BIOL 413: Tree of Life: Lab Practical 2
1/96
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
97 Terms
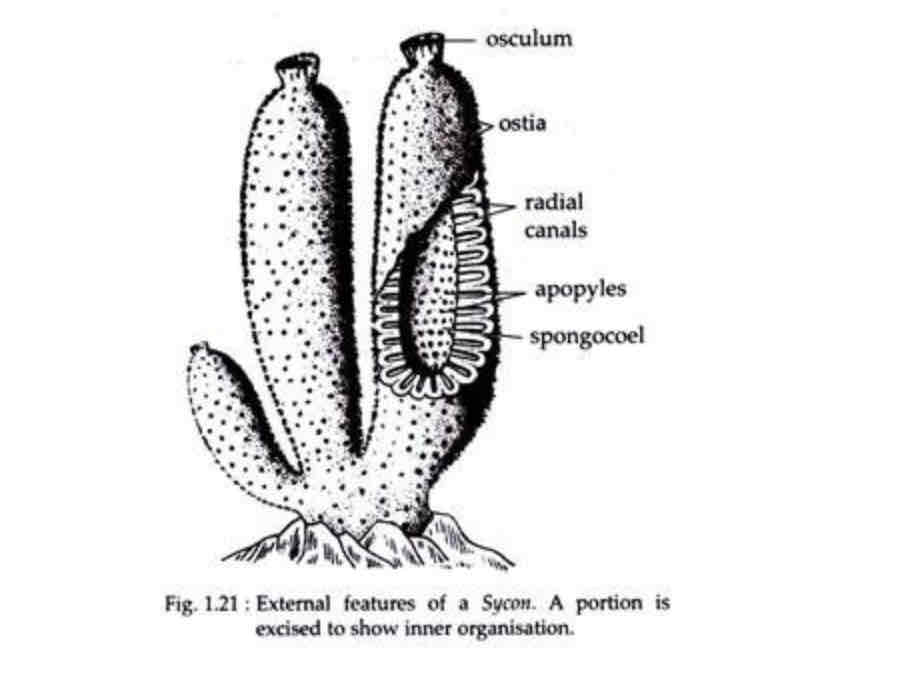
Scypha
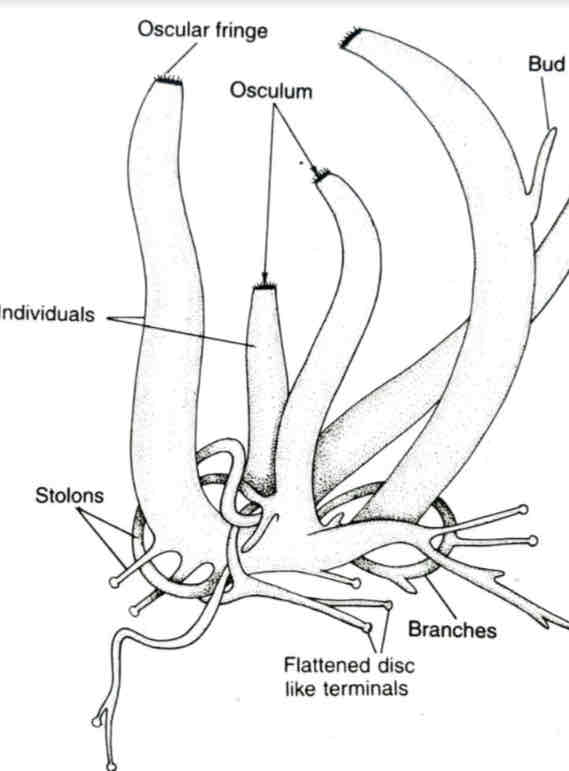
Leucosolenia
Ostia
Pores in the sponge in which water enters
Osculum
