Biology: Midterm Study Guide
1/244
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
245 Terms
Organism
any living thing that carries out the major characteristics of life
What are the 8 characteristics of life
1. Grow + Develop
2. Genetic Code
3. Reproduce
4. Respond to Stimuli
5. Organized
6. Use + Make Energy
7. Cells
8. Homeostasis
Grow
living things increase in size by increasing size + number of cells
Develop
process that involves changes, maturation, + specialization of cells
What is the difference between grow + develop
Grow --> increase numbers + sizes of cells in the body
Develop --> cells that mature to meet the needs of that organism
What is an example of grow + develop (1 for each)
Grow -->
Develop --> a butterfly (stages of life until it becomes a butterfly)
Describe DNA
molecule that carries genetic info for the development + functioning of an organism
What are the 2 types of reproduction
1. asexual
2. sexual
Asexual
reproduction involving ONE parent producing GENETICALLY IDENTICAL offspring
Sexual
reproduction involving two parents contributing genetic info to create UNIQUE OFFSPRING
Explain the differences between asexual + sexual
Asexual --> one parent = clone
Sexual --> two parents = unique offspring
Respond to Stimuli
how an organism responds to the environment to help it survive + adapt
What are the 5 levels of organization (smallest to biggest)
1. cells
2. tissues
3. organs
4. organ systems
5. organisms
True or False: Cells are made up of organisms
False --> cells are the smallest level + all added together to create organisms
What are the 2 types of use + make energy
1. photosynthesis
2. cellular respiration
Photosynthesis
process plants use to make energy
Celluar Respiration
chemical process used by people to take oxygen + glucose
What is the difference between photosynthesis + cellular respiration
Photosynthesis --> plants use sun to make energy
Cellular Respiration --> humans eat things to make energy
What are the four types of cells
1. unicellular
2. multicellular
3. prokaryote
4. eularyote
Unicellular
one-celled organism (example: bacteria)
Multicellular
more than one cell (example: humans)
Prokaryote
has no nucleus + membrane-bound (example: bacteria)
Eukaryote
has true nucleus + membrane-bound organelles (example: all other organisms)
Homeostasis
process where organisms maintain a relatively stable internal environment
Give 2 examples of homeostasis
1. hot --> sweating
2. cold --> shivering
What is the difference between homeostasis + respond to stimuli
Homeostasis --> internal
Respond to Stimuli --> external
What are 3 other essentials for life
1. water
2. proper internal temp/pressure
3. oxygen
Living (Hint: 3 things)
