BIO/BIOCHEM REVIEW
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
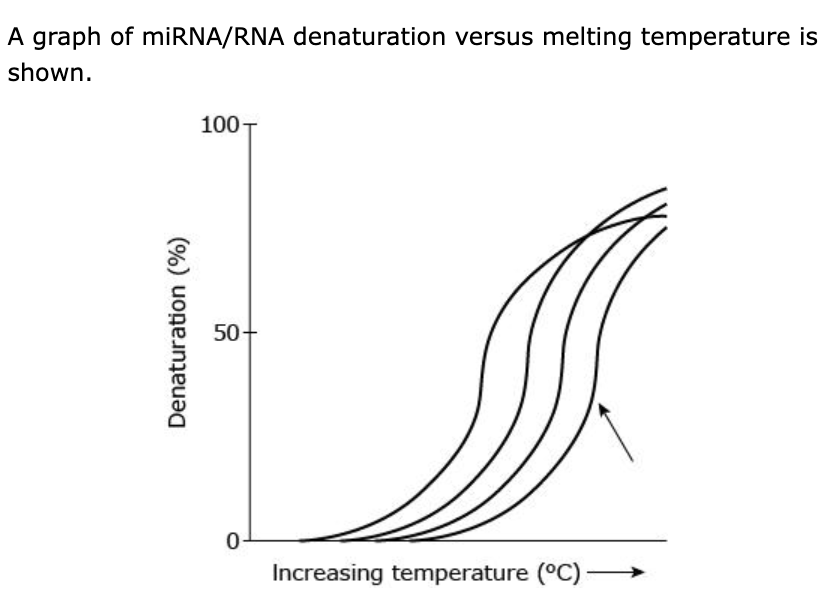
The arrow in the graph indicates the curve representing the melting temperature for which miRNA, assuming 100% base complementarity with its target sequence?
A. miR-142-5p
B. miR-223
C. miR-10b
D. miR-30a-3p
previously chose A
A. In nucleic acid duplex structures, the higher GC-content correlates with more stable duplex, which means the higher melting temperature. miR-30a-3p has the highest CG-content (11) and therefore its duplex will have the highest melting point. Comparatively, miR-142-5p has only 7 G+C.
B. In nucleic acid duplexes, the higher the GC-content correlates with more stable duplex. miR-223 has only 9 G+C, compared to miR-30a-3p which has 11.
C. In nucleic acid duplex structures, higher the GC-content correlates with more stable duplex and thus higher melting temperature. miR-10b has only 10 G+C, compared to miR-30a-3p which has 11.
D. In nucleic acid duplex structures, higher GC-content correlates with more stable duplex and thus higher melting temperature. miR-30a-3p has 11 G+C, and comparatively has the highest GC-content than the other miRs
Which amino acid exhibits a beta-branched side chain?
A. Alanine
B. Leucine
C. Isoleucine
D. Glycine
previously chose B
A. Alanine does not contain a branched side chain.
B. Leucine contains a gamma-branched side chain, not a beta-branched chain.
C. Isoleucine contains a beta-branched side chain.
D. Glycine does not contain a branched side chain.
Which membrane transporter is electrogenic and translocates a net charge across the membrane?
A. Na+− H+ exchanger
B. Na+−Cl- cotransporter
C. Na+−glucose cotransporter
D. GLUT2 facilitative glucose transporter
previously chose B
A. The Na+–H+ exchanger is an antiporter in which the transport of one Na+ is coupled with the transport of one H+ in the opposite direction. This results in no net translocation of charge.
B. The Na+–Cl– cotransporter transports one Na+ and one Cl– in the same direction. Therefore, there is no net movement of charge and this is an electroneutral process.
C. The Na+–glucose cotransporter transports Na+ cations and glucose into the cell. This process is electrogenic, as it results in the net movement of positively charged molecules into the cell.
D. As glucose is not a charged molecule, GLUT2 activity will not be associated with the net movement of charged molecules. Consequently, GLUT2 activity represents an electroneutral transport process.
In which of the following cellular locations does EPO most likely initially bind EPOR in erythrocyte precursor cells?
A. Cytosol
B. Endoplasmic reticulum
C. Nucleus
D. Plasma membrane
previously chose C
A. EPO is a glycoprotein and, therefore, cannot cross the membrane. Consequently, EPOR would not likely be positioned within the cytosol.
B. The endoplasmic reticulum is a site for protein glycosylation, but not the likely site where EPOR localizes. Instead, since EPO is a glycoprotein, it cannot cross the membrane, and must bind to receptors on the cell surface.