Where the water is expelled from the sponge
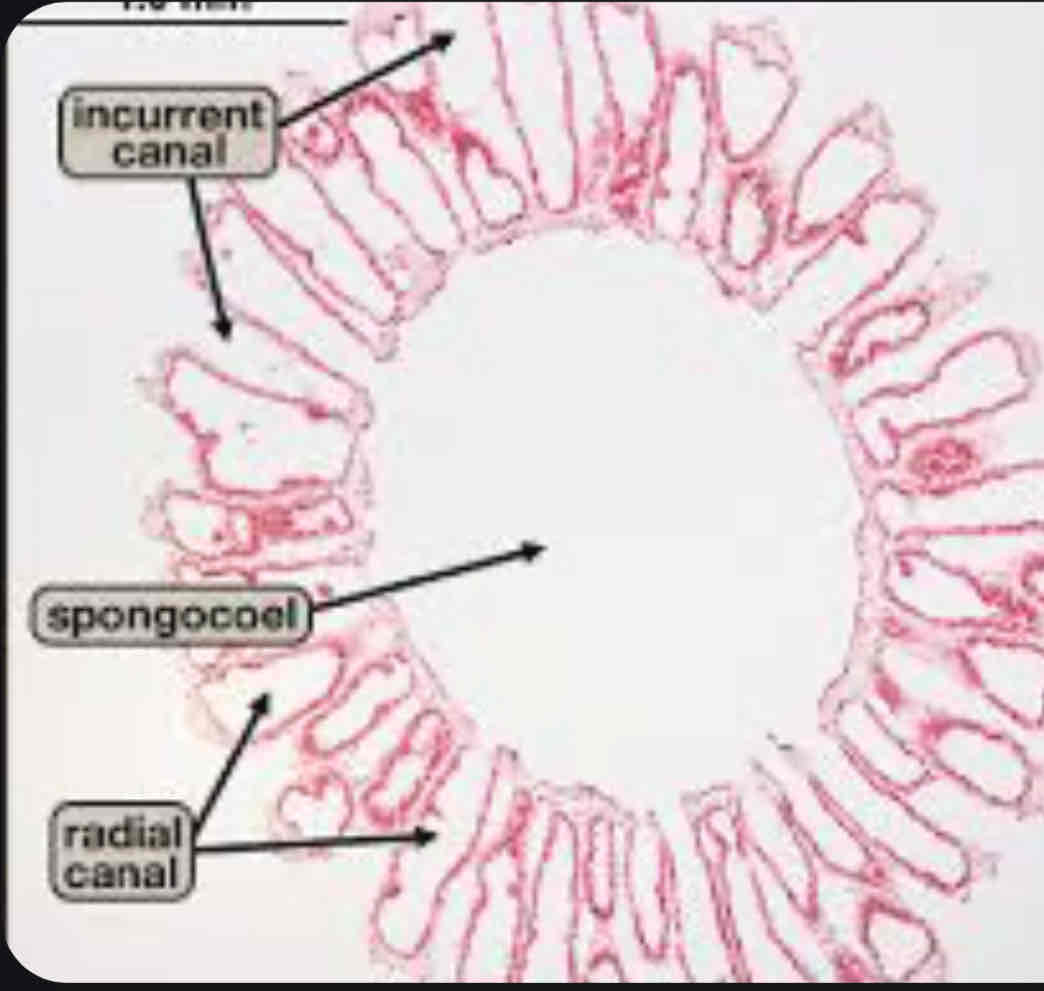
Sponge cross section
Radial Canal
Canal in which water flows after entering via ostia
Incurrent canal
Between radial canals
Spongeocel
Sponge cavity
Spongin Fiber
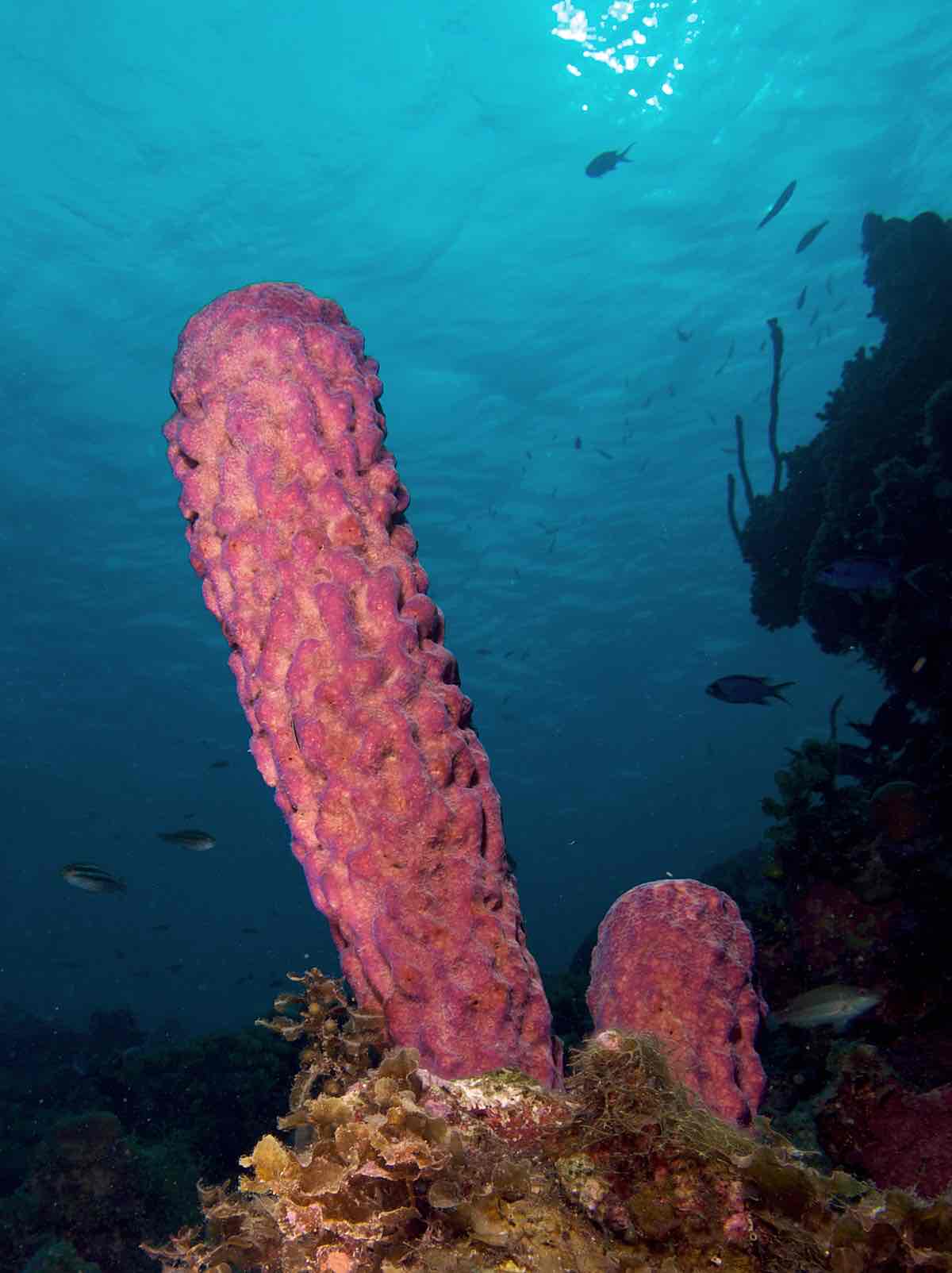

