Ecology Week 2
1/201
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
202 Terms
Some individuals contribute more offspring to next generation than others.
The mechanism of evolution
Darwin originally used the phrase descent with modification.
Natural Selection
Apparent good fit to environment.
Match between organisms and their environment
Result of Natural selection
adaptation
Replace immutability of species with evolution
change is standard/normal process
Darwin and Wallace
variation observed was simply the imperfect copies of the transcendental ideal form of the essence
ex. triangles
greek essentialism
God is content, unchanging, perfect, no extinction
implies imperfection
plentitude
universe is not static and is changing
reformation ideas
Tyco Brahe 1572
birth of a star
Earth moved around the sun (helopcentrism)
Copernicus
Sun spots and craters on the moon
Galileo
Volcanoes, earthquakes, sedimentary rocks, fossils
evidence for change
Successive catastrophes (great floods)
catastrophism
slow change in small steps
gradualism
Uniformitarianism
James Hutton
Physical processes at present same as in the past; land forms produced by same physical processes
Uniformitarianism
Principle of geology, changes in earth gradually accepted.
Charles Lyell 1830
Internal forces and inheritance of acquired traits
Lamarcks Mechanism
Unknown internal mechanism causes differences between parent and offspring
Internal forces
Use of disuse of trait alters trait through lifetime, which is then passed to offspring
Inheritance of acquired traits
Galapagos finches - looked like they were related, bills vary in size but they are one species.
John Gould 1837
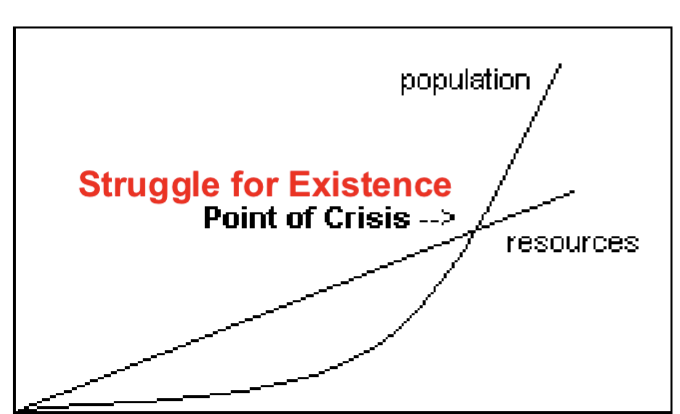
Essay on Population Growth
Malthus
Two major points made by Darwin
descent with modification and mechanism for the evolutionary process
Darwins Ideas
evolution is gradual, natural selection (both accepted)
evolution is not progressive (mixed)
Objections to Darwins theories
heredity, gaps between form in nature, complex organs
The genesis of species
irreducible complexity (wing, eye, flagellum)
(not reasonable; example the eye needs all parts to work)
Mivart 1871
Blending inheritance (genetic principles)
heredity
separation of germ cells and somatic cells- no inheritance of environmentally induced acquired characters
Weissman
Necessary mechanism of heredity- No blending
Mendel
The two groups of scientists who were fighting in the schools of thought 1900-1920
Mendelians and biometricians
Discontinuous variation
De Vries and Bateson
Mendelians
Continuous Variation
Weldon and Pearson
Biometricians
Natural selection could work on all observed variation and Mendels Laws
Evolution = heritable variation x selection
Neo-darwinism
Who plays important roles in Neo Darwinism?
Fisher, Haldane, Wright
Macromutations do not occur but a lot of little micro mutations do
Ernst Mayr 1942
Systematists
Fossil evidence was compatible with the population genetic mechanisms of Neodarwinism
George Gaylord Simpson 1944
Paleontologists
Explains diversity and unity of life
All organisms are related through descent from a
common ancestor that lived in the pastImplies that relationships among organisms can be
represented by a branching tre
Descent with modification
1. (More offspring are produced
than survive)
2. Variation among individuals
3. Inheritance of variation
4. Individuals with favorable characteristics are
more likely to survive and reproduce
Differential survival and reproduction related
to this variation–Selection
Requirements for evolution by natural selection
compact structures consisting of long strands of DNA wound around proteins
chromosomes
a single trait is affected by several genes; enables phenotypes to span a range of values in a population
ex. human body height
polygenic
Phenotype distributions are ___ shaped graphically
bell-shaped
a single gene affects multiple traits
Example:
The frizzle gene in chickens causes feathers to curl outward, but also causes other
variations including faster metabolism, slower digestion, and less frequent egg
laying.
pleiotropy
the expression of one gene is controlled by another gene
Example:
Mouse hair color is determined by a gene that codes for black or brown pigments.
