Intro to Histology: Cartilage, Osseous Tissues, Bone Cells, How Bones Grow
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
Histology
the study of the microscopic structure of tissues.
4 main categories of tissue types
including epithelial, connective, muscle, and neural tissues.
Epithelial Tissue
(lines things. ie, inner layer of skin or heart)
Connective Tissue
bones[a type of connective tissue].
(provides structure, stores energy, transports materials throughout the body)
Muscle Tissues
(contracts)
Neural Tissue
(connects, sends signals)
3 components of connective tissue
cells, fibers, ground substance
3 Connective tissue Fibers
collagen fibers
reticular fibers
elastic fibers
Supportive Connective Tissue
(dense matrix of collagen and elastic fibers in rubbery ground substance to create support for body.)
Matrix
firm gel, containing chondroitin sulfates
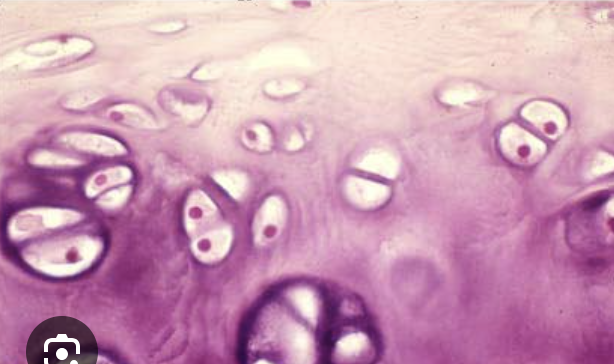
what are these
chondrocytes in lacunae
perichondrium
dense irregular tissue that surrounds most cartilage.
cartilage is _______
avascular (heals slower than bone)
bone is_______
vascular (heals faster than cartilage)
Antiangiogenesis Factor
chemical produced by chondrocytes
Hyaline cartilage
closely packed collagen fibers. (supports larynx, trochlea, part of nasal septum) provides stiff but flexible support and reduces friction between bony surfaces.
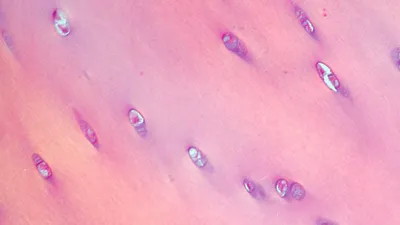
what is this?
Hyaline Cartilage
Fibrocartilage
little ground substance (between femur and tibia, pubic symphysis, intervertebral disks). resists compression, prevents bone to bone contact, shock absorbtion
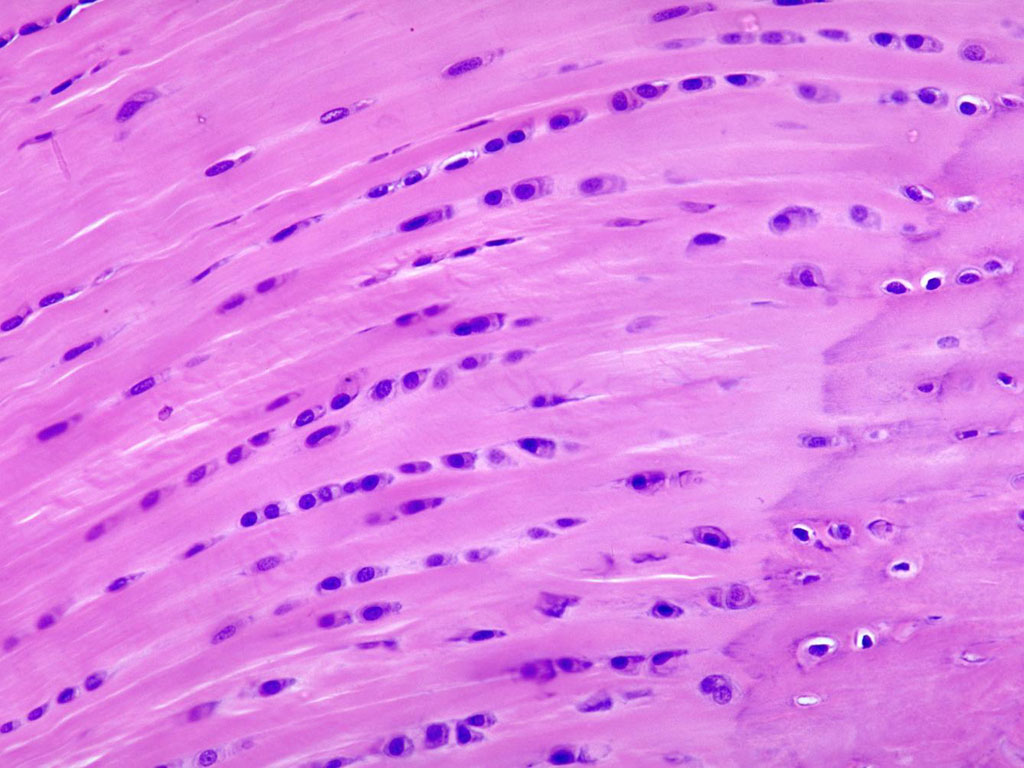
What is this?
