A&P Unit 4: Integumentary System
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
Integument
the skin
Largest organ in the body (16% of body weight)
What 4 tissues make up the skin?
stratified squamous
areolar
dense irregular
adipose
Functions of the skin
protection, homeostasis, energy storage, sensation, secretion
What layers make up the skin?
Epidermis, dermis, hypodermis
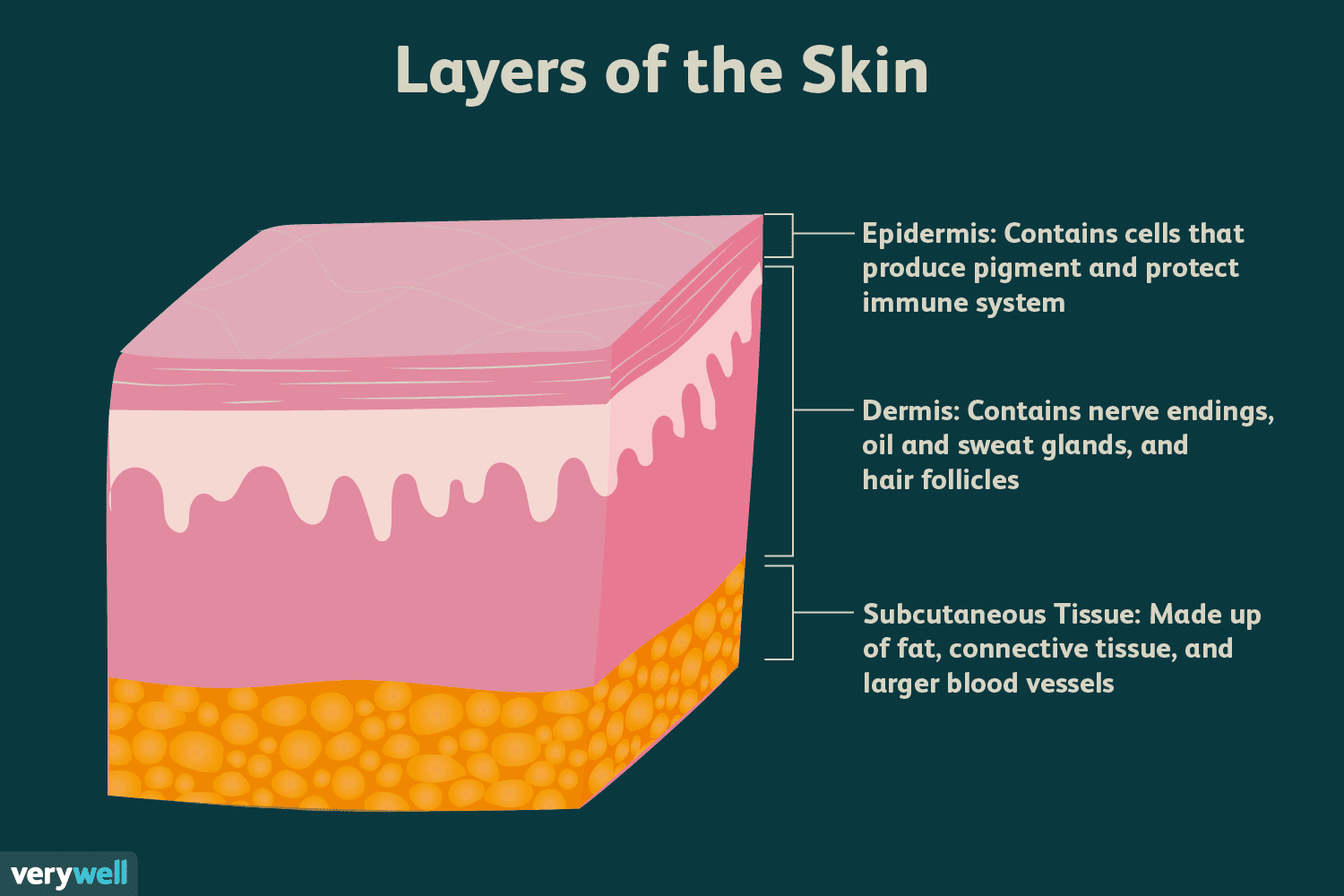
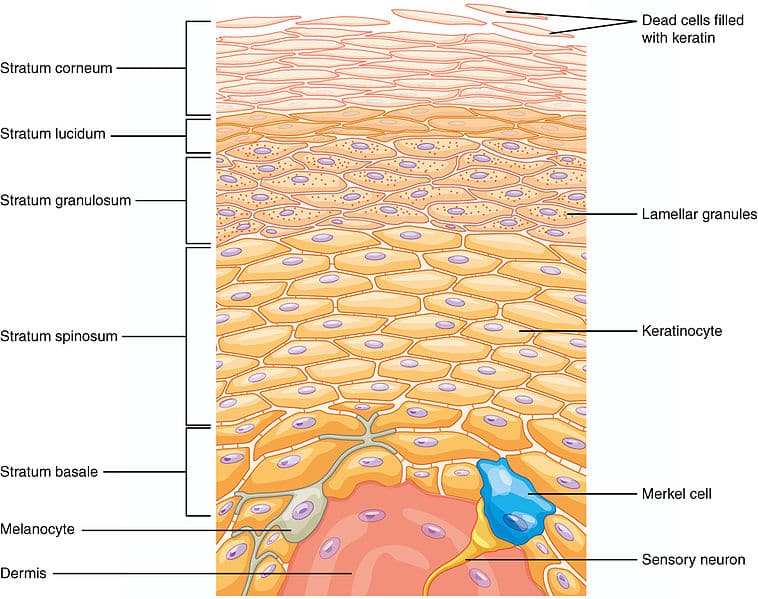
Epidermis
Cells divide in bottom layer and r gradually pushed upwards
has melanocytes
Pheomelanin vs Eumelanin?
pheomelanin- red/yellow and found in lips nipples, and some hair types (red hair)
Eumelanin- black/brown and most common type found in skin and hair
Rickets
softening of bone in children caused by vitamin D deficiency
Stratum spinosum
cells begin forming desmosomes to attach to e/o in layers
Stratum granulosum
cells begin producing large amounts of keratin and eventually die due to lack of oxygen from the dermis
Keratin
durable, water resistant protein found in hair, skin, and nails
Stratum lucidum
clear layer of dead, keratinized cells
only present in areas of the body w/ thick skin (palms and soles of feet)
Epidermal ridges
Increases surface area for oxygen diffusion from the dermis; found in thick skin epidermis
causes fingerprints and footprints
Stratum corneum
oldest layer of cells; cells r dead, flattened and keratinized
Ceramides
type of intercellular lipid that seal the spaces between cells, creating a water resistant barrier
Cyanosis
bluing of the skin caused by poor circulation/ low oxygen levels
Jaundice
yellowing of skin due to liver not filtering bilirubin, a product of red blood cell metabolism
Albinism
genetic disorder that prevents the body from making melanin
harlequin ichthyosis
genetic disorder that results in thickened skin
skin doesnt produce lipids to maintain skin barrier so skin looks red, cracked, irritated
epidermolysis bullosa
genetic condition that result in easy blistering of the skin and mucous membranes. Blisters occur with minor trauma or friction and are painful. Its severity can range from mild to fatal
psoriasis
autoimmune disease in which skin cells build up and form scales and itchy, dry patches.
