instrumental delivery
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
what is an instrumental delivery referring to?
vaginal delivery assisted by a ventouse suction cup or forceps
what percentage of births in the UK are instrumental?
10%
can instrumental deliveries take place on labour wards?
yes normally - but if any concerns then woman may be transferred to theatre to perform caesarean
what is used to reduce maternal infection with instrumental delivery?
co-amoxiclav
what are the indications for an instrumental delivery?
- failure to progress
- foetal distress
- maternal exhaustion
- control of head in various foetal positions
- epidural use
what are the risks to the mother?
- PPH
- episiotomy
- perineal tears
- injury to anal sphincter
- incontinence of bladder or bowel
- nerve injury (obturator or femoral)
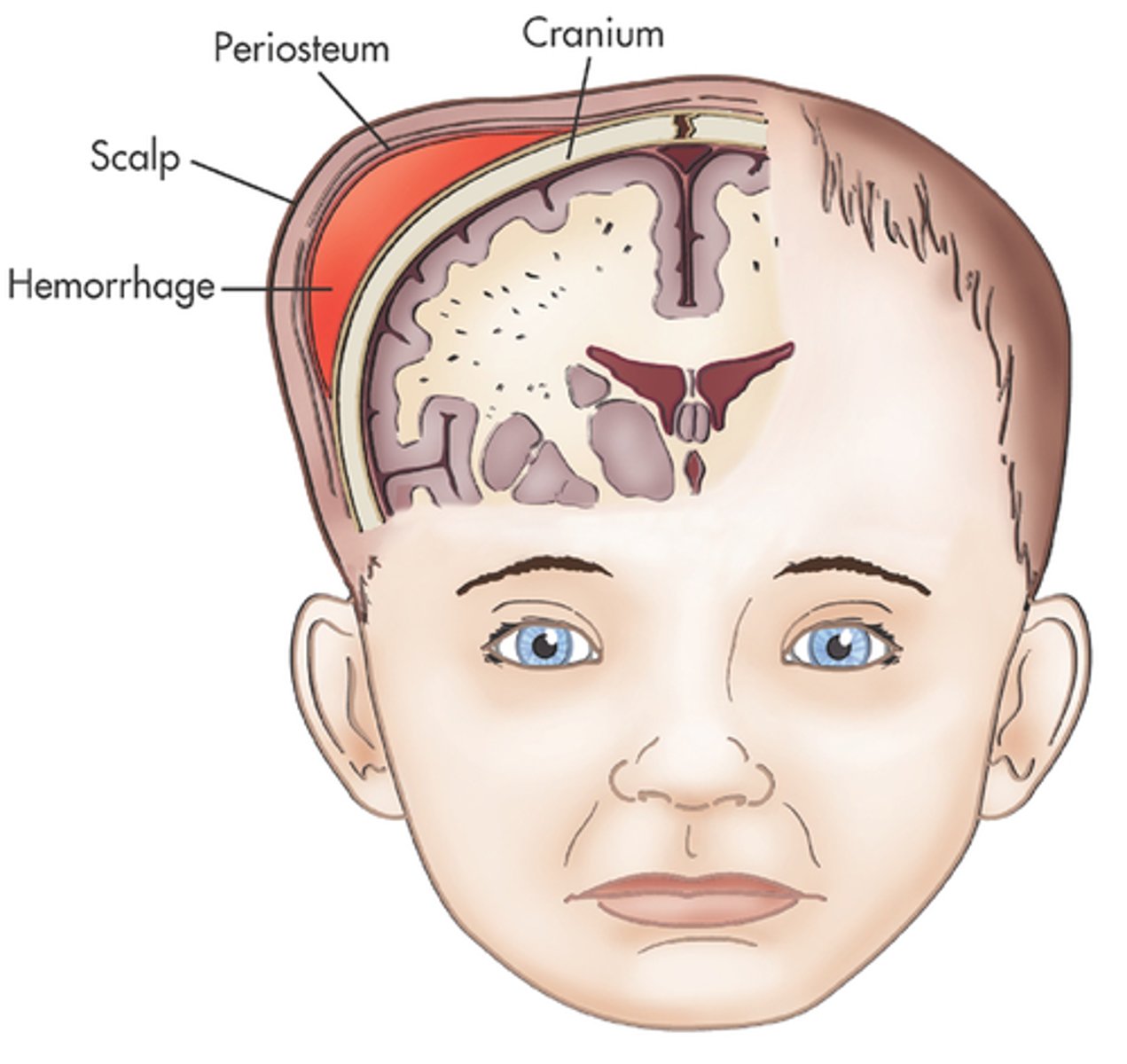
what is the key risk for the baby in ventouse delivery?