Fibrocartilage
Elastic Cartilage
numerous elastic fibers. (external ear, auditory canal) provides support but tolerates distortion without damage and can return to its original shape.
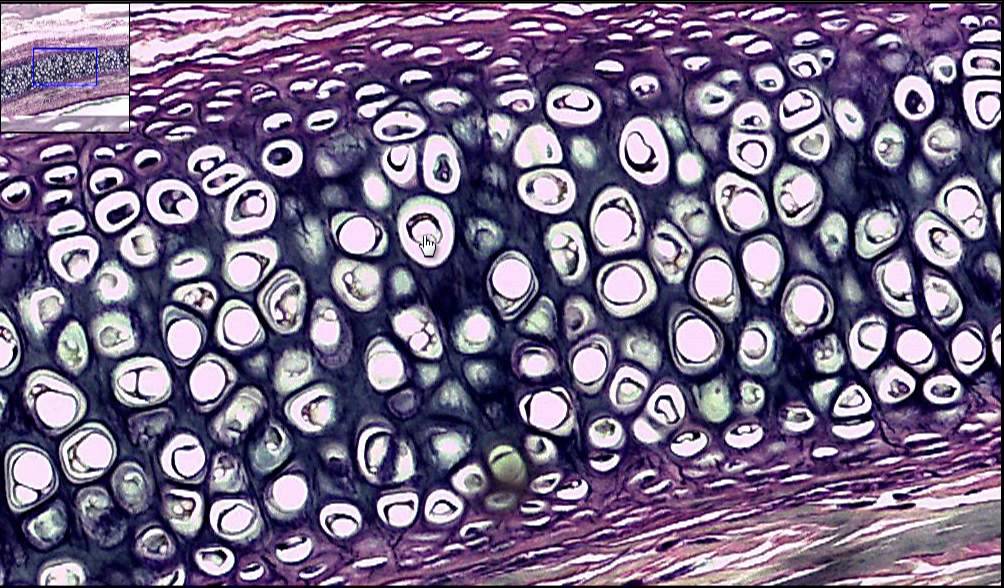
what is this?
elastic cartilage
Osseous tissues meaning…?
bone tissues
Extracellular matrix
1/3 matrix is collagen fibers. 2/3 of matrix is hydroxyapatite
Periosteum
thin membrane on outside of bone
Endosteum
a membrane that lines the inner surfaces of bone
Perforating Fibers
collagen fibers of periosteum.
connects with collagen fibers in bone
connects with fibers of joints
Osteoprogenitor
the “babies.” stem(mesenchymal) cells divide to produce osteoblasts
Osteoblasts
the “teenagers.” immature bone cells that secrete osteoid (which is a matrix that becomes calcified in bone & becomes bone)
Osteocytes
the “adults.” mature bone cells that come from osteoblasts that have been surrounded in calcified bone (inside lacunae chambers)
Osteoclasts
NOT related to osteo progenitor, osteoblasts, or osteocytes.
Giant multi-nucleated cells that dissolve bone tissue to remodel bone and release stored minerals.
ie, the bone dissolving cells!!!