characteristics of cancerous cells (ABCDE rule)
asymmetrical, border irregularity, color change, diameter greater than 6mm, evolution/changes over time
Dermis
made of areolar tissue w/ nerves and blood vessels that deliver nutrients to epidermis
reticular layer made of dense connective tissue that gives skin its strength and flexibility
hypodermis
mostly made of adipose
provides insulation, shock absorption, and an energy reserve
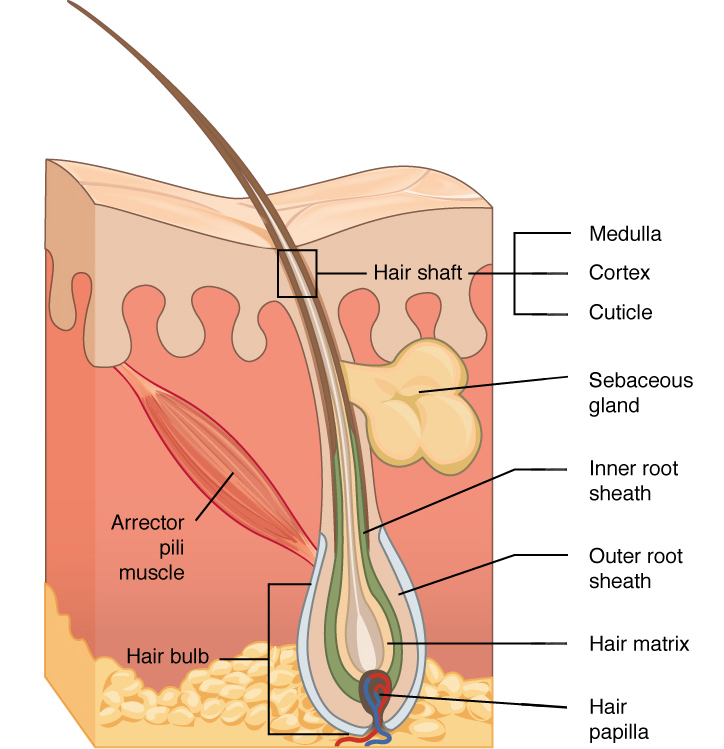
hair papilla
contains nerves and blood vessels