Sponge

Ctenophore
Comb rows
Help ctenophore move
Colloblast
Sticky cells used by ctenophores to capture prey
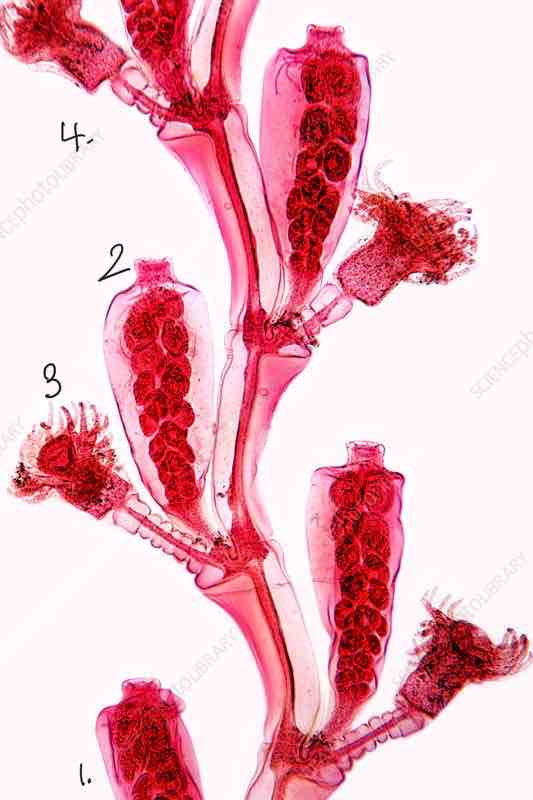
Obelia: aboral end, reproductive polyp, feeding polyp, oral end
Ctenophore symmetry
Biradial
Cnidarian symmetry
Radial
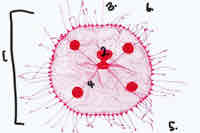
Obelia Medusa: umbrellas manbrium, tentacle, radial canal, aboral end, oral end
Manbrium
Mouth

Hydra: mouth, stalk, basal disk, aboral end, oral end
Medusa are ____
Mobile
Polyps are ___
Sessile

