Gross Anatomy of Long Bones and axial skeleton
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Using a sectioned real bone or plastic model identify the following parts of a bone. You will not be able to see all the features listed below on the plastic bones
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
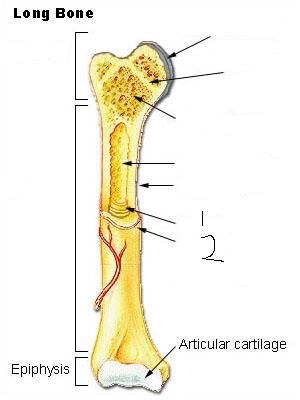
Epiphysis
Epiphyseal plate
Epiphyseal line
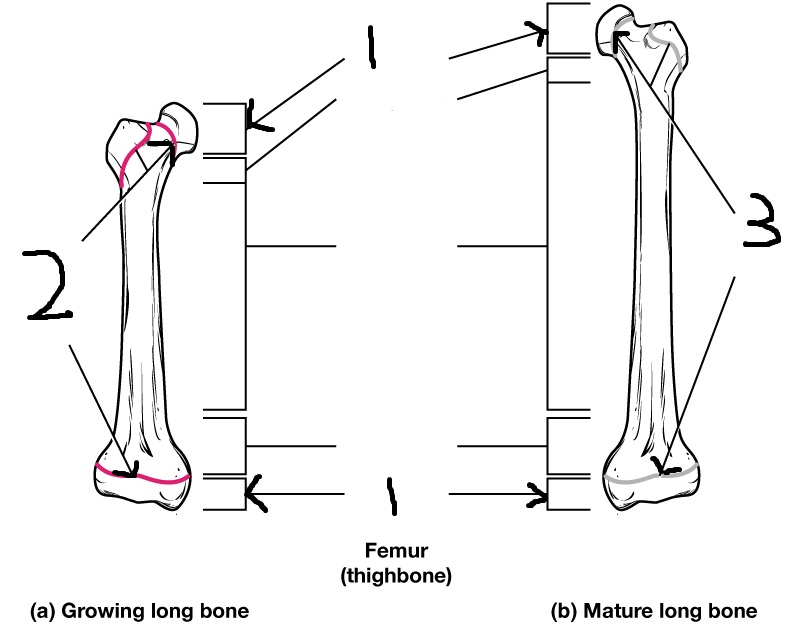
Diaphysis (often referred to as “shaft”)
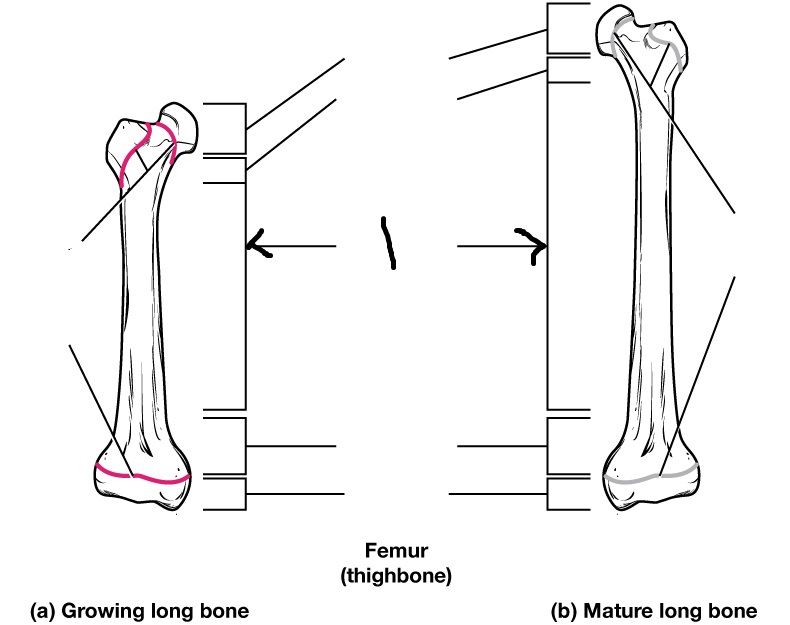
Medullary cavity
articular cartilage
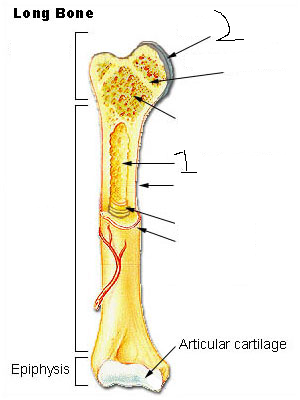
Endosteum
Periosteum
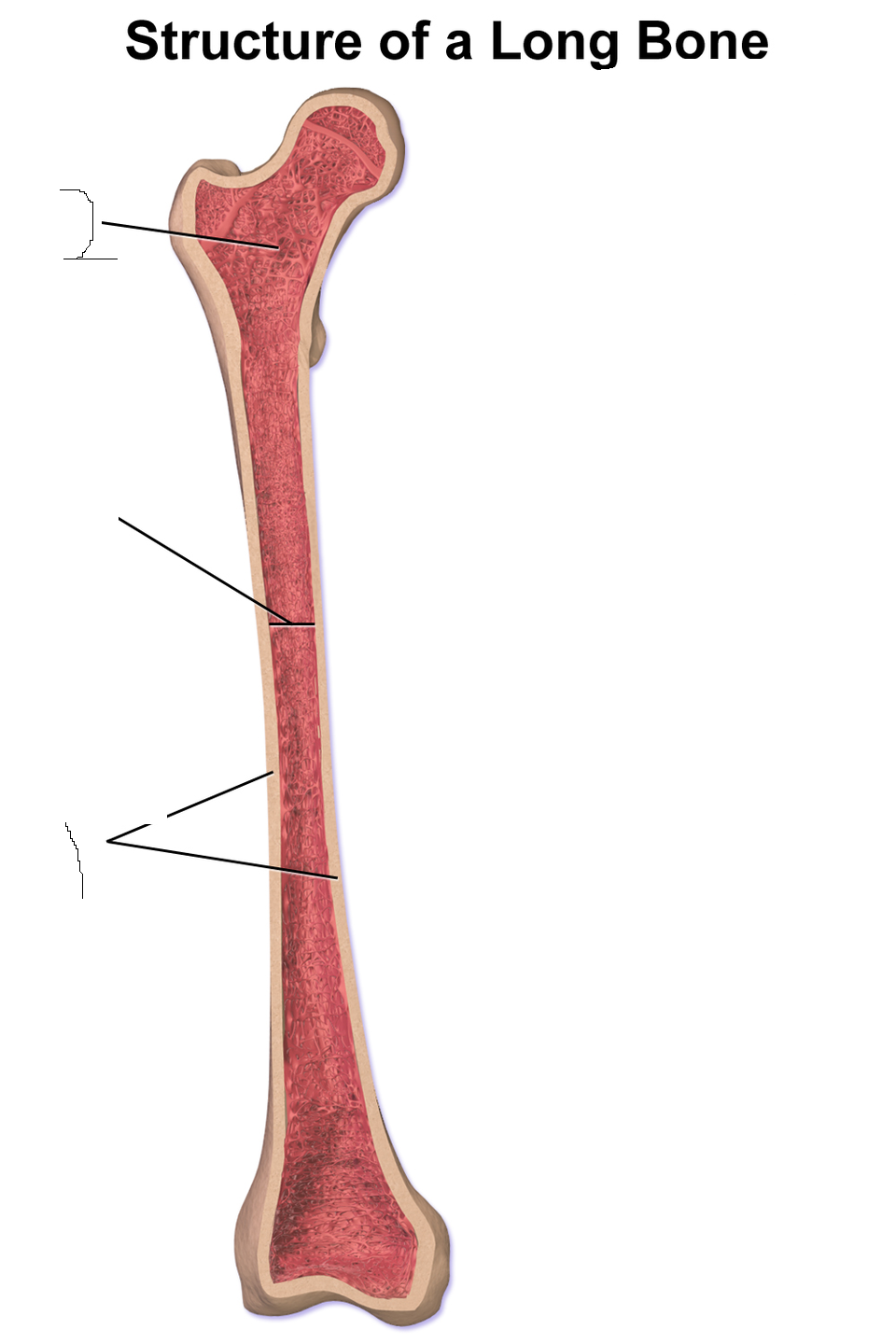