cephalohaematoma
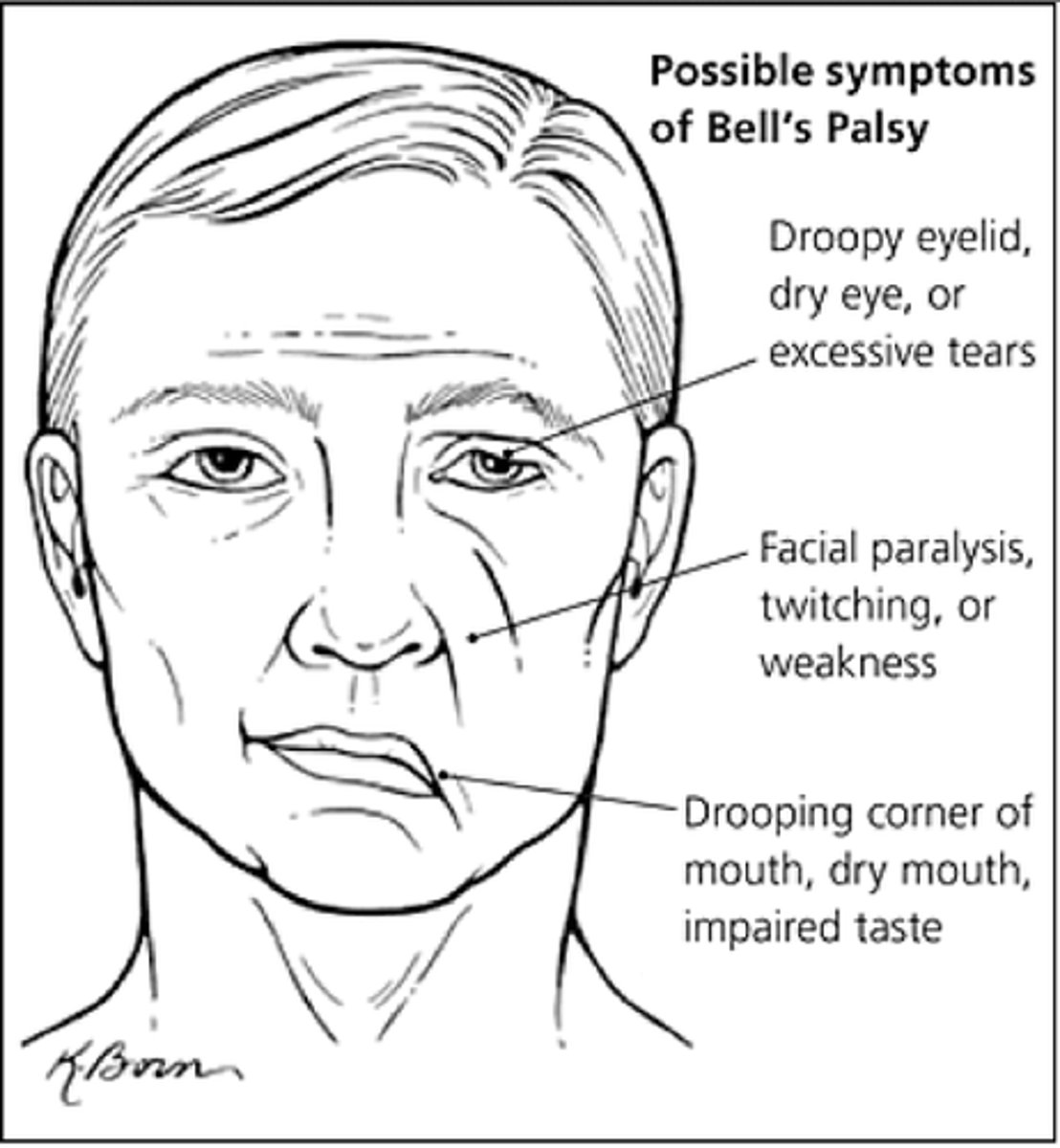
what is the key risk for the baby in forceps delivery?