Physalia
Physalia live in ____ in the ocean
Surface
Aurelia life cycle
Planula larva → Scyphistoma → Strombolian → Medusa
Corals have cnidae(T/F)
True
Metridum: epidermis, septum, pharynx, gastrular cavity
Groups of Platyhelminthes
Tubellaria, Cestoda, Trematoda,
Tubellaria
Free living flatworm
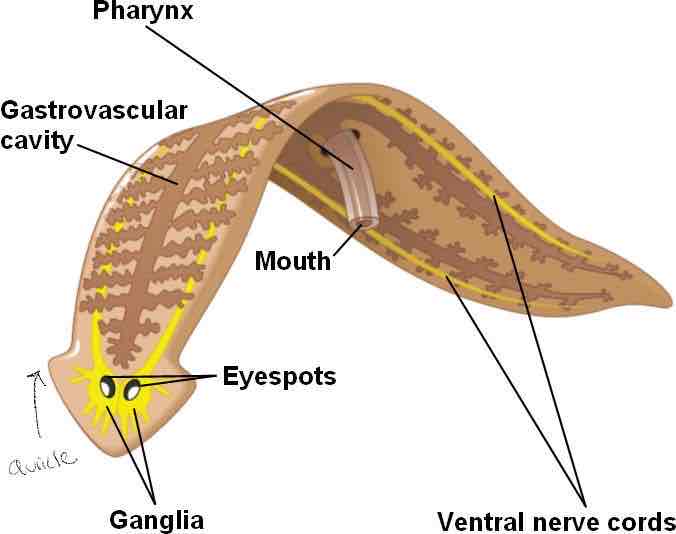
Planaria: pharyngeal cavity, eyespot, gastrovascular cavity, pharynx, mouth, auricle
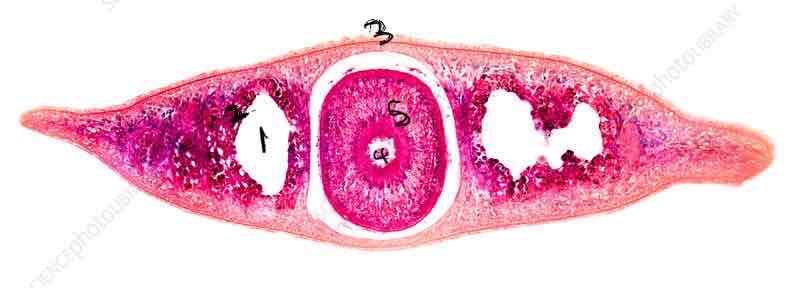
Planaria cross section: gut cavity, gastrocavity, epidermis, pharynx, pharyngeal cavity
Cestoda
Tapeworm, parasitic
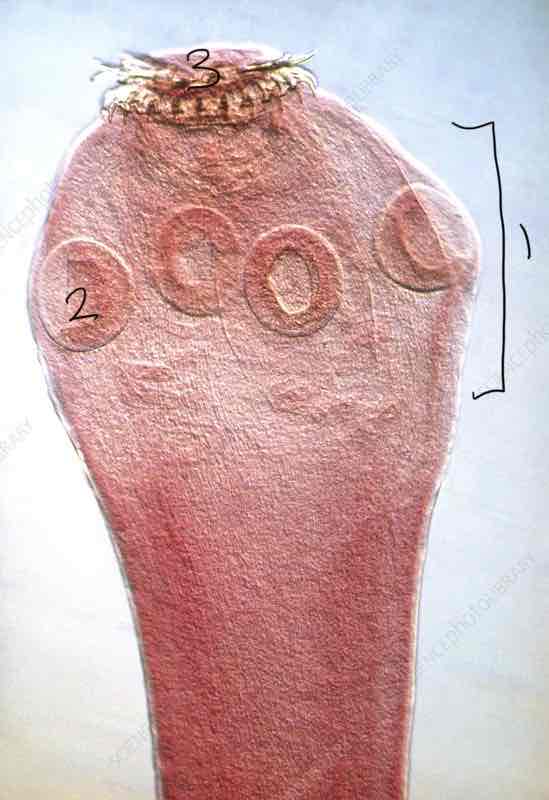
Taenia pisiformis: Scolex, Sucker, Rostellum
Trematoda
Fluke, parasite
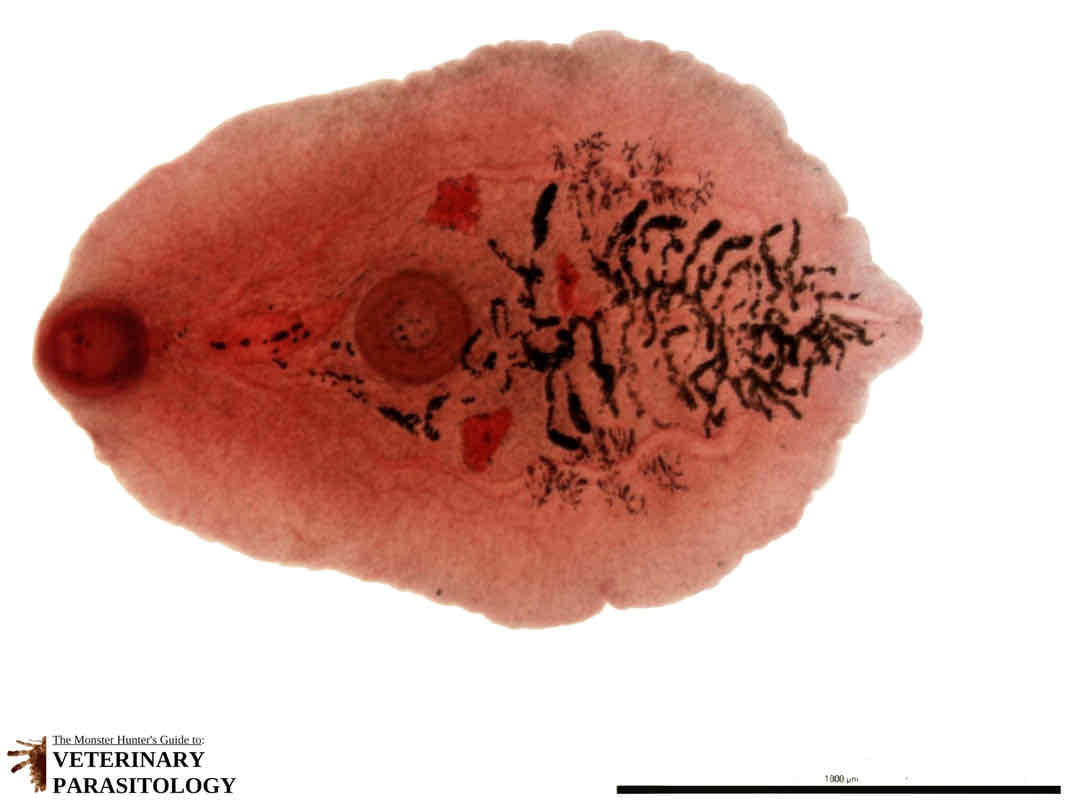
Eurytrema: oral and ventral sucker, cecum
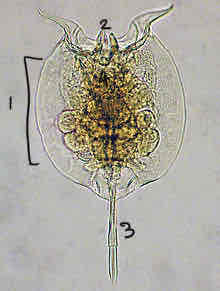
Rotifera, Brachinous: trunk, Cornea, foot, mastax
Cornea
Crown of cillia around mouth for locomotion and feeding
Mastax
Jaws found in pharynx, used to grind food