Compact bone
Spongy bone
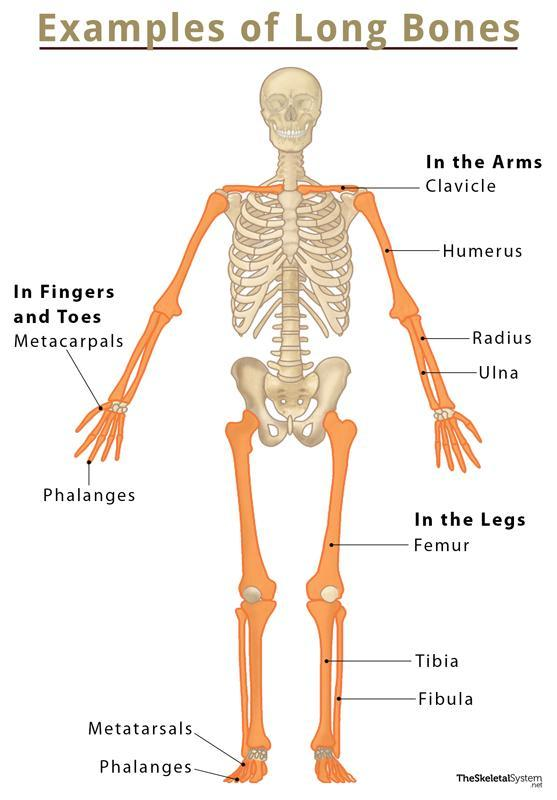
Long Bone
Longer than wide; cylindrical shaft (diaphysis) with two ends (epiphyses). Examples: humerus, radius, femur, tibia
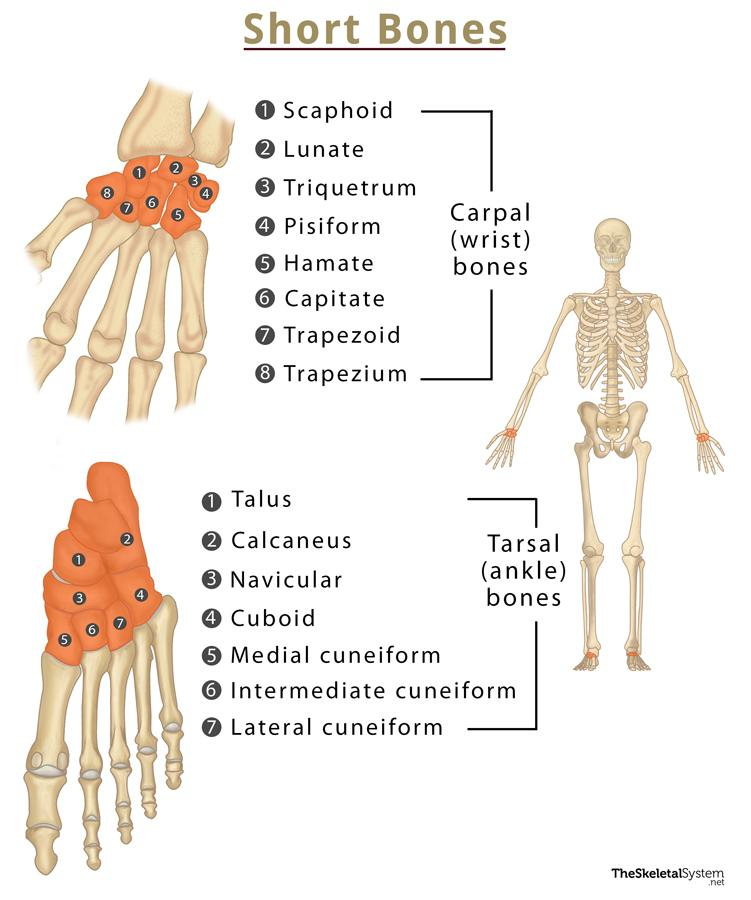
short Bone
Small, cube-shaped; roughly equal length, width, and thickness. Provide stability with limited movement.
Key Examples
Examples: carpals (wrist), tarsals (ankle).
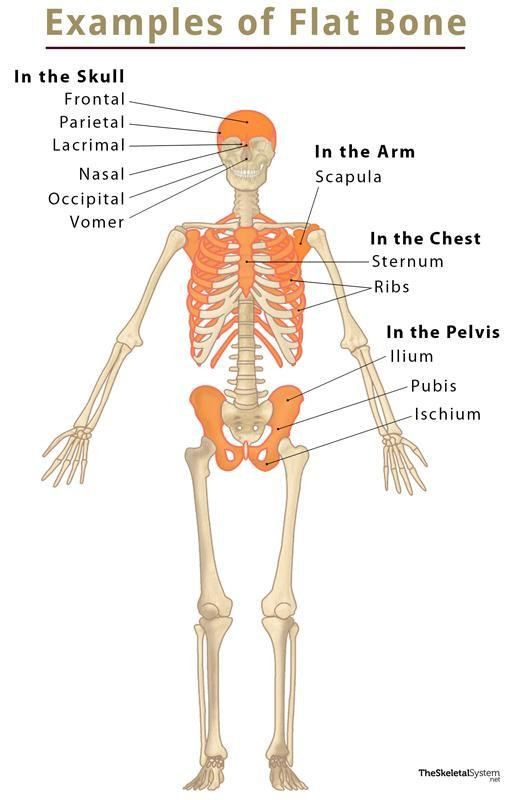
flat bone
Thin, broad, often curved. Protects organs and offers wide muscle-attachment surface.
Structure: two layers of compact bone with spongy bone between, no true marrow cavity.
Examples: skull bones, sternum, ribs, scapula.
