QUIZ COMPNET REVIEWER
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
MAC
media access control
VLAN
virtual local area network
mdix
medium-dependent interface crossover
CEF
Cisco Express Forwarding
FIB
Forwarding Information Base
HTTPS
HyperText Transfer Protocol Secure
EIGRP
Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol
SVI
Switched Virtual Interface
OSPF
Open Shortest Path First
IGRP
Interior Gateway Routing Protocol
HWIC
High Speed WAN Interface Card
POST
Power-on self-test
3 uses of static routes
Smaller networks that are not expected to grow
Routing to and from stub networks
Stub network accessed by a single route and has one neighbor
172.16.3.0 is a stub network
A single default route to represent a path to any network not found in the routing table.
Use default route on R1 to point to R2 for all other networks
Consideration when selecting switches
Cost
Port Density
Power
Reliability
Port Speed
Frame buffers
Scalability
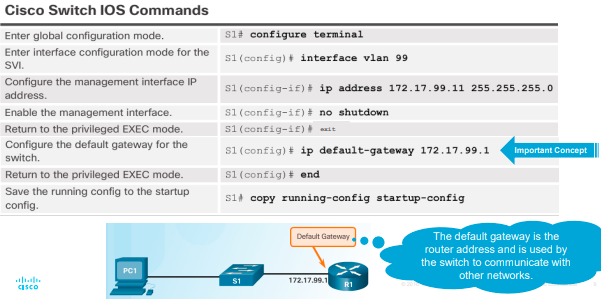
Configuring Basic Switch Management Access with IPv4 (cisco switch ios commands)
configure terminal
interface vlan 99
ip address 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0
no shutdown
exit
ip default-gateway 172.17.99.1
end
copy running-config startup-config
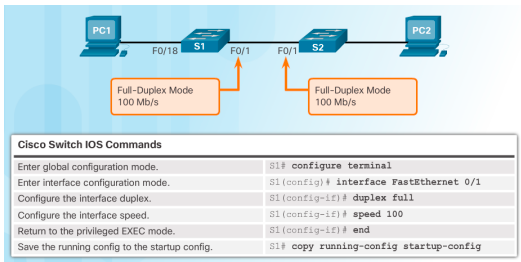
Configure Switch Ports at the Physical Layer (cisco switch ios commands)
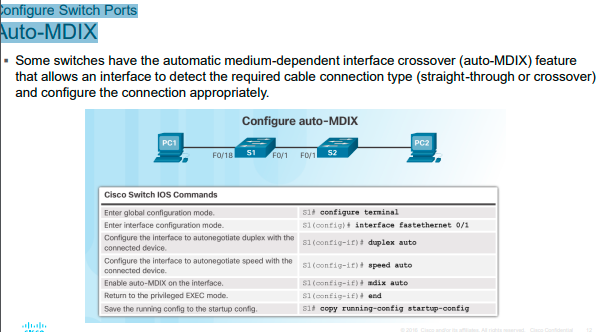
Configure Switch Ports Auto-MDIX
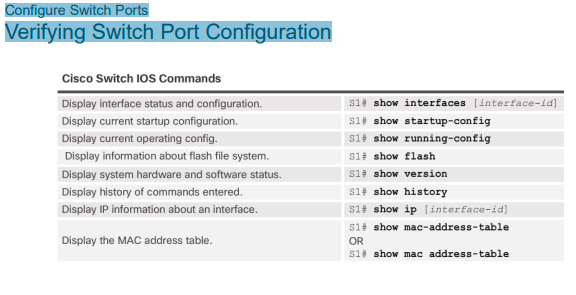
Configure Switch Ports Verifying Switch Port Configuration
Error checking
After receiving the entire frame, the switch compares the frame-check-sequence (FCS) value in the last field against its own FCS calculations. Only error-free frames are forwarded
Access layer
provides network access to the user.
Distribution layer
interfaces between the access layer and the core layer. Provides functions such as:
aggregating Layer 2 broadcast domains and Layer 3 routing boundaries.
providing intelligent switching, routing, and network access policy functions to access the rest of the network.
Core layer
is the network backbone. It provides fault isolation and high-speed backbone connectivity.
Automatic buffering
ingress port buffering provides the flexibility to support any mix of Ethernet speeds
Router
Connects one network to another network. Determines the best route to the destination before forwarding traffic to the next router along the path. Responsible for routing traffic between networks. Routing table used to determine the most efficient path to reach the destination.
Super route
a network address with a mask less than the classful mask, for example, a summary address.
Physical topology
arrangement of the cables, network devices, and end systems; it describes how the network devices are actually interconnected with wires and cables
Logical topology
describes the path over which the data is transferred in a network and how the network devices appear connected to network users
Network route
a network route that has a subnet mask equal to that of the classful mask.