facial nerve palsy
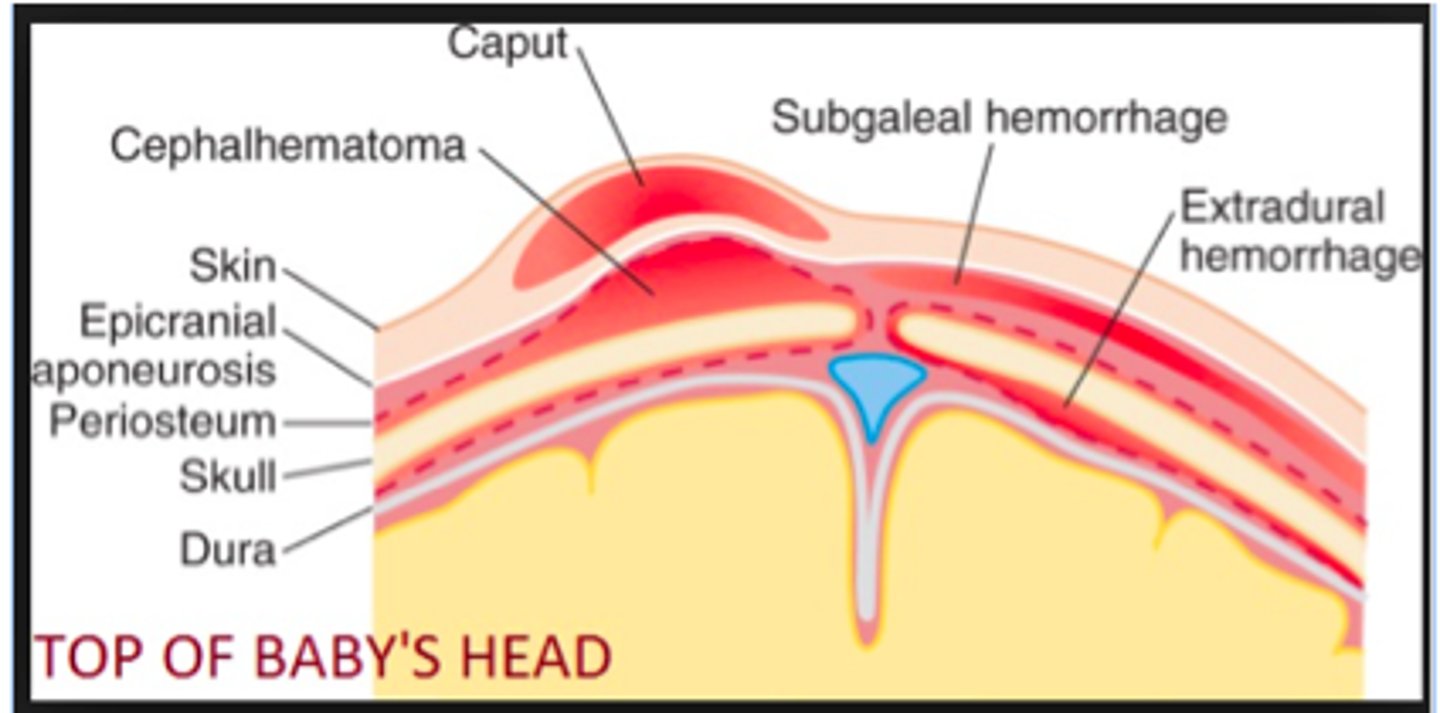
what are the more rare, serious risks to the baby?