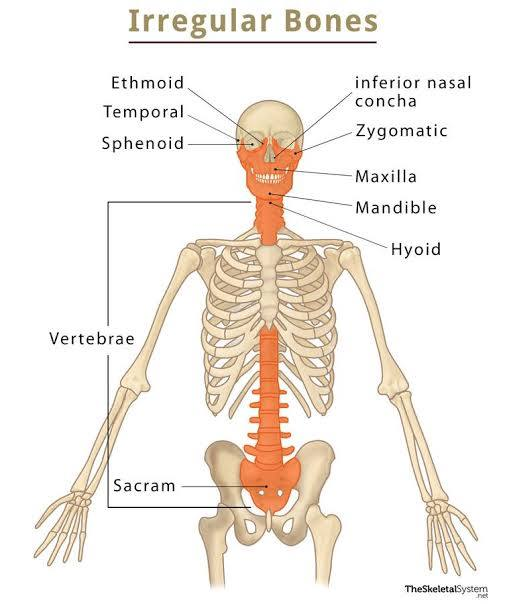
irregular Bone
Complex, irregular shape—doesn’t fit long/short/flat. Provide protection, support, and muscle attachment. Examples: vertebrae, sphenoid, ethmoid, some facial bones (e.g., mandible).
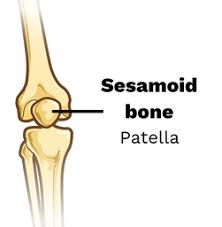
sesamoid Bone
Small, round bones that develop inside tendons where they pass over joints.
Function: Reduce friction, modify pressure, and increase mechanical leverage.
