W1 - Cerebral Cortex, Cerebral White Matter
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
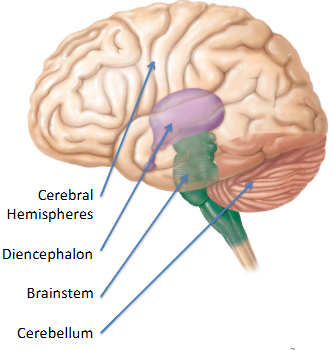
Composition of the Brain
R/L Cerebral Hemispheres (Cerebrum)
Diencephalon
Brainstem
Cerebellum
Cerebrum Composition
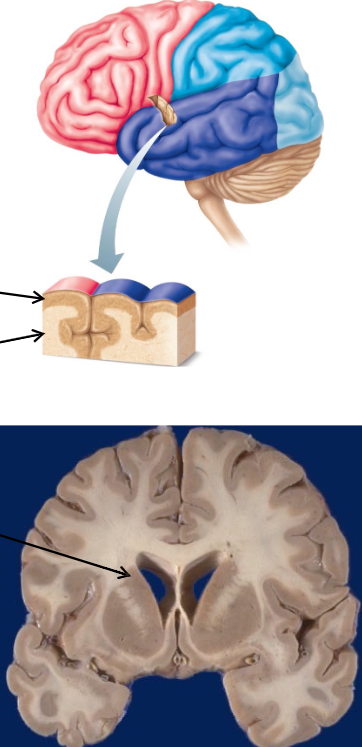
Cerebral Cortex = outer crust of cerebral gray matter, location of conscious mind
Cerebral White Matter = neuron fiber tracts deep to the cerebral cortex
Basal Nuclei (Basal Ganglia) = islands of gray matter buried within the white matter
Limbic System = gray and white matter structures dispersed thruout the cerebrum
Gross Anatomical Features of the Brain
gyri = folds that increase SA, numerous
sulci = shallow grooves between the gyri
fissure = deep grooves that sep larger portions of the cerebrum
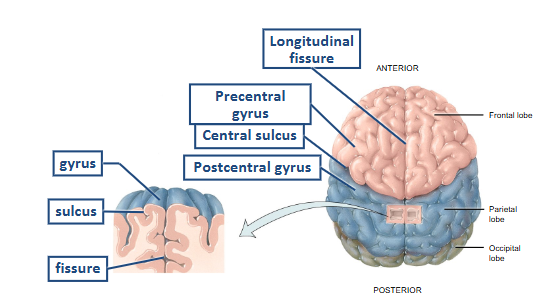
Lobes of the Cerebral Hemisphere
frontal
parietal
occipital
temporal
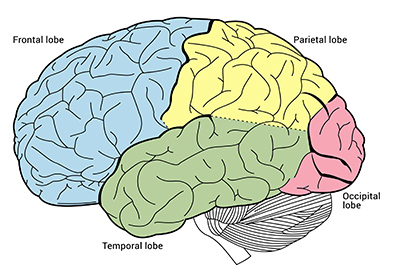
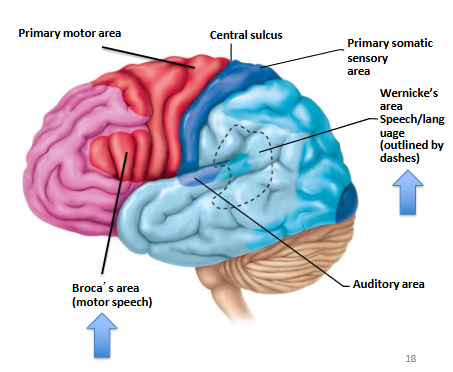
Frontal Lobe
contains primary motor cortex- voluntary control of skeletal muscles
Parietal Lobe
contains primary somatosensory cortex- conscious perception of touch, pressure, pain, vibration, temp
Occipital Lobe
contains visual cortex- conscious perception of visual stimuli
Temporal Lobe
contains auditory cortex and olfactory cortex- conscious perception of auditory and olfactory stimuli
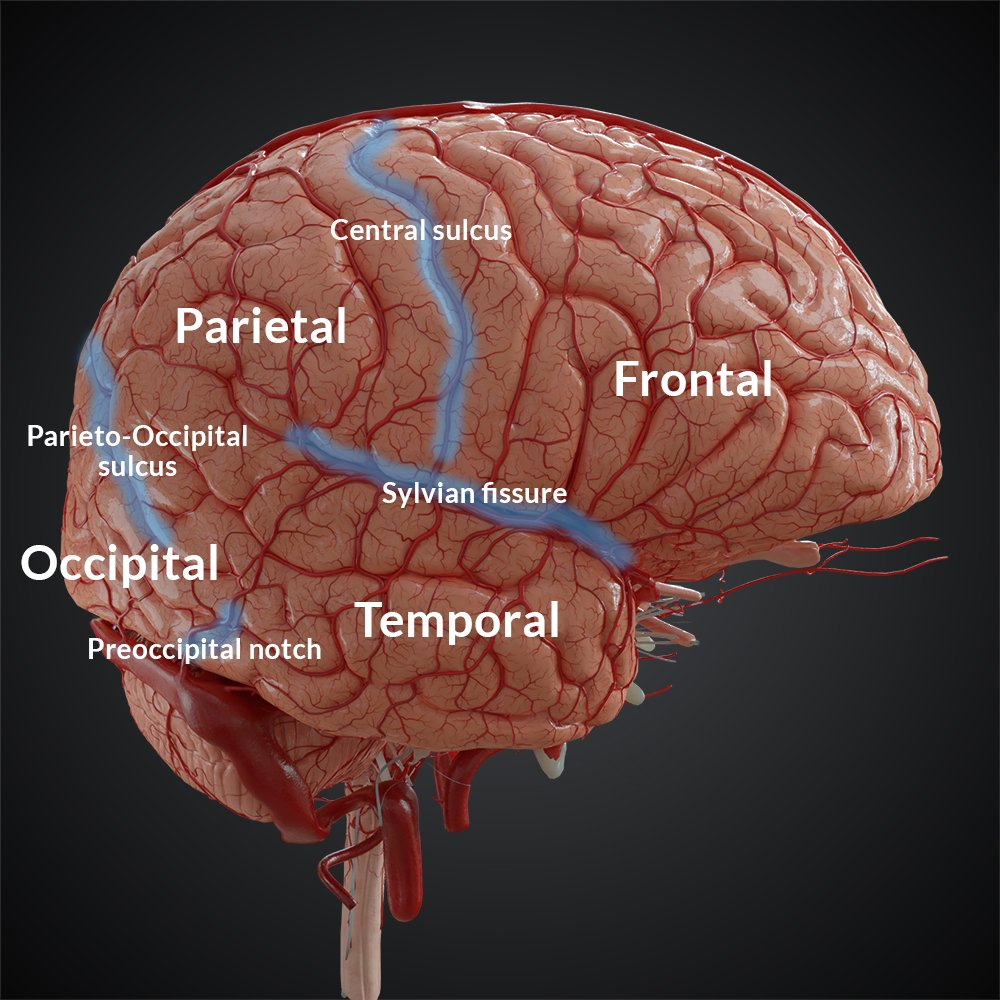