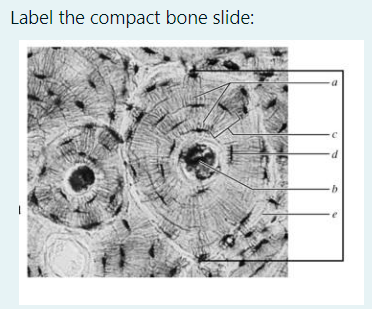
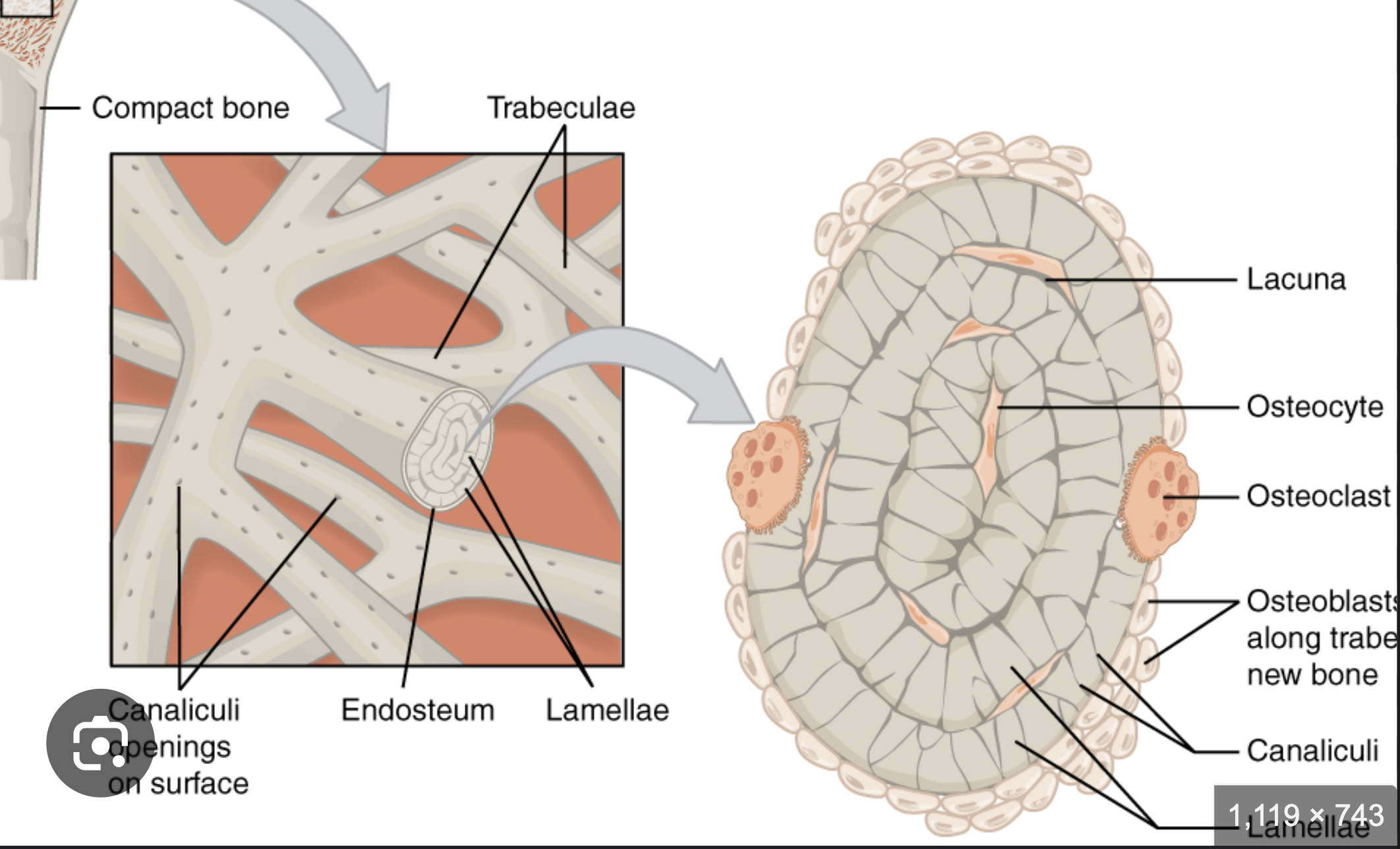
thick line: osteon
a. canaliculi (the little light grey lines that run outward from central canal)
b. central canal
c. concentric lamellae (the layers)
d. lacunae (with osteocytes in them)
e. interstitial lamellae (space between one osteon and another)
EXTRA: circumferential lamellae is the LARGEST ring that is NOT in the osteon. It runs along the periosteum.
