exam improvement bio
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
Why is ethanol added when extracting DNA from a fruit?
To precipitate the DNA
Differences between product of meiosis and mitosis…
mitosis - 2 cells, genetically identical, body cells, diploid
meiosis - 4 cells, genetically different, sex cells, haploid
Vaccine working:
they are immune to (disease)
because the vaccination contained an antigen / bacteria have antigens
memory lymphocytes
leading to the production of antibodies
leading to a secondary (immune) response


memory lymphocytes
are a type of white blood cell, which forms a crucial part of the body’s immune system. Their key function is to remember specific pathogens, for example bacteria or viruses, that the body has encountered before.
why do bacteria become resistant to medicinal drugs
people do not finish their course (of the drug) / overuse / repeated exposure to antibiotic.
natural selection occurs / evolution
some bacteria have a mutation / genetic variation
these resistant bacteria survive / resistant bacteria reproduce
why was the three domain system introduced?
improved genetic analysis
DNA/RNA (screening/sequencing)
Domain theory is based on genetics
differences between coding and non-coding DNA
enzymes don’t forget
increased chance of collision
substrate complexes formed
why do people no get vaccinated
concerns over side effects of immunisation / concerns over the risk of allergic reactions
medical reason for not being immunised
too young for vaccination programme
no access to healthcare
how does the lens refract the light more?
by becoming thicker
functions of reflex arc:
rapid response
protect the body in response to danger
involuntary automatic response
advantages and disadvantages of vaccination
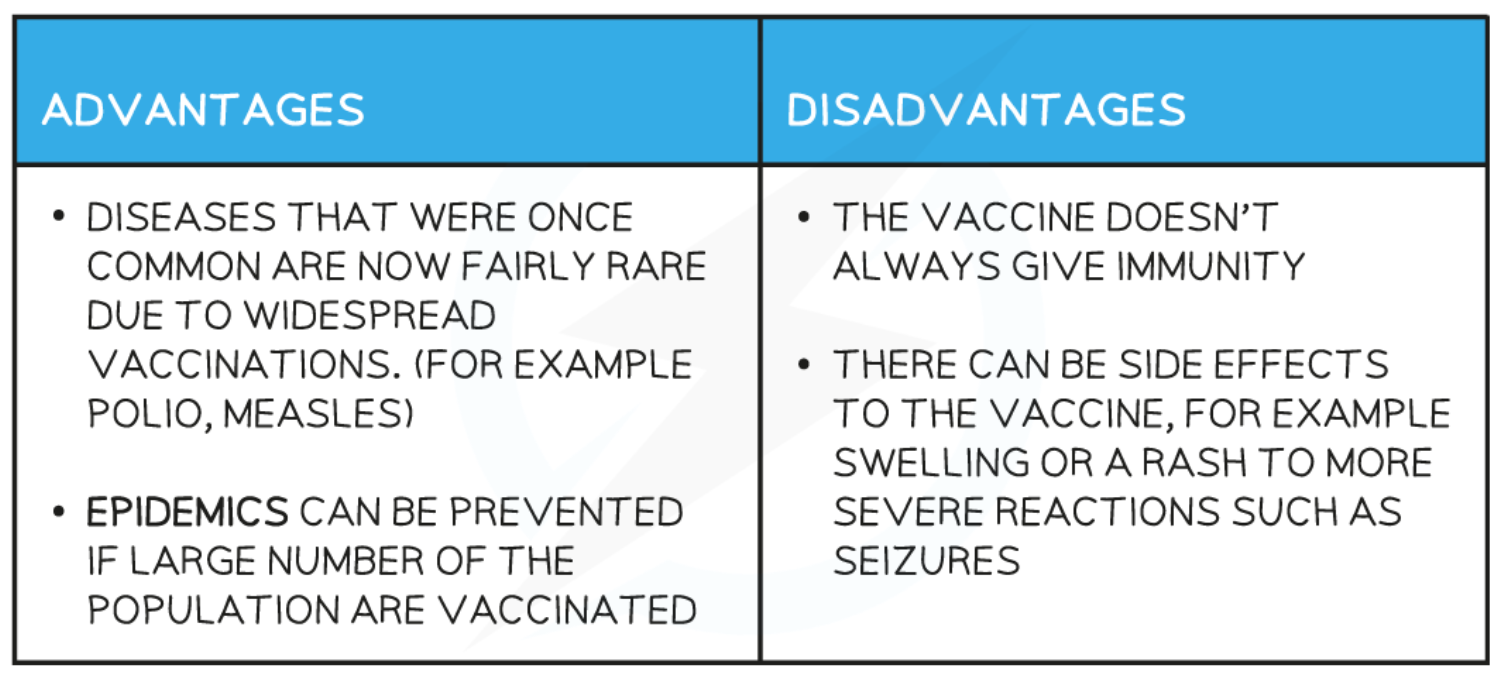

herd immunity
If a large number of the population are vaccinated, it is unlikely that an unvaccinated individual will become infected with the pathogen