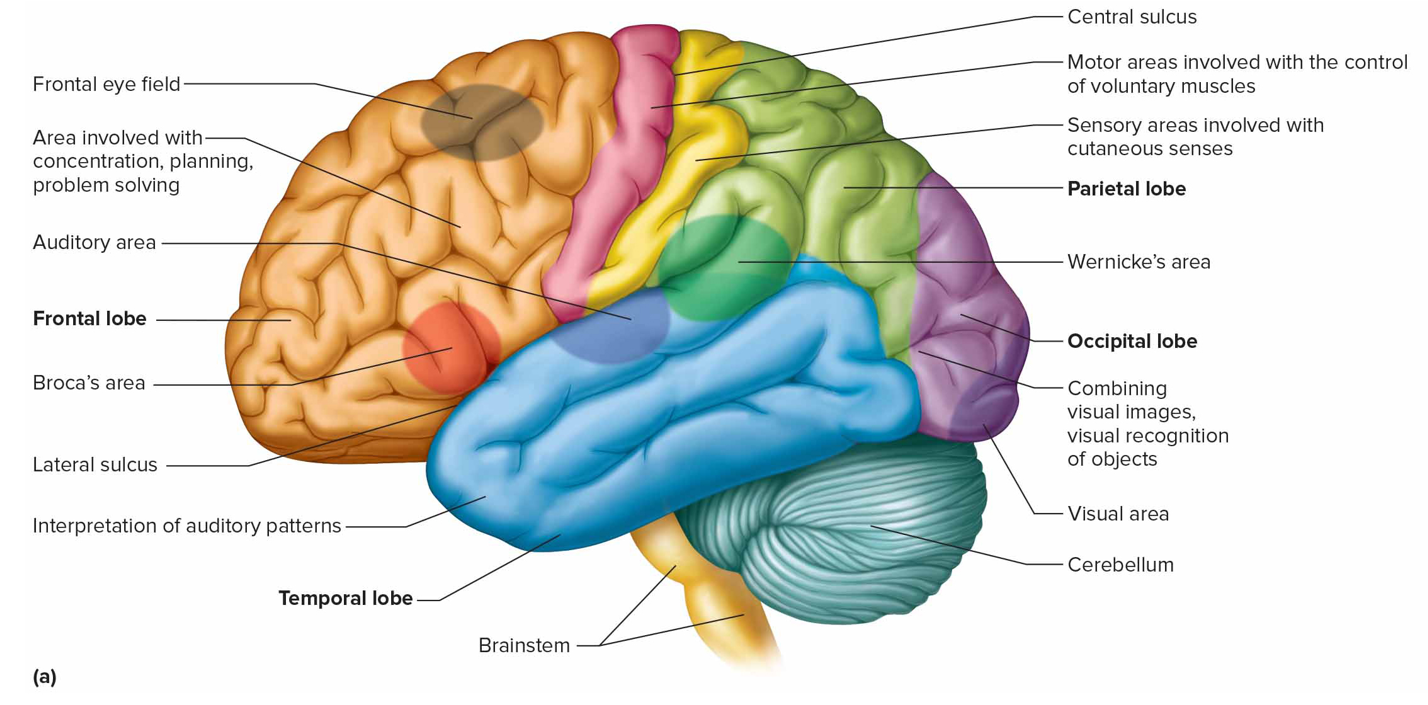
Occipital lobe association areas function
Analyze + combine visual images w/other sensory exps
Insula association area function
Translate sensory info into emotional responses
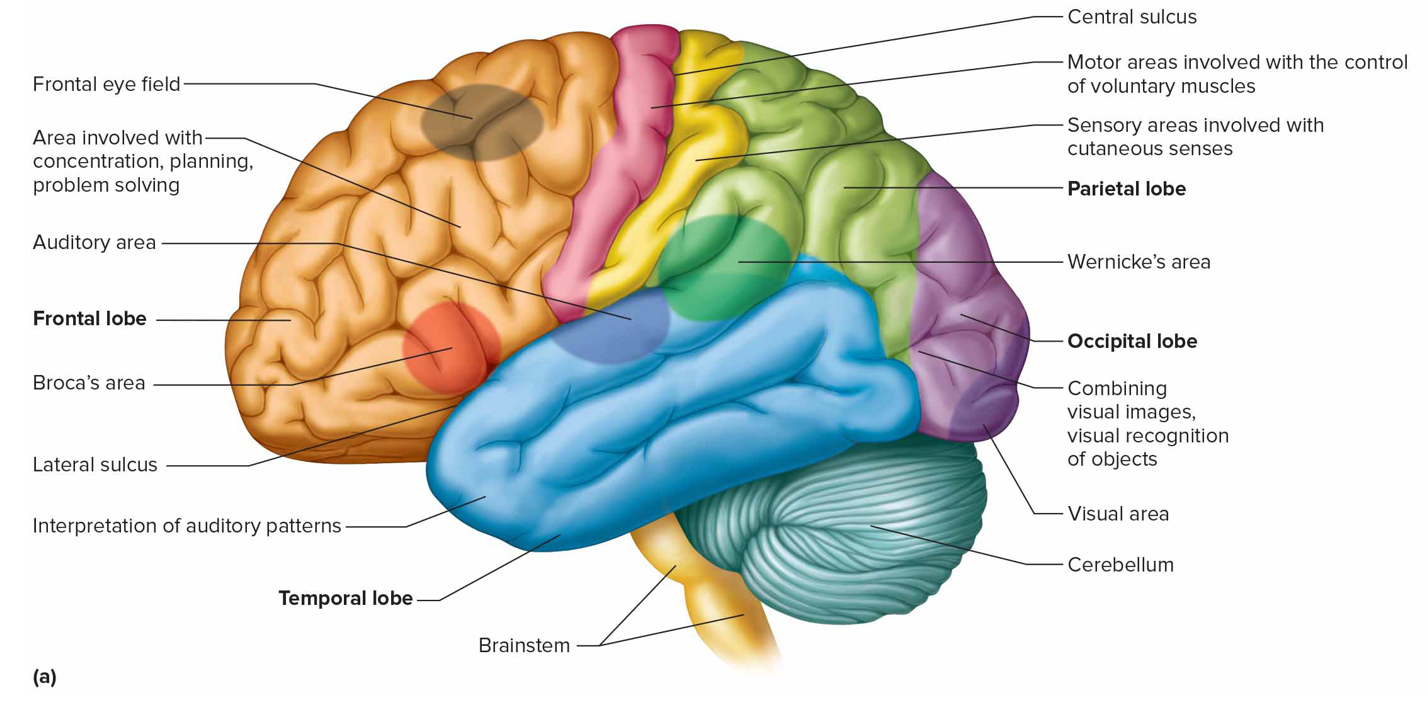
Where are the primary motor areas (motor cortex) + function
Frontal lobes; control voluntary muscles
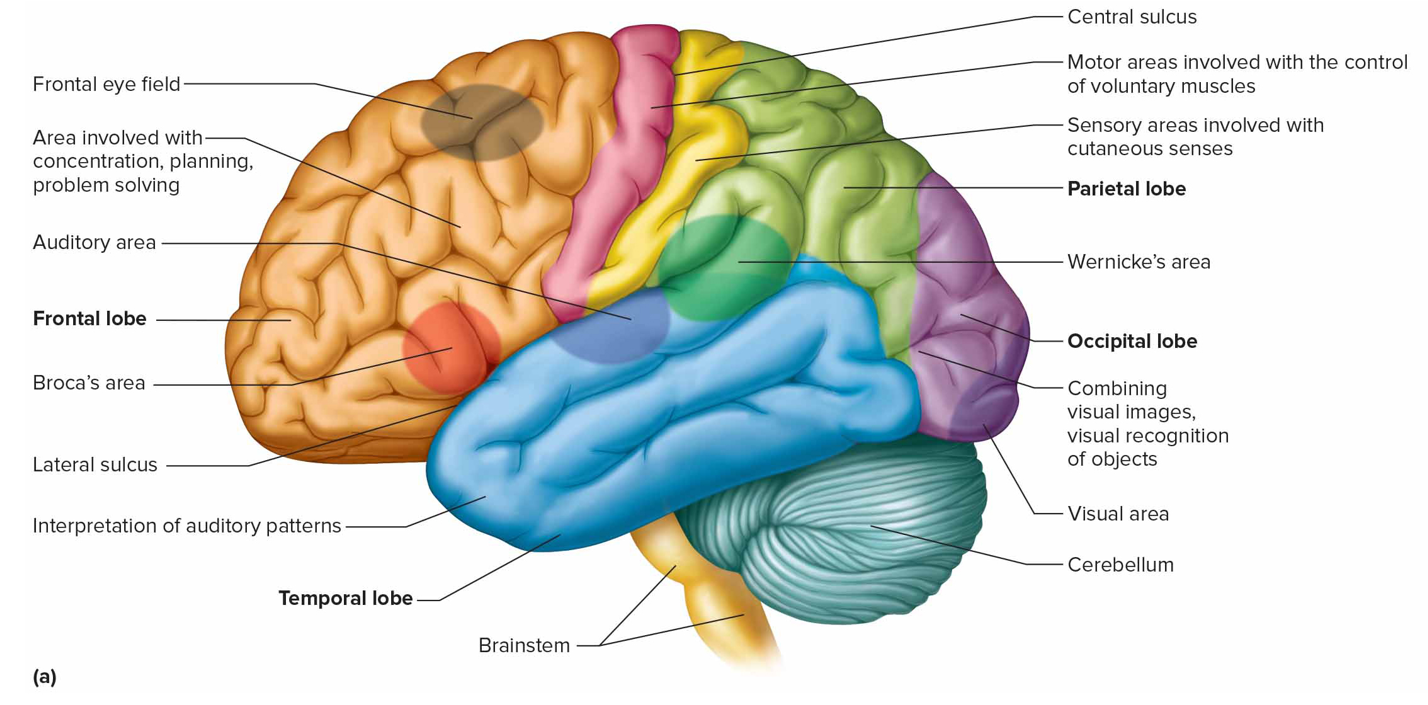
Broca’s area (m)
Anterior to primary motor cortex in left hemisphere that controls speech muscles
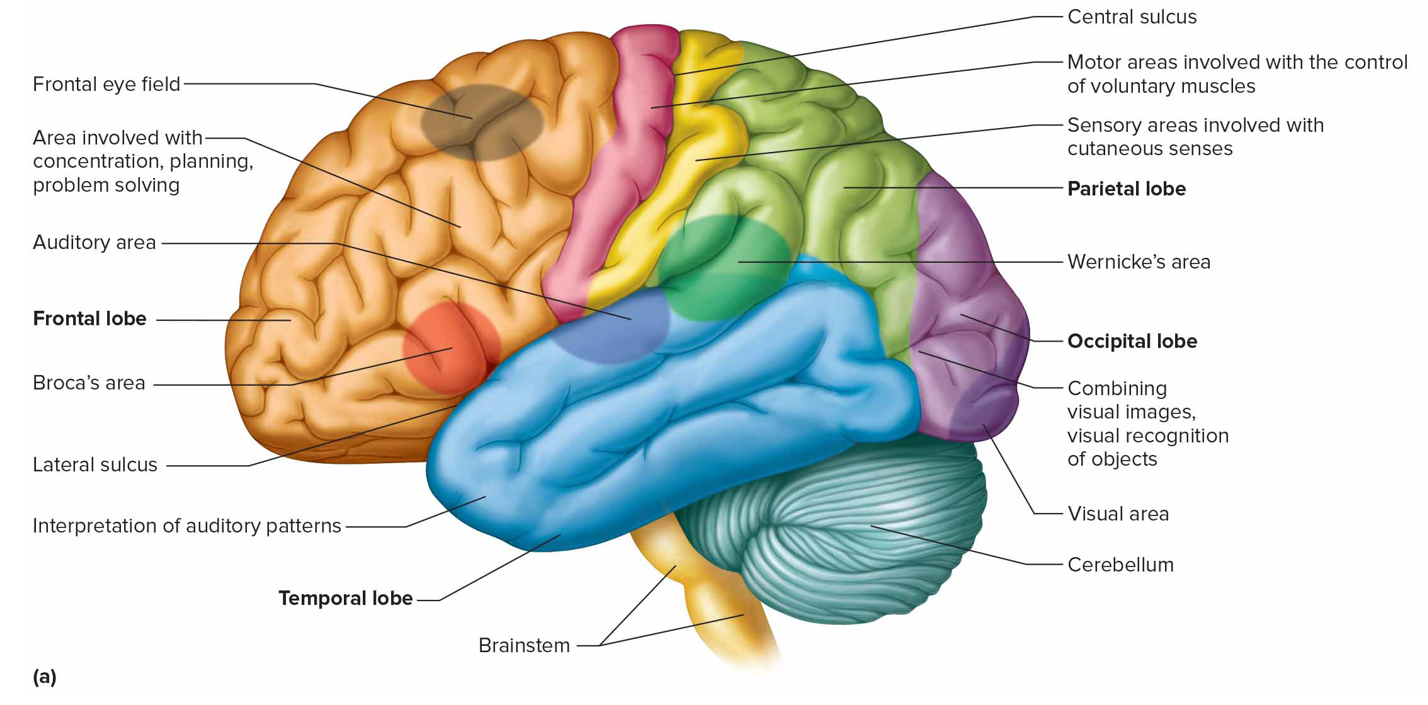
Frontal eye field
Above Broca’s area controlling voluntary movements of eyes + lids
What does the dominant hemisphere control
Speech, writing, reading, verbal, analytical, computational; L hem dom in most ppl
What does the nondominant hemisphere control
Nonverbal tasks, motor tasks involving orientation in space, interpreting musical + visual patterns, emotional + intuitive thought process
How does short-term (working) memory work
Neurons connected in a circuit stimulated repeatedly →
Impulse flow ceases = memory cease unless enters long-term mem via memory consolidation
How does long-term memory work
Changes structure/function of neurons, makes new synaptic connections by inc branching of processes
Long-term potentiation: inc in nt release + effectiveness of synaptic transmission upon repeated stim
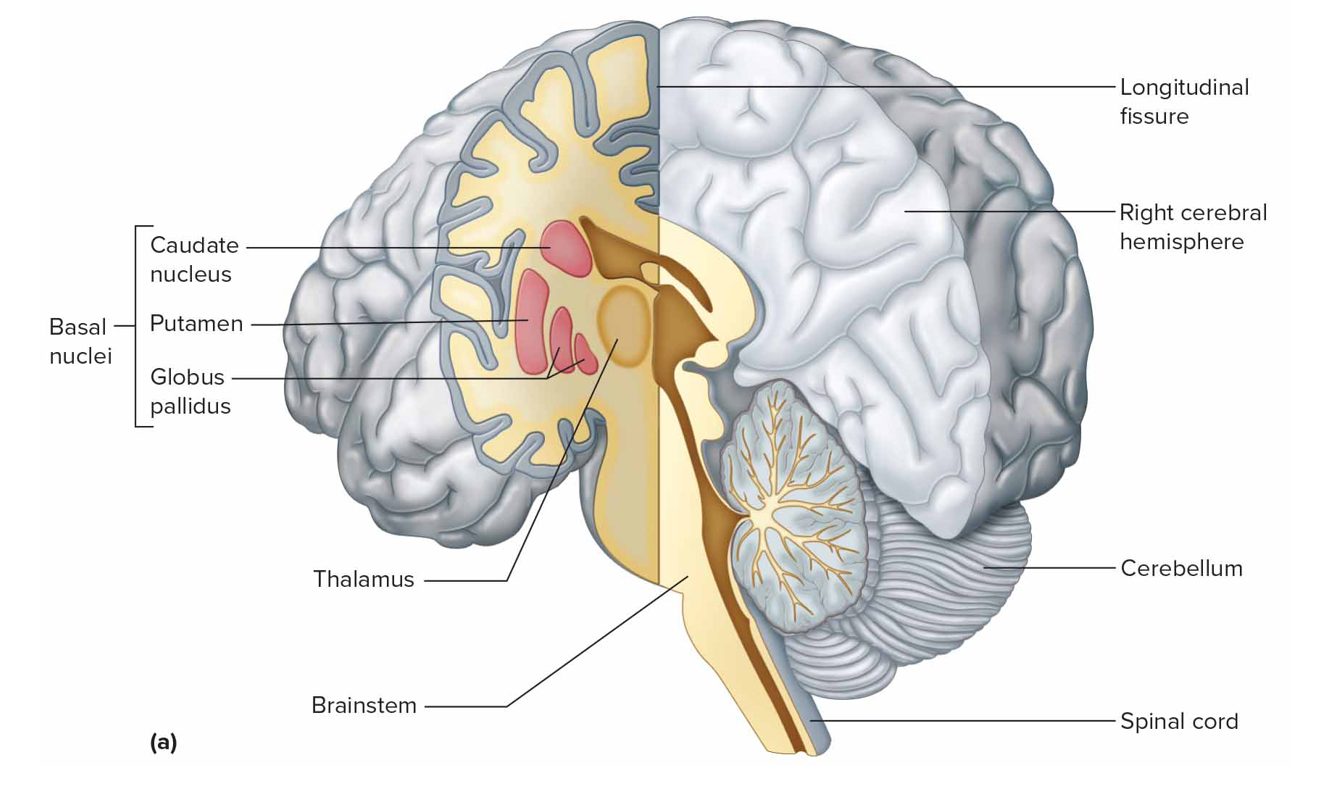
What is the basal nuclei
Masses of gray matter deep within cerebral hems that prod dopamine + help control voluntary movement; caudate nucleus, putamen, globus pallidus
Parkinsons disease (PD)
Neurons degen in substantia nigra (prod dopamine) so less reaches basal nuclei; no treatment