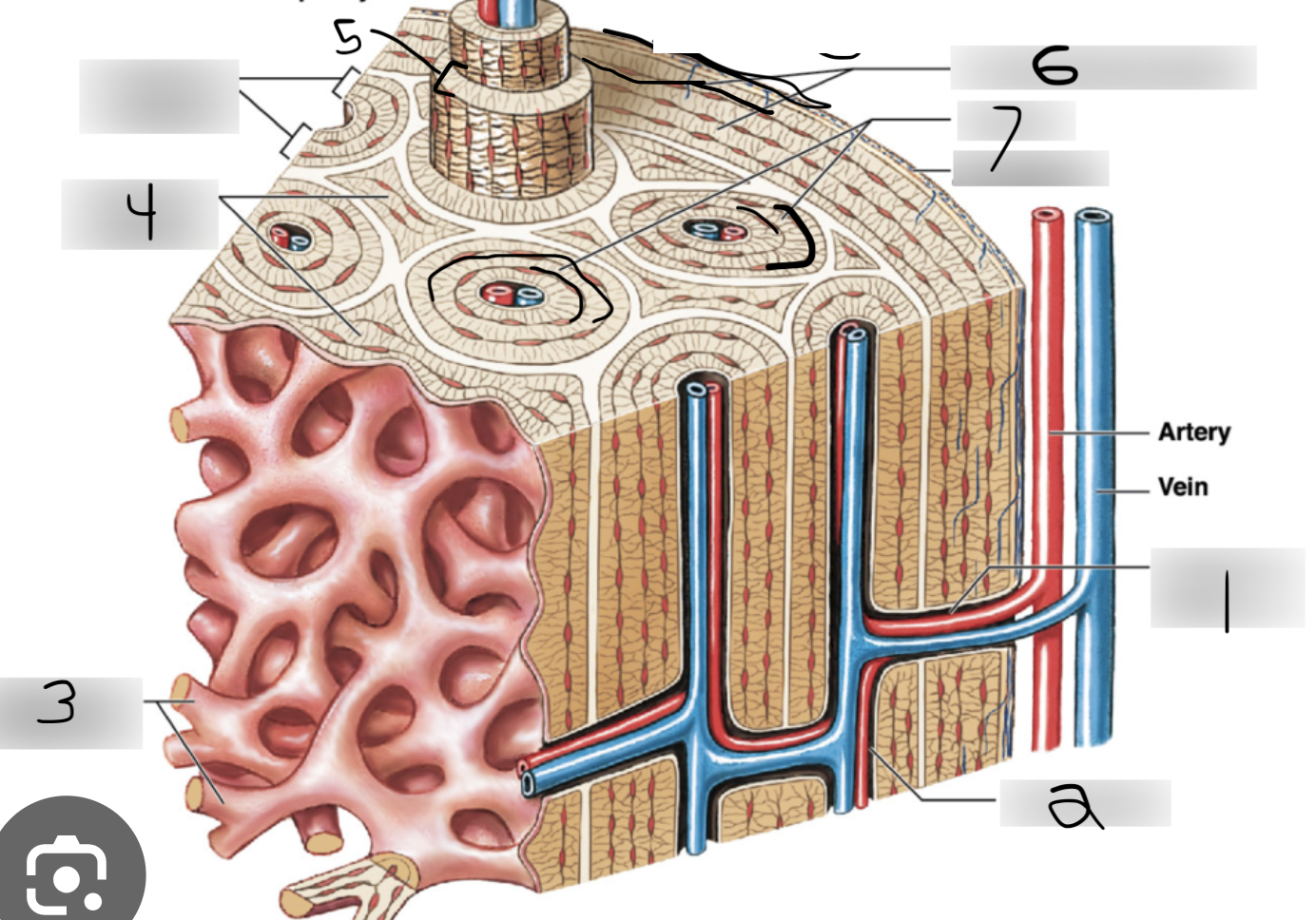
perforating canals
central canals
spongy bone
Interstitial lamellae
concentric lamellae
circumferential lamellae
canaliculi (the little squiggly lines moving outward from central canal)
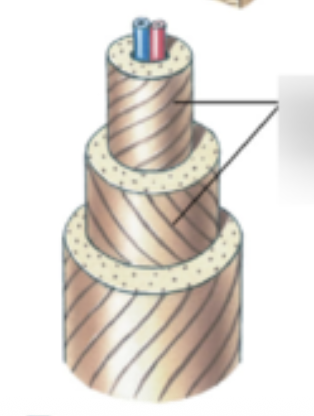
collagen fibers in the osteon
Spongy bone
where bones are not heavily stressed or where stresses comes from many directions
lighter than compact bone
houses red & yellow marrow
system of trabeculae. NOT osteons
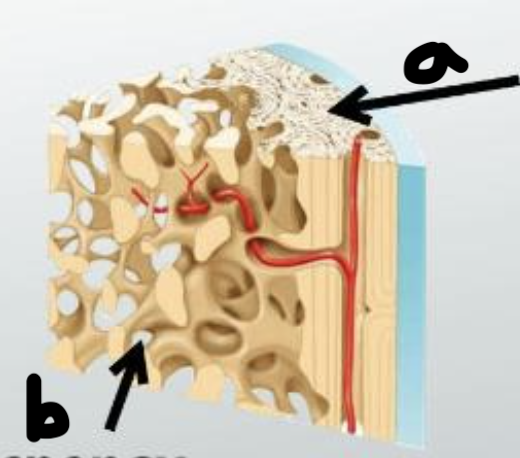
a. compact bone
b. spongy bone
Red marrow
blood vessels
forms blood cells
supplies nutrients to osteocytes in spongy bone
found in epiphyses of long bone, interior of large bones
Yellow marrow
in some bones, spongy bone holds yellow marrow
it’s yellow bc it stores fat
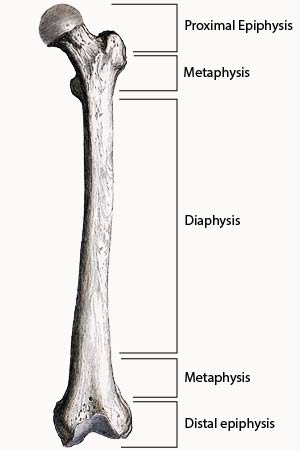
Where yellow marrow is located
medullary cavity within diaphysis
Periosteum outer layer
dense, irregular connective tissue, fibrous layer
Periosteum inner layer
cellular layer, every type of cell except for osteocytes
Bone Development steps
human bones begin as cartilage
osteogenesis: bone formation
ossification: process of replacing other tissues with bone. (2 types. endochondral and intramembrous)
intramembranous ossification
stem cells cluster & split into osteoblasts
osteoblasts secrete osteoid