1. show all 8 characteristics of life
2. living things = organisms
3. part of a living organism (ex: arm/leaves = alive for a short period of time after detachment)
Give 3 examples of living
1. plants
2. animals
3. humans
Dormant (Hint: 2 things)
1. don't show characteristics of life until placed in the right environment
2. alive but NOT ACTIVE
Give 3 examples of dormant
1. seeds
2. fertilized eggs
3. yeast
Dead (Hint: 1 thing)
1. alive at one time but no longer
Give 3 examples of dead
1. animals have died
2. leaves fallen off trees
3. snake sheds dead skin
Nonliving (Hint: 2 things)
1. have NEVER been alive
2. anything process = nonliving
Give 3 examples of nonliving
1. fire
2. rocks
3. wind
Scientific Method
logical + systematic approach/process to problem solving + organized way of using evidence to learn about the natural world
What are the 7 steps of the Scientific Method
1. Problem/Question
2. Observatio/Research
3. Formulate Hypothesis
4. Experiment
5. Collect + Analyze Results
6. Conclusion
7. Communicate Results
Problem/Question (Hint: 2 things)
1. develop testable question/problem
2. must be solved through experimentation
Observation/Research (Hint: 1 thing)
1. make observations/research topic
Formulate Hypothesis (Hint: 2 things)
1. predict possible answer/explanation to the problem/question
2. If the independent variable, then the dependent variable