Brachiopod: Lingula: values, pedicle
Difference between Brachiopod and bi valve shells
Brachiopods are symmetrical down the middle, bi valve mirror by the plane they open
Traits of Brachiopods
Bilaterally symmetrical, lophophore
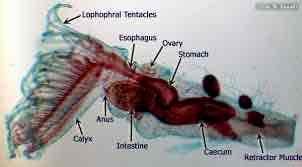
Bryozoan: mouth, anus, esophagus, intestine
Bryozoans are colonial because
They are made up of numerous small zooecium

Fossil Bryozoa: Zoecium
Bryozoans do not have Cnidae(T/F)
True
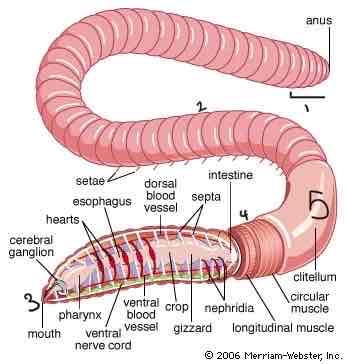
Annelid: Pygidium, annuli, prostonium, peristomium, cliteum
Clitellum
Aids in copulation, collects sperm and egg
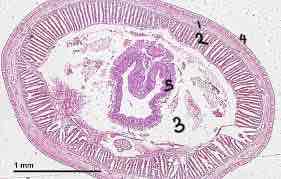
Earthworm cross section: circular muscle, longitudinal muscle, Coelom, epidermis, intestine
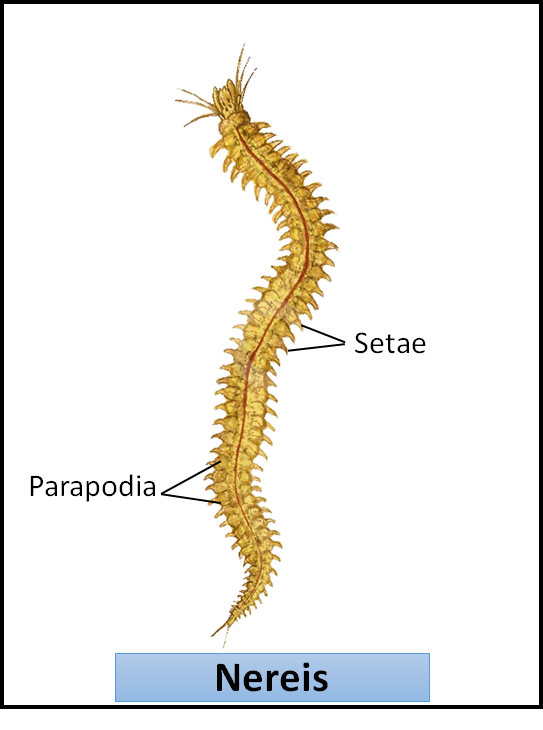
Nereis
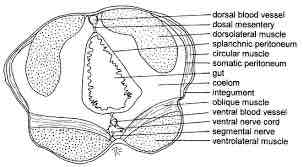
Polychete: Neanthes: circular muscle, longitudinal muscle, colem, epidermis, intestine

Leech: anterior and posterior sucker
Which leech sucker is more likely to be attached to substrate?
Posterior sucker
Parapodia are found on
Polychetes
Setae are found on
Annelids other than leeches
Natural history of earth worms and polychetes
Free living