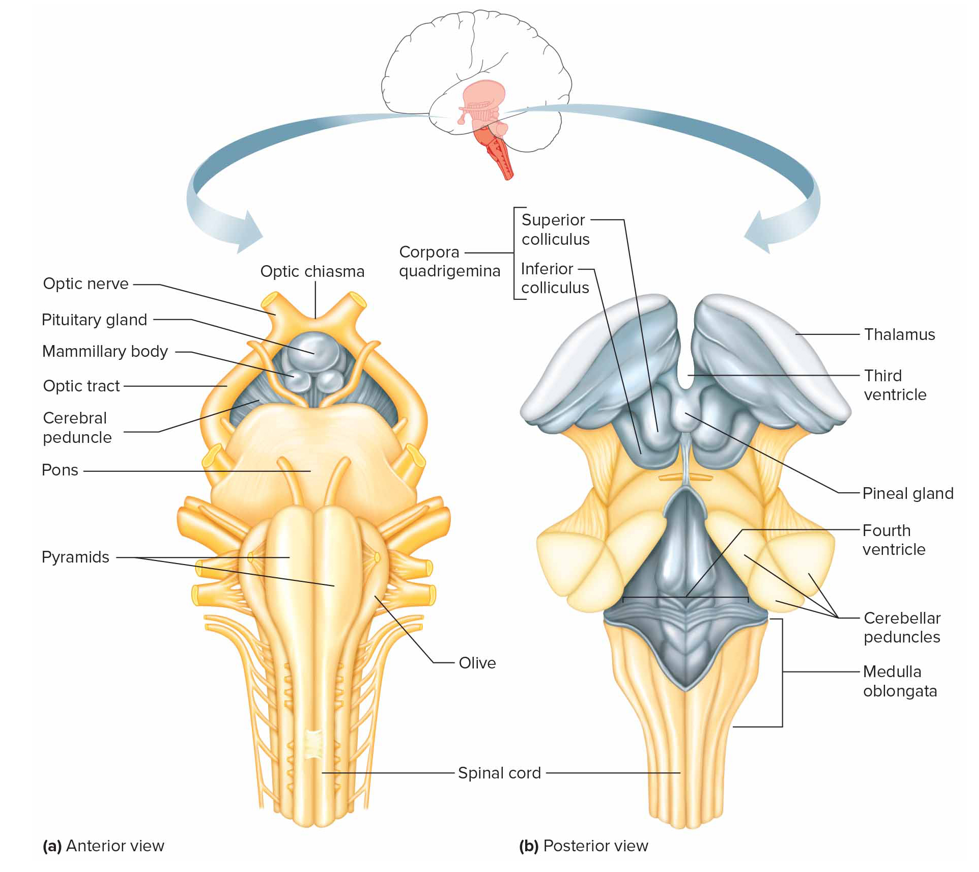
Where is the diencephalon + what is it made of
Btw cerebral hemispheres above brain stem, made of gray matter
thalamus, hypothalamus, optic tracts, optic chiasma, infundibulum, posterior pituitary, mammillary bodies, pineal gland
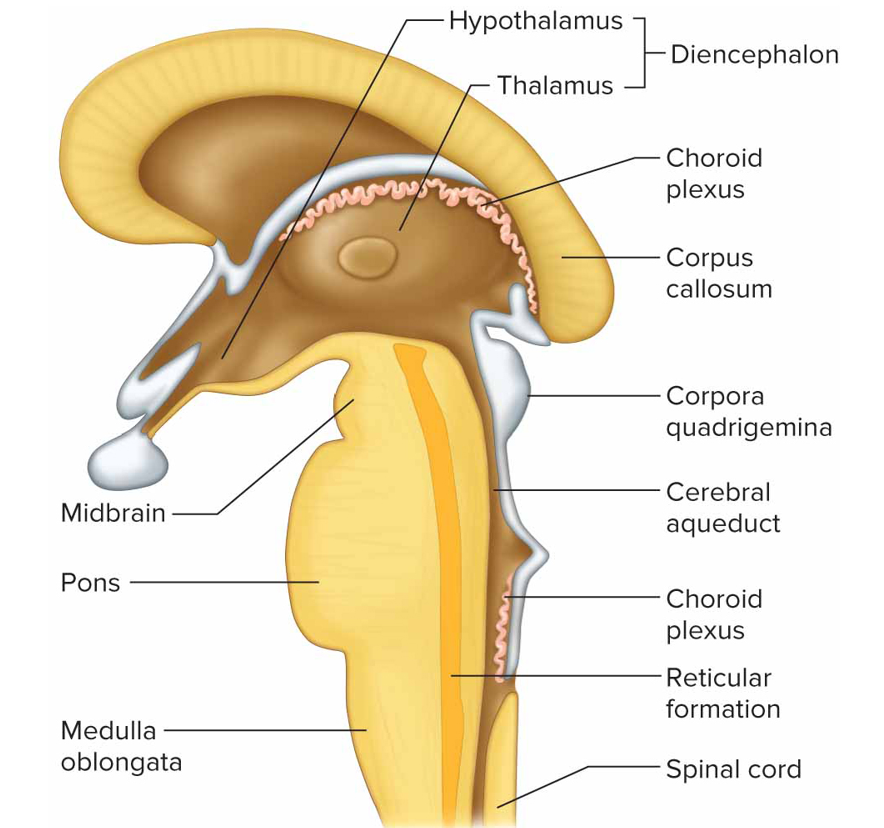
Thalamus function
Receive all sensory impulses (no smell) ascending to cc
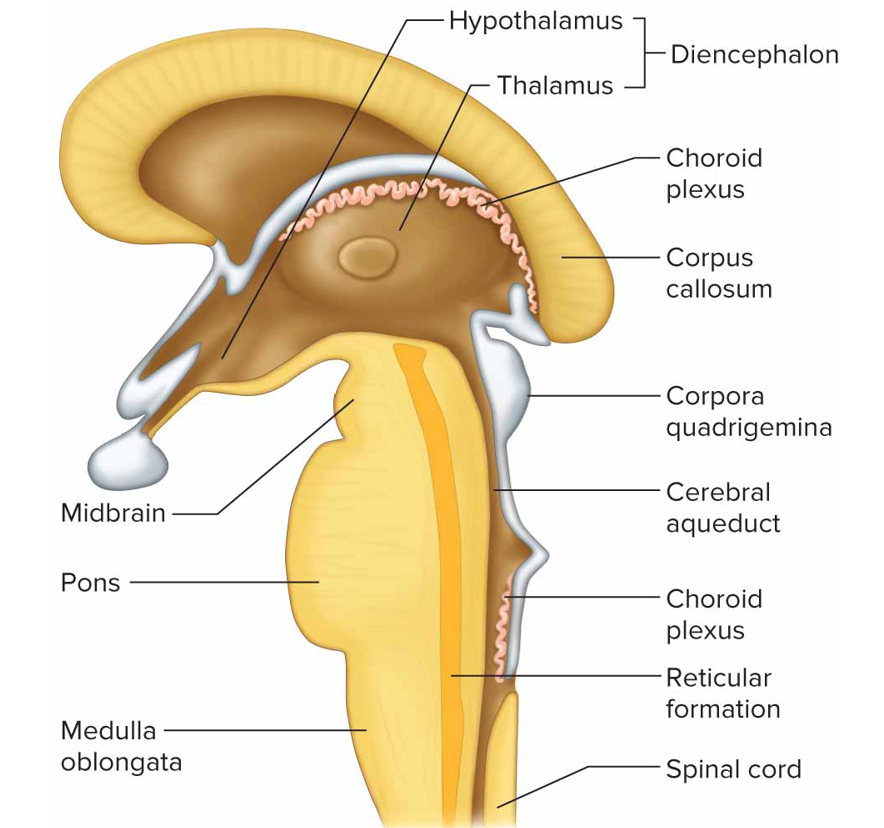
Hypothalamus function
Maintain homeostasis by regulating visceral activities like heart rate, bp, body temp, water + electrolyte bal, hunger, body weight, sleep + wakefulness, pituitary function; links nervous + endocrine sys
Limbic system function
Controls emotional responses, feelings, behavior oriented toward survival
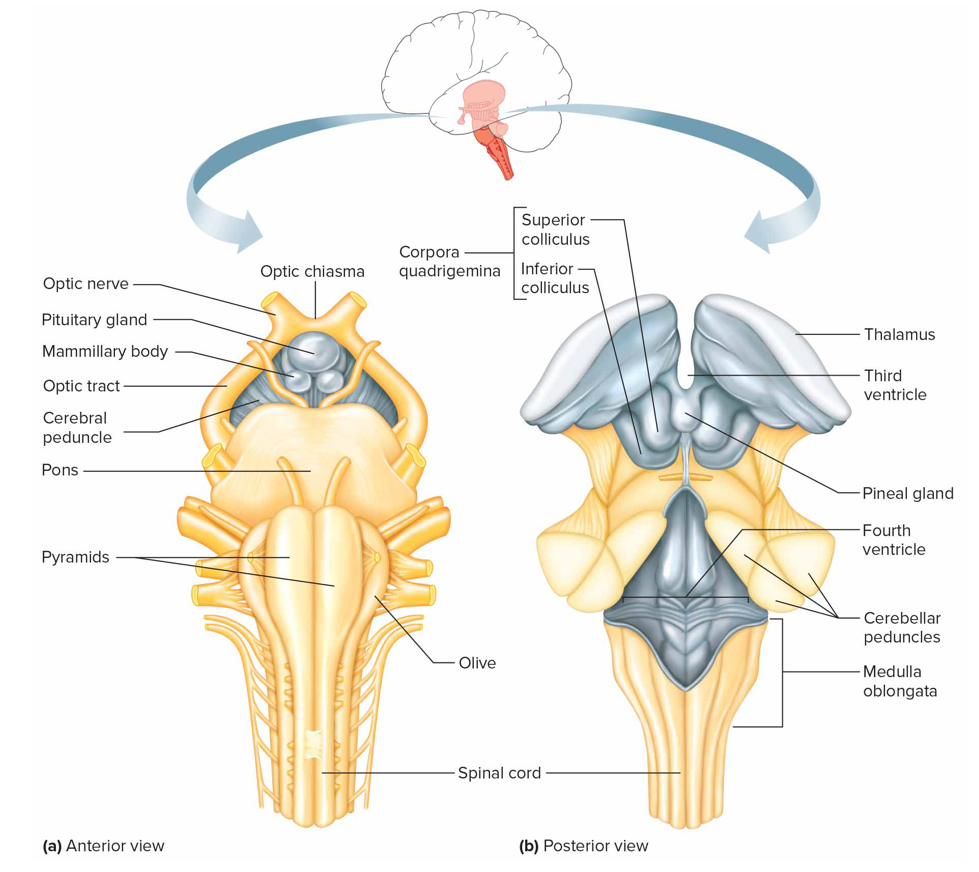
Brainstem function + composed of
Connects brain to spinal cord + contains nerve fiber tracts and gray matter masses; midbrain, pons, medulla oblongata
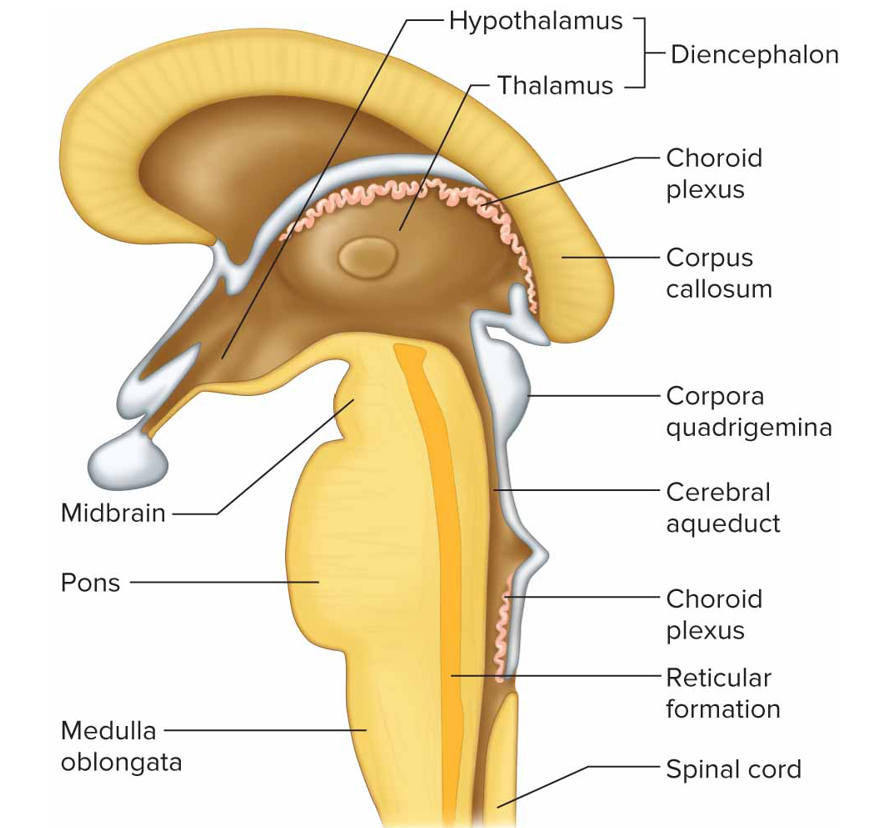
Midbrain
Btw dien + pons containing bundles of fiber that join lwr parts of brainstem + spinal cord w/higher part of brain
Cerebral aqueduct: connects 3 to 4 ventricle
Cerebral peduncle: main motor pathways that connect cerebrum to lwr potions of nervous sys
Corpora quadrigemina: centers for visual + auditory reflexes
Red nucleus: postural reflexes
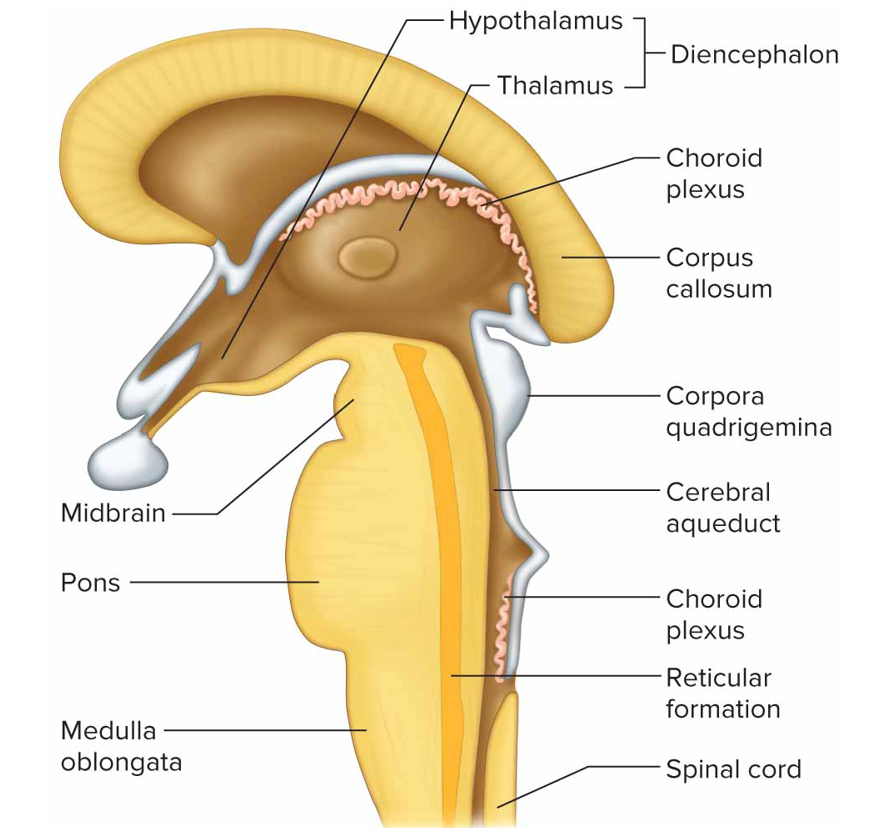
Pons function
Relay nerve impulses btw medulla oblongata & cerebrum + cerebrum to cerebellum; helps reg breathing rthyme
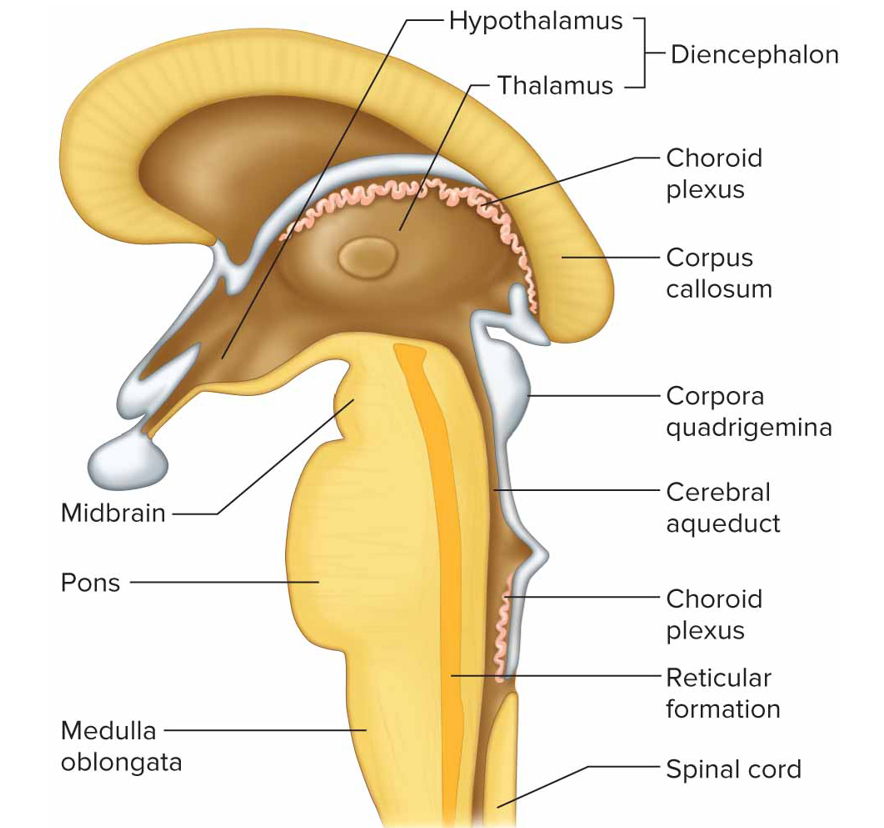
Medulla oblongata functions