Example: Patella (kneecap) is the largest; others can occur in hands and feet.
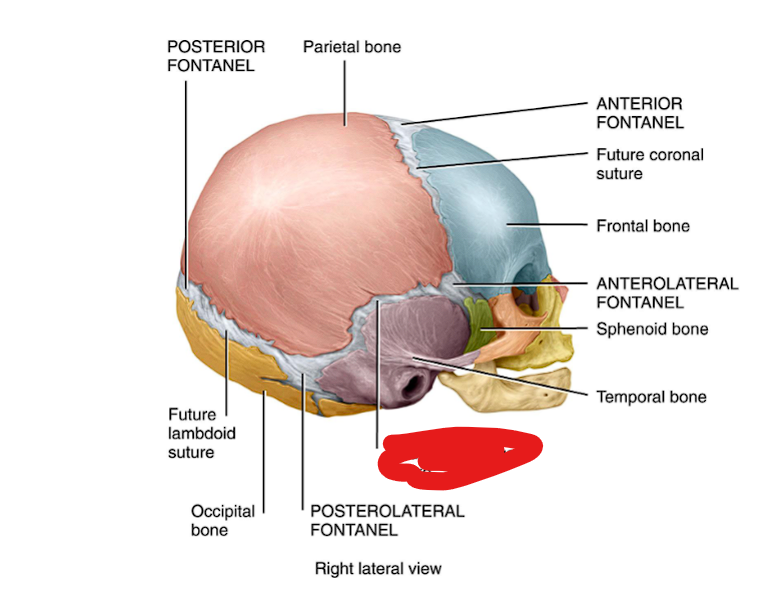
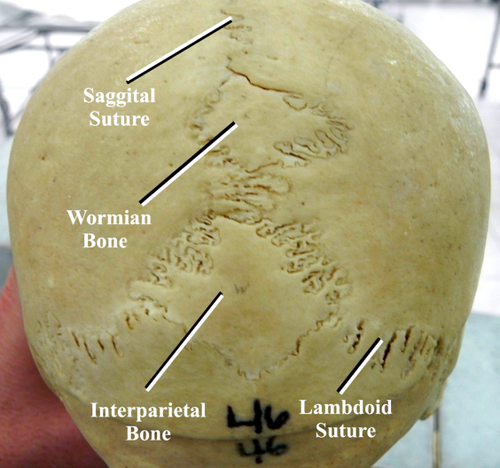
sutural or Wormian bone
Small, irregular bones that form within the sutures (joints) of the skull.
Function: Fill gaps and add stability between cranial bones.
Examples: tiny bones along the lambdoid suture (between parietal & occipital bones)