C. EPO is not able to cross the membrane to reach the nucleus, as it is a glycoprotein. Consequently, EPOR is not likely positioned within the nucleus.
D. EPO, being a glycoprotein, cannot cross the cell membrane. Consequently, it is likely that EPOR is located on the surface of the plasma membrane.
Which comparison best determines whether IFNγ is necessary for antidepressant-induced increases in the expression of p11?
Expression levels of p11 in:
A. wild-type mice versus IFNγ knockout mice, both treated with p11
B. wild-type mice versus IFNγ knockout mice, both treated with an SSRI
C. wild-type mice treated with IFNγ versus wild-type mice treated with an SSRI
D. wild-type mice treated with IFNγ versus wild-type mice treated with ibuprofen
previously chose A
A. While it may be possible to measure changes in p11 levels above those that resulted from administration of p11, this is not the best experimental design. Specifically, both groups should be treated with an antidepressant, or SSRI.
B. In order to study antidepressant-induced increases in p11 expression, both test groups must be given an antidepressant, or SSRI. TO study the additional effect of IFNγ, on test group should be non-affected (wild-type) and the other should lack IFNγ (IFNγ knockout).
C. Both test groups should be treated with an antidepressant (SSRI) for comparison purposes.
D. Both test groups should be treated with an antidepressant (SSRI) for comparison purposes; ibuprofen is not an antidepressant.
Which biochemical technique requires a pH gradient?
A. Limited proteolysis
B. Southern blotting
C. Isoelectric focusing
D. SDS-PAGE
previously chose D
A. Proteolysis involves the cleavage of peptide bonds and does not require a pH gradient.
B. Southern blotting is a technique to identify specific DNA fragments and does not require a pH gradient.
C. Isoelectric focusing separates proteins based on their pIs. The technique uses an electric field and a pH gradient which causes proteins to stop moving at a pH equal to their pI.
D. SDS-PAGE is a technique to separate proteins based on their size and does not require a pH gradient.
Which type of reaction has a Keq > 1 and is kinetically fast?
A. Endergonic with high activation energy level
B. Endergonic with low activation energy level
C. Exergonic with high activation energy level
D. Exergonic with low activation energy level
previously chose B
A. A reaction that has a Keq > 1 is exergonic, not endergonic. Additionally, a high activation energy results in a kinetically slow, and not a fast reaction.
B. A reaction that has a Keq > 1 is exergonic, not endergonic.
C. A high activation energy results in slow, not fast, reaction kinetics.
D. A reaction that has a Keq > 1 is exergonic and a low activation energy results in fast reaction kinetics.
In response to changing glucose levels, which events occur at time points A and B?
A. Hepatocytes secrete glucagon at point A, and the pancreatic alpha cells secrete insulin at point B.
B. Pancreatic alpha cells secrete glucagon at point A, and pancreatic beta cells secrete insulin at point B.
C. Pancreatic alpha cells secrete insulin at point A, and hepatocytes secrete glucagon at point B.
D. Pancreatic beta cells secrete insulin at point A, and pancreatic alpha cells secrete glucagon at point B.
previously chose B
A. Glucagon is secreted by pancreatic alpha cells, not the liver. Furthermore, insulin is secreted by pancreatic beta cells, not pancreatic alpha cells.
B. High levels of circulating glucose stimulate insulin, not glucagon, secretion. Low levels of glucose stimulate glucagon, not insulin secretion.
C. Pancreatic alpha cells secrete glucagon, not insulin. Hepatocytes do not secrete glucagon.
D. Insulin is secreted in response to high blood glucose levels (point A) by pancreatic beta cells. Conversely, glucagon is secreted in response to low blood glucose levels (point B) from pancreatic alpha cells.
How does the Unit Membrane Model differ from the Fluid Mosaic Model?
A. The location of proteins differs in the two models.
B. The Unit Membrane Model has a monomolecular layer of protein on each surface, while the Fluid Mosaic Model has a bimolecular layer of protein on each surface.
C. The Unit Membrane Model has one layer of phospholipids, while the Fluid Mosaic Model has two layers.
D. The Unit Membrane Model contains dissolved protein, while the Fluid Mosaic Model is coated with a monomolecular layer of protein on each surface.
previously chose B
A. The Unit membrane Model indicates that the proteins form a monomolecular layer both outside and inside the phospholipid bilayer and that the proteins do no penetrate the phospholipid layer. in the Fluid Mosaic Model, the proteins are inserted in the phospholipid bilayer
B. Based on the Unit Membrane Model, the proteins form a monomolecular layer on both sides, inside and outside, of the phospholipids bilayer. However, in the Fluid Mosaic Model, proteins do not form a bimolecular layer on each side. Instead, in the Fluid Mosaic Model, the proteins cross the phospholipid bilayer.