Contains cardiac, vasomotor, respiratory control center, nonvital reflex control centers (coughing, sneezing, swallowing, vomiting)
What is reticular formation
Network of nerve fibers scattered throughout brainstem that filters incoming sensory info, passing some to cc + discarding unimp ones; arouses cc into wakefulness + decreased activity causes sleep
Non-rapid eye movement (Non-REM) sleep
Slow wave sleep when person is tired, dec activity of reticular formation, restful+ dreamless, reduced bp + respiratory rate
Rapid eye movement (REM) sleep
Aka parafoxical sleep bc some brain areas r active; heart + resp rates irregular + dreams
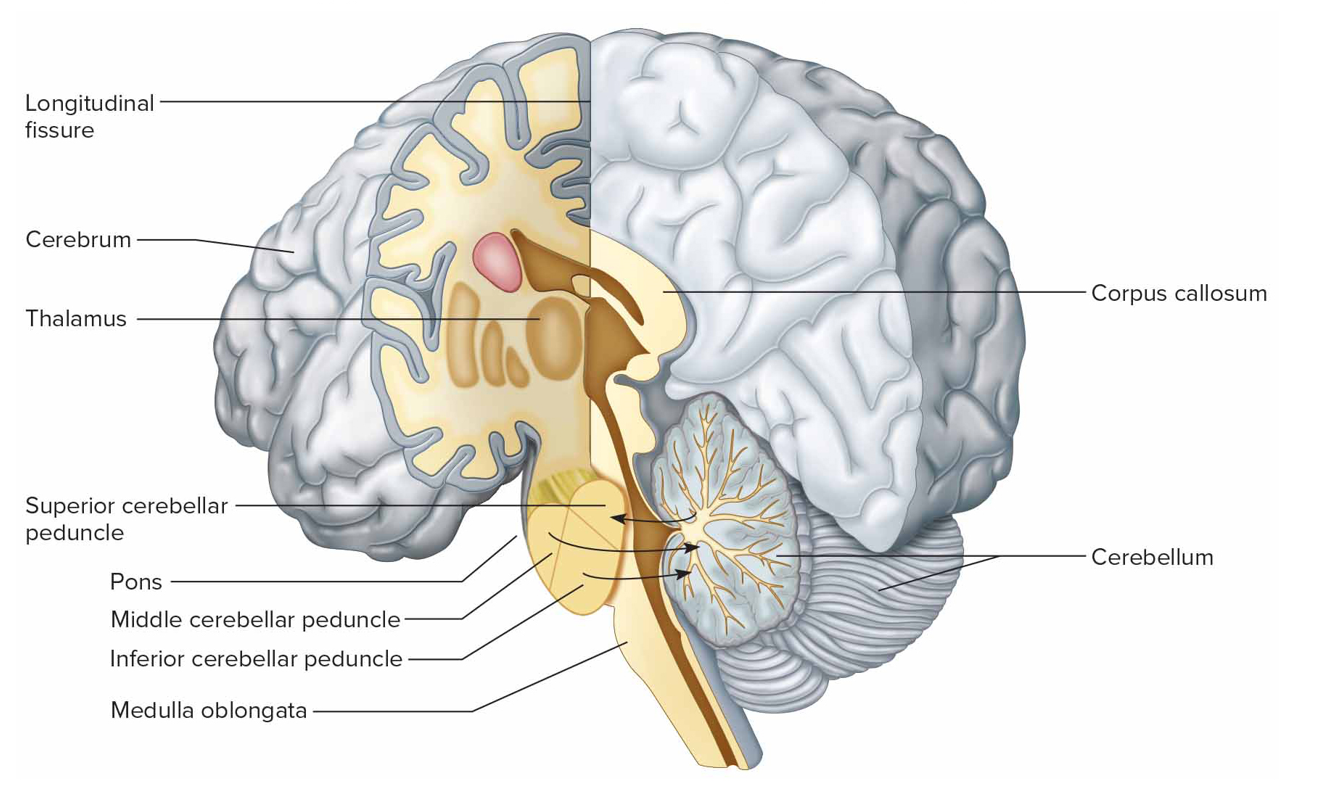
Cerebellum functions
Integrates sensory info concerning positions of body parts, coordinates skeletal muscle, maintains posture
Two hemis separated by falx cerebelli
Vermis connects hemispheres
Cerebellar cortex (gray matter)
Arbor vitae (white matter)
Cerebellar peduncles
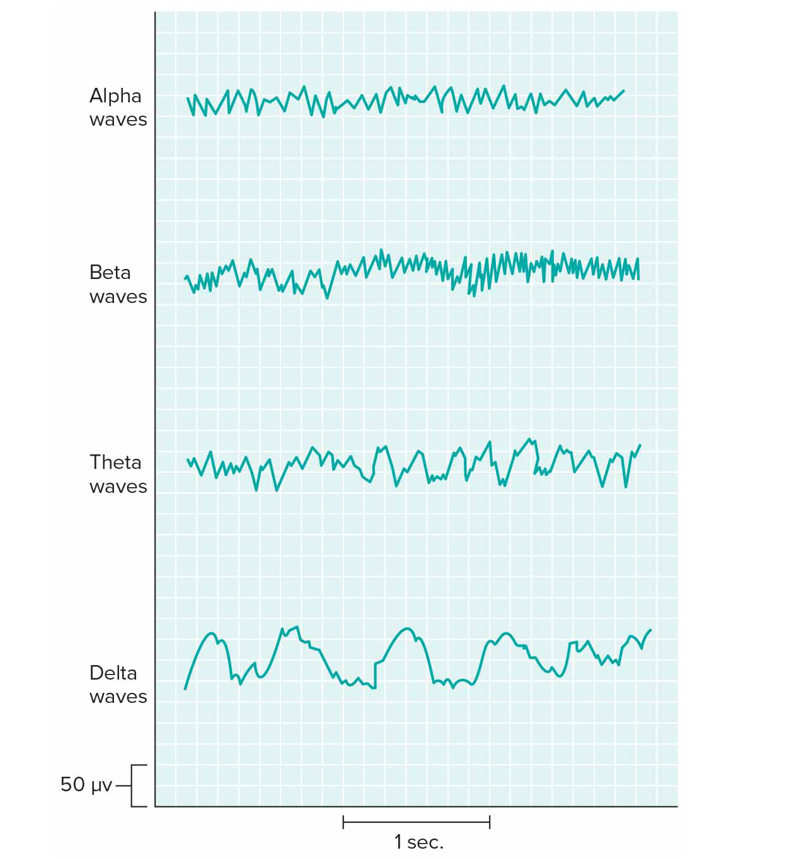
What are brain waves
Recordings of fluctuating electrical changes in brain recorded from EEG via electrodes on scalp that detect electrical changes in extracellular fluid of brain
Alpha: awake, resting eyes closed
Beta: active mental activity, under tension
Theta: mostly in children, some in adults during sleep/stress
Delta: during sleep
Spinal cord
Consists of 31 segments that each give rise to a pair of spinal nerves; grouped according to lvl of vertebra they associated w; nerve pairs numbered from superior to inferior within groups
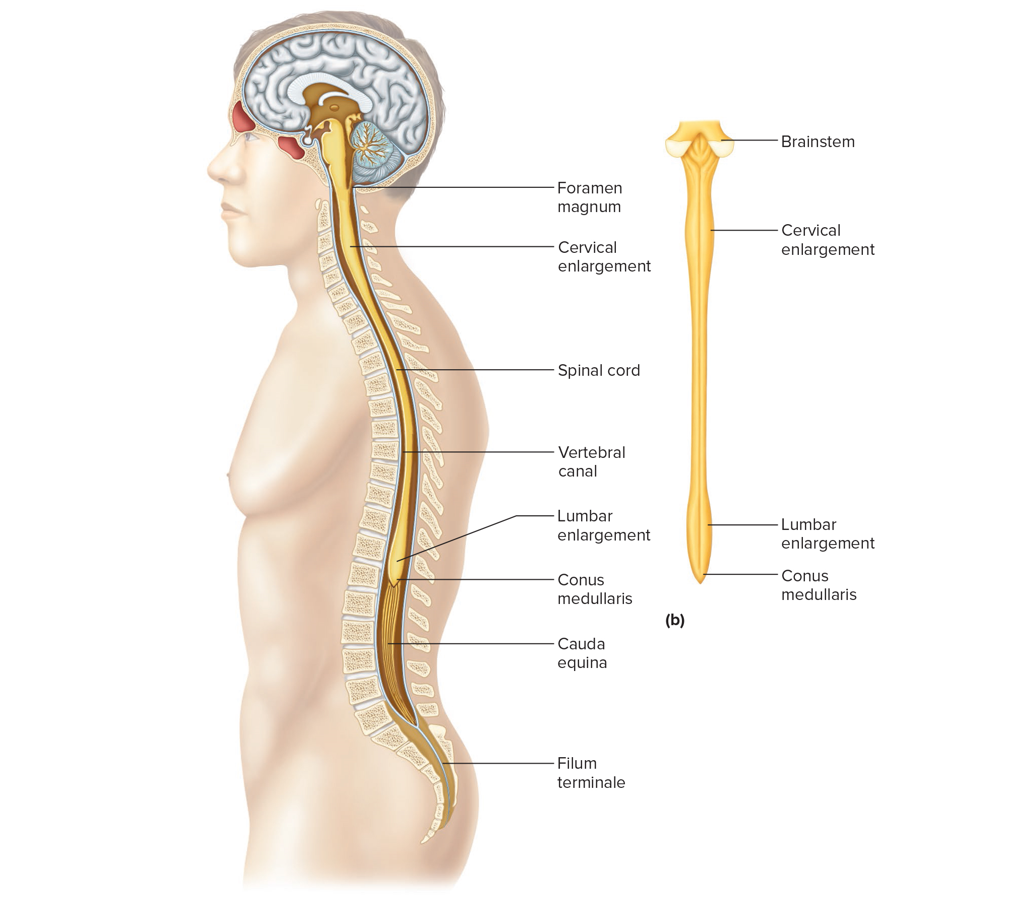
Longitudinal section of the sc
Cervical enlargement: supplies nerves to upper limbs
