Taxation: part 2 - Week 6
1/13
Earn XP
Description and Tags
In context of resource use
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
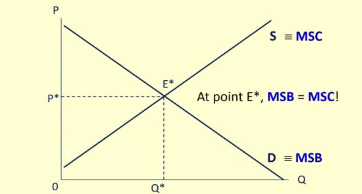
Allocative efficiency
Is achieved when we push the resource use to the point where the MSB is equal to the MSC
Allocatively efficient
At point E*, MSB = MSC (Marginal Social Benefit = Marginal Social Cost. The marginal benefit of resources is equal to the resource cost of resources to society.
Allocatively inefficient
At the new market equilibrium with the unit tax (E1), MSC < MSB = not allocatively efficient. This is because there is an additional cost in producing the good, however at the expense of providing goods exactly at that tax per unit
Subsidy
For every unit purchased, the government pays s£ per unit. Requires a budget on how a government can finance this
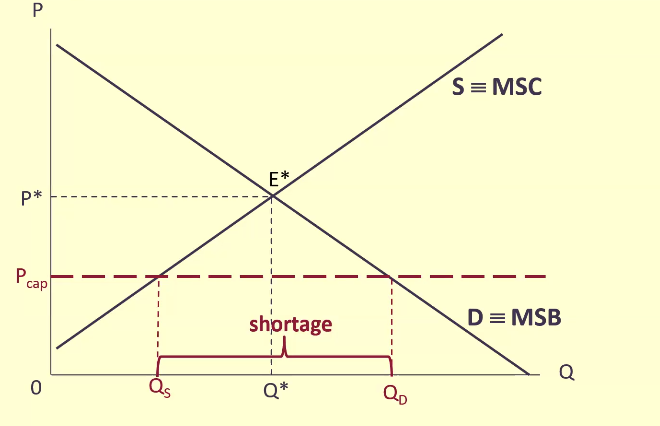
Price ceiling
Price cap. Makes a product more affordable to consumers
Shortage
Quantity demanded > Quantity supplied. Occurs in a price ceiling
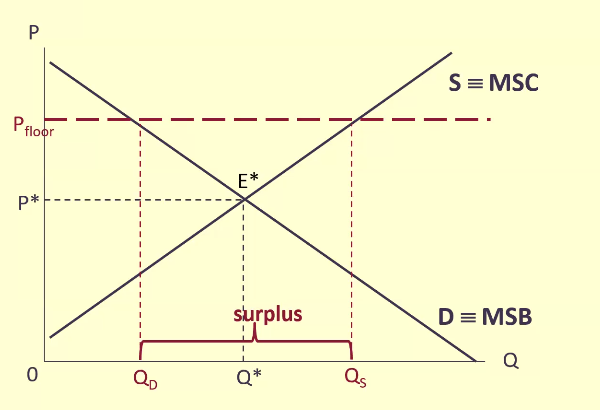
Price floor
Is set above what the market would deliver; the equilibrium price
Surplus
When excess occurs, we observe downward pressure on price.
MPC
Marginal partial cost
MEC
Marginal external cost
MSC
MPC + MEC
Market failure
Positive or negative externalities mean market failure. In a sense that, we don’t anticipate the market would deliver E*, it will deliver something else
MSC
Marginal Social Cost. The cost to society in order to produce a good
MSB
Marginal Social Benefit. The benefit to society in order to produce a good