Ionic Bonding
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
part 1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
How are metal ions formed?
metal atoms lose electrons from their outer shell
How are non-metal ions formed?
Non-metal atoms gain electrons
Which elements does ionic bonding occur between?
metal and non-metal
Describe how electrons are transferred:
Electrons are lost from one metal atom and transferred to a non-metal atom
State what is formed as a result of this transfer
Cation (positively charged ion)
& anion (negatively charged ion)
Define ‘ionic bond’:
Electrostatic force of attraction between oppositely charged ions
Describe the structure of an ionic compound:
Giant 3D lattice structure made up of oppositely charged ions
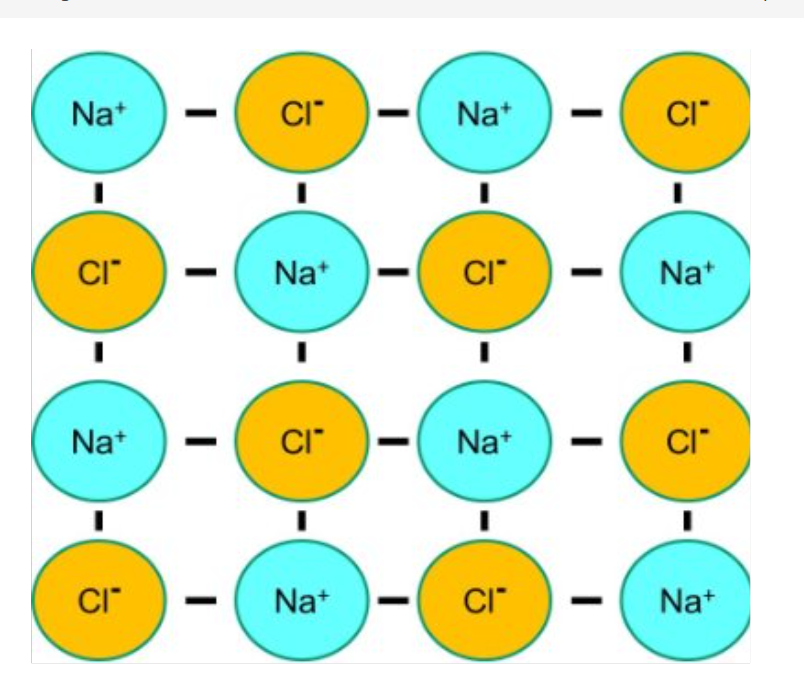
Evaluate the effectiveness of this model:
+ Identifies the ions & charges
+ Accentuates bonds/attractions
- Misrepresents the size of ions
- Bonds are not sticks
- Only shows 2D structure

Evaluate the effectiveness of this model:
+ Shows 3D structure of lattice
+ Shows differing ion size
- Attractions are unclear
- Charges are not present
- Ions aren't coloured
What are the properties of ionic compounds?
1. High melting and boiling points
2. Hard and brittle
3. Does not conduct electricity when solid
4. Conducts electricity when molten or dissolved in water
Explain why ionic solids have high melting points:
Strong electrostatic forces of attraction between ions
Ions held in a giant lattice
→ Large amount of energy needed to break apart ions
What do MP and BP of ionic compounds depend on?
Ionic charge
Ionic radius
Explain the effect of ionic charge on the melting point:
The higher the ionic charge, the greater the electrostatic forces of attraction between the ions.
The higher the melting point of the ionic compound as more energy is required to overcome the electrostatic forces of attraction.
Explain the effect of ionic radius on the melting point:
The smaller the ionic radius, the greater the electrostatic forces of attraction between the ions.
The higher the melting point of the ionic compound as more energy is required to overcome the electrostatic forces of attraction.
Explain why ionic compounds are brittle:
When layers of ions are moved past each other the ions with the same charge repel each other, this causes the solid to split.
Explain why ionic compound only conduct electricity when molten/ dissolved:
Ions are free to move and carry charge when molten/ in aqueous solution- but are fixed when in a lattice (solid state).
What does PANIC stand for?
Positive Anode Negative Is Cathode
Explain how electrolysis is evidence of ionic bonding:
Different ions have different colours in solution (only some transition).
Colour separation during electrolysis is evidence of the presence of ions in ionic compounds.