Lumbar enlargement: supplies nerves to lwr limbs
Conus medullaris: tapering region below lumbar enlargement
Filum teminale: cord of ct that anchors sc to coccyx
Cauda equina: group of lumbar + sacral nerves extending down from conus med in vertebal canal
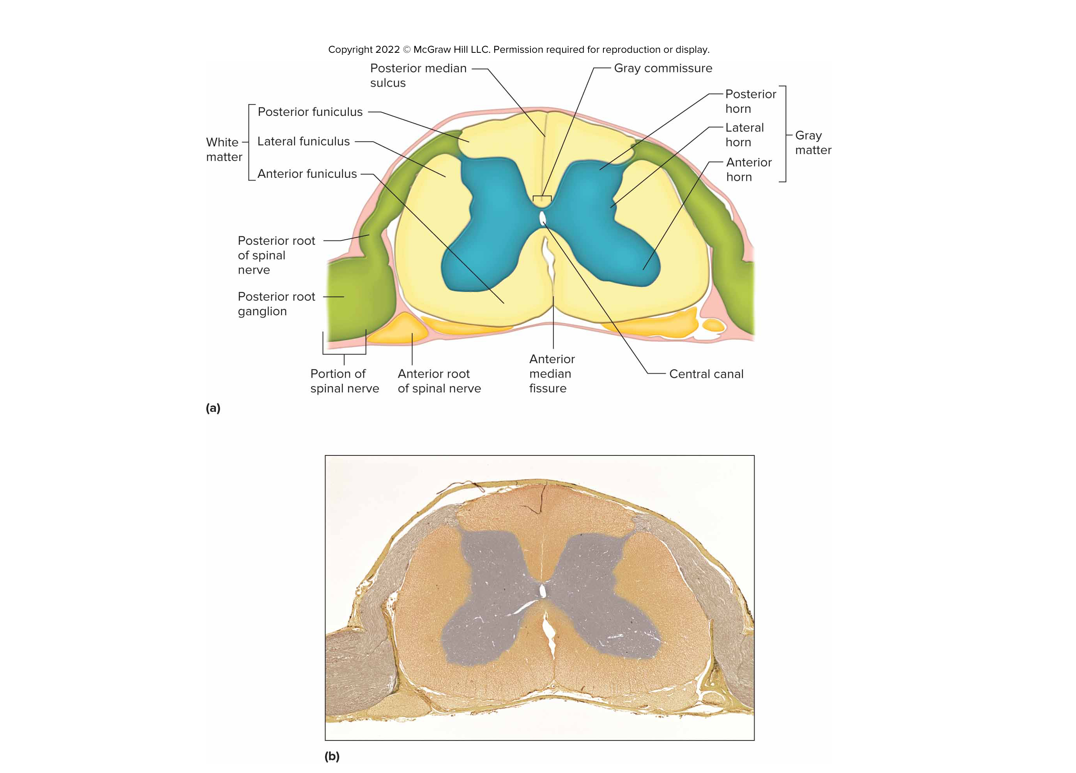
Cross section of the sc
Anterior median fissure + posterior median sulcus: grooves that extend whole length of sc
White matter surrounds core of gray matter
Gray commissure surrounds central canal
Gm arranged in horns, wm in funiculi
Posterior roots contain sensory neurons, cell bodies outside sc in posterior root ganglia
Anterior roots contain motor neurons
Sc functions
Center for spinal reflexes, pathway for impulses to + from brain
What is a reflex
Automatic subconscious response to a stimulus within/outside body; maintain homeo by controlling invol processes
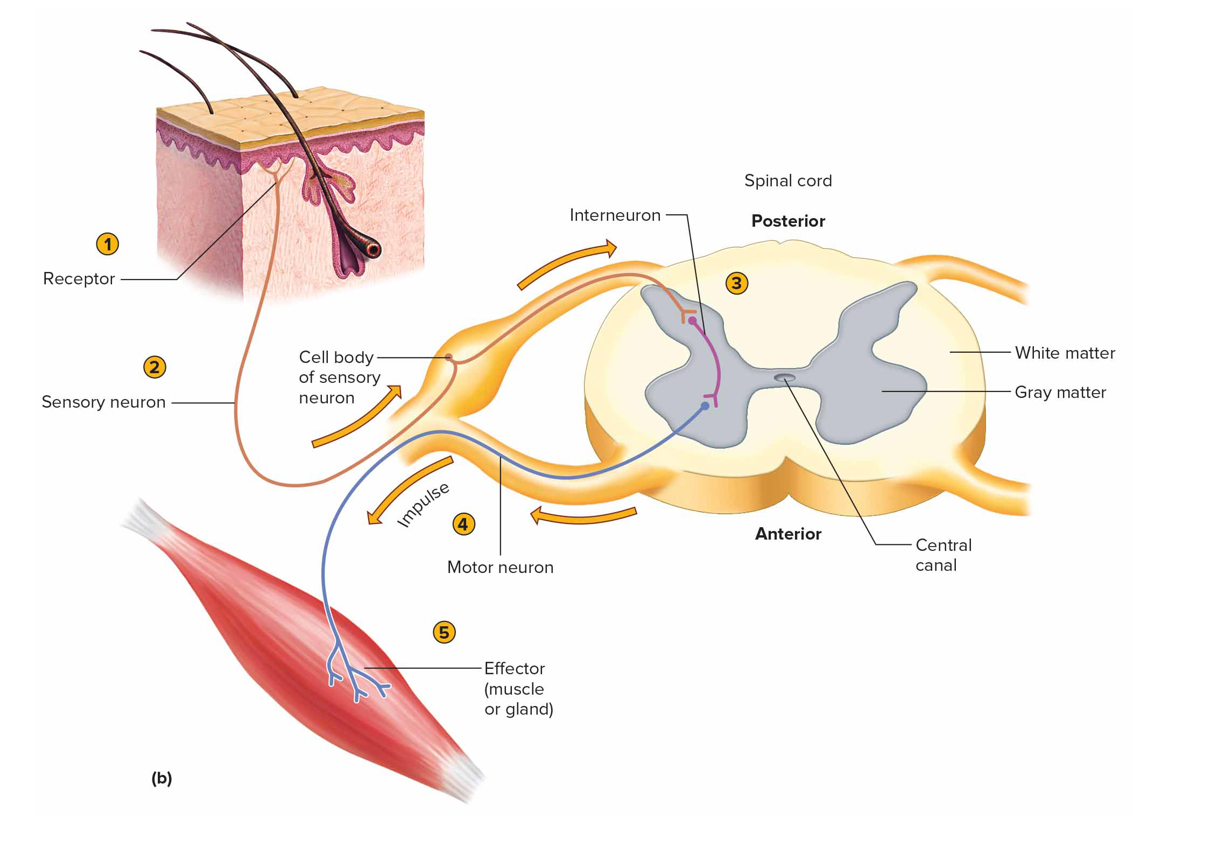
What is a reflex arc
Neural pathway made of a sensory receptor, ≥2 neurons, effector (simple ra only sensory + motor neurons)
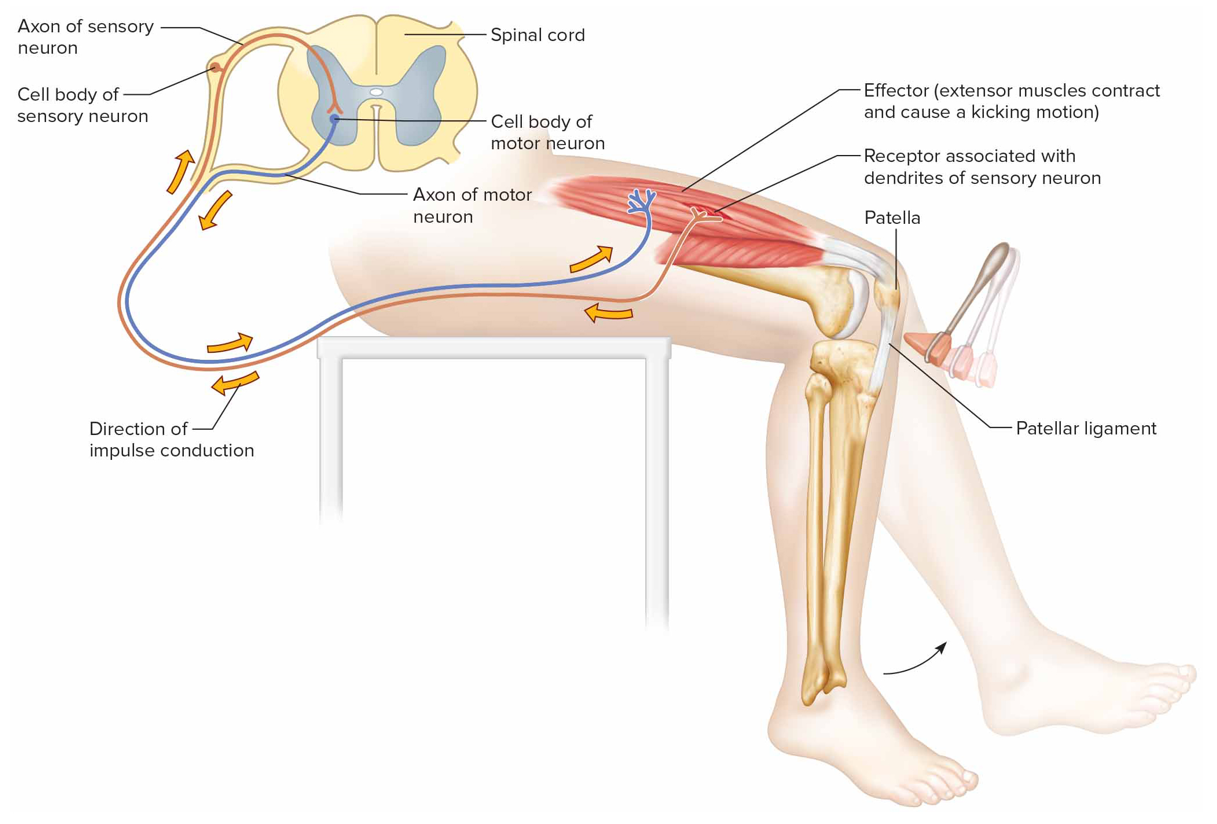
Monosynaptic (stretch) reflex
2 neurons (sensory + motor), 1 sc synapse, helps maintain upright posture; ie knee jerk reflex
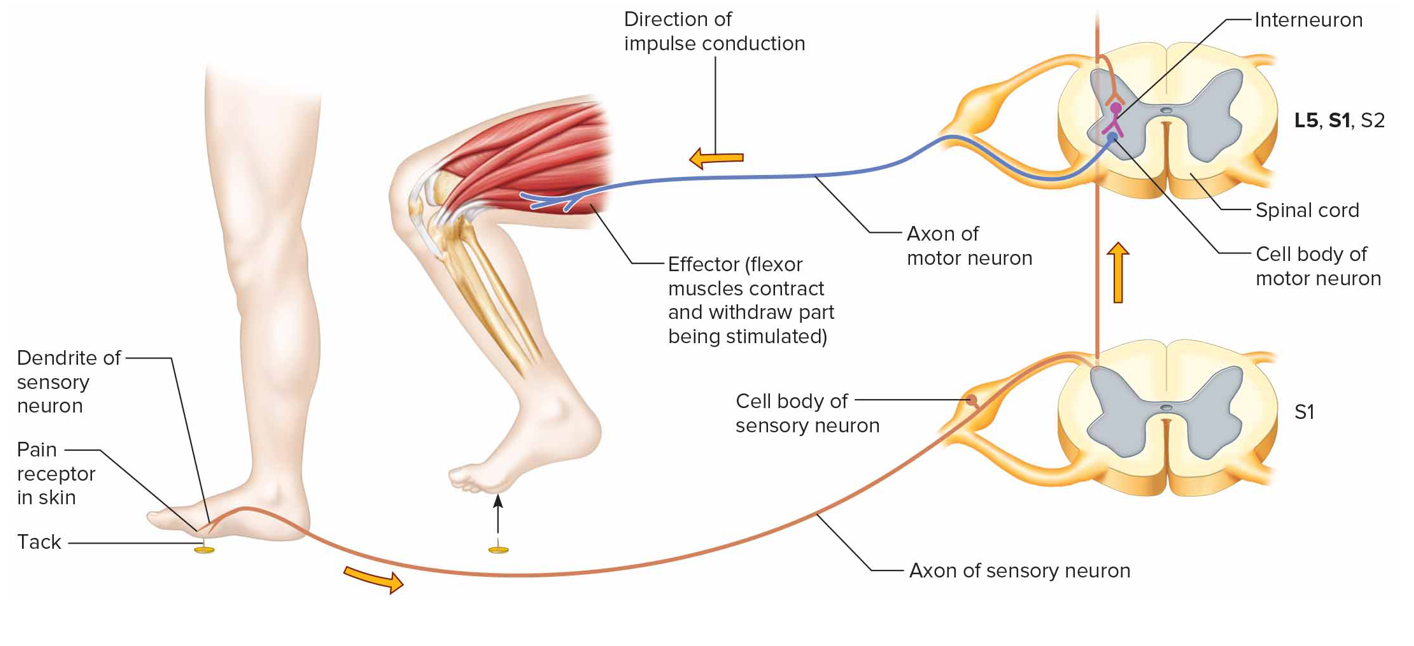
Withdrawal reflex
Polysnaptic (sensory, interneuron, motor), reciprocal innervation: flexors contract, extensors inhibited; when person touch smth painful
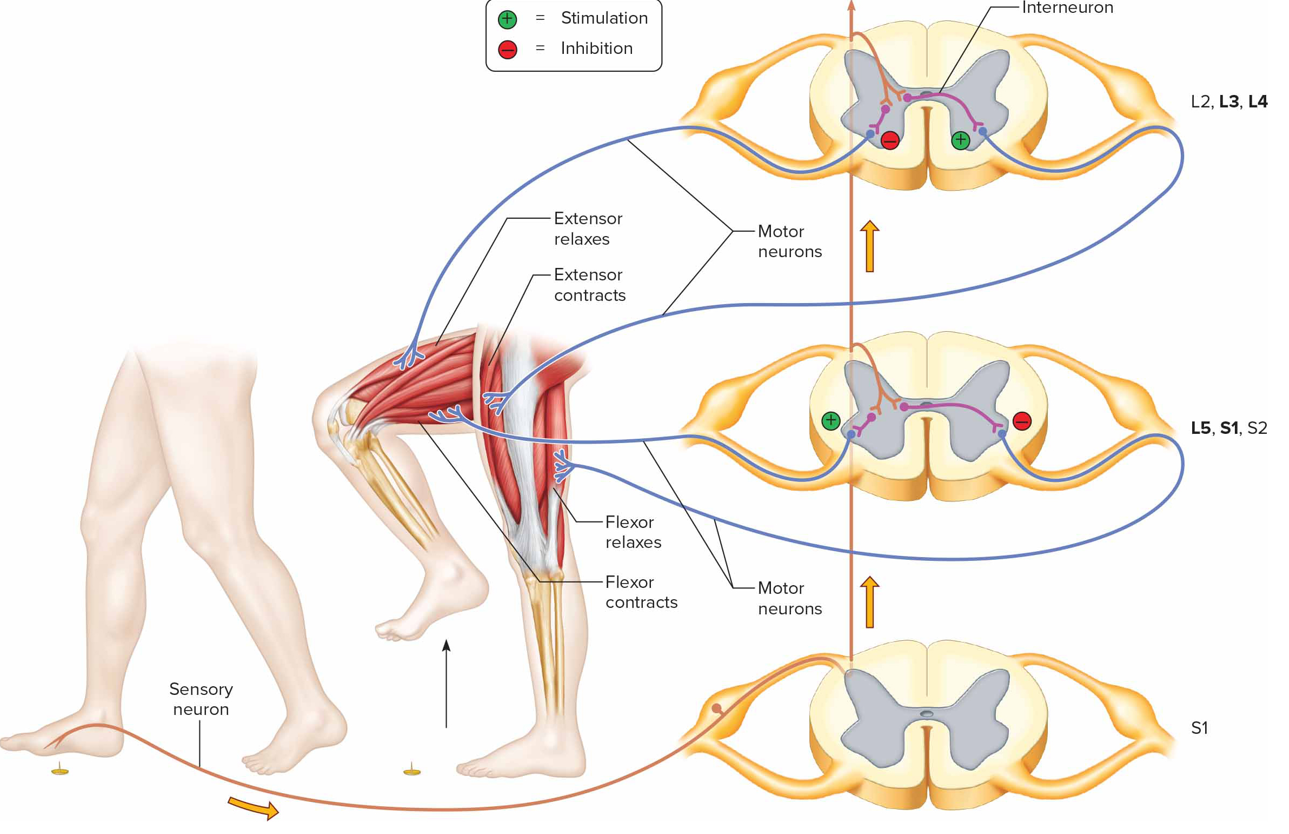
Cross extensor reflex
During withdrawal reflex, flexors on affected (ipsilateral) side contract + extensors inhibited; entensors on contralateral side contract, flexors inhibited