developing bone grows outward in spicules
some osteoblasts are trapped inside bony pockets, so they become osteocytes
**this all happens in the ossification center
Blood vessels grow into area of ossification
Spicules fuse together and some blood vessels become trapped in developing bone
**initially intramembranous bone consists of spongy bone only
remodeling around blood vessels produces osteons of compact bone
as growth slows, connective tissue around bone becomes periosteum
collagen fibers
straight, strong

collagen fibers
Areolar tissue (beneath the skin or around organs. Binds them)
Dense connective tissue (tendons and ligaments)
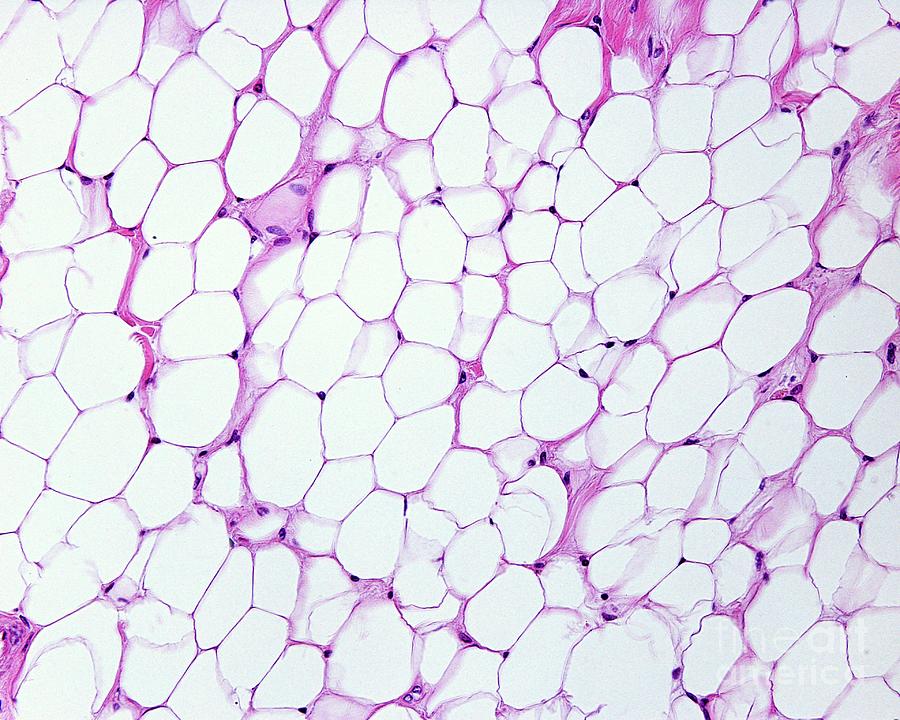
Adipose tissue ( located inside of skin or around organs. insulates, energy storage )
reticular fibers
small, branch
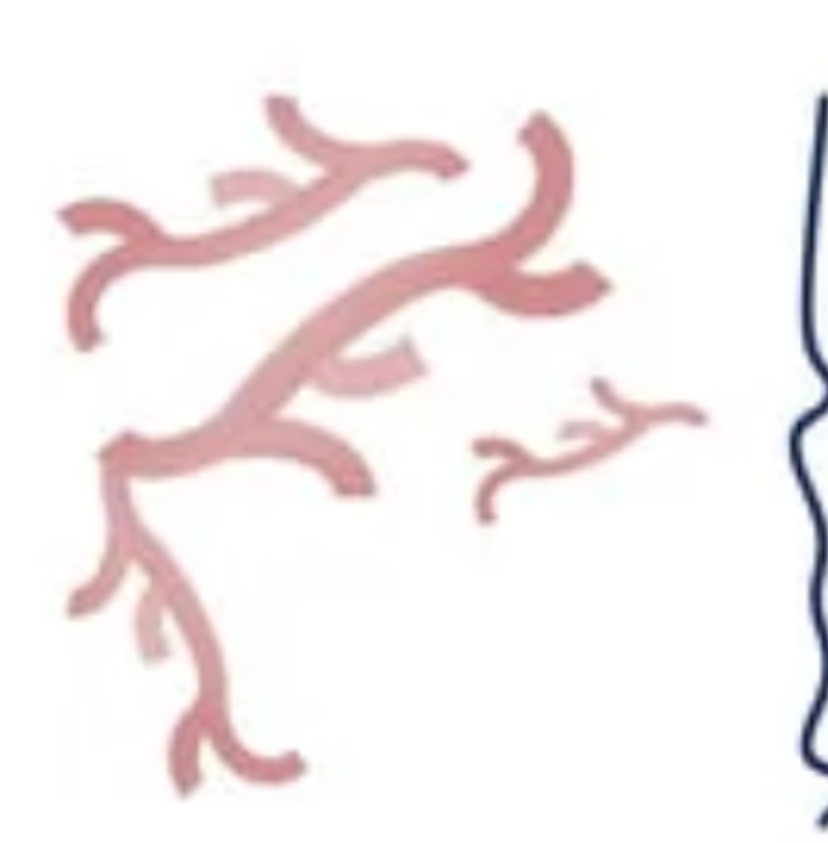
Mesh like network
Reticular fibers
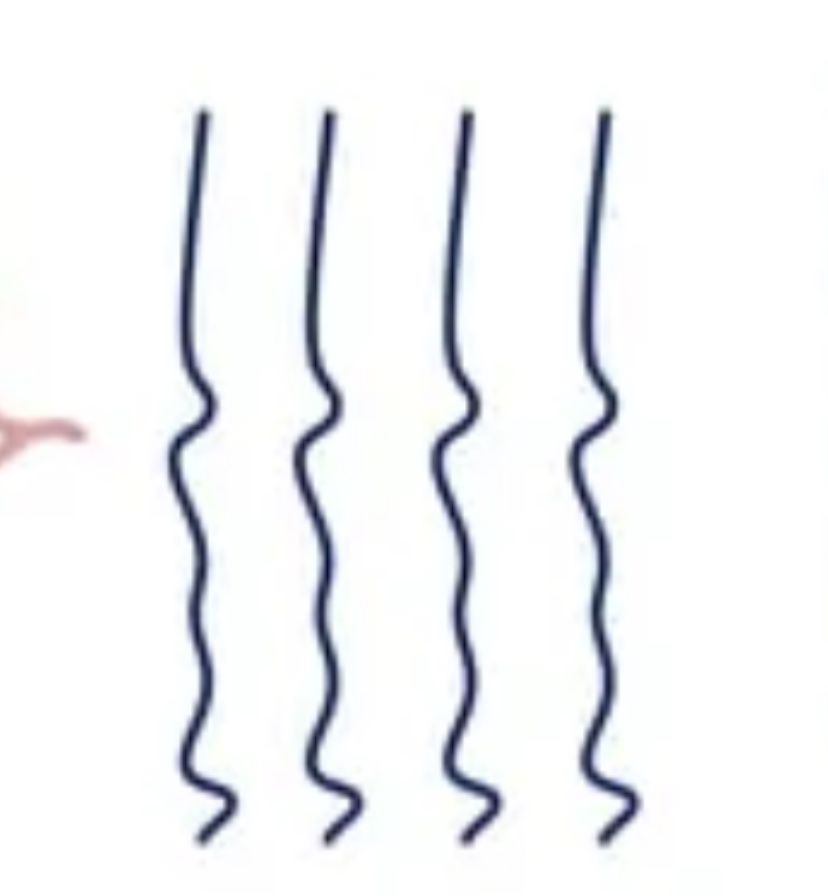
Branching fibers
Elastic fibers
elastic fibers
stretches and returns to original shape after being stretched or compressed
where endochondral ossification occurs
in cartilage
where intramembrous ossification occurs
in deep layers of skin
Endochondral ossification
Mesenchymal (stem) cells are split into chondroblasts, which then secretes hyaline cartilage, which is then formed into a ‘model’ of the bone it is going to be