A second gene determines whether the hair will have any pigments at all.
epistasis
when two alleles both contribute to the phenotype (e.g., flower color in snapdragons)
codominant
Collection of alleles from all individuals in a population
gene pool
the process of making haploid gametes in which the combination of alleles that are placed into a given gamete could be any combination of those possessed by the diploid parent
random assortment
a random change in the sequence of nucleotides in regions of DNA that controls the expression of a gene.
mutation
silent mutations are called ___
no detectable effect
synonymous
An example of a mutation causing a disease that is resistant to antibacterial drugs.
MDR-TB
the reshuffling of genes that can occur as DNA is copied during meiosis and chromosomes exchange genetic material.
helps the immune system rapidly evolve
Recombination
During meiosis, pairs of homologous chromosomes (one from each parent) can exchange DNA resulting in____
can also occur between nonhomologous chromosomes
crossing over
change in allele frequency over time
evolution
Mutation
Migration
Genetic Drift
Selection (Natural selection)
Selection (Sexual selection or non-random mating)
mechanisms of evolution
a process that occurs when genetic variation is lost due
to random variation in mating, mortality, fecundity, and inheritance
Random changes
Genetic drift
a reduction of genetic diversity in a population due to a large reduction in population size (ex. from loss of food)
can prevent a population from adapting to future environmental changes, such as emergent disease.
ex.In Illinois, the population of greater prairie chickens declined from 12 million to 72
birds after the 1960’
bottleneck effect
when a small number of individuals leave a large population to colonize a new area and bring with them only a small amount of genetic variation.
can cause additional reductions in genetic variation.
ex. water hyacinth from South America, A single genotype dominates 75% of the
invasive populations, and 80% of these populations are composed of a single genotype.
founder effect
the process by which certain phenotypes are favored to survive and reproduce over other phenotypes.
differential survival and reproduction, some survive more than others
selection
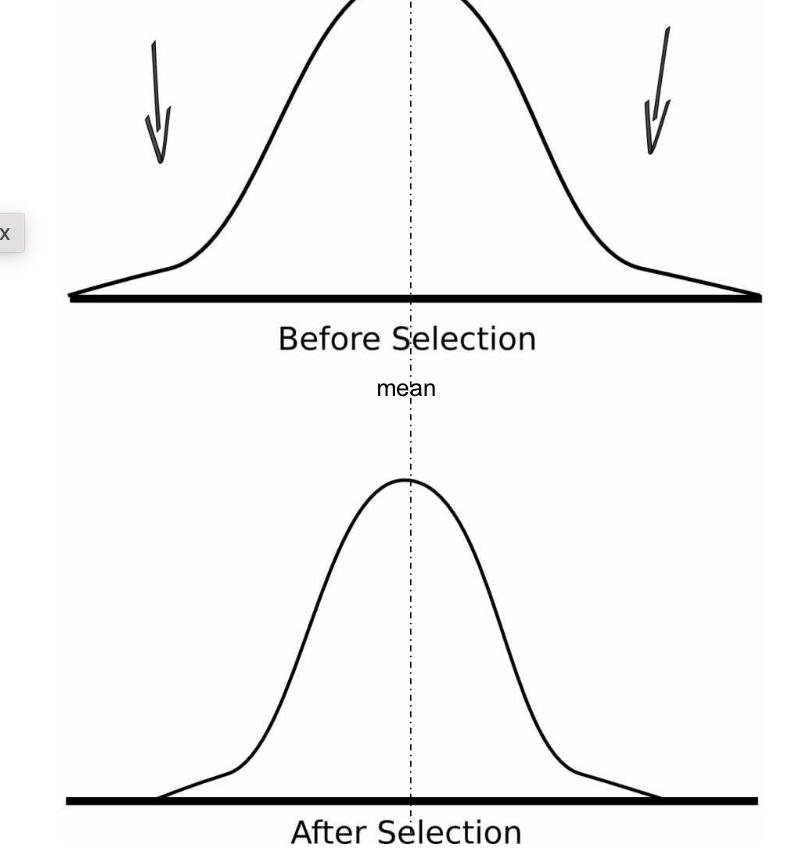
when individuals with intermediate phenotypes have higher survival and reproductive success than those with extreme phenotypes.
removes harmful genetic variation, generates little evolutionary change, occurs when environment is relatively unchanging.
progeny has more narrow distribution of phenotypes than parents
stabilizing selection
model used to quantify evolution
Hardy Weinberg Principle
assumes no evolution
null hypothesis
all copies of all alleles in a population
gene pool
What must be true if no evolution is occurring in assumption with Hardy Weinberg?
