Neutralisation and pH scale
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
strong acids
ionise COMPLETELY in water
all the acid particles dissociate to release lots of H+ ions
concentrated acids
a higher ratio of acid compared to water
weak acids
do not fully ionise in solution
only a small proportion of acid particles dissociate to release H+ ions
this is REVERSIBLE
it sets up an EQUILIBRIUM between dissociated and dissociated acid
the equilibrium lies well to the left since only a few acid particles dissociate to release H+ ions
dilute acids
a small ratio of acid compared to water
pH
measure of the concentration of H+ ions
How does pH increase/decrease as concentration of H+ ions increase/decrease?
for every increase/decrease of 1 pH, the concentration of H+ ions decreases/increases by a factor of 10
Factor H+ ion concentration changes by = 10difference in pH
Neutralisation
acids release H+ ions when dissolved in water
alkalis release OH- ions when dissolved in water
these form H2O
neutralisation ionic equation
H+ + OH- —> H2O
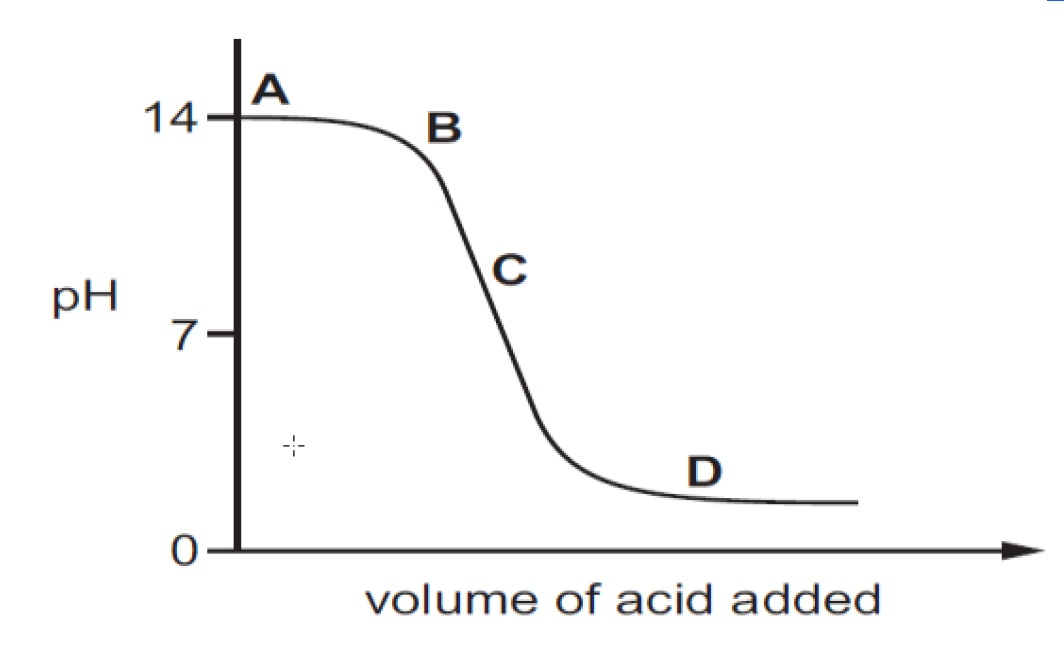
Describe and explain the trends in this graph
pH falls gradually at first as acid added
then more rapidly as alkali is completely neutralised
At pH 7, this is the equivalence point- how much acid neutralises alkali
then pH falls slowly again as excess acid is added
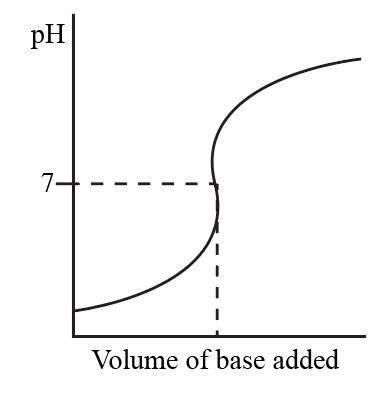
Describe and explain the trends in this graph
pH rises gradually at first as alkali added
then more rapidly as acid is completely neutralised
At pH 7, this is the equivalence point- how much alkali neutralises acid
then pH increases slowly again as excess alkali is added