- subgaleal haemorrhage - most serious
- intracranial haemorrhage
- skull fracture
- spinal cord injury
what is a subgaleal haemorrhage?
bleeding between the epicranial aponeurosis of the scalp and the periosteum
what is a ventouse?
suction cup on a cord
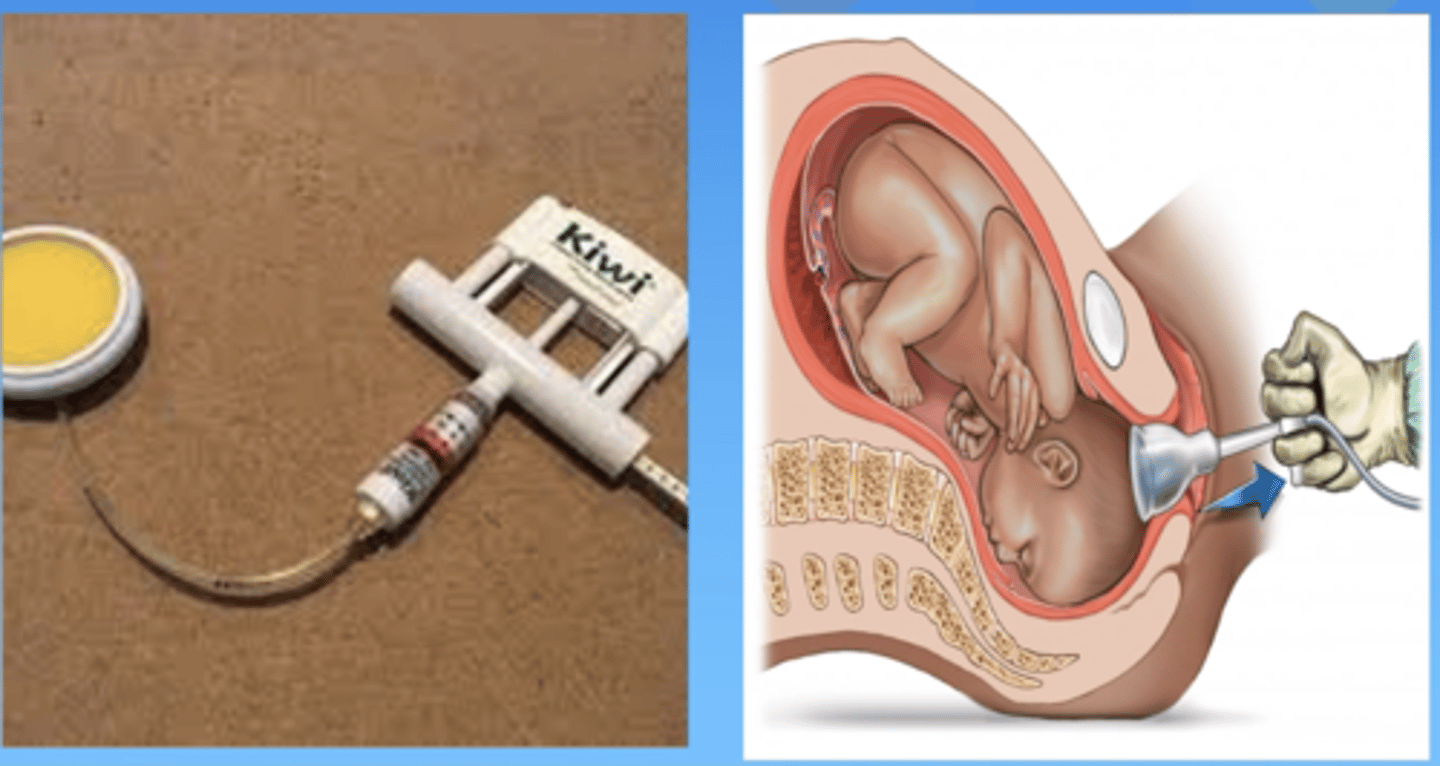
how does a ventouse work?
suction cup attaches to baby's head and the doctor/midwife carefully pulls cord to help baby our
what are forceps?