Fissures of the Brain (Sylvian fissure = Lateral Fissure/Sulcus)
Insula
located deep within the lateral fissure- involved in sensory processing, emotions and self awareness
Hemispheric Functionality
while both hems are involved in most functions, they are specialized
LT = language, numerical and scientific skills
RT = complex visual-spatial skills, communicate emotional significance to events and language, music perception
Pre/Post- Central Gyrus aka
primary motor/sensory cortex
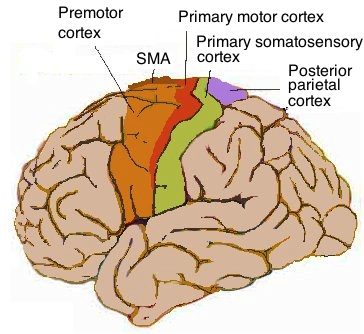
A lesion in the Somatosensory Area
causes contralateral loss of sensations, can perceive sensation but cannot tell the degree or origin
A lesion in the Primary Motor Area
contralateral paralysis
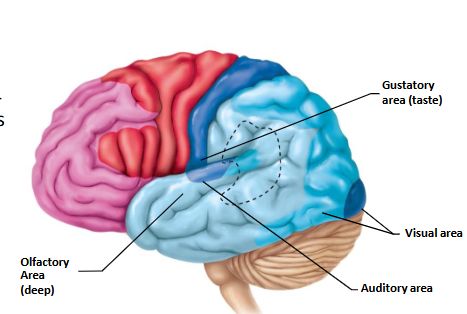
Special Sense Areas of the Cerebral Cortex
Insula = Gustatory (taste)
Occipital = Visual
Temporal = Olfactory, Auditory
Special Cerebral Cortex Areas for Speech and Language
Broca’s Area = speech muscles
Wernicke’s Area = permits recognition of spoken and written language, create plan of speech
Types of Tracts within Cerebral White Matter
association = confined to the same hem
commissural = run between R/L hems
projection = project to and from the cerebral cortex and form asc/desc tracts
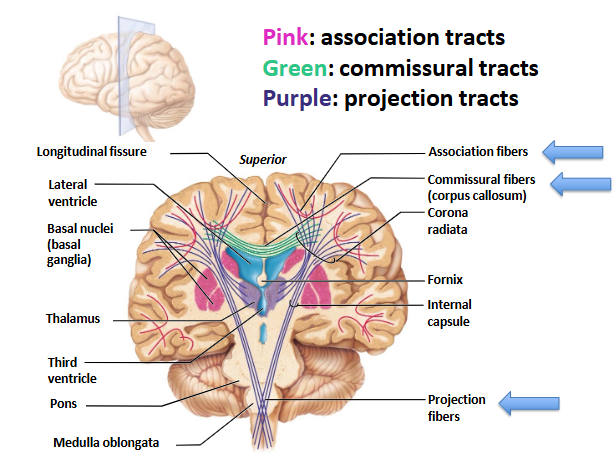
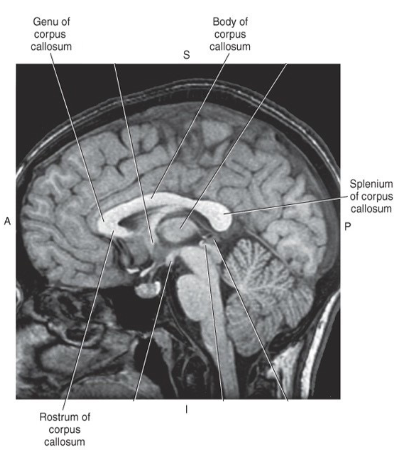
Corpus Callosum
important white matter commissural tract
components: rostrum, genu, body, splenium