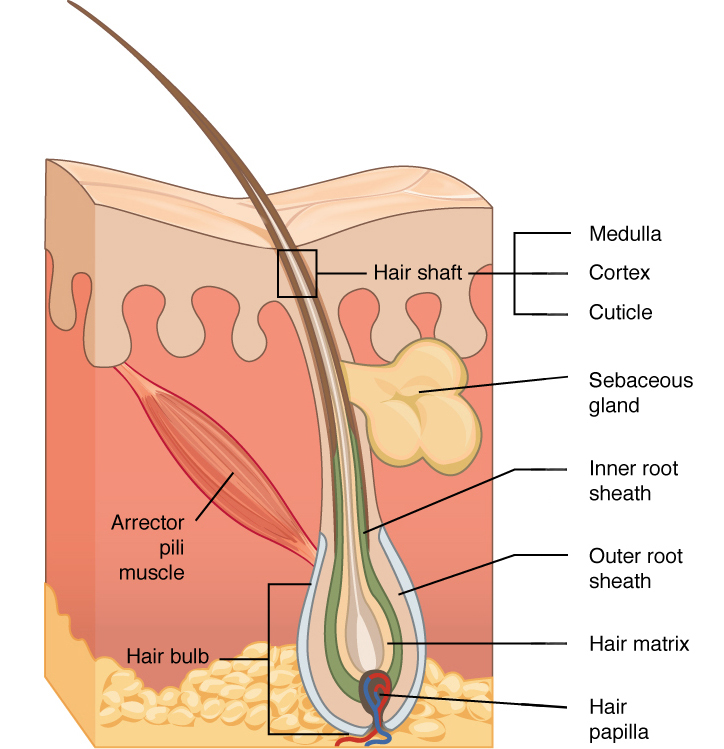
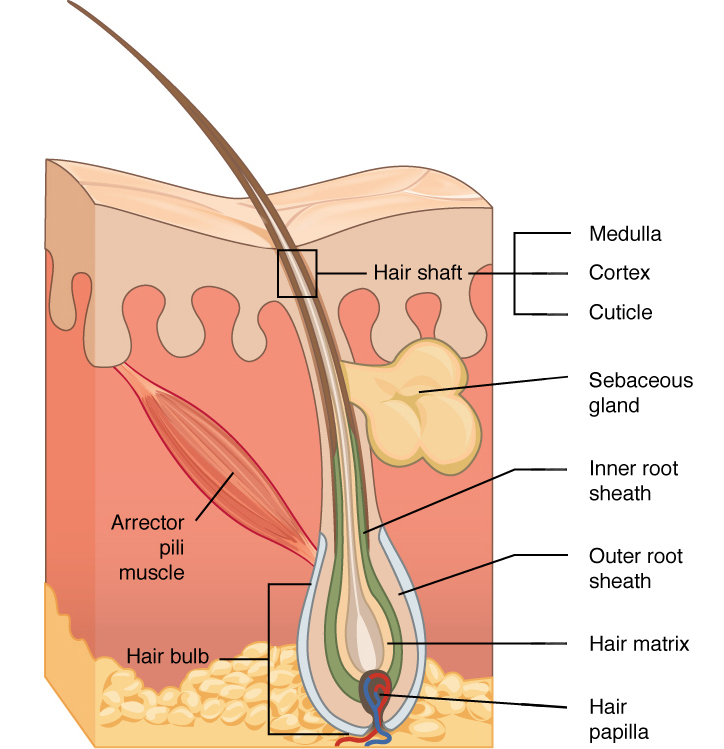
hair matrix
contains stem cells that continuously divide
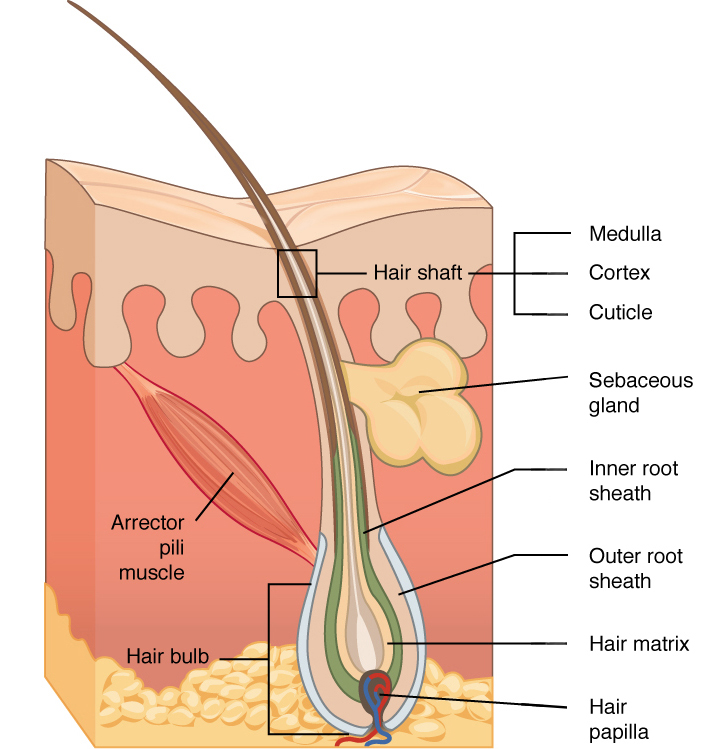
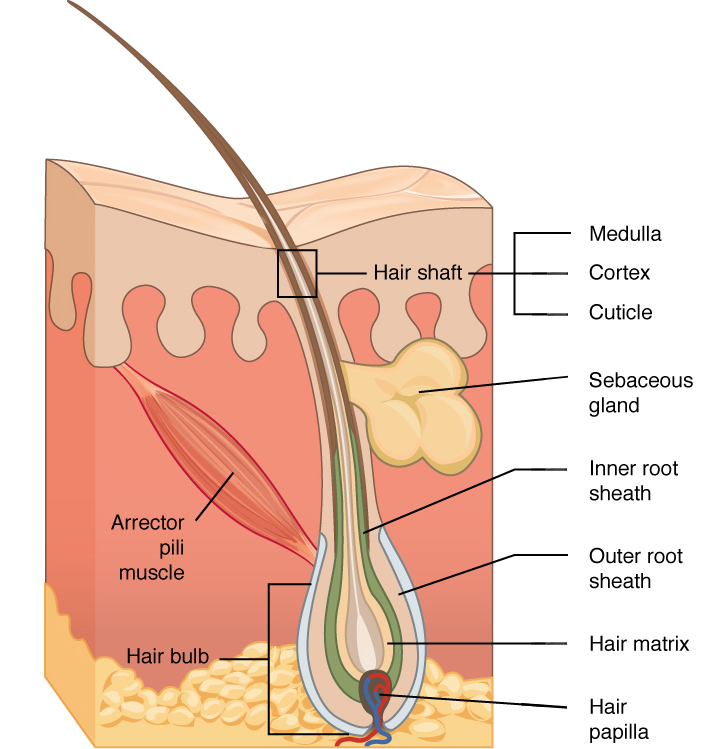
root sheath
extension of stratum spinosum that surrounds the hair root
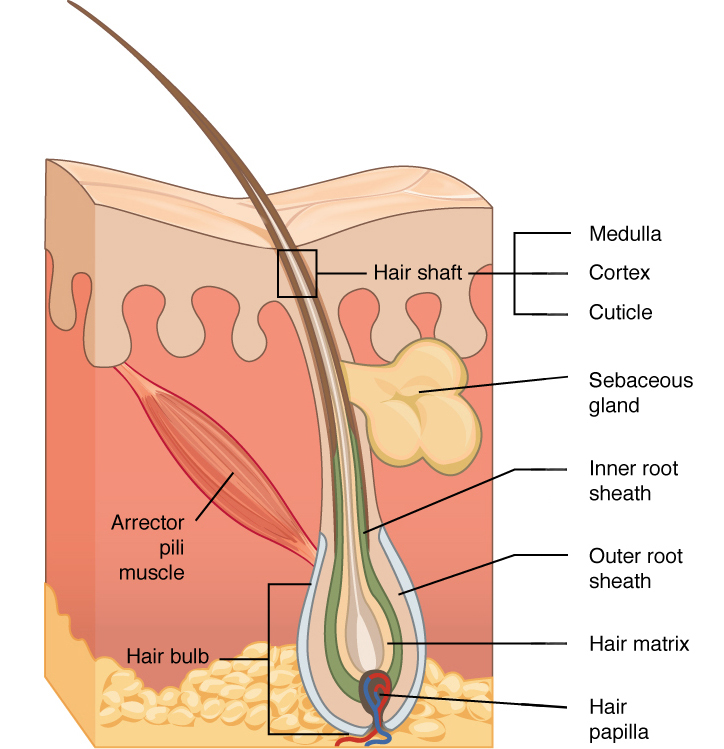
arrector pili muscle
band of muscle that attaches each hair follicle to the epidermis
makes hair stand up right and sensation of goosebumps
hair root vs hair shaft?