Independent Variable
factor intentionally changed by the experimenter
Dependent Variable
variable affected by a change in the independent variable (variable that's measured)
Experiment (Hint: 2 things)
1. devleop + follow procedure (includes detailed material list)
2. outcome must be measurable (quantifiable)
Control Group
serves as standard of comparison (no treatment + normal conditions
Constants
variables that remained the same throughout the whole experiment
Explain 2 types of data
1. qualitative data --> color + texture
2. quantitative data -- numerical data
Collect + Analyze Data (Hint: 1 thing)
1. include tables, graphs, + pictures
Conclusion (Hint: 2 things)
1. summary based on evidence or facts
2. must include 5 things
What are the 5 things conclusion musty have
1. restate the hypothesis
2. was it correct or incorrect
3. bring in relevant data
4. mention any errors
5. recommendation for further study/possible improvements to the procedure
Communicate Results (Hint: 2 things)
1. present to peers
2. peer review
Peer Review
a review by people with similar professional qualifications (ensures method is valid + results well supported by relevant data)
Scientific Law (Hint: 3 things)
1. description of observation NOT AN EXPLINATION
2. usually mathematical expression
3. laws don't become theories
Scientific Theory
well-tested explanation that unifies a wide range of observations + a hypothesis that allows scientists to make predictions
Scientific Models
simple representation of a complex model (helps scientists get a better understanding)
Traditional Classification
classifying organisms based on visible traits
Taxonomy
1. Science of classification
2. classifies by observable traits
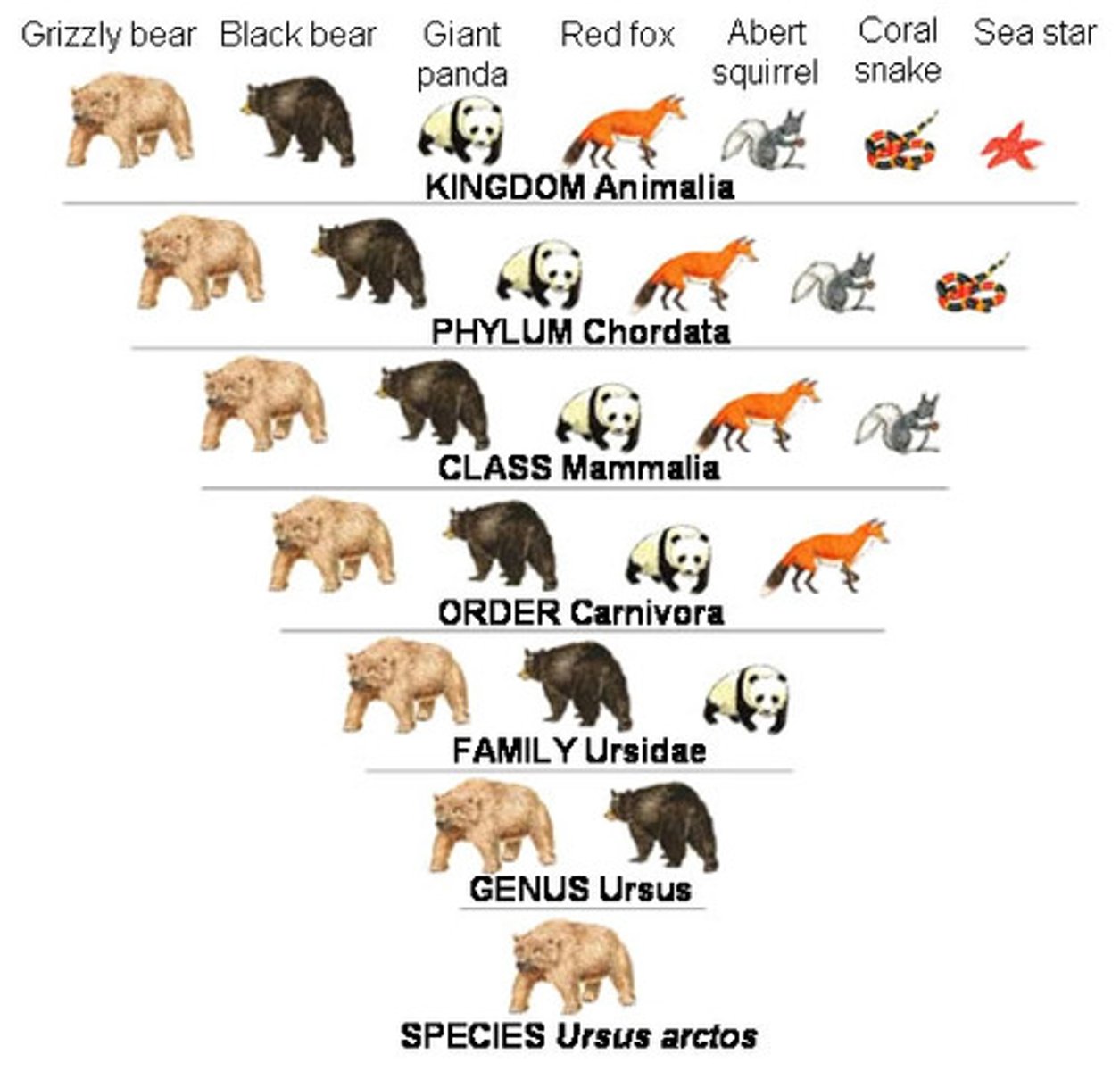
Charles Linnaeus
father of taxonomy
True or False: For traditional classification, organisms are based on geneitc code
False --> traditional classification is based on physical features
Dichotomous Key (Hint: 2 things)
1. used to identify organisms
2. series of either/or questions (about visible traits)
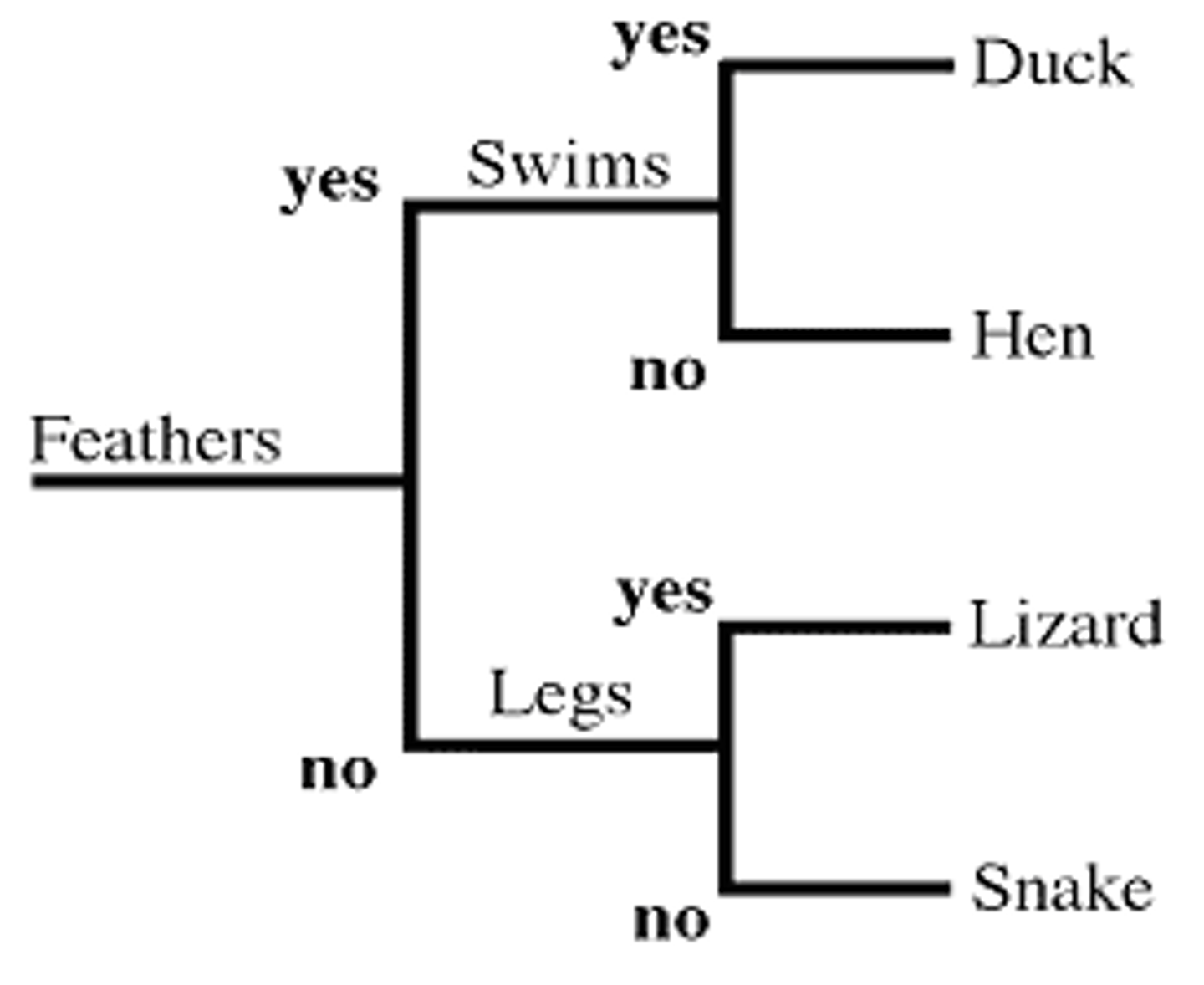
What are the names used in a dichotomous key (Hint: 2 names)
1. common name
1. scientific name
True or False: Using the common name in a dichotomous key is better than using the scientific name
False --> Using the scientific name is better because organisms could have different names around the world
What are the parts of the scientific name (Hint: 2 things)
1. Genus
2. species
Binomial Nomenclature
2-part scientific name (based on genus + species)

What is the format of Binomial Nomenclature (Hint: 3 things)
1. Genus (G capitalized)
2. species (s lowercase)
3. everything is italicized
Taxa