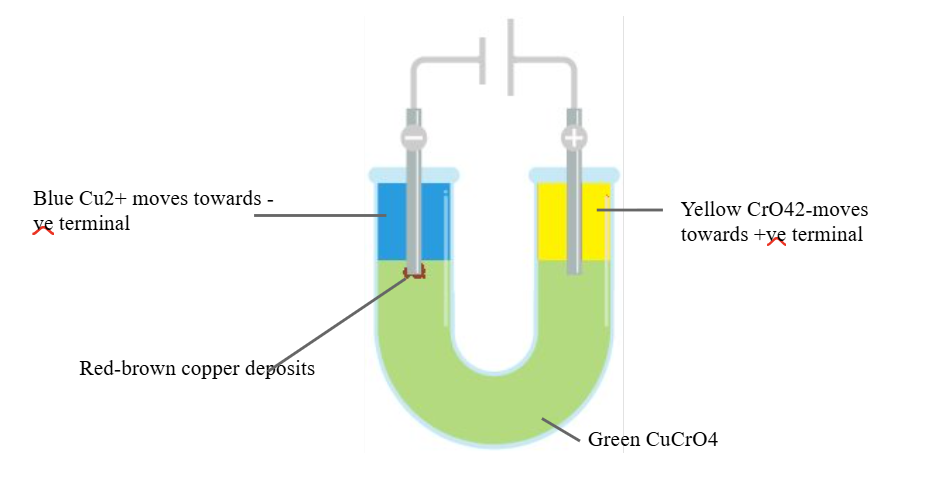
What are the 3 ways of providing evidence for ionic bonding?
Properties
Electrolysis
Electron density maps
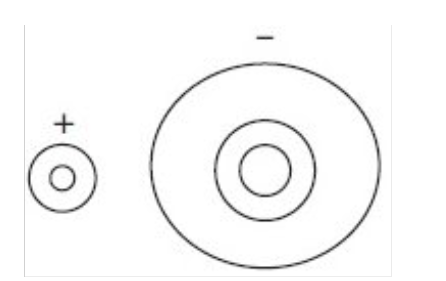
What does an electron density map show?
The probability of finding electrons
→ these patterns can provide evidence of ionic bonding
Electron density map for ionic compounds:
No electron density between ions or contour lines surrounding both ions showing two discrete ions
Size of the circles (lines) = size of the ion
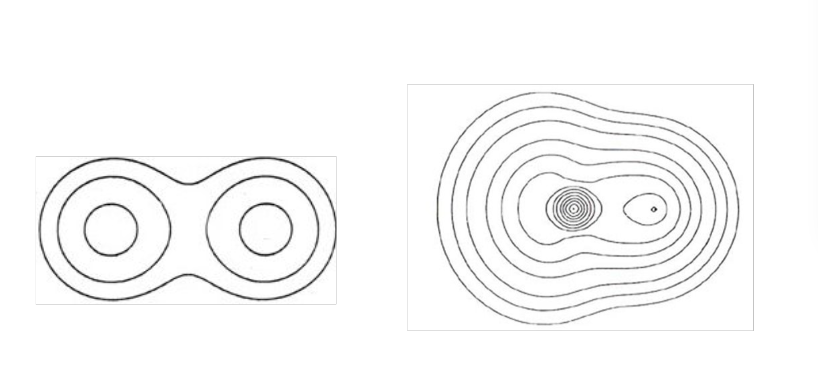
Electron density map for covalent molecules:
Contour lines surrounding atoms means overlapping areas of electron density.
There is electron density between ions.
What do cations with a greater charge density have?
Larger polarizing power
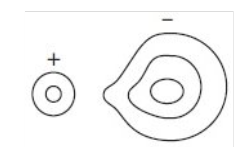
Describe what is happening:
Polarization is the distortion of the electron clouds of the anion by the cation. A cation has polarising power (it pulls electron density towards it), an anion is polarisable.
When does polarisation occur?
Polarisation occurs if the anion is large
and if the cation is small
or if the cation has a large ionic charge
Ionic compounds with polarisation are ionic with covalent character.
Explain the melting and boiling points of metals:
Metals with a smaller ionic radius and a greater charge have mire delocalised electrons per cation.
Electrostatic FOA between the metal ion and delocalised electron are much stronger.
More energy is required to overcome these forces.
Summarise the three types of evidence for the existence of ions:

Define metallic bonding:
The electrostatic forces of attraction between positive metal cations and a sea of delocalised electrons
Explain malleability and ductility of metals:
Layers slide over each other but stay together due the electrostatic forces of attraction between the electrons and the cations
Explain conductivity of metals:
Delocalised electrons are free to move
Explain high BP of metals:
Strong electrostatic forces of attraction between metal cations and delocalised electrons
Explain why the melting point of sodium is lower than that of magnesium:
Magnesium has a smaller ionic radius and a greater charge (Mg2+). Therefore, it has two delocalised electrons per cation, stronger electrostatic forces of attraction, more energy required to break bonds, higher melting point.