two large metal tongs that can attach together
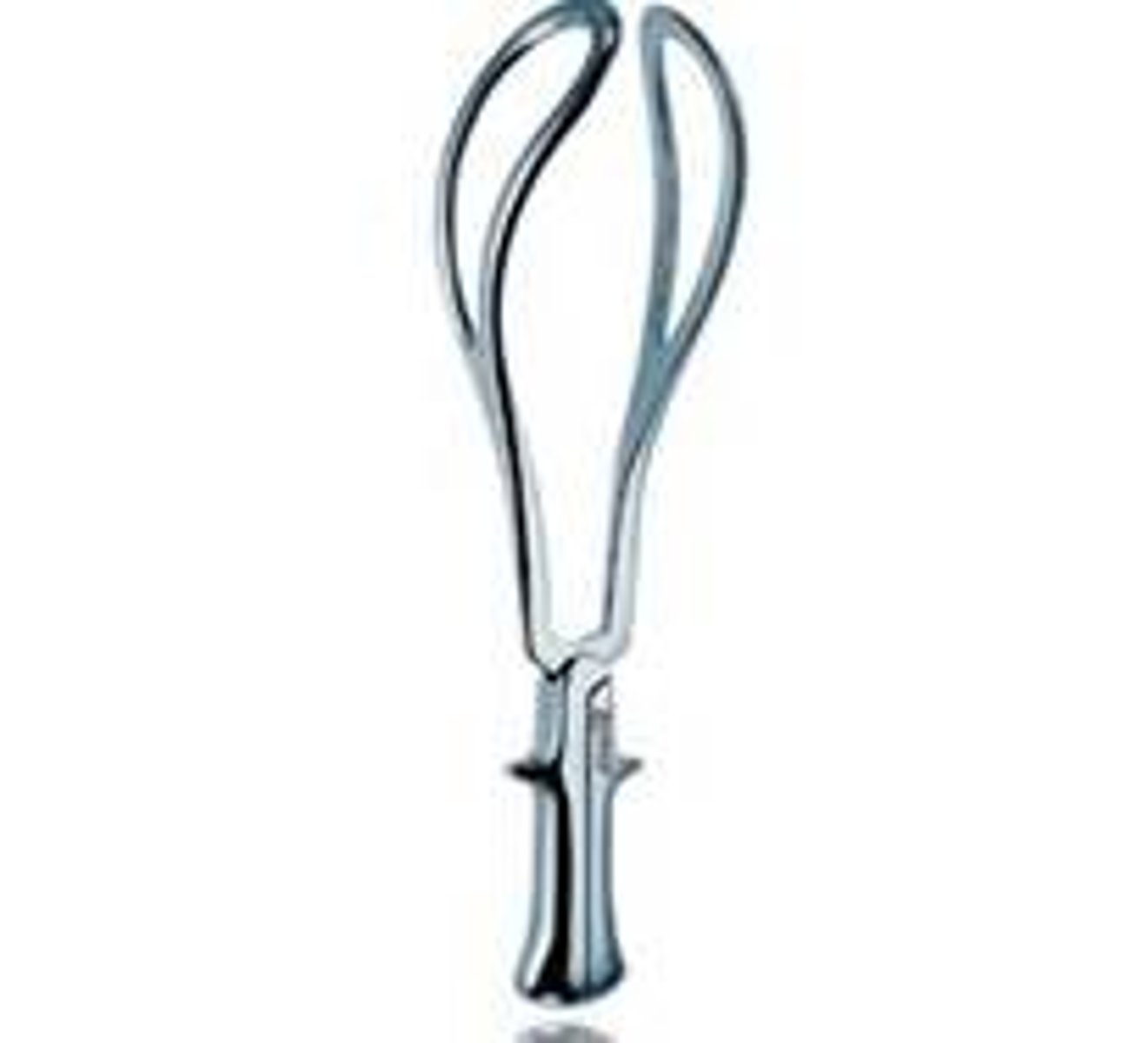
what are the two curves of the forceps?
cephalic curve - to match the baby's head
maternal curve - to match the vaginal canal
how do forceps work?
place one in, and then the other, attach them and they go round the babies head to grip and, so they can gently pull the baby out
what are the two main nerves that may be injured for the mother?
femoral and obturator
how long do the nerve injuries usually last?
6-8 weeks
what are the signs of femoral nerve injury?
- weak flexion of hip
- weak extension of knee
- loss of patella reflex
what are the signs of obturator nerve injury?
- weakness of hip adduction and rotation
- numbness of medial thigh
what is the next step of management if there is no foetal descent after 3 "pulls" with an instrument?
C-section