C. In both models, the phospholipids form a bilayer.
D. The passage indicates exactly the opposite: it is the Unit Membrane Model that suggests the phospholipid bilayer is coated on both sides by a monolayer of proteins, while the Fluid Mosaic Model suggests that proteins are dissolved in the bilayer.
Which of the following observations would invalidate the Unit Membrane Model?
A. When a thin section of membrane is observed using a microscope at high magnification, two layers of phospholipid heads are observed.
B. Thermodynamic measurements indicate that the phospholipid heads are exposed to water.
C. When a membrane is frozen and then split from surface to surface, proteins are observed within the hydrocarbon chains.
D. Thermodynamic measurements indicate that the phospholipid tails are hidden inside the membrane, away from exposure to water.
previously chose D
A. This should be seen as proof of the presence of the phospholipid bilayer. The Unit Membrane Model indicates the presence of a phospholipid bilayer.
B. Based on the description of the Unit Membrane Model, the phospholipid heads are hydrophilic, and are therefore expected to face water.
C. According to the Unit Membrane Model, the proteins form a monolayer on the outer and inner surfaces of the phospholipid bilayer. Thus, when this bilayer is split, there should not be proteins observed within hydrocarbon chains. Instead, the proteins should be equally separated by the split.
D. The presence of the hydrophobic tails buried within the phospholipid bilayer is described in the Unit Membrane Model.
The information in the passage best supports which hypothesis?
A. Exercise prevents glucose uptake.
B. Exercise promotes less effective cellular respiration.
C. Exocrine secretions of skeletal muscle act on adipose tissue.
D. Endocrine secretions of adipose tissue act on skeletal muscle.
previously chose A
A. The information in the passage indicates that exercise correlates with increased FNDC5 expression. Additionally, mice overexpressing FNDC5 exhibit lower nonfasting glucose levels, most likely because of higher, not lower, cellular glucose uptake.
B. According to the pathway suggested by the information in the passage, exercise ultimately increases UCP1 levels which in turn degrades the proton gradient that drives oxidative phosphorylation. More energy is dissipated as heat and less is used to synthesize ATP
C. The passage notes that irisin is secreted into blood and therefore it would be an endocrine, not an exocrine, secretion of skeletal muscle.
D. The passage notes that irisin is a protein formed by cleaving the extracellular domain of FNDC5 which is expressed in skeletal muscles, not adipose tissues.
Mice that overexpress PGC-1α specifically in their skeletal muscles are most likely to exhibit which phenotype relative to wild-type mice?
A. Lower body weight
B. Lower body temperature
C. Higher physical activity
D. Higher nonfasting blood glucose levels
previously chose D
A. Based on the passage, overexpression of PGC-1α in skeletal muscle leads to increased subcutaneous fat UCP1 expression, and this UCP1 expression leads to more energy being dissipated as heat. Therefore, mice that overexpress PGC-1α specifically in their skeletal muscles most likely weight less than do wild-type mice.
B. Based on the passage, increased subcutaneous fat UCP1 expression leads to increased thermogenesis and higher, not lower, body temperature.
C. According to the pathway suggested by the information in the passage, physical activity and exercise are upstream, not downstream of skeletal muscle PGC-1α expression.
D. PGC-1α overexpression in skeletal muscle leads to increased FNDC5 expression. Based on the passage, mice overexpressing FNDC5 exhibit lower, not higher, nonfasting glucose levels.
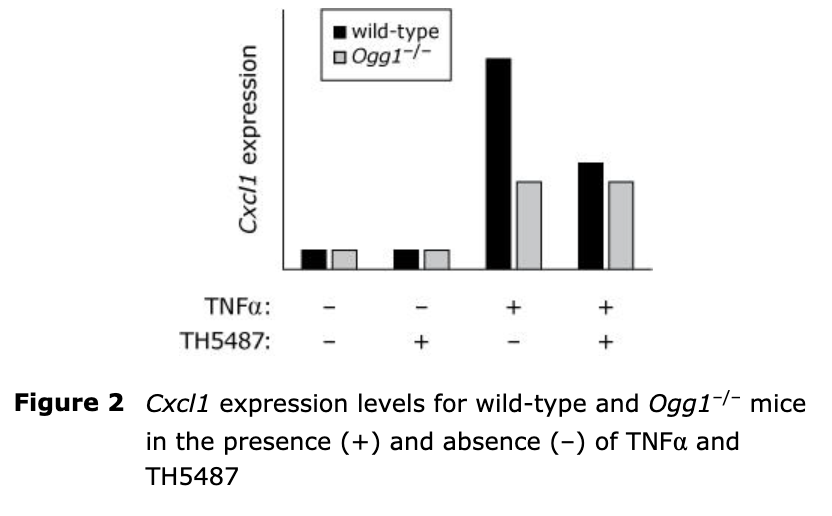
Based on data shown in Figure 2, what are the effects of OGG1 and TH5487 on Cxcl1 expression?