Nudibranch
Polyplacophoras are also known as
Chitons

Chiton: 8 shell plates, girdle
Chitons use ___ to stick to walls and __ to eat
Muscular foot, radula
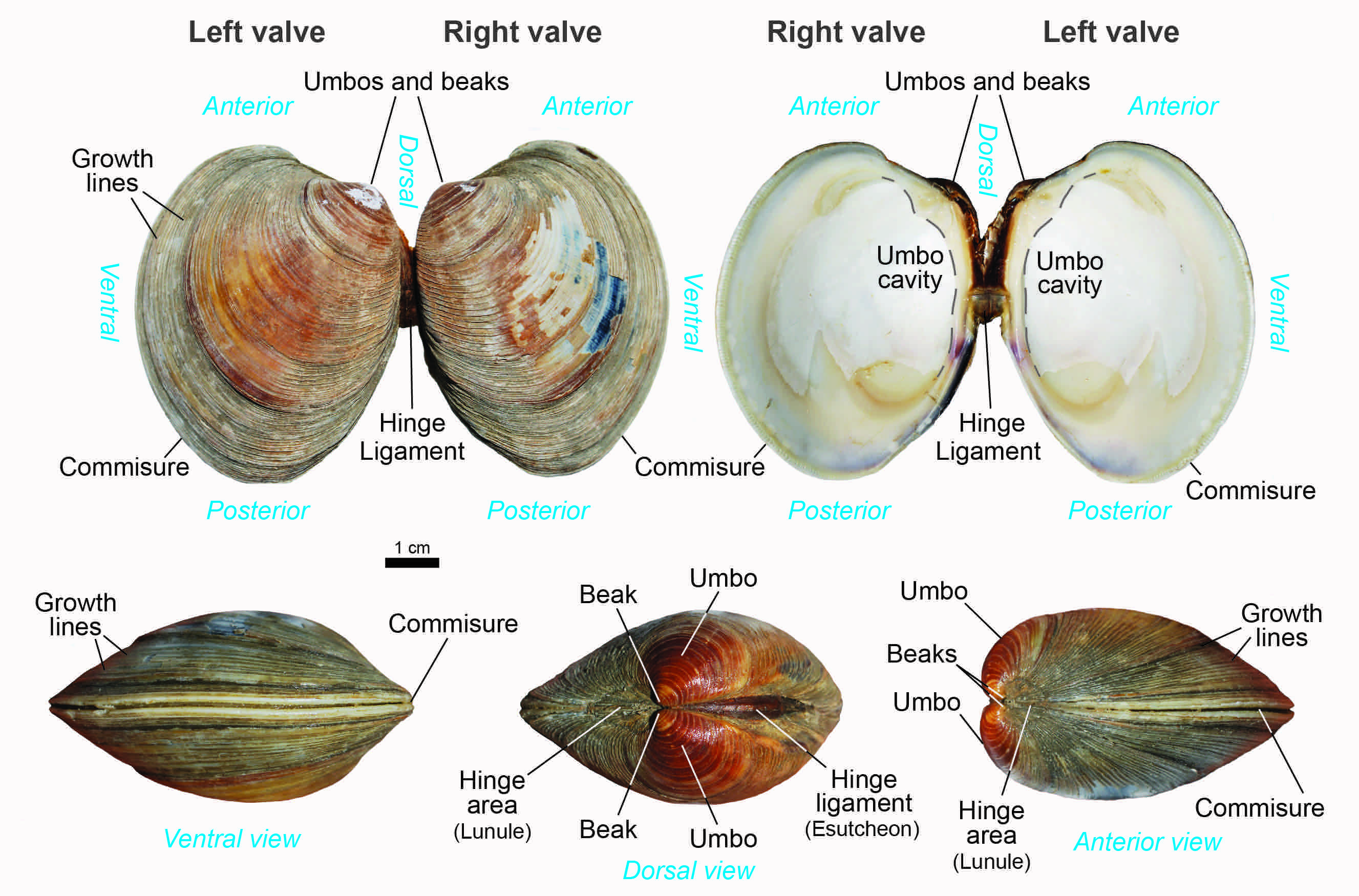
Bivalve: Umbo, anterior, posterior
Bivalva lack a radula because
They are filter feeding

Scaphopod
Gastropod shell characteristics
Conical spiral wound around a central axis
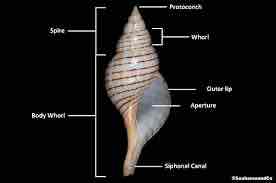
Gastropods shell anatomy
Radula
Dextral
Right side of shell
Sinistral
Left side shell
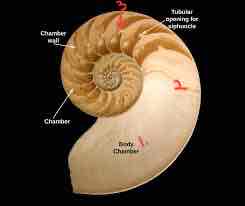
Nauntalis: body chamber, siphuncle, septa
Nautilus characteristics
Shell, no ink sac, 38 arms
Squids have __ arms
10
Octopus have __ arms
8
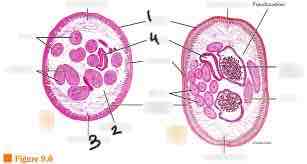
Nematode: epidermis, psudocelom, longitudinal muscle,intestine
Nematodes do not have
Circular muscle
Tardigrade anatomy
Five segmenta, head, 4 legs
Onycophoran novelty
Oral papillae, annulated antennae, one pair of jaws, lopopod walking legs
Arthropod traits
Appendicular joints, specialization of body segments