Reflexes usage
Used to assess nervous system condition: extent of ns damage, effectiveness of anesthetics
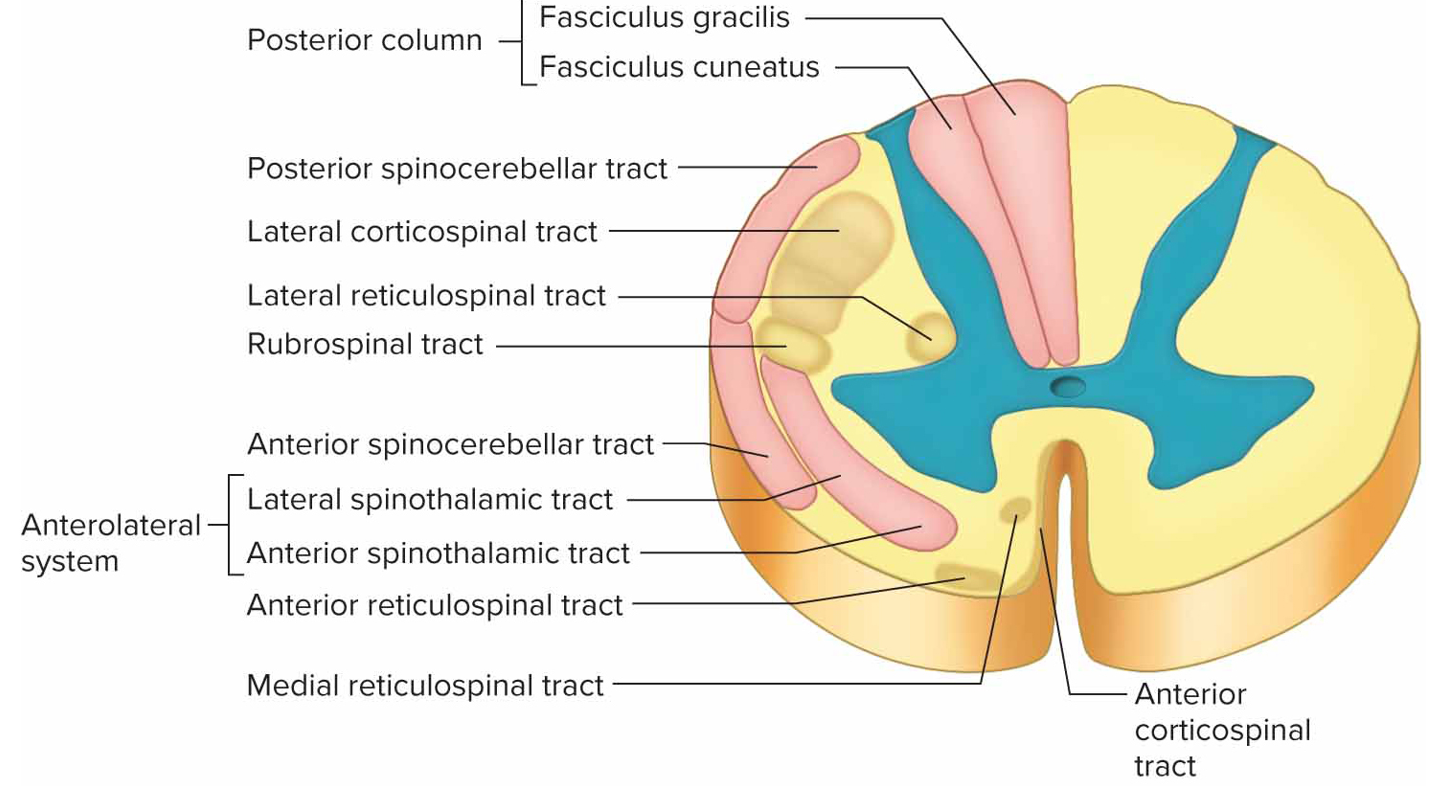
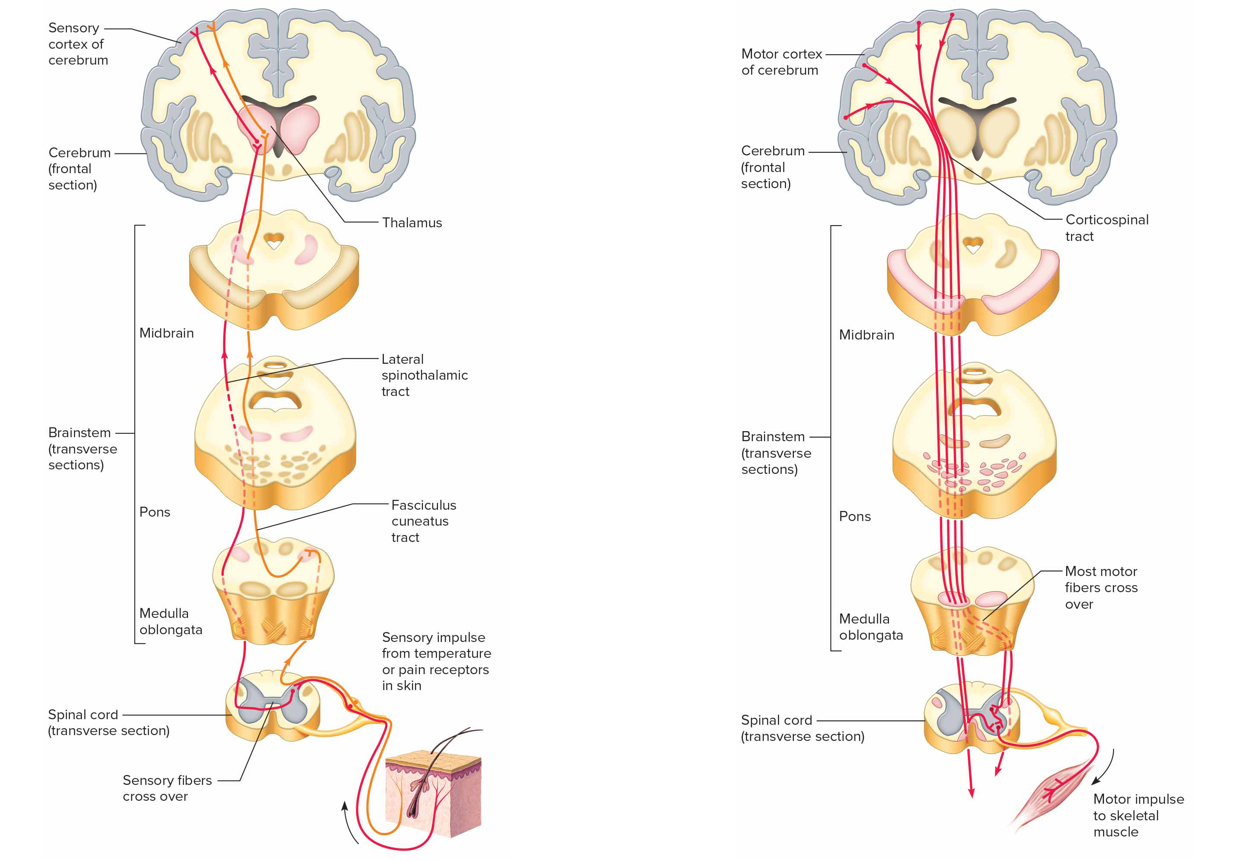
Ascending tracts
Conduct sensory impulses to brain (pink): fasciculus gracilis + cuneatus, spinothalamic tracts, spinocerebellar tracts
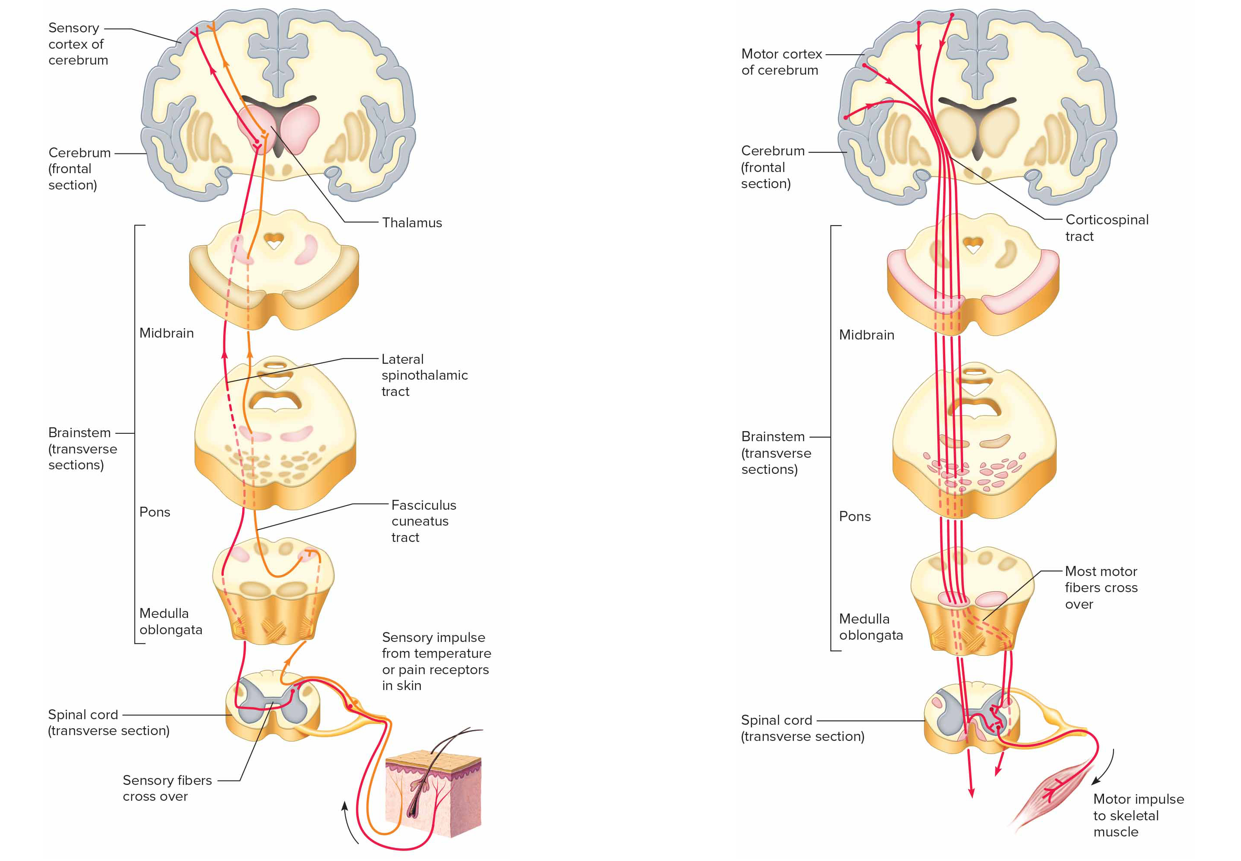
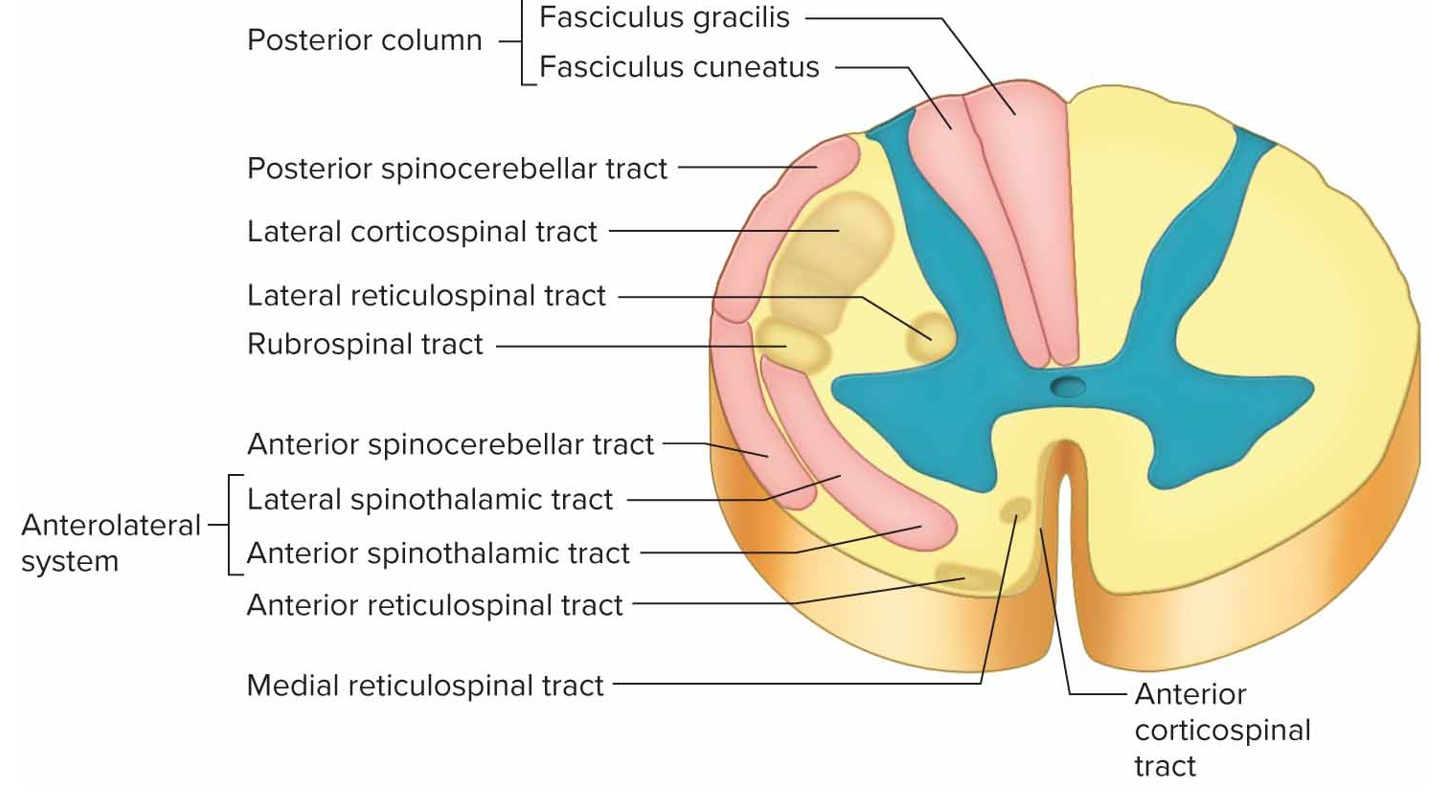
Descending tracts
Conduct motor impulses from brain to effectors via motor neurons (light brown): corticospinal tracts, reticulospinal tracts, rubrospinal tract
Amyotropic lateral sclerosis (ALS)/Lou Gehrig’s Disease
Degen of motor neurons in sc, braintem, cc from overactive microglia that kills neurons or buildup of oxygen-free radicals that neurons/astrocytes cannot counter; no cure
Sc injuries
Compression/distortion of sc → damage/death of neurons
injury to ascending tracts → sensation loss
injury to descending tracts → motor function loss, paralysis
Somatic nervous system
Cranial + spinal nerves that connect CNS to skin + skeletal muscles (conscious activities)
Autonomic nervous system
Cranial + spinal nerves that connect CNS to viscera (subconscious activities)
What are nerves and nerve fibers
Nerves = bundles of axons; nerve fibers = axons
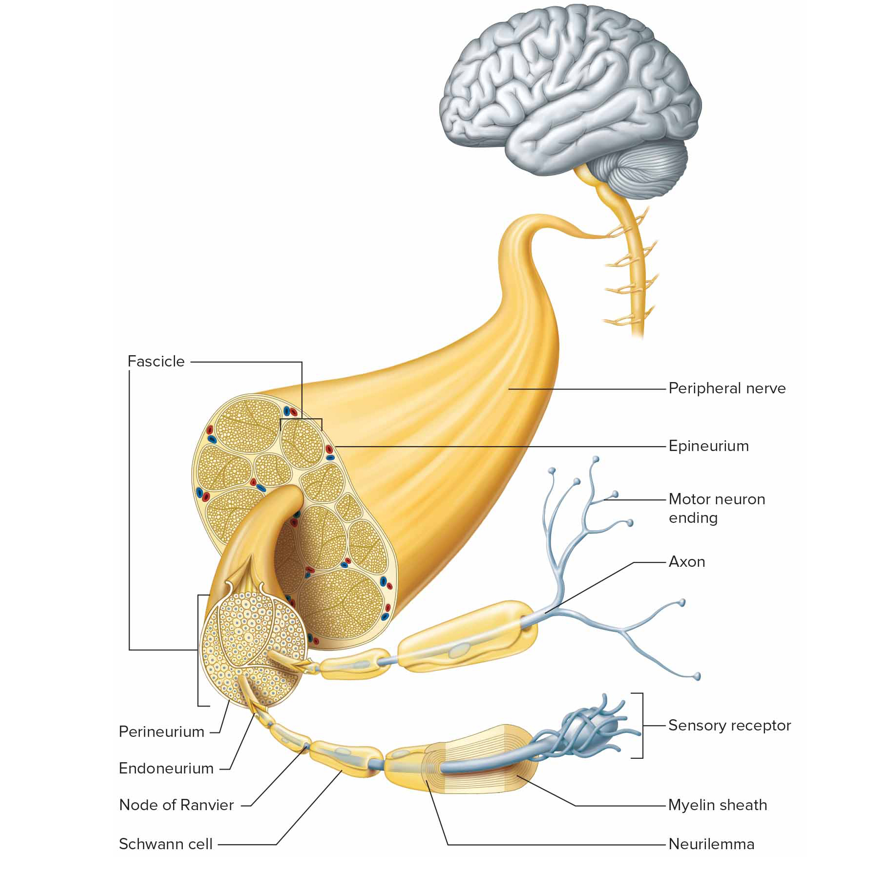
Types of connective tissue coverings for nerves
Endoneurium: loose ct that surrounds individual axons
Perineurium: lct that surrounds fascicles
Epineurium: dct that surrounds a group of fascicles
Mixed nerves
contain both sensory + motor nerve fibers; most nerves + all spinal nerves are mixed (except first pair)