chondroblasts turn into chondrocytes, and calcify into the cartilage model, and more bone calcifies along the diaphysis(shaft) when blood lines the outer sides of it.
blood penetrates bone on diaphysis, creating the primary ossification center as the inside of the bone begins to calcify
osteoclasts hollow out center of spongy bone in diaphysis, creating medullary cavity.
Blood then penetrates the epiphyses of the bone and calcifies it, creating the secondary ossification centers.
A strip of hyaline cartilage called the epiphyseal plate (growth plate) remains between the diaphysis and epiphysis, allowing bone to continue growing in length until adulthood, ie, when the space is completely closed
Endochondral Ossification
chondrocytes are near the center of a cartilage model of a future bone grow, causing lacunae to grow too, causing calcification of cartilage. chondorcytes die from lack of nutrients.
since there are no chondrocytes to release Antiangiogenesis Factor, blood vessels grow into perichondrium surrounding the diaphysis with a thin layer of calcified bone.
Blood supply to periosteum increases, and blood vessels move to core of bone causing cartilage matrix to break down. osteoids replace matrix with spongy bone. this all occurs in the primary ossification center
as bone enlarges, osteoclasts appear and begin to erode trabeculae(spongy bone) in center of diaphysis. appositional growth.
centers of epiphysis calcify in secondary ossification center
epiphysis filled with spongy bone and remaining is articular cartilage. epiphyseal plate cartilage. remains for bones to continue to grow throughout puberty.
Epiphyseal plate growth at youth
grows at even pace w/ diaphysis bone.
Epiphyseal plate growth at puberty
grows slower than the diaphysis bone, causing the epiphyseal plate (cartilage) growth to be overtaken and the gap is eventually closed.
nutrient artery and vain
single pair of large blood vessels that enter diaphysis through nutrient foramen.
mataphyseal vessels location
in metaphysis
periosteal vessel location
in periosteum
Calcitonin
decrease in osteoclast production so that bone preserves calcium
decrease in calcium absorption in intestine
increase in amount of Ca2+ ions peed out
GOAL: decrease amt of calcium
parathyroid hormone (PTH)
increase in osteoclast production so that bone releases calcium
increase in calcium absorption in intestine
decrease in amt of Ca2+ ions peed out
GOAL: increase amt of calcium
3 cartilages
Hyaline (medium)
Elastic (soft)
Fibrocartilage (tough)
all made of fibers, have chondrocytes in lacunae, rubbery ground substance, and antiogenesis factor
Spongy Bone:
TRABECULAE, not osteon