hair root- living cells
hair shaft- dead cells
apocrine sweat glands
secrete an oily fluid
only found in armpits and genitals
degraded by bacteria, causing body odor
Merocrine sweat glands
secrete saltwater to cool the body down
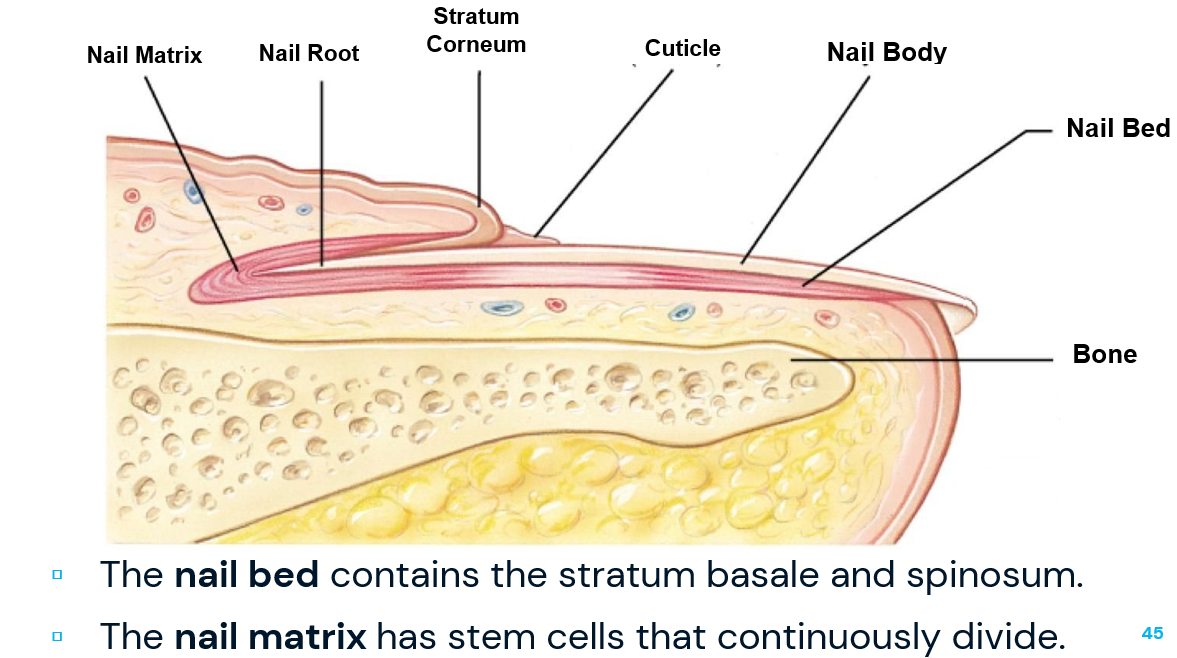
nail bed
contains stratum basale and spinosum
nail matrix
has stem cells that continuously divide
male pattern baldness
genetic trait where hair follicles respond to testosterone by producingfiner, lighter hair
alopecia
autoimmune disorder that affects all hair follicles