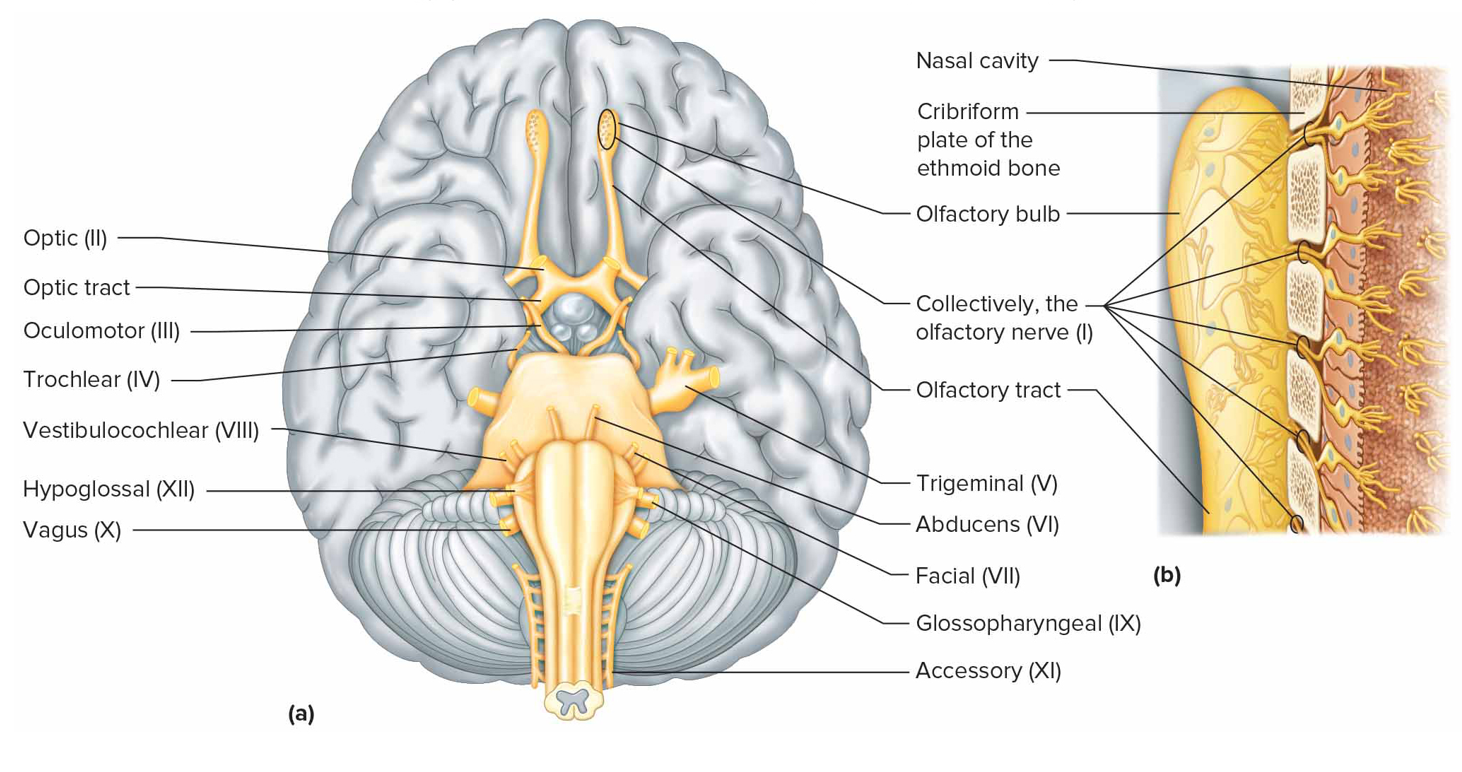
Cranial nerves
12 pairs on underside of brain
First pair has fibers starting in nasal cavity
Second pair originates in eyes, fibers synapse in thalamus
Cranial nerve I
Olfactory nerve (s): bipolar neurons, olfactory receptor cells pass through cribriform plate + enter olfactory bulbs
Cranial nerve II
Optic nerve (s): neuron cell bodies form ganglion layers of retina + pass through optic foramina of orbits
Cranial nerve III
Oculomotor nerve (mostly m, proprioceptive fibers are s): raises eyelids; motor impulses to involuntary muscles that focus lens, adjust light entering eye (aNS)
Cranial nerve IV
Trochlear nerve (mostly m, proprioceptive fibers are s): smallest pair that motor impulses to one pair of muscles that move the eye
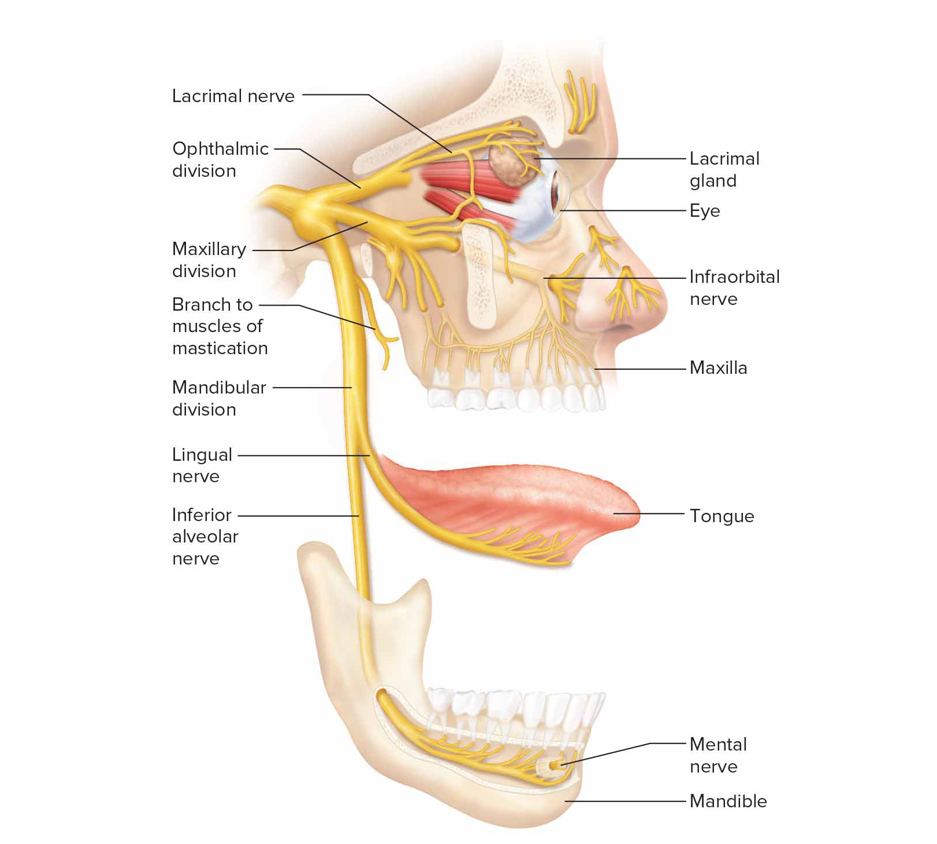
Cranial nerve V
Trigeminal nerve (mx): largest pair that has 3 large sensory branches + motor impulses to mastication muscle
Ophthalmic: sensory from surface of eyes, tear glands, scalp, forehead, upper eyelids
Maxillary: upper teeth + gum + lip, palate, face skin
Mandibular: scalp, jaw skin, lwr teeth + gum + lip
Cranial nerve VI
Abducens nerve (mostly m, proprioceptive fibers are s): motor impulses to one pair of muscles that move the eye
Cranial nerve VII
Facial nerve (mx): sensory from taste receptors + motor impulses to muscles of facial expression, tear + salivary glands
Cranial nerve VIII
Vestibulocochlear aka acoustic/auditory (s)
Vestibular branch: sensory from equilibrium receptors of ear
Cochlear branch: sensory from hearing receptors
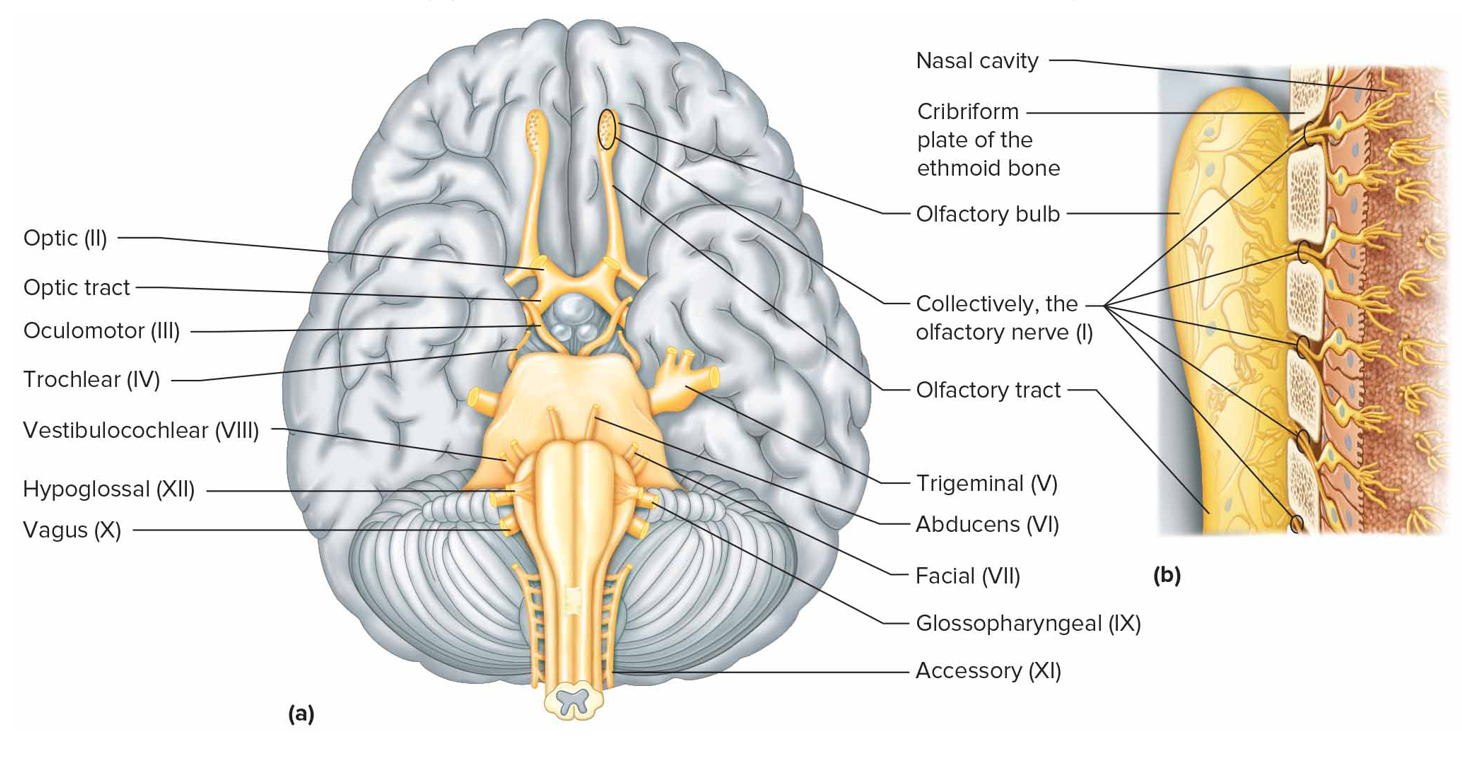
Cranial nerve IX
Glossopharyngeal (mx)