group/level of organization where organisms are classified
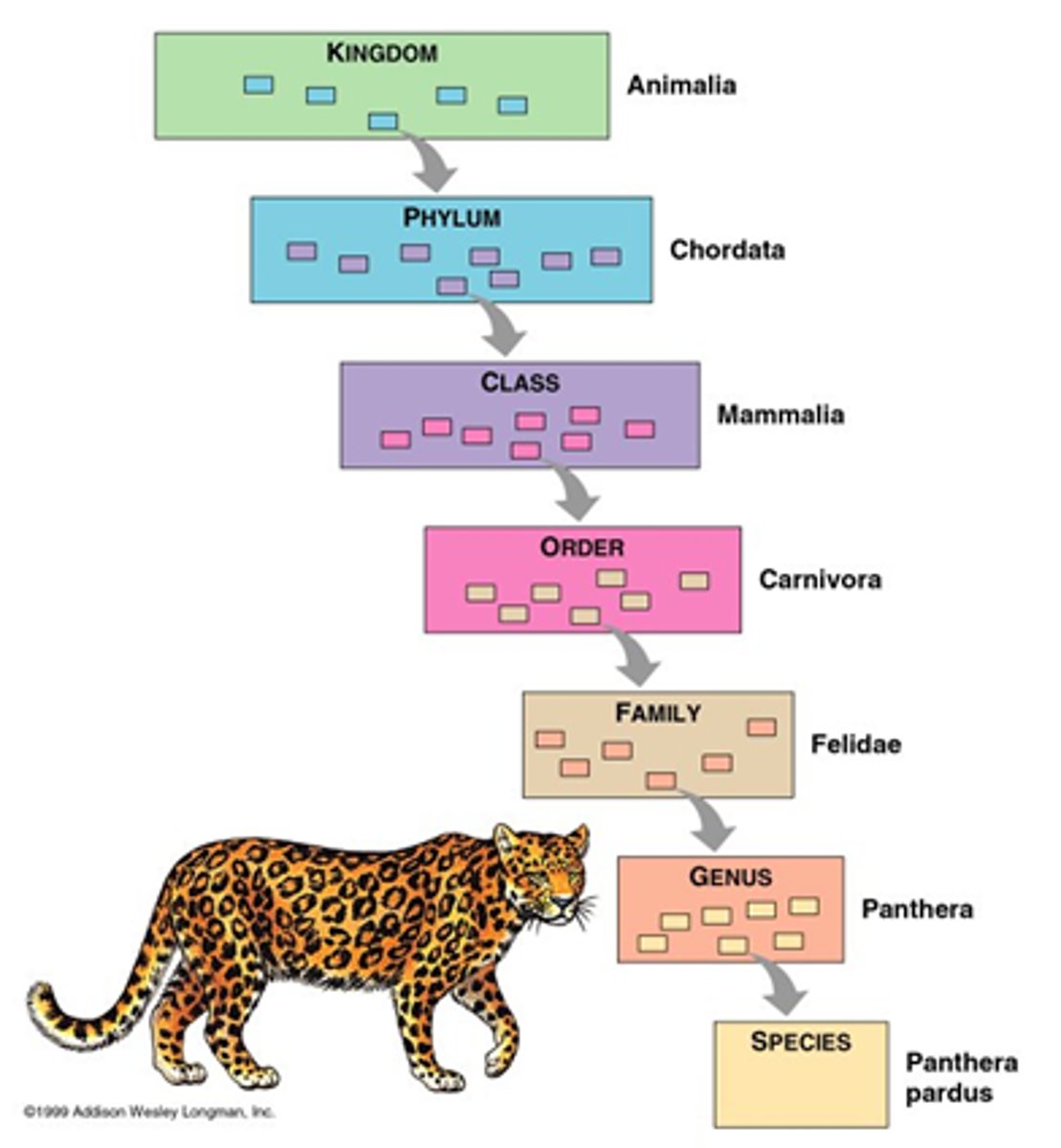
What are the taxa levels (general --> specific)
1. Domain
2. Kingdom
3. Phylum
4. Class
5. Order
6. Family
7. Genus
8. Species
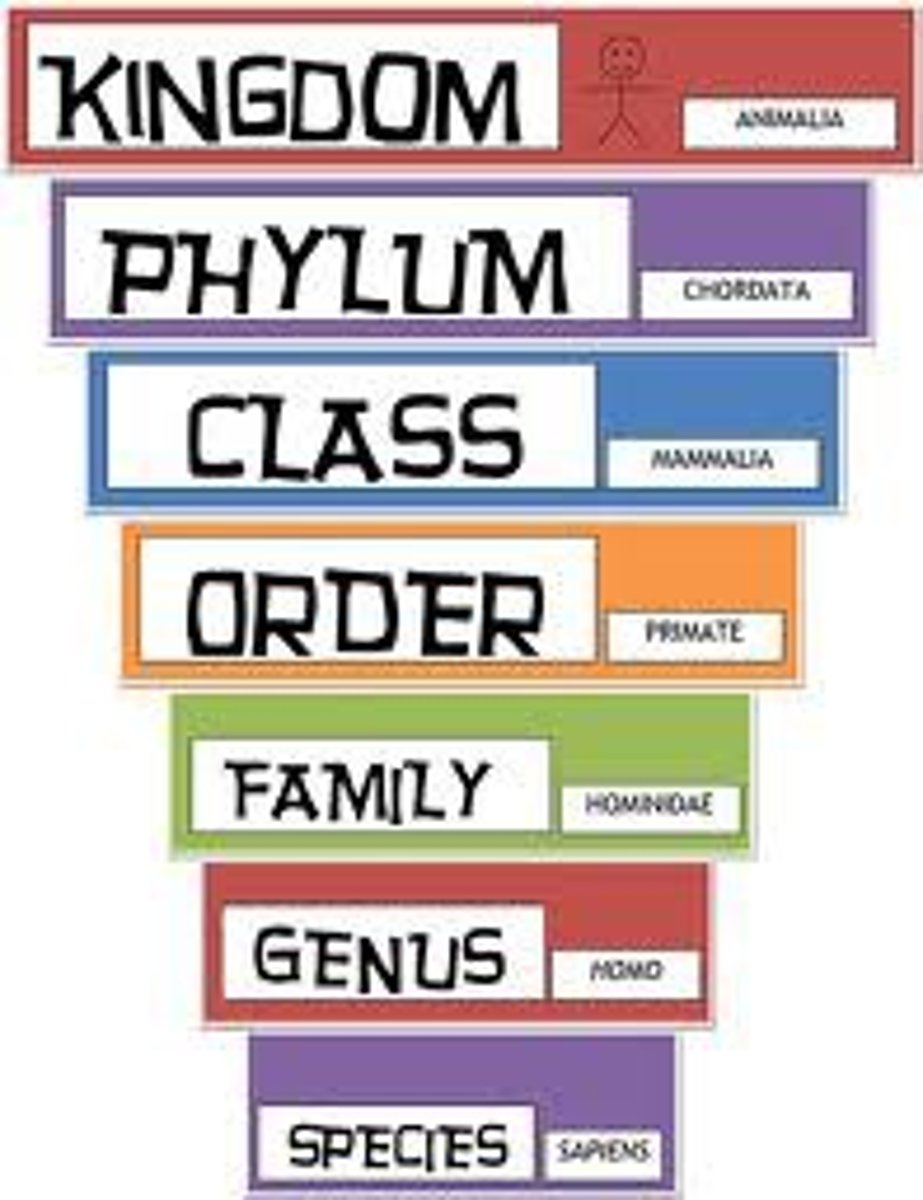
How to tell if organisms are related (using their names)
by looking to see if they have similar genus or species (if they have similar species, more related compared to having similar genuses)
How to tell if organisms are related (using a diagram)
the closer they are together on the diagram
What are the pros and cons of traditional classification
Pro = easy to use --> see if they have the same visible traits
Con = inaccurate --> doesn't accurately show evolutionary history
When can species reproduce viable offspring
species are from the same biological species
Viable Offspring (Hint: 2 things)
offspring that can:
1. survive on their own
2. reproduce successfully
(examples: lions or tigers)
Nonviable Offspring (Hint: 2 things)
offspring that CAN'T:
1. survive on their own
2. reproduce
(example: ligers --> lions + tigers)
Modern Classification
arrangement of organisms into orderly groups based on their similarities and evolutionary relationships
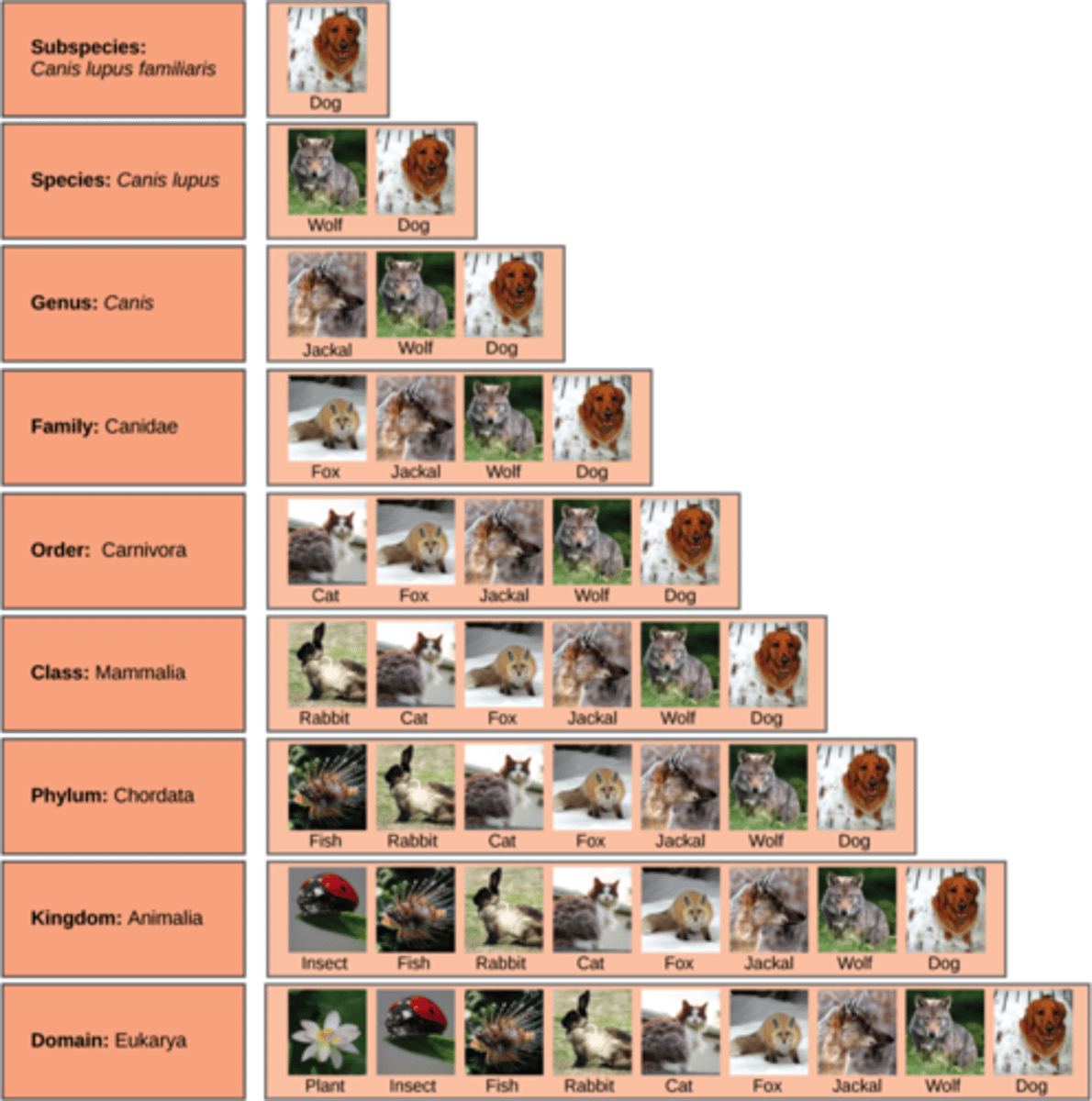
What are the pros and cons of modern classification
Pros = more accurate + shows how close different organisms are related