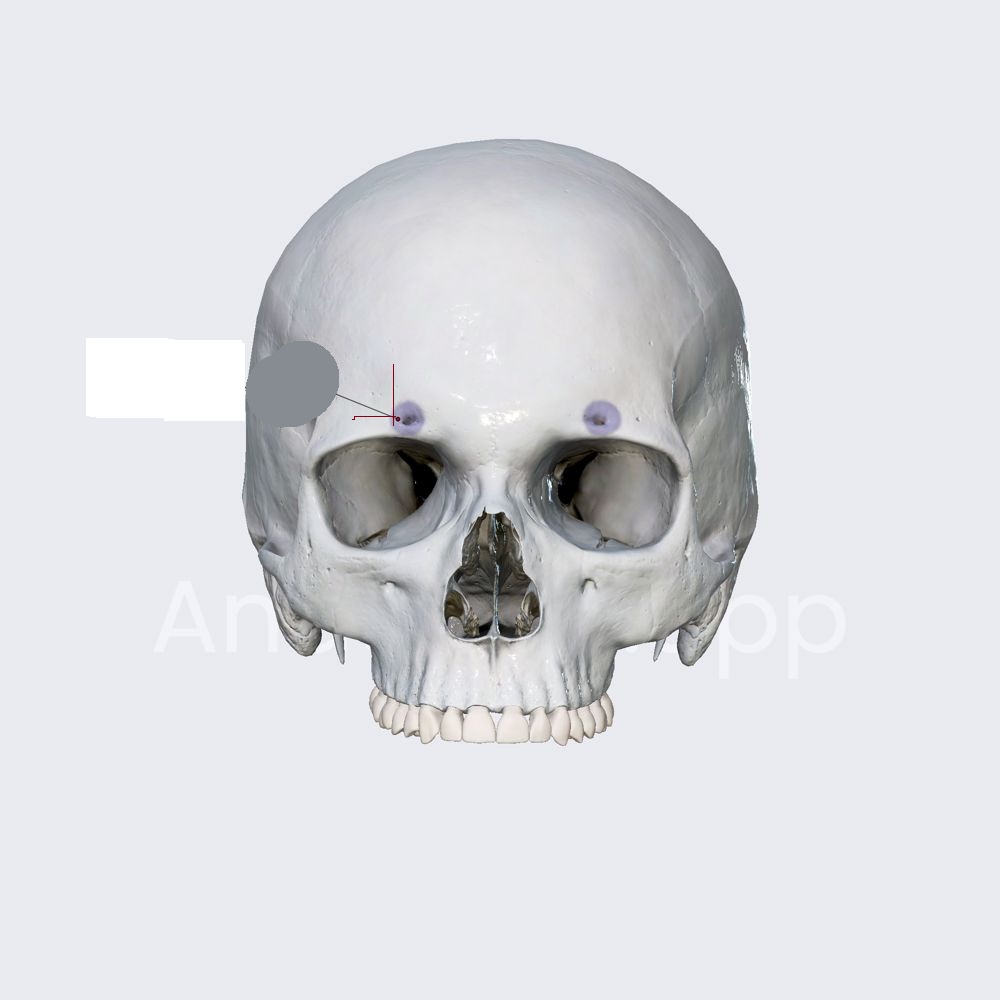
Superoribtal foramen
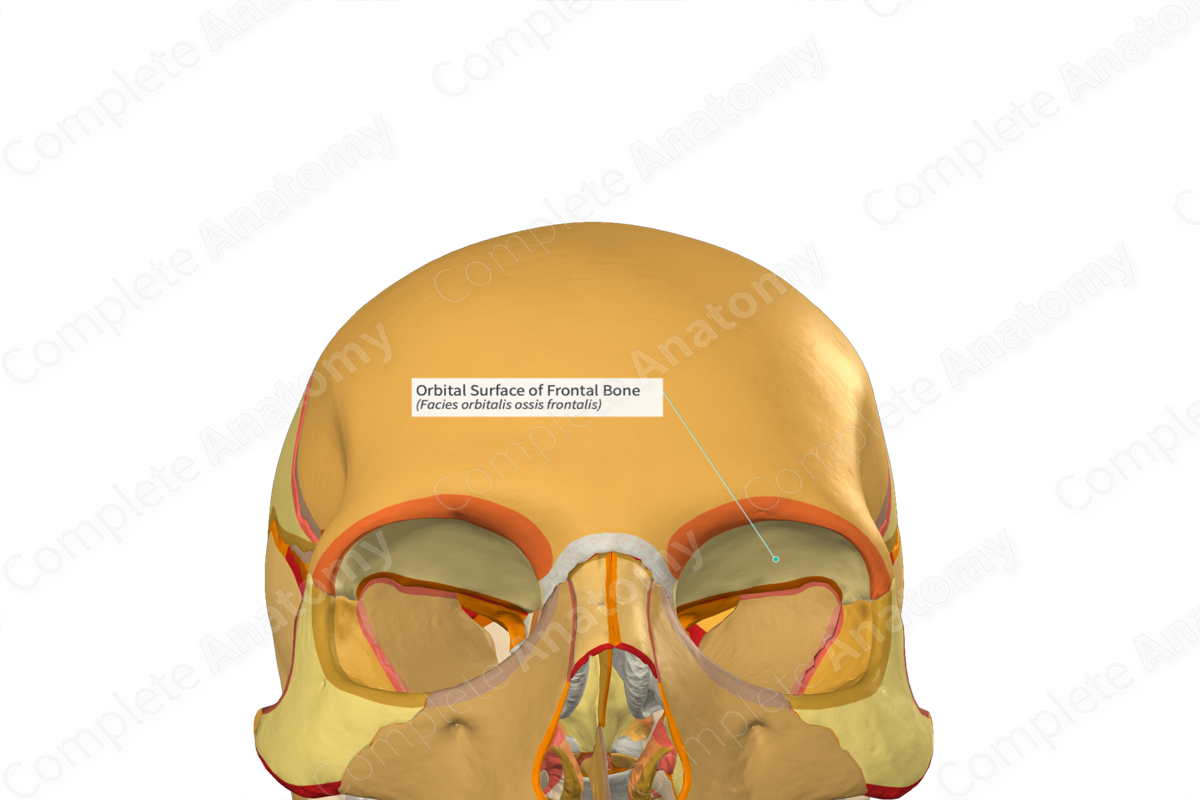
Frontal plate
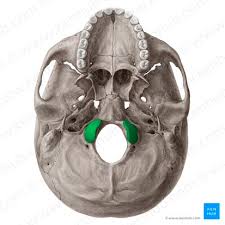
Occipital condyles
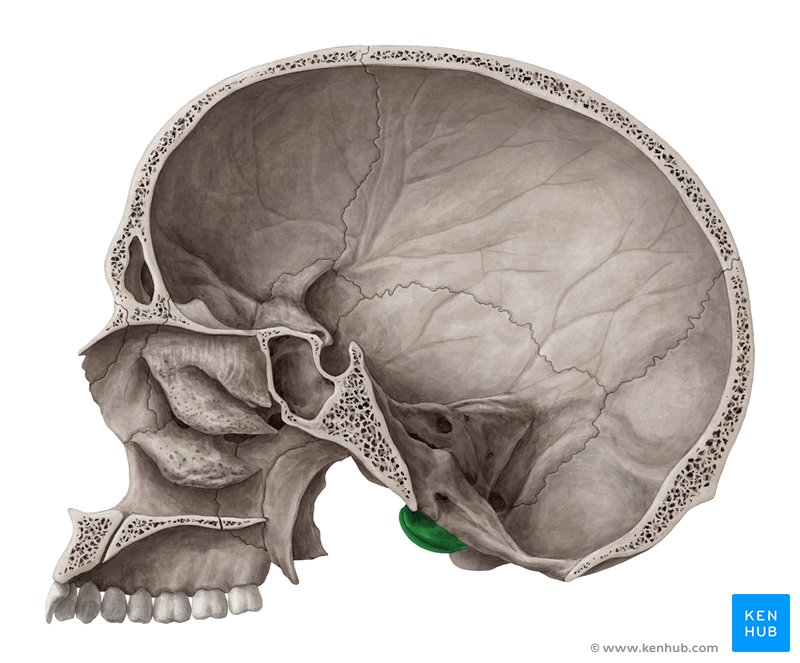
Zygomatic process and zygomatic arch
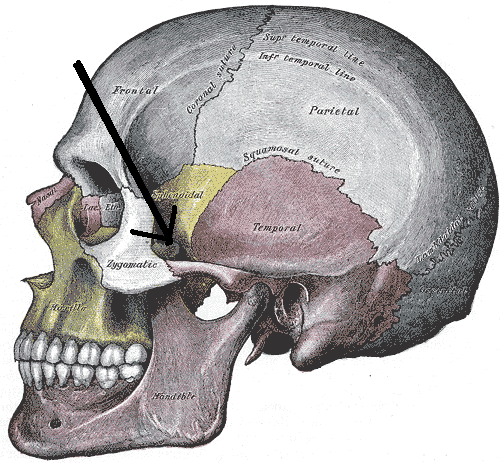
Squamous portion of temporal bone
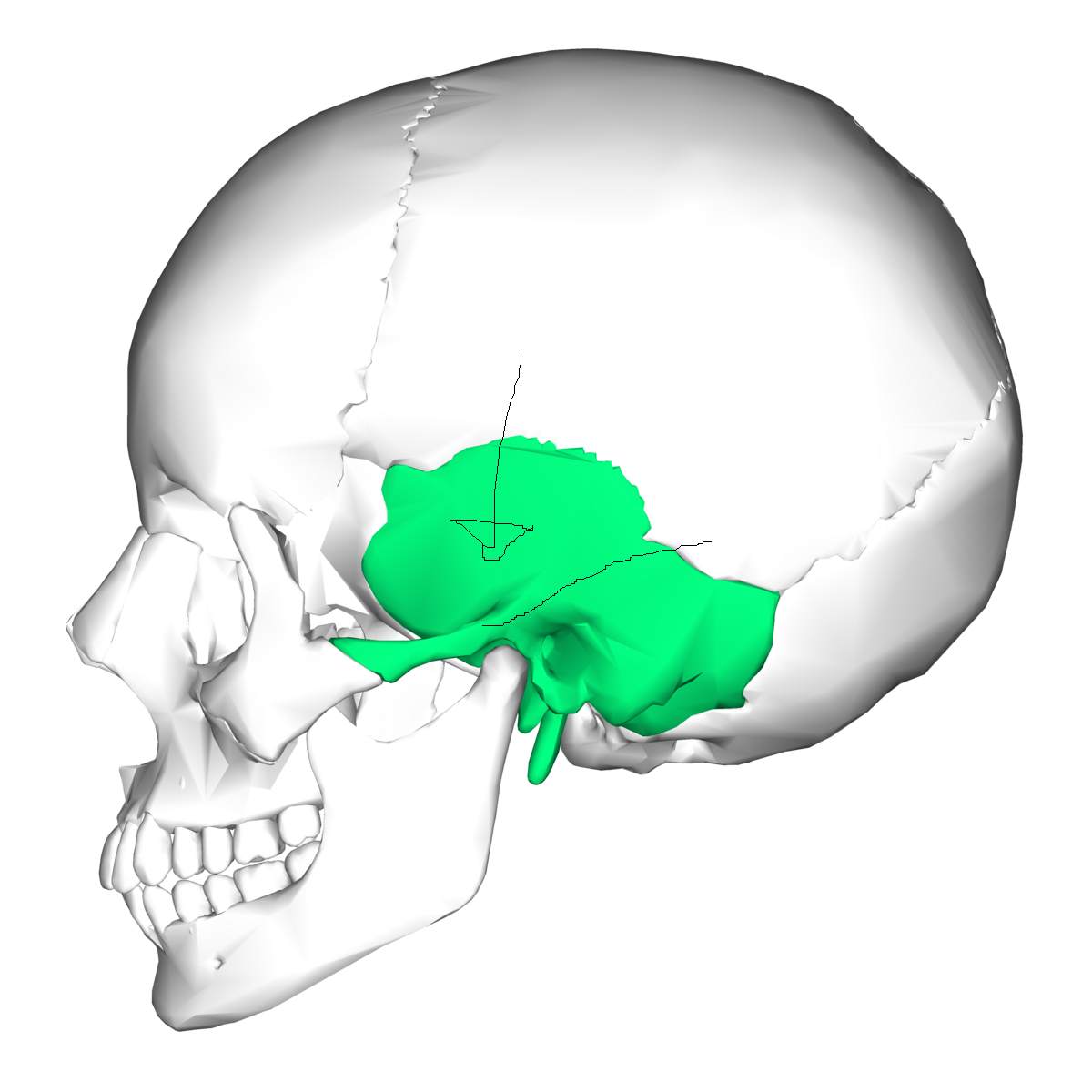
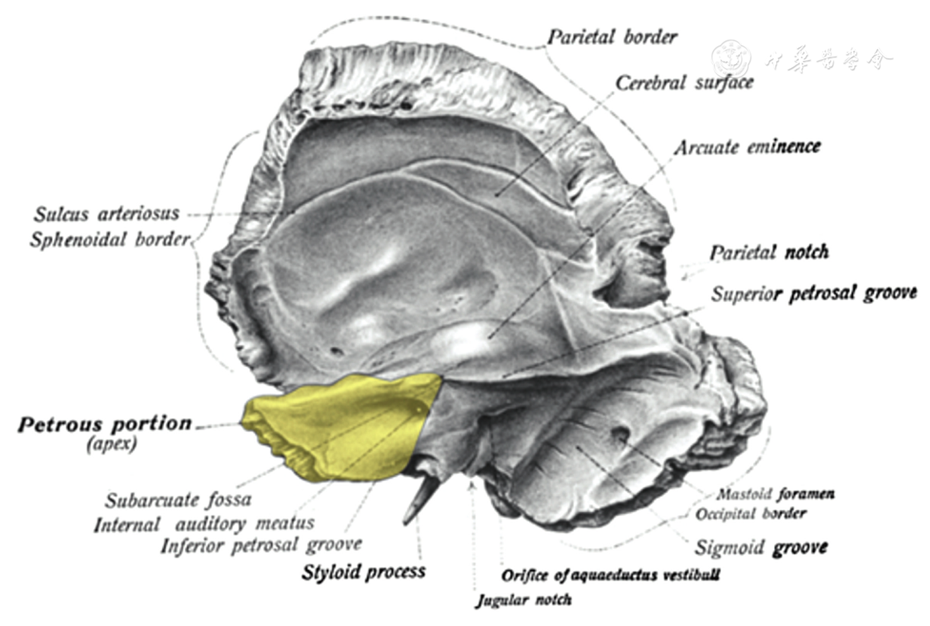