OGG1 reduces the TNFα induced Cxcl1 expression.
OGG1 stimulates the TNFα induced Cxcl1 expression.
TH5487 reduces the OGG1-mediated Cxcl1 expression.
TH5487 stimulates the OGG1-mediated Cxcl1 expression.
A. I and III only
B. I and IV only
C. II and III only
D. II and IV only
previously chose A
A. The figure shows that in wild-type cells exposed to TNFα, the OGG1-deficient cells exhibit reduced Cxcl1 expression levels, indicating that OGG1 does not reduce the TNFα-induced Cxcl1 expression. Thus, option I is incorrect.
B. The figure shows that compared to untreated wild-type cells, TH5487-treated wild-type cells exhibit reduced OGG1-mediated Cxcl1 expression, inferring that TH5487 does not stimulate the OGG1-mediated Cxcl1 expression. Thus, IV is incorrect. Option I is incorrect because OGG1 does not reduce the TNFα-induced Cxcl1 expression.
C. The figure shows that in wild-type cells exposed to TNFα, the OGG1-deficient cells exhibit reduced Cxcl1 expression levels, indicating that OGG1 stimulates the TNFα-induced Cxcl1 expression. Furthermore, the figure shows that compared to untreated wild-type cells, TH5487-treated wild-type cells exhibit reduced OGG1-mediated Cxcl1 expression, inferring that TH5487 inhibits the OGG1-mediated Cxcl1 expression.
D. The figure shows that, compared to untreated wild-type cells, TH5487-treated wild-type cells exhibit reduced OGG1-mediated Cxcl1 expression, inferring that TH5487 does not stimulate the OGG1-mediated Cxcl1 expression. Thus, IV is incorrect.
In an enzyme-catalyzed reaction where enzyme concentration is held constant and substrate concentration is relatively low, which kinetic parameter will increase with the addition of more substrate?
(Note: Other than substrate concentration, assume no other changes to reaction conditions.)
A. KM
B. kcat
C. Vmax
D. V0
previously chose B
A. KM, the rate constant of a reaction, does not change with changes in substrate concentration.
B. Kcat is the reaction turnover number and does not change with changes in substrate concentration.
C. Vmax is the maximum velocity of a reaction and is a constant property which does not change with the addition of more substrate.
D. V0 is the initial velocity of an enzymatic reaction. At low concentrations of substrate and constant enzyme concentration, adding more substrate will increase V0 until the maximal velocity is reached.
If the RB mutants cannot bind to E2F, then:
A. cell division arrest will not occur.
B. E7 will not bind to these mutants.
C. CDK4 cannot phosphorylate these mutants.
D. E2F will bind to E7
Previously chose D
A. The passage indicates that binding of RB to E2F is required for arresting the cell in G1. Consequently, if an RB mutant is unable to bind E2F, then E2F would remain unbound, and the cell would not become arrested in G1.
B. E7 and E2F do not use the same mechanism of action in binding RB. Specifically, wild-type RB and the RB mutants all arrested cells in G1, indicating interaction with E2F at a site other than the pocket domain. By contrast, the RB mutants are insensitive to modulation by E7, indicating that E7 interacts with RB at the pocket domain. Consequently, it is unlikely that the binding of RB to E2F would impact the binding of RB to E7.
C. According to the passage, CDK4 phosphorylation of RB controls RB binding to E2F, RB binding to E2F does not control CDK4 phosphorylation of RB.
D. E2F and E7 work independently in regulating RB function. There is no information in the passage suggesting that E2F directly binds E7.
The LXCXE motif is described as being "highly conserved." Certain parts of the genome, such as that encoding the LXCXE motif, are highly conserved because they are:
A. vital to an organism's survival.
B. chemically incapable of mutation.
C. stored in vesicles for later secretion.
D. stored in cell compartments where they are unlikely to be secreted.
previously chose D
A. From an evolutionary point of view, DNA sequences that are vital to an organism's life are conserved among species.
B. Mutations can affect any portion of DNA.
C. DNA is stored in the nucleus, not in vesicles.
D. The fragment is stored in the nucleus and it is unlikely to be secreted, however this is not the definition of "highly conserved." Instead, genomic conservation refers to maintaining sequence similarity across species.