Assumes: only diploid organisms, species that reproduce sexually and uses a trait has two alleles.
No migration, mutation, or selection occurs.
Random mating occurs and there is a large population size
Hardy Weinberg equation for individuals
1=p2+2pq+q2
Hardy Weinberg equation for allele frequency
1=p+q
Genetic contribution to next generation
Fitness
Fitness compared to other individuals
relative fitness
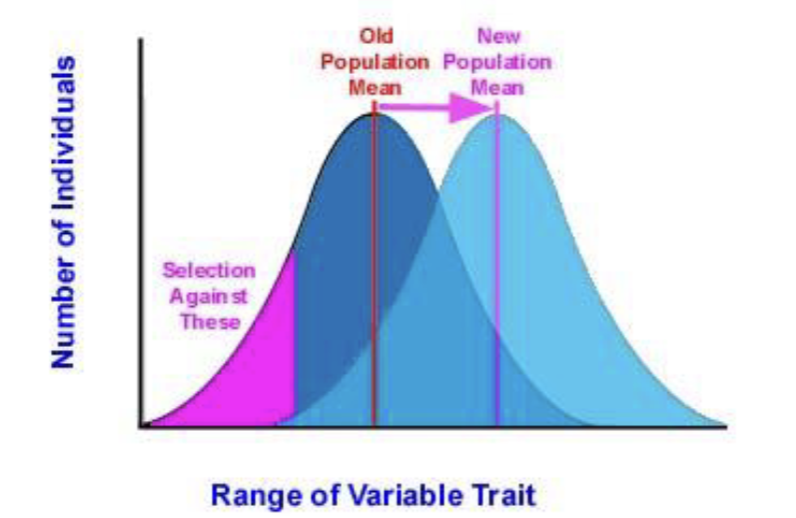
when individuals with extreme phenotypes experience higher fitness than the average population phenotype.
ex. drought on Galapagos islands increased production of large seeds, birds with large beaks able to consume large seeds - this trait was selected for : beak depth increased
directional selection
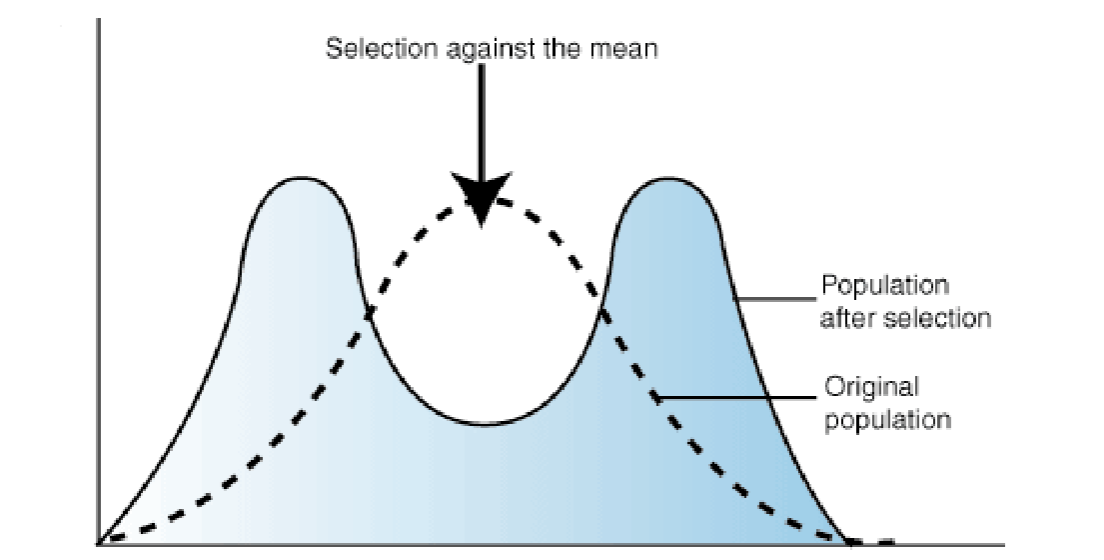
when individuals with either extreme phenotype experience higher fitness than individuals with an intermediate phenotype.
ex. mexican spadefoot toad can be carnivorous, omnivorous, or intermediate consumer
disruptive selection
the evolution of populations; affected by random processes and selection.
microevolution
Selection in which humans decide which individuals will breed; breeding
is done with a preconceived goal for the traits in the population (e.g., dogs, wild mustard).
artificial selection
favors trait combinations that provide higher fitness to an individual
May be multiple ways to improve fitness that are favored by natural selection
is an ecological process; individuals interact with their environment,
and traits that lead to greater fitness in an environment are passed on.Ex. Fish prefer to consume large prey (e.g., amphipods).