Cons = more time-consuming
What is the difference between traditional and modern classification
Traditional --> based on visible traits
Modern --> uses DNA, evolutionary relationships, + common ancestry
What are modern classifications based on + explain them (Hint: 2 things)
1. Fossils --> remains/evidence of any organism that once lived on earth
2. DNA --> unique genetic code/set of instructions explaining how something is made up
What are the 2 types of fossils
1. Body Fossils --> remains of dead organisms/imprint remains made
2. Trace Fossils --> what organisms left behind
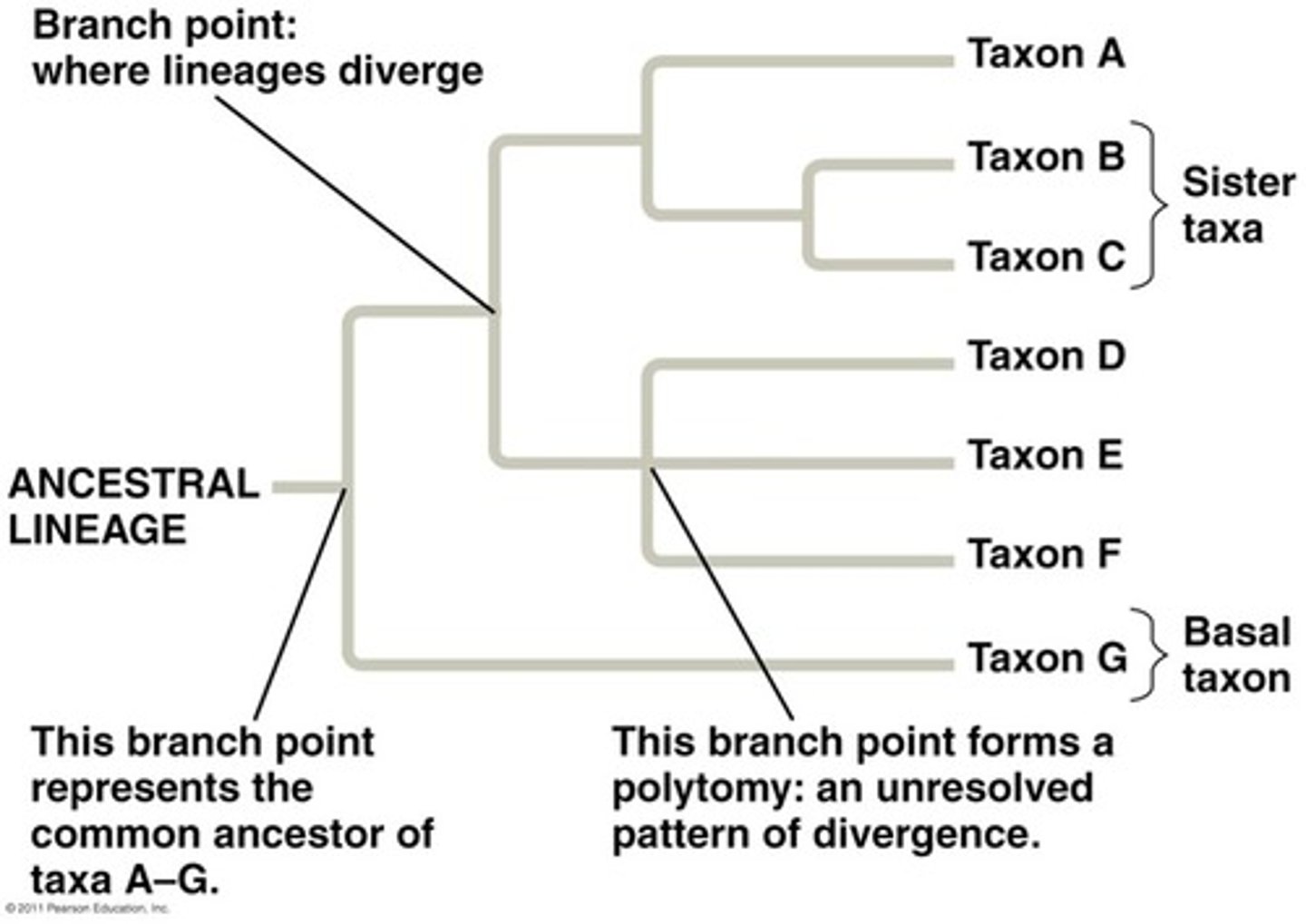
Phylogeny
evolutionary history of species/group of related species
Cladistics
analysis of evolutionary relationships
Cladogram
Diagram --> shows evolutionary relationships among group of organisms
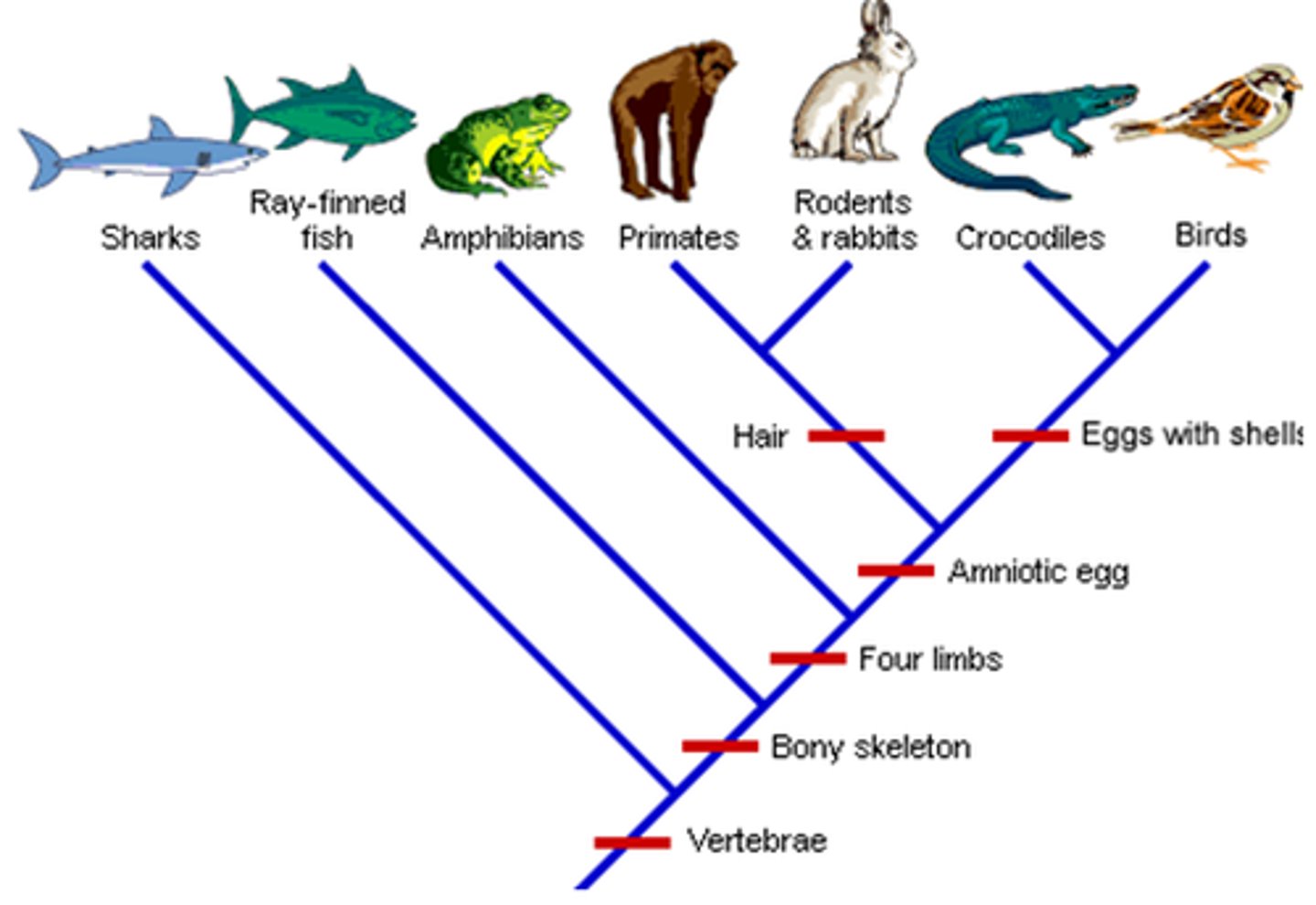
Clade
A group of species w/ single common ancestor
Phylogenetic Tree
family tree --> shows evolutionary relationships thought to exist among groups of organisms
Common Ancestor
first trait all descendants shared (based on fossils/DNA)
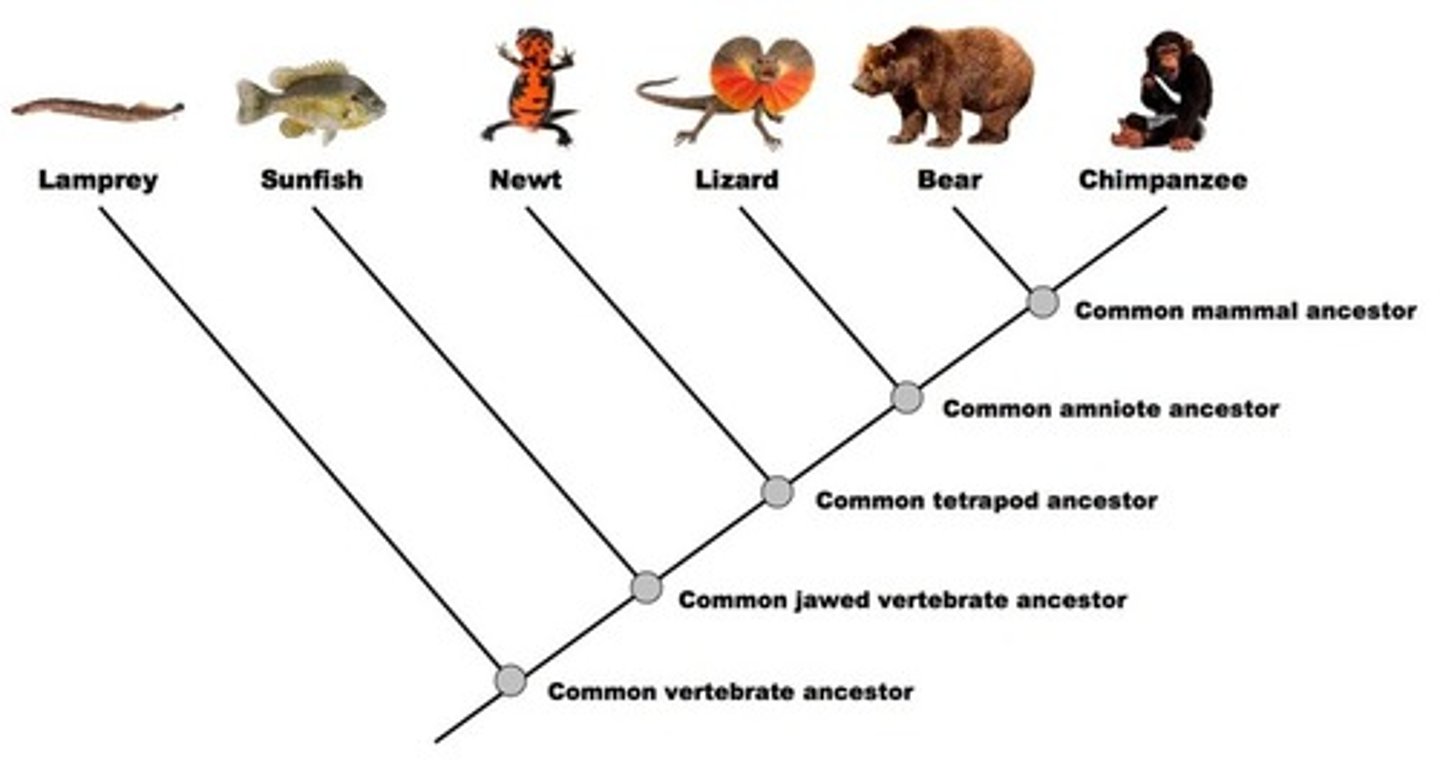
Lineages
Lines --> showing what each trait organism had leading up to the species
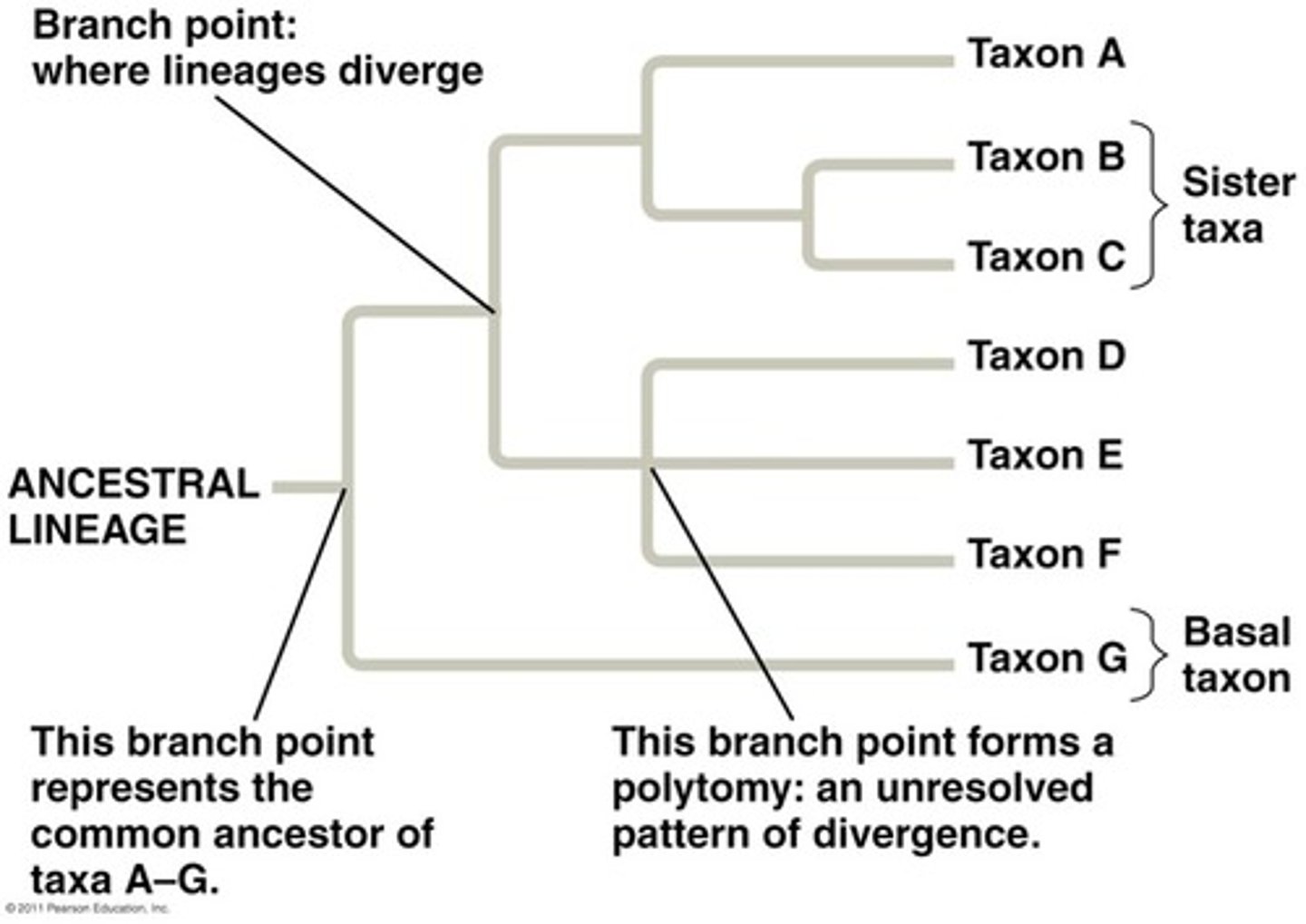
Speciation/Nodes
where lineage splits (result in separation)

Derived Traits