Sensory from pharynx, tonsils, part of tongue
Motor impulses to salivary glands + pharynx muscles
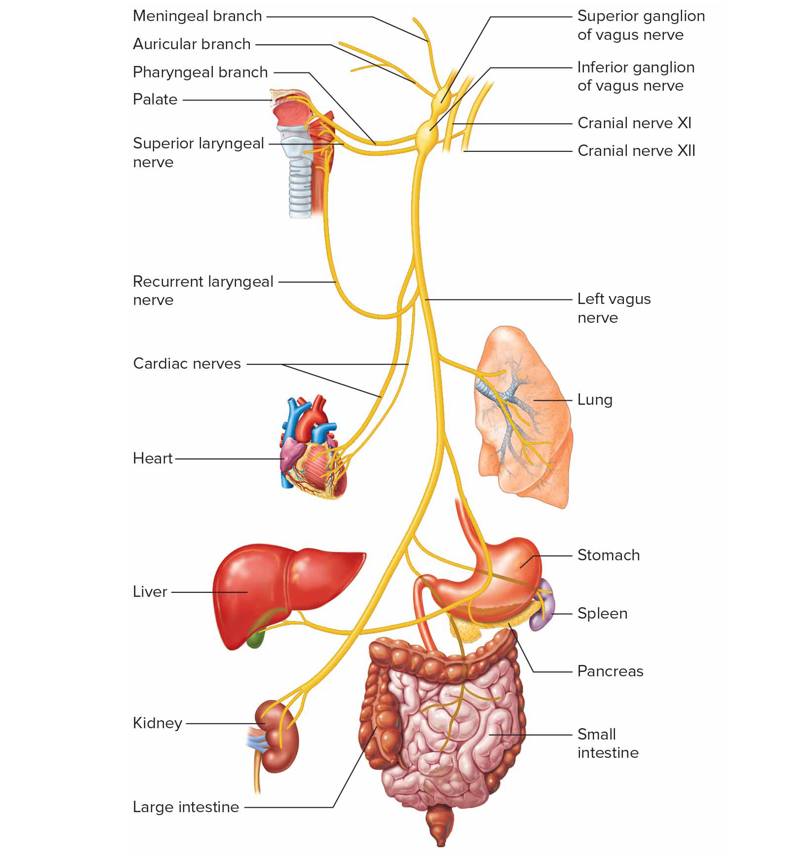
Cranial nerve X
Vagus (mx)
Somatic motor impulses to pharynx muscle + larynx for speech + swallowing
Autonomic motor impulses to heart + other viscera of thorax + abdomen
Sensory from pharynx, larynx, esophagus, thorax + abdomen viscera
Cranial nerve XI
Accessory (mostly m, proprioceptive fibers are s)
Cranial branch: joins vagus n; motor impulses to soft palate, pharynx, laynx muscles
Spinal branch: motor to muscles of neck + back
Cranial nerve XII
Hypoglossal (mostly m, proprioceptive fibers are s): motor impulses to muscles of the tongue for speaking, chewing, swallowing
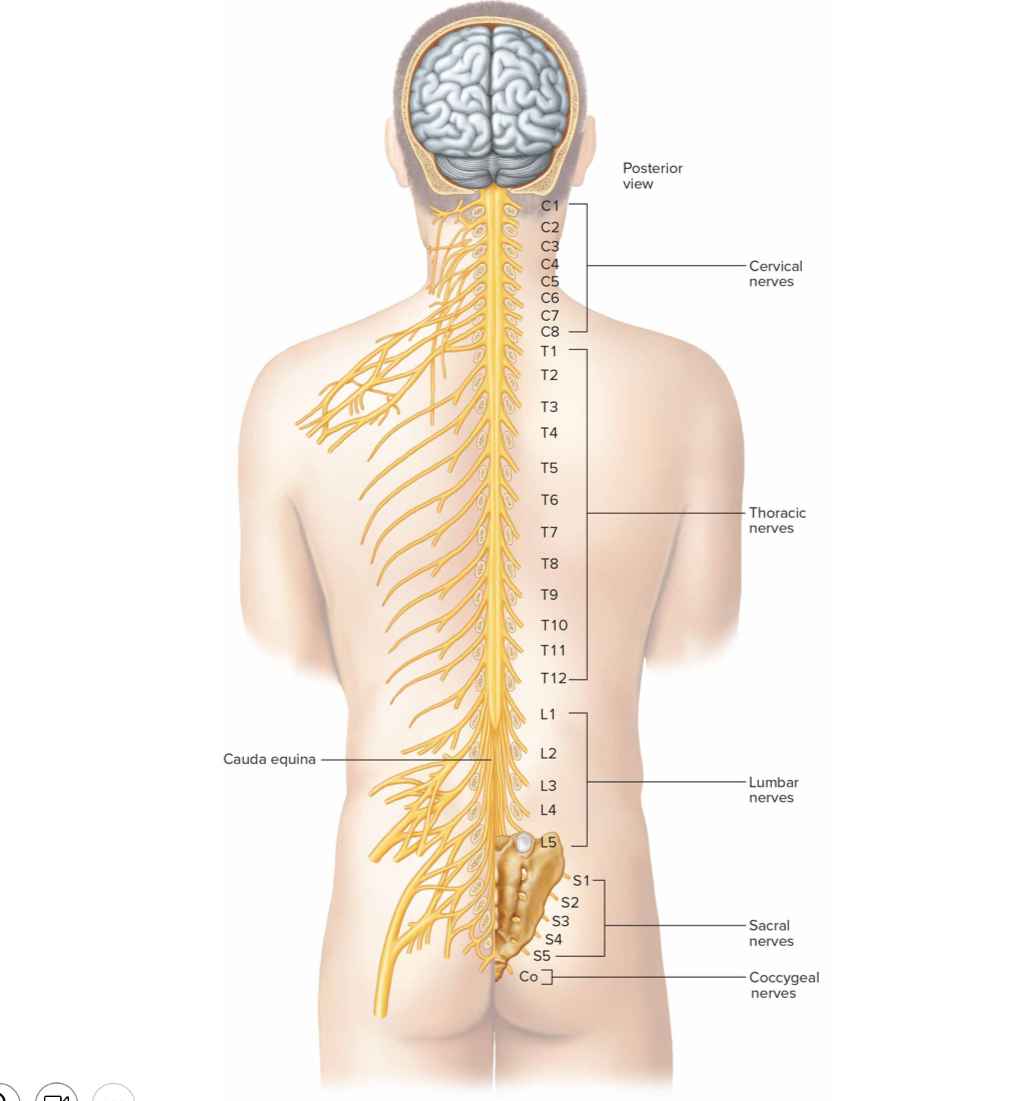
How many pairs of spinal nerves are there
31 pairs
8 cervical (C1-C8)
12 thoracic (T1-T12)
5 lumbar (L1-L5)
5 sacral (S1-S5)
`1 coccygeal nerve
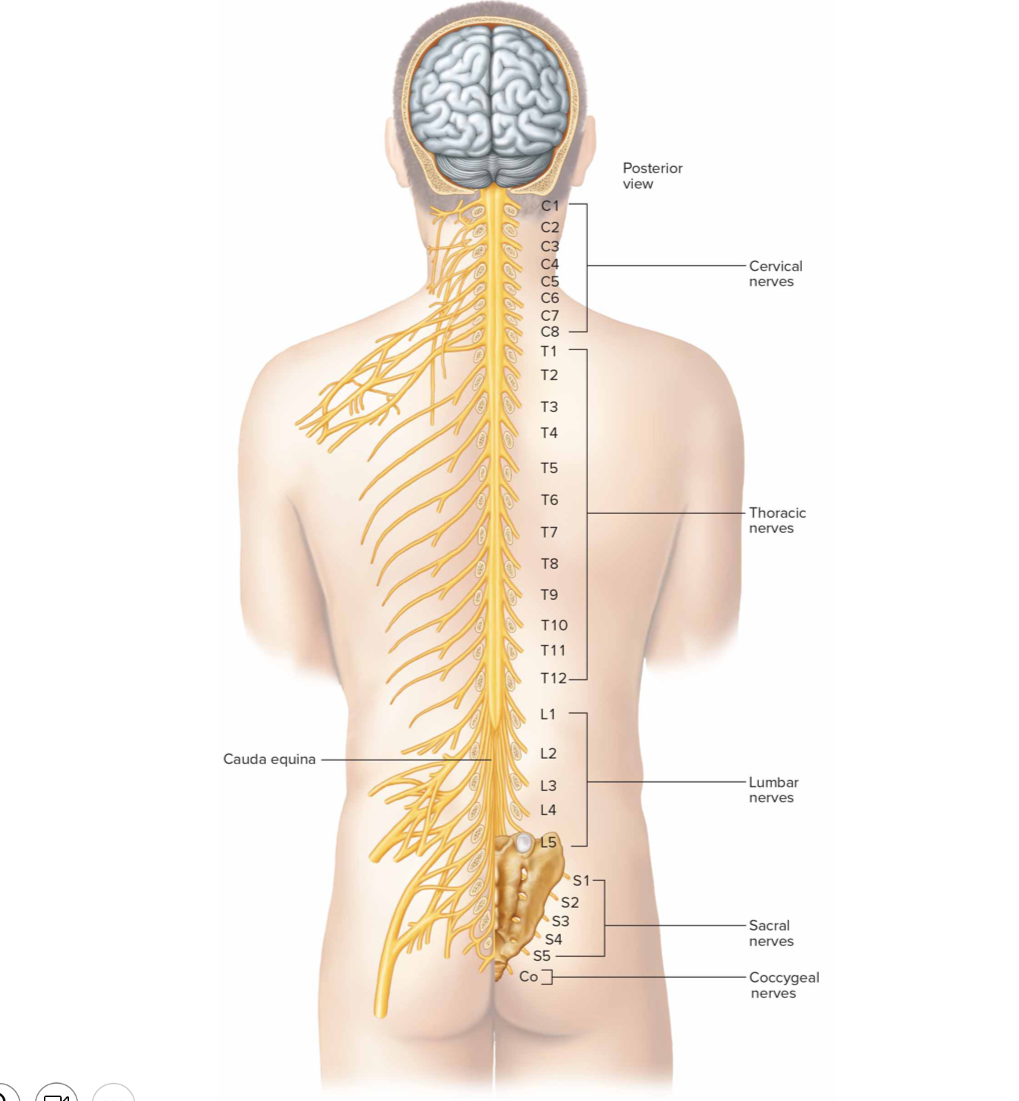
What is the cauda equina formed by
descending roots of lumbar, sacral, coccygeal nerves
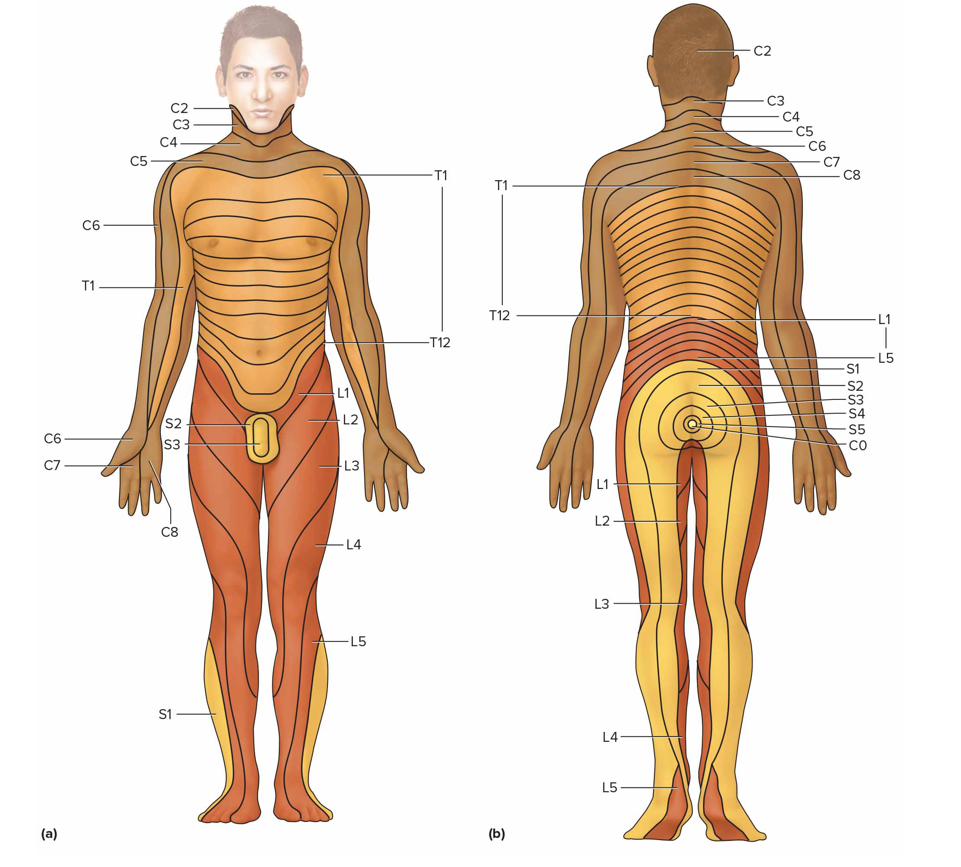
What is the dermatome of spinal nerves
An area of skin innervated by sensory nerve fibers of particular sn (in all sn below C1)
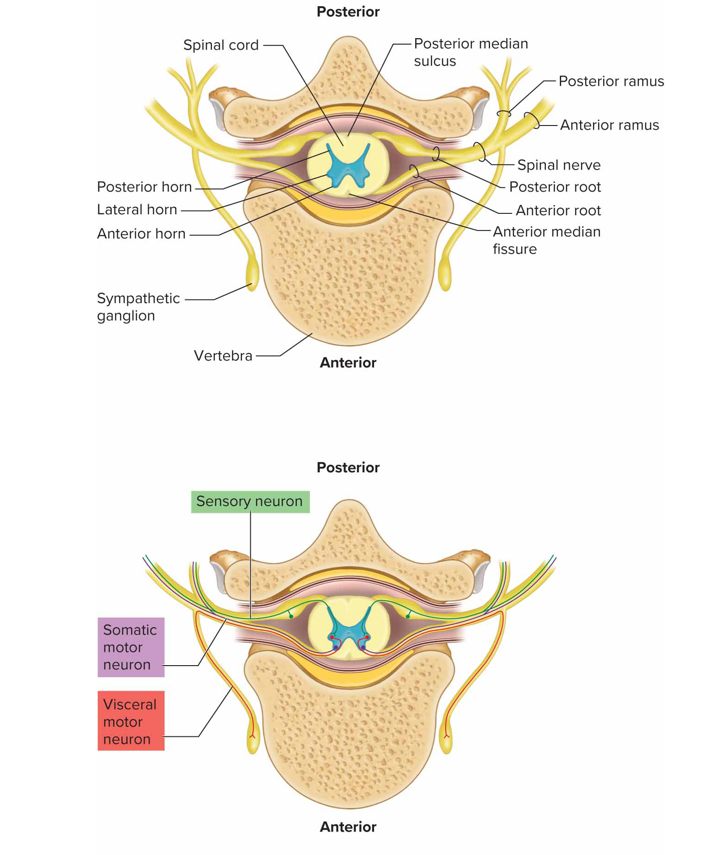
What does the anterior (ventral/motor) root of a spinal n contain
Axons of motor neurons whose cell bodies are in the sc
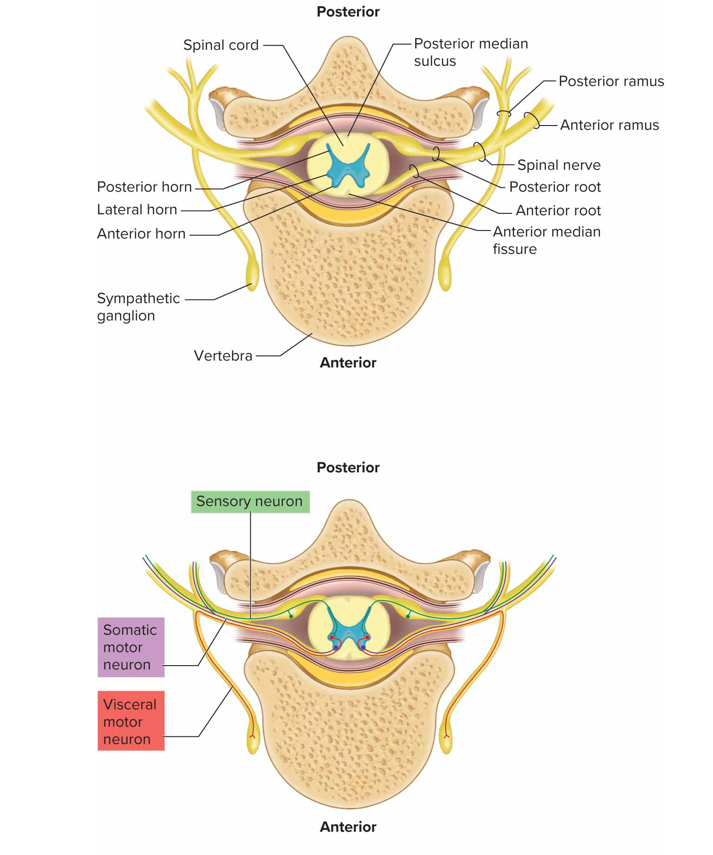
What does the posterior (dorsal/sensory) root of a spinal n contain
Axons of sensory neurons; posterior root ganglion contains cell bodies of sensory neurons that conduct impulses from periphery into spinal cord