Merostomata, Horeshoe crab: compound eye, carapace, abdomen, telson, Cephalthorax
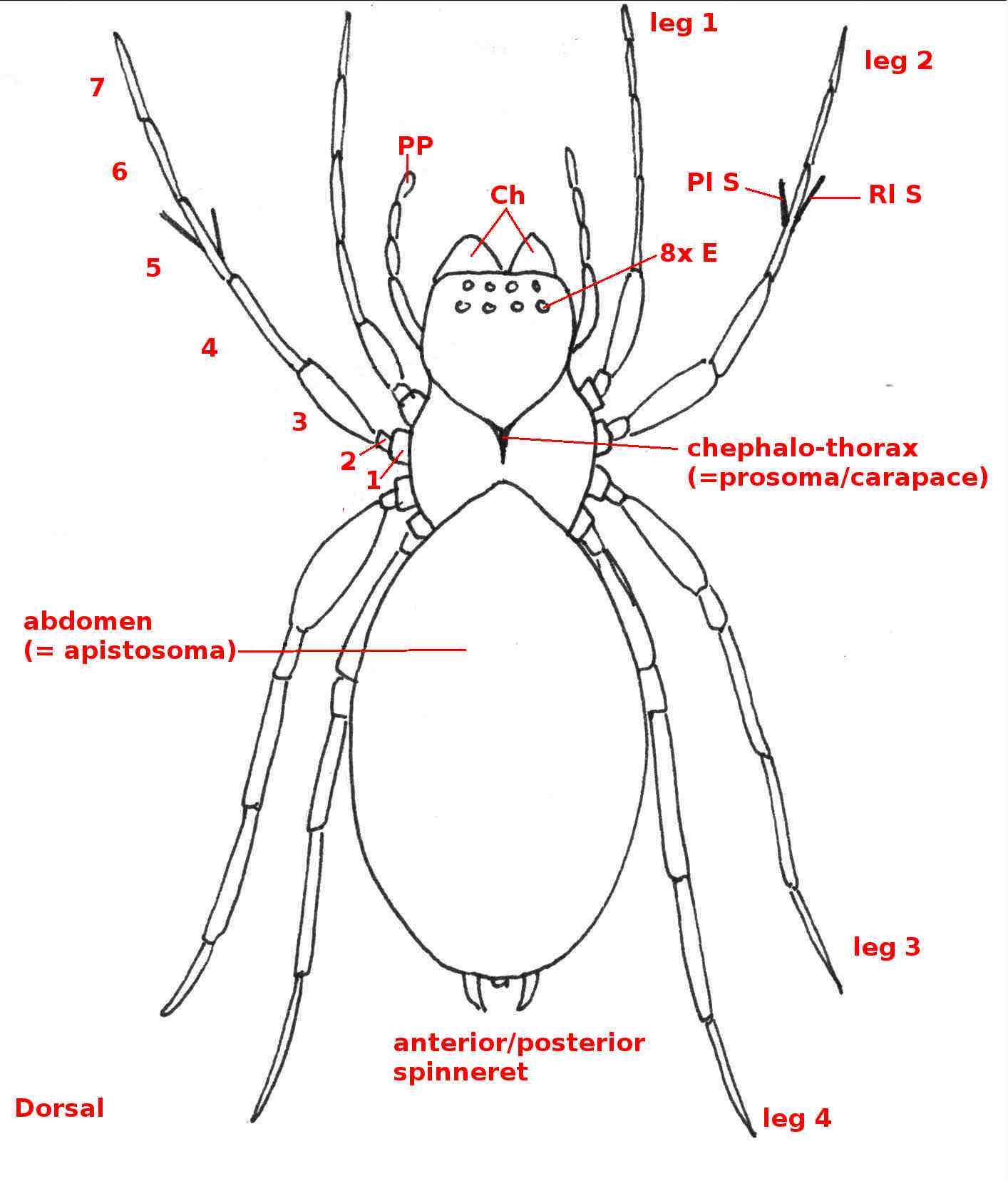
Arachnida: pedipalp, chelicerae, 6 appendages, 4 pairs of walking legs