trait present in organisms allowed to evolve from last common ancestor (more than 2 species share trait)
Shared Traits
trait where only 2 species have in common
What is the difference between derived + shared traits
Derived --> more than 2 species have same trait (on cladogram)
Shared --> ONLY 2 species have same trait (on cladogram)
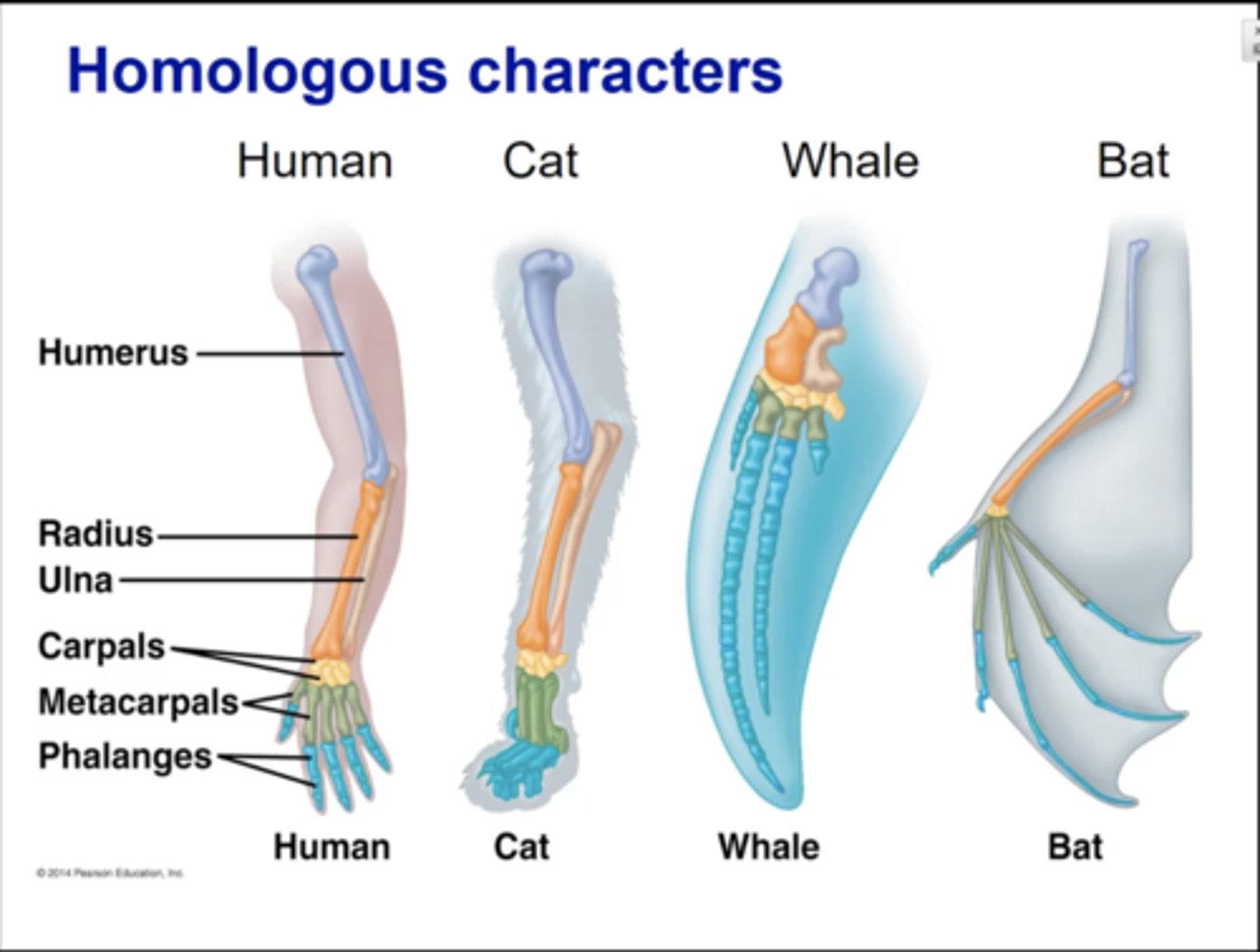
Homologous Characters (Hint: 2 things)
1. traits found in different organisms that are similar
2. inherited from common ancestor w/ same trait
Analogous Characters (Hint: 2 things)
1. similar functions (have different structures)
2. developed traits to help them live
What is the difference between homologous and analogous characters
Homologous --> common trait + inherited from common ancestor
Analogous --> similar functions + not inherited from common ancestor
Domain
most general classification
What are the 3 domains
1. Bacteria
2. Archaea
3. Eukaryota
Kingdom
Second largest group in taxonomic hierarchy (more specific than domain)
What are the 6 kingdoms
1. Archaebacteria
2. Eubacteria
3. Protista
4. Fungi
5. Plantae
6. Animalia
Which kingdoms go under the domain: Bacteria
1. Eubacteria
Which kingdoms go under the domain: Archea
1. Archeabacteria
Which kingdoms go under the domain: Eukarya
1. Protista
2. Fungi
3. Plantae
4. Animalia
Prokaryotic
NO nuclues
Eukaryotic
HAS nucleus