NS - Anxiety (with Insomnia)
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
What is Anxiety?
- Anxiety is a feeling of unease, like worry or fear, and it can be beneficial for cases like survival
- It can be intermittent or chronic, and the source of anxiety can be certain events/situations or irrational
What are the symptoms of Anxiety?
- Psychological symptoms can include avoidance behaviour, social disturbances, concentration/memory issues
- Physiological symptoms can include dizziness, nausea, increased heart rate and breathing rate, pins+needles
- Symptoms are somewhat similar to depression
What are the causes of Anxiety?
- Causes tend to be environmentally linked, with slight genetic predisposition to developing anxiety
- Examples of causes can be traumatic events, physical/mental health, and drugs and medication
Describe the different Anxiety Disorders (1)
- Generalised Anxiety Disorder (GAD) = manifesting from no known stimulus, with low level anxiety at all times
- Specific Phobias = often irrational phobias (fears) are causes of anxious feelings
- Social Phobias = Selective Mutism is an example (unable to speak in certain social situations)
- Separation Anxiety = seen most in younger people with separation from people or environments
Describe the different Anxiety Disorders (2)
- Obsessive Compulsive Disorder (OCD) = obsessions involve controlling things and compulsions include not doing things that are believed to be unfortunate for them (can become debilitating)
- Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) = reliving unpleasant memories, manifesting as flashbacks or nightmares
- Panic Disorder = suffering panic attacks from no apparent triggers
What are the Brain regions mediating anxiety?
- Amygdala = important in mediating fear and anxiety response
- Hippocampus = important for memory management
- If one is compromised, fear/anxiety can be enhanced
What is the difference between Anxiolytics and Hypnotics?
- Anxiolytics are used to treat anxiety (usually debilitating), treating the psychological (eg. nervousness) and physical symptoms (eg. palpitations)
- Hypnotics are used to treat insomnia, where anxiety may cause insomnia
- Both types of drugs are work as CNS depressants
What are the drug classes used for Anxiety and Insomnia?
- GABA-A Receptor modulators include Barbiturates, Benzodiazepines and Z-drugs
- 5HT-1A Receptor agonists
- Beta-Adrenoreceptor antagonists
- Antihistamines
How do the GABA-A Receptor modulator class of drugs work?
- Barbiturates stabilise the open position of the receptor, leading to greater hyper-polarisation (not used anymore as it has many off-target effects)
- Benzodiazepines bind to the Alpha 2 - Gamma site of the receptor, stabilising the active form of the receptor, increasing GABA affinity (fewer off-target effects and reduced risk of OD)
- Z-drugs act on Alpha-Gamma site of the receptor, but structure difference causes hypnotic effects
Describe the clinical decision making concepts used in choosing a GABA-A Receptor modulator drug
- Longer action drugs are used more for anxiety, while shorter action drugs are used more for insomnia (don't want sedative effect past sleep time)
- Long term use may lead to addiction
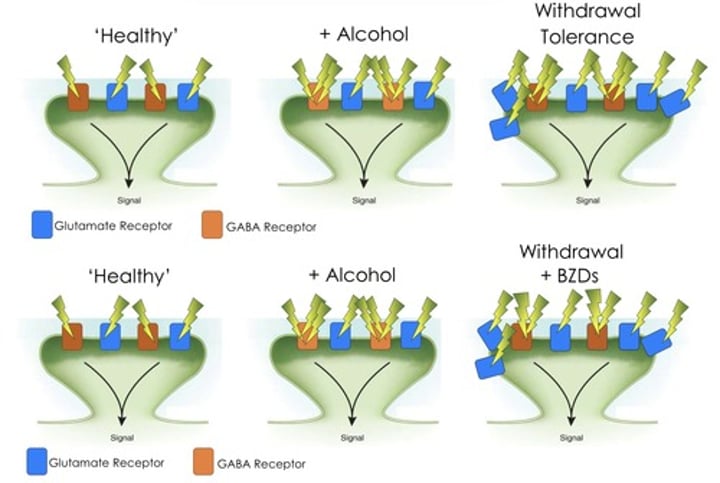
- Tolerance/withdrawal may be built where number of excitatory Glutamate receptors increase at synapses, which may cause E-I stimuli imbalances
- Benzodiazepines can be used to treat alcohol dependence as same benzodiazepine tolerance/withdrawal occurs with alcohol
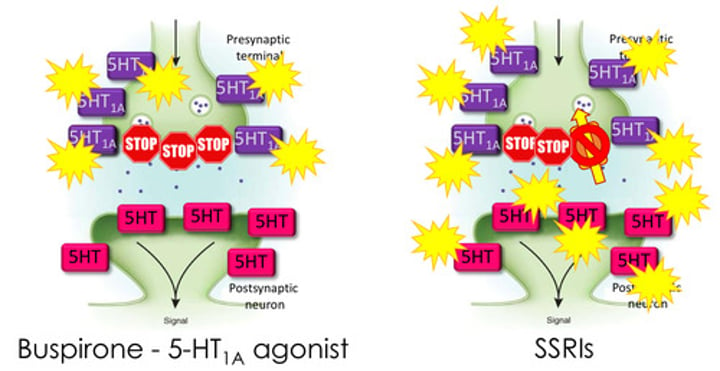
How do 5HT-1A Receptor agonists work?
- 5HT-1A is an metabotropic auto-receptor found pre-synaptically to prevent further release of Serotonin
- Drugs like Buspirone that continually activate 5HT-1A lead to fewer 5HT-1A receptors pre-synaptically
- Fewer autoreceptors mean increased serotonergic drive at synapses (similar effect to SSRIs which act post-synaptically)
How do Beta-Adrenoreceptor antagonists treat anxiety?
- Antagonism of Beta-Adrenergic receptors lead to reduction of peripheral symptoms like tachycardia or increased blood pressure
- This treats the physical symptoms of anxiety, rather than the psychological symptoms
How are Anti-Histamines used for anxiety and insomnia?
- Anti-Histamines are used for their sedative/hypnotic effects
- This is done by antagonism of CNS Histamine receptors which are responsible for wakefulness