therefore small prey size is selected for
Natural Selection
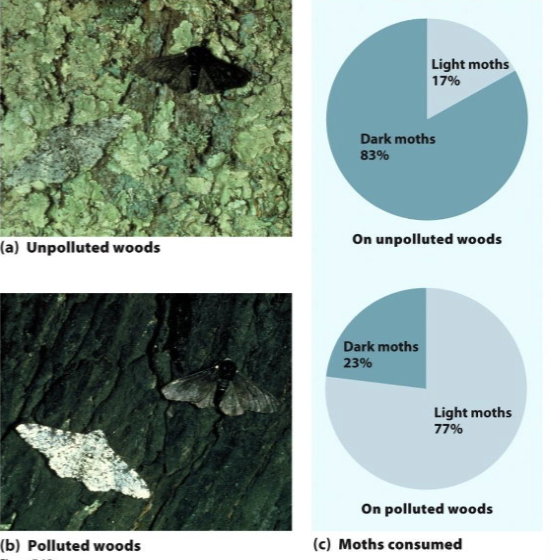
a phenomenon in which industrial activities cause habitats to become darker due to pollution; individuals possessing darker phenotypes are favored by selection.
*can be reversed
industrial melanism
evolution at higher levels of organization including species, genera, families, orders, and phyla.
macroevolution
the evolution of new species
speciation
hypothesized patterns of relatedness among different groups such as populations, species, or genera; depict which groups evolved from other groups.
Phylogenetic trees
the evolution of new species through the process of geographic isolation
*occurs when a single population is separated by a geographic event (formation of a river)
isolated populations have genetic drift and founder effects, evolving separately
Over time they cannot interbreed and they evolve into new species
allopatric speciation
the evolution of new species without geographic isolation
ex. Cichlid fish in Lake Tanganyika have evolved into 200 unique species from a single common ancestor
Speciation appears to have been facilitated by the presence of distinct habitats throughout the lake, with distinct types of food resources.
sympatric speciation
a species that contains three or more sets of chromosomes; can also give rise to sympatric speciation
arises when homologous chromosomes fail to separate during meiosis, producing diploid gametes. If a diploid egg is fertilized by a haploid sperm, a _______ will develop
unable to breed with a diploid and is genetically distinct from its parents
polyploid
frequency of homozygous dominant
p²
frequency of heterozygous
2pq
frequency of homozygous recessive
q²
Solving Hardy Weinberg Steps
What do you know? genotype or phenotype- equation 1, allele frequency- equation 2
What do you want to know? genotype or phenotype- equation1 allele frequency- equation 2
Solve using equations p/q are standard for dominant/ recessive
look up practice problem
http://www.k-state.edu/parasitology/biology198/hardwein.html
Seemingly good fit of the organism to the environment
adaptation
Water is resistant to changing states; helps prevent bodies of
water from freezing solid during winter
Dissolved compounds, such as salts, lowers freezing temperature.
High specific heat (energy required to raise temperature by 1°C).
thermal properties of water
at its highest density at 4°C.
ice is less dense than liquid so it floats .
density of water
Some body tissues are more dense than water (e.g., bone); some
are less dense (e.g., fats)
examples: fish have gas filled _____ that can equalize their density with that of the surrounding water
swim bladders
some algae can use ______ to help them float to the top of water which helps them capture sunlight to photosynthesize
droplets of oil as flotation devices
the thickness of a fluid that causes objects to encounter resistance as they move through it.
viscosity
water has a ____ viscosity
high
_______ reduce drag
streamlined bodies
organisms rely on drag for movement, high drag - the water moves them. This happens by
long-filamentous appendages
Aquatic organisms need variable amounts of essential elements,
such as ________to build organic compounds
CHONPS
Water is a powerful solvent (because it is _____) that is able to
dissolve many substances, which makes them accessible to
organisms
polar
When dissolved compounds precipitate out, ______ are formed
Example: Calcium carbonate (CaCO3)
precipitates out and forms limestone.
habitats
when acids are dissolved in water, the water becomes toxic which creates ______ which effects bodies of water and can kill organisms with high pH
acid rain
Water moves to equalize _____ concentrations in different
locations
solute
membranes that allow only particular molecules to pass through; reduces free movement of solutes
semipermeable membranes
movement of water across a semipermeable membrane
osmosis
the force with which a solution attracts water by osmosis
osmotic potiental
mechanisms organisms use to maintain a proper solute balance
osmoregulation
tissue solute concentrations are higher than surrounding water
hyperosmotic
tissue solute concentrations are lower than surrounding water.
hyposmotic