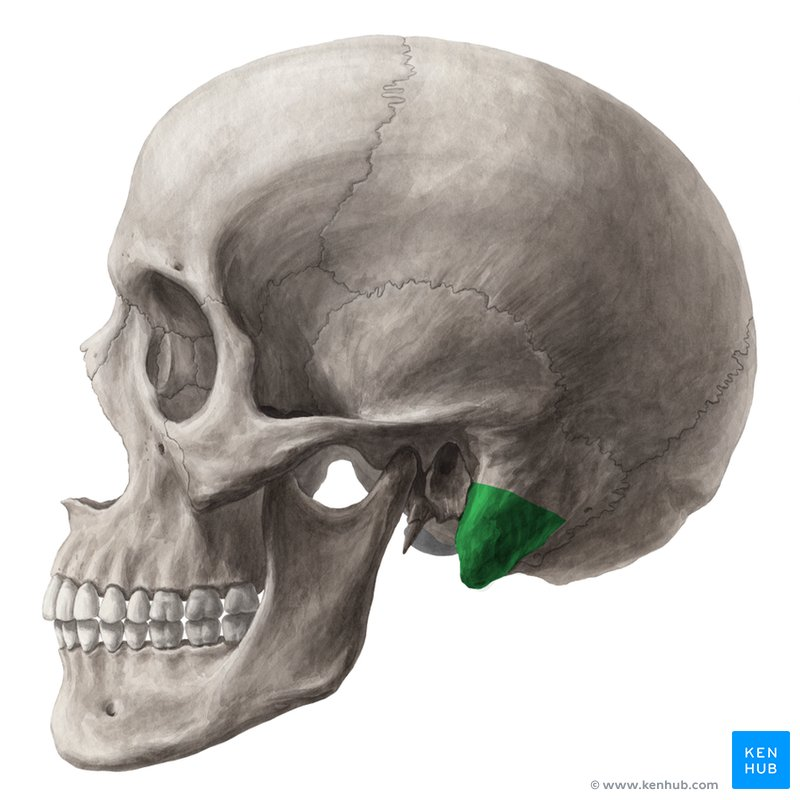
Petrous portion *
d. Mastoid process
e. Styloid process
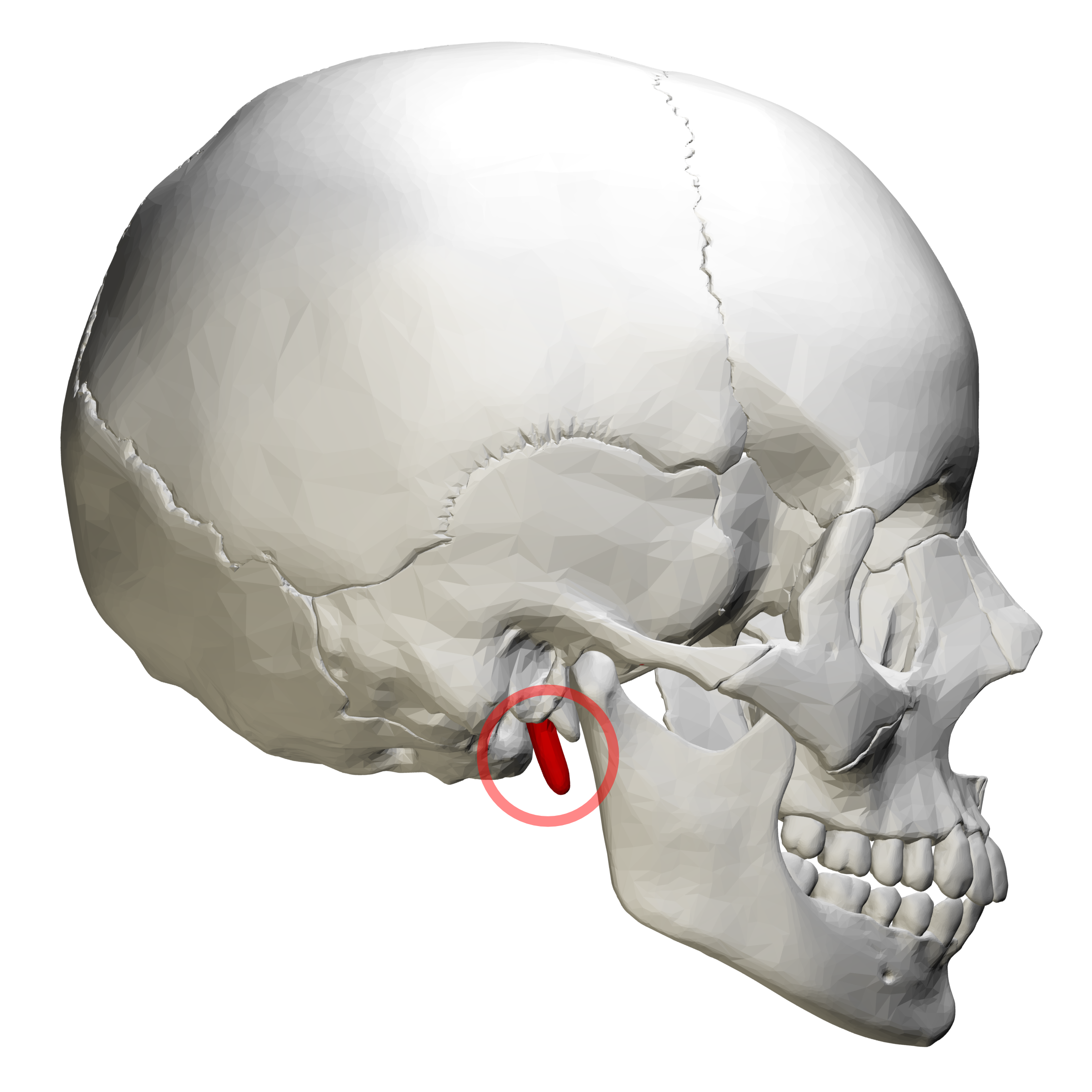
f. External auditory meatus
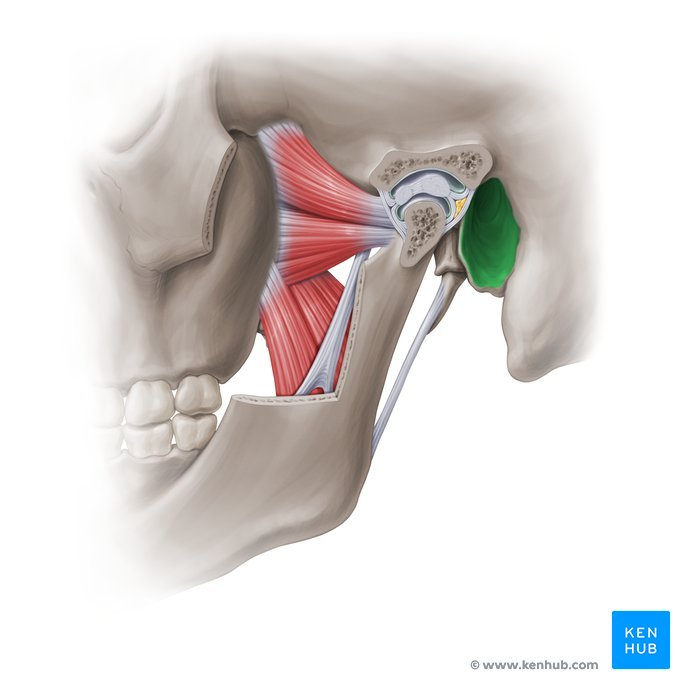
g. Carotid canal
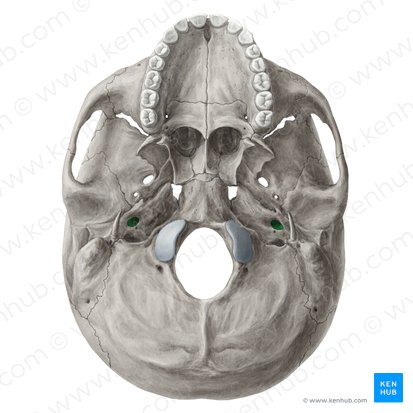
h. Internal auditory meatus
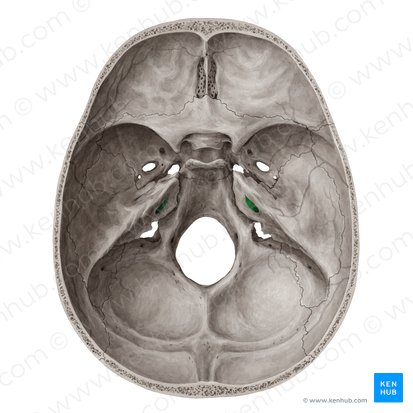
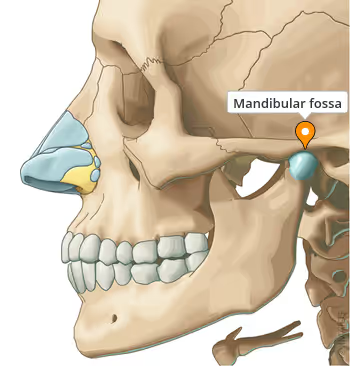
i. Mandibular fossa
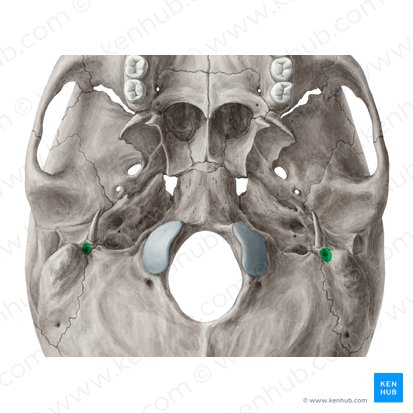