Mandibulata, giant centipede: attenae, poison claws, head
Insect traits
Head, thorax, abdomen
Echiodermata synapomorphy
Endoskeleton, pentraradically symmetrical, and water vascular system
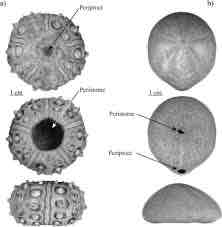
Echinoidea, sea urchin

Enchinoidea, sand dollar

Ophiuroidea, brittle star

Ophiurodiea, basket star

Crinoidea, sea lilies

Crinoidea, feather star

Asteroidea, star fish

Holothuroidea, sea cucumber
Madreporite
Sieve plate at external opening of water vascular system, water travels through
No Madreporite
Crinoidea
Internal Madreporite
Holotheridae
Teeth in sand dollars cannot be
Protracted
Notochord
Flexible Rod structure found in all chordates
Key vertebrate traits
Vertebrae, endoskeleton, neural crest tissue,
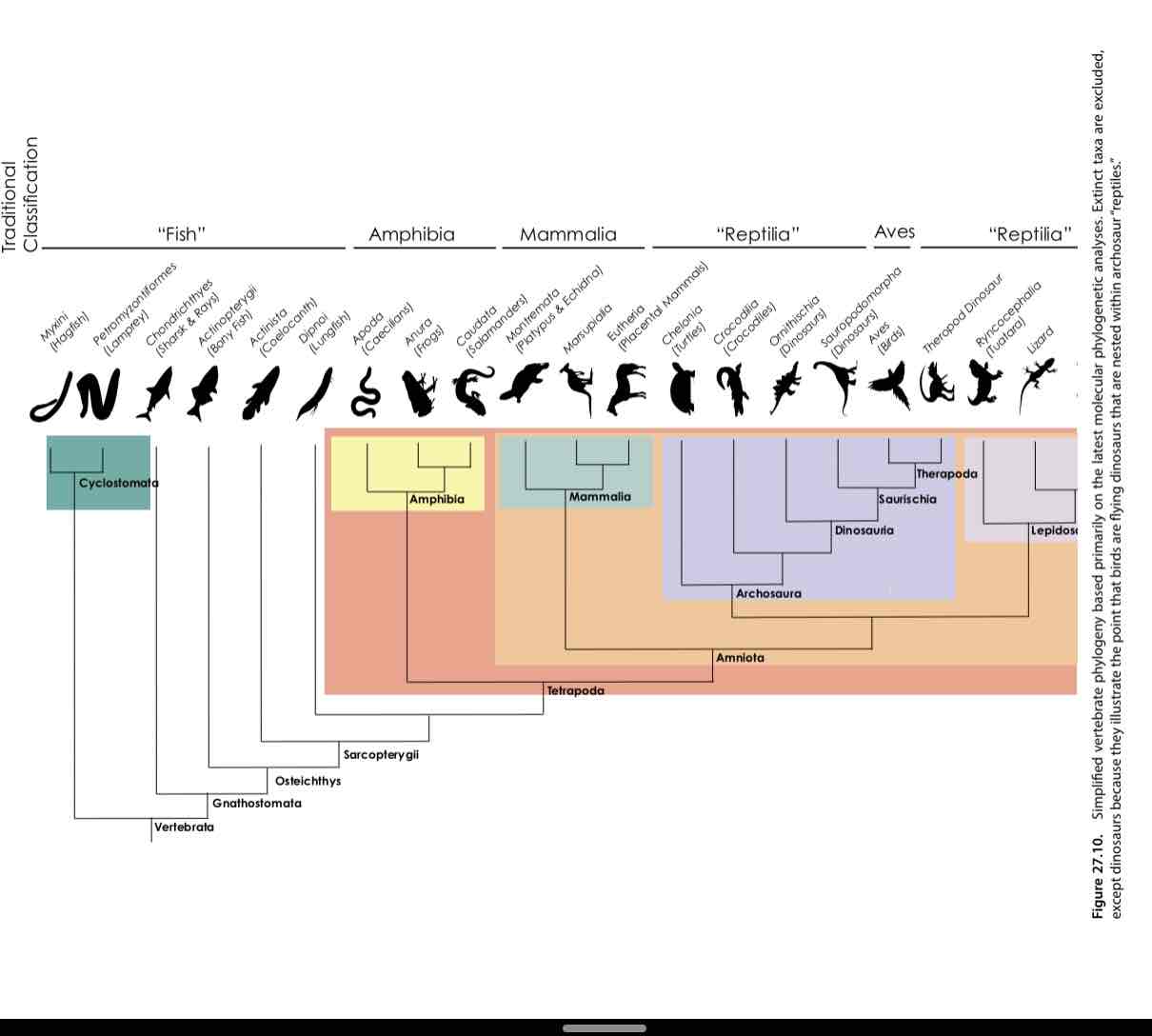
Evolutionary relationships of vertebrates
Preservation techniques
Alcohol, taxidermy, skeletal staining, bone bleaching
Natural history
How or where an organism lives