What are spinal n formed by
Union of anterior + posterior roots
What are nerve plexuses
Complex network formed by anterior rami (branches) of sn; not in T1-T12 because anterior rami become intercostal n
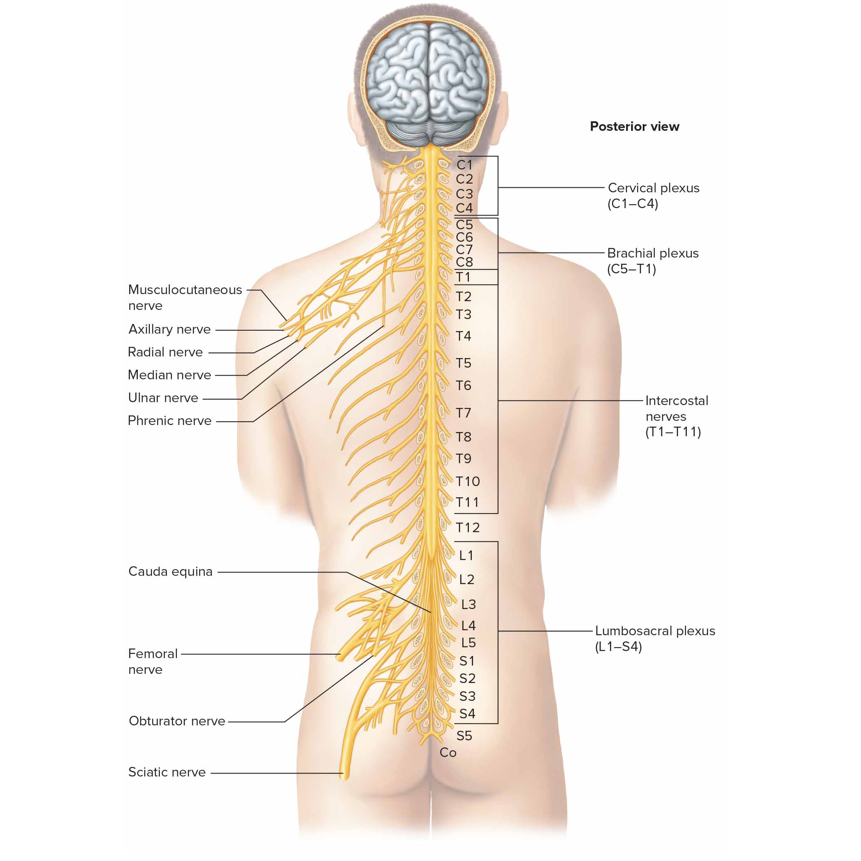
Cervical plexus
Formed by anterior rami of C1-C4 lying deep in the neck, supplies neck muscles + skin'; C3-C5 nerve roots contribute to phrenic n → transmit motor pulses to diaphragm
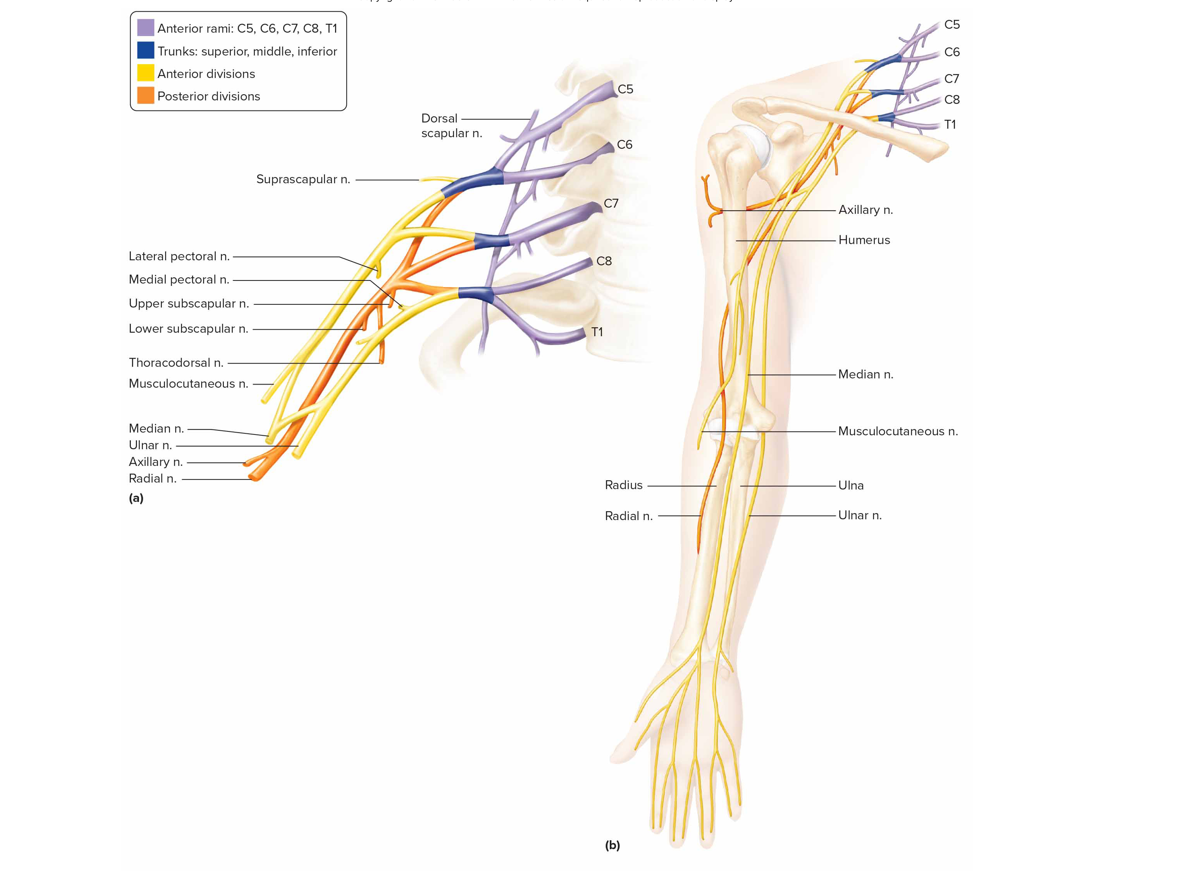
Brachial plexus
Formed by anterior rami C5-T1 lies deep in shoulder
Musculocutaneous n: supple anterior arm muscles, forearm skin
Ulnar + median n: forearm + hand muscles, hand skin
Radial n: post arm muscles, forearm + hand skin
Axillary n: muscle + skin of ant, lat, post arms
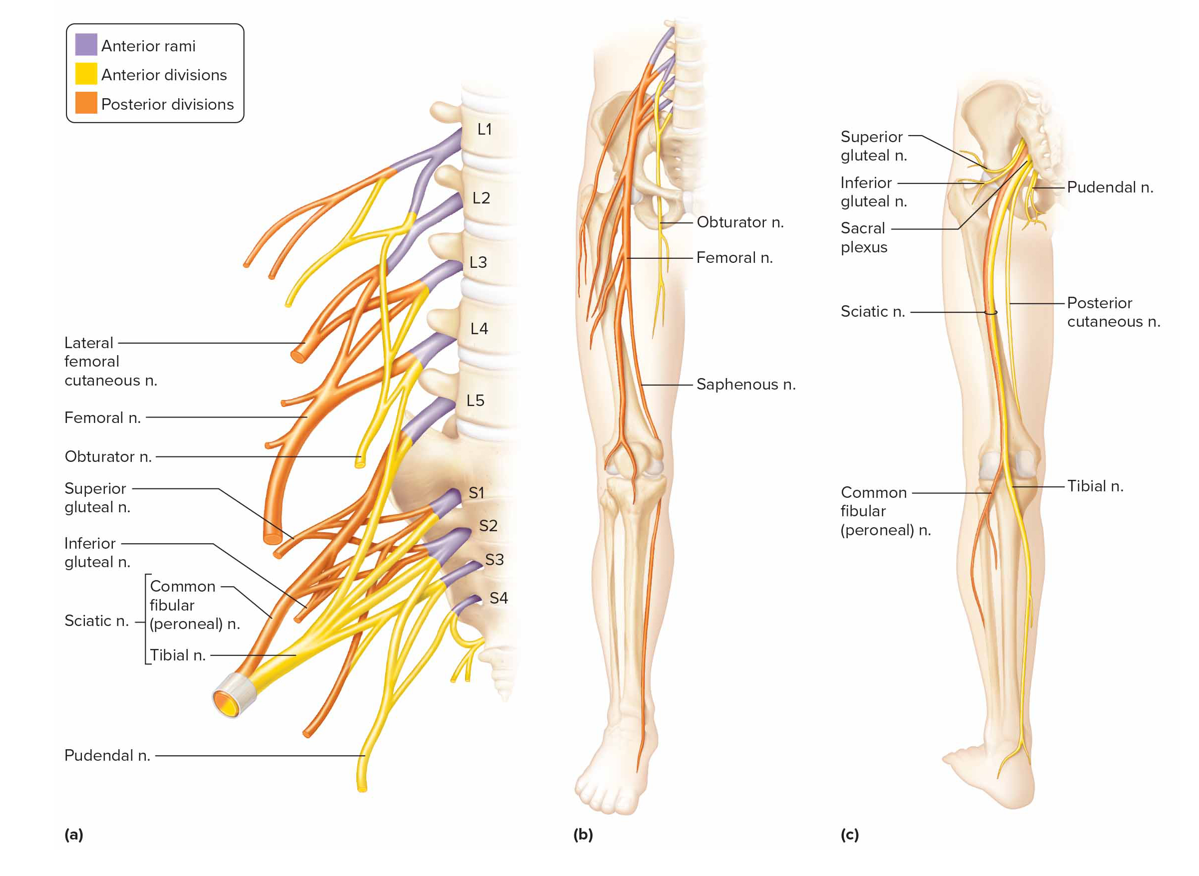
Lumbosacral plexus
Formed by ant branches of L1-S4 roots
Obturator n: supply motor impulses to adductors
Femoral n: motor impulses to ant thigh musc, sens impulses from thigh + leg skin
Sciatic n: muscle + skin of thighs, legs, feet; largest + longest n
Whiplash
Sudden bending of the neck, compression of c plexus n → persistent headache, neck pain
Thoracic outlet syndrome
Pressure on b plexus from continuous flexion of arm (painting/typing) → neck, shoulder, upper limb pain
Sciatica
Compression of intervertebral disc in lumbar region → pain in lwr back, gluteal region, thigh, calf, foot
Carpal tunnel syndrome
Repeated movements of hand inflame tendons that pass through carpal tunnel (space btw wrist bones); swelling in tendons compresses median n → arm + wrist pain
What does the ANS control
Visceral activities + preps body for exercise