j. Jugular foramen ( as part of articulated skull)
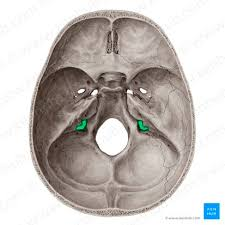
* k. stylomastoid foramen
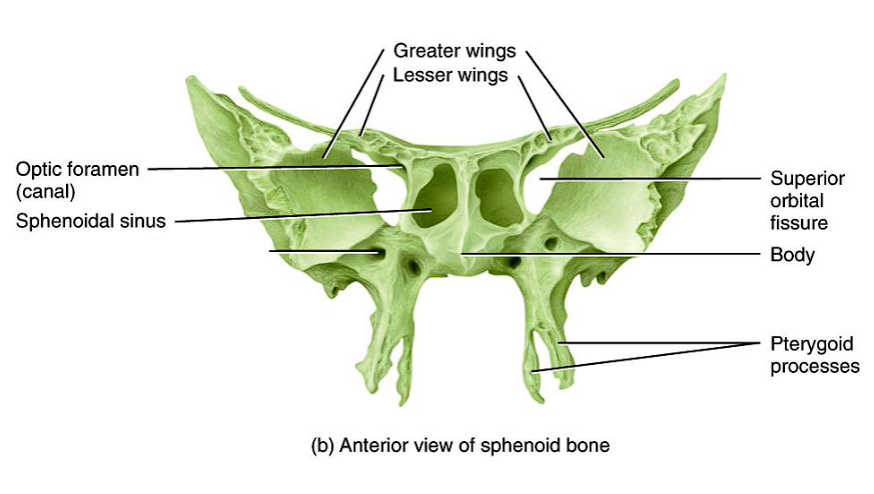
5. Sphenoid bone
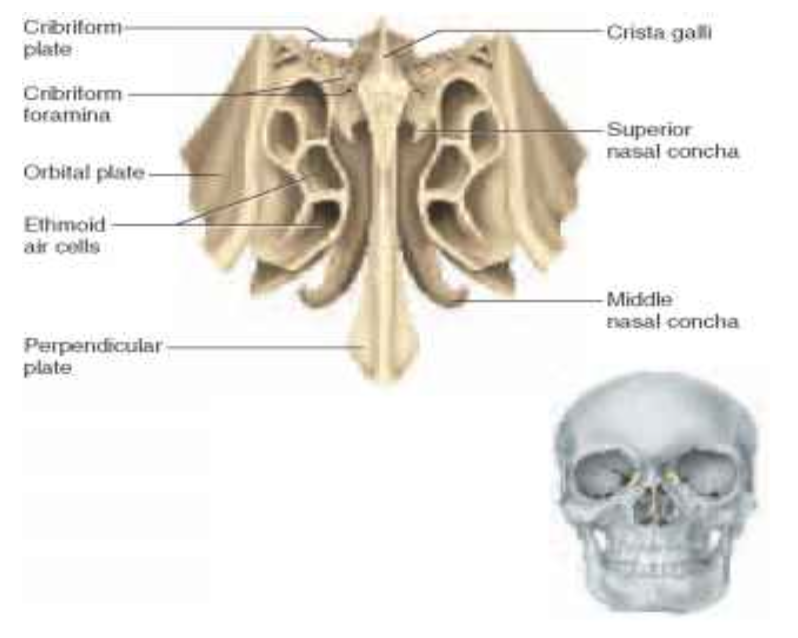
. Ethmoid bone
a. Cribriform plate w/ olfactory foramina
b. Perpendicular plate
c. Crista galli
d. Ethmoidal sinuses (internal structure)
e. Middle nasal conchae
f. Superior nasal conchae
g. Orbital surface (of maxilla) (be able to identify bone from within orbit)
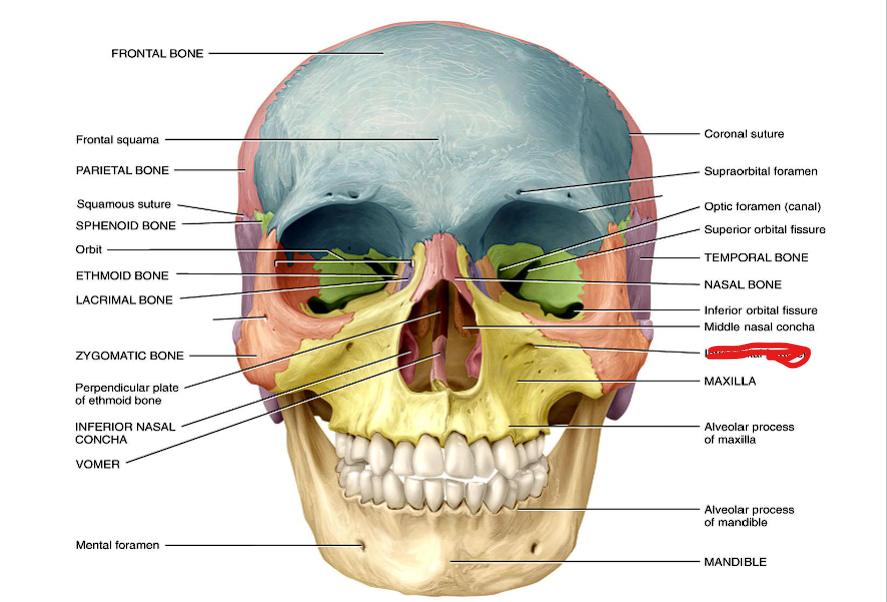
Indraorbital foramen
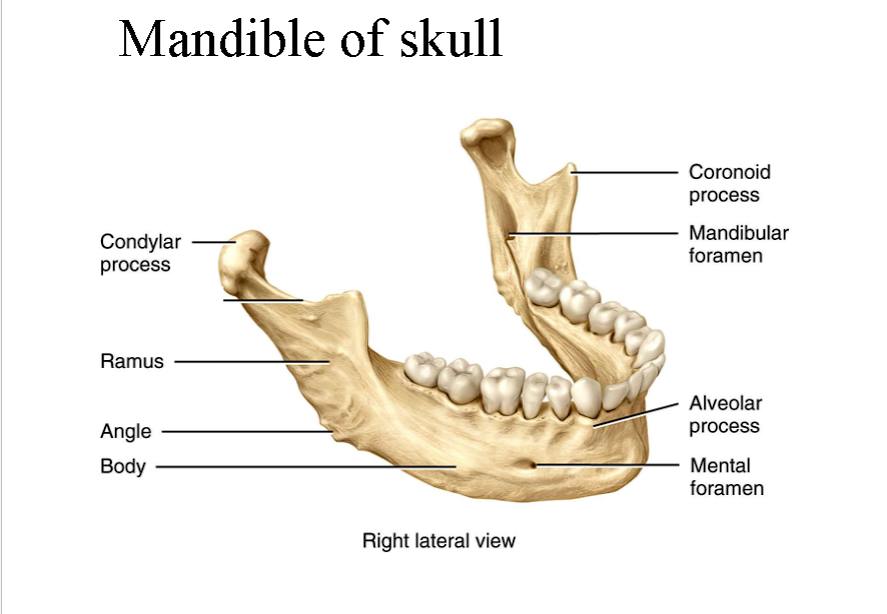
mandible
Temporal process and zygomatic arch
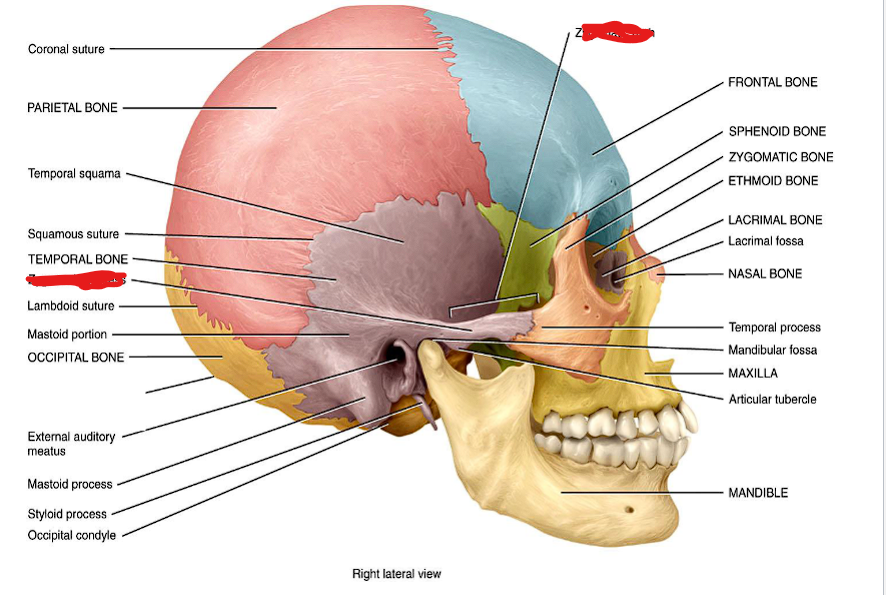
Coronal suture
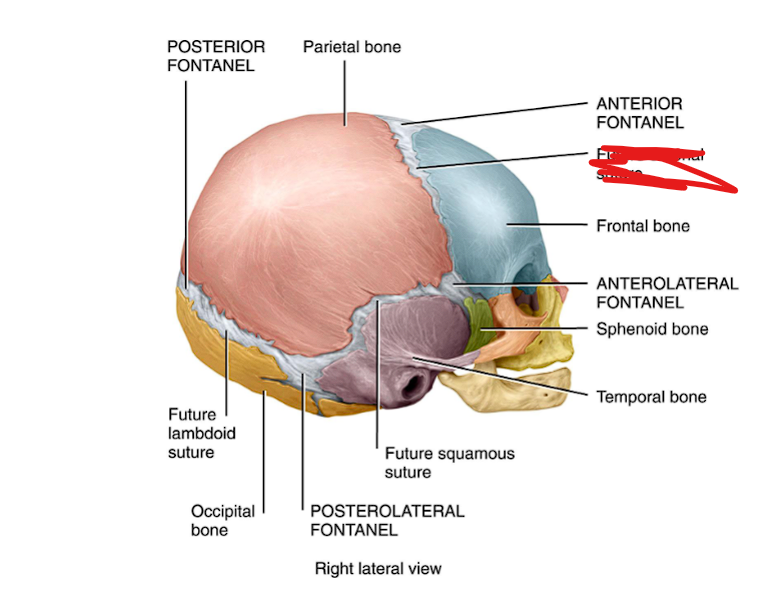
Sagittal suture
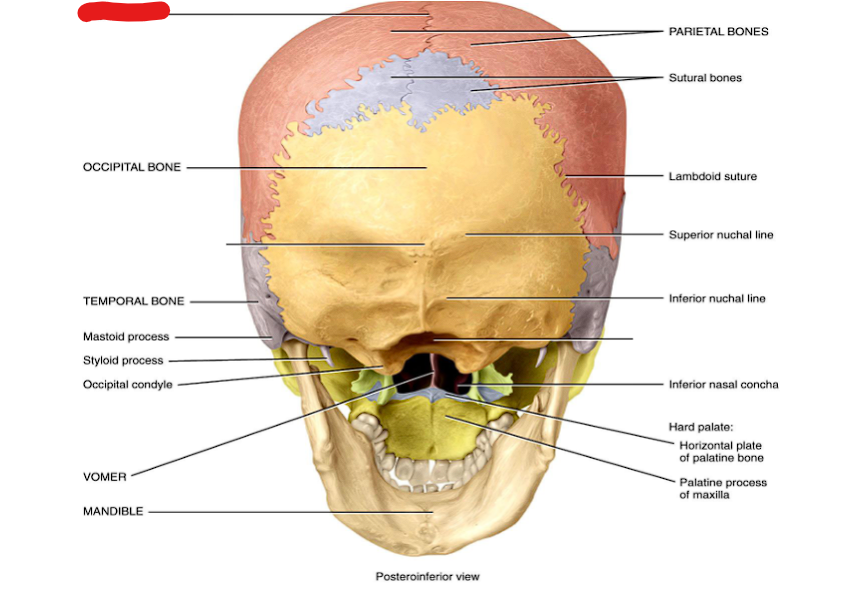
Lambdoid suture
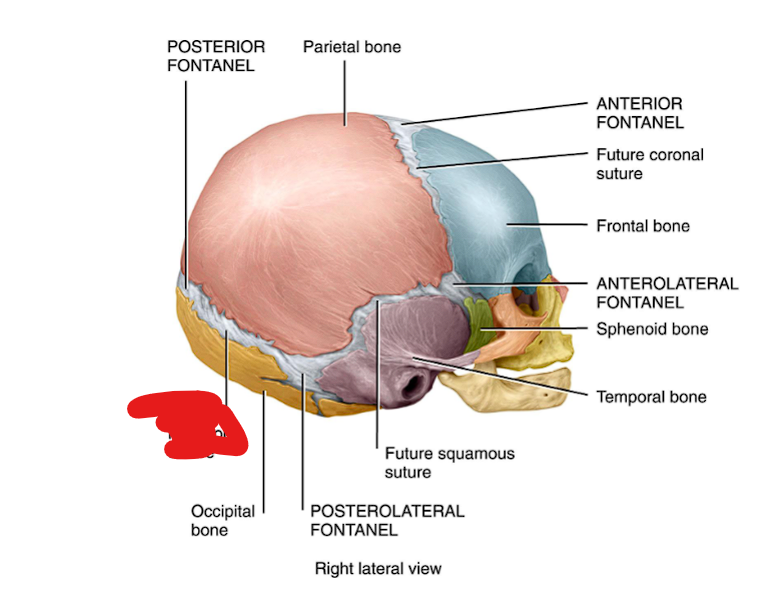
Squamosal suture