animal breeding system
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
Breeding systems
These are various ways of evaluation and selection of desired genetic traits in a breed or species.
Mating systems
These are various ways in which members of a given species arrange themselves to copulate (monogamy, polygamy).
Straightbreeding
Mating animals of the same breed
Crossbreeding
Mating animals of different breeds
Systems in straightbreeding
Purebred breeding
Inbreeding
Outcrossing
Grading up
Purebred
an animal of a particular breed that has the characteristics of the breed to which it belongs.
Parents of the animal is also purebred
They are usually registered in purebred association
Purebred
Ancestors can be traced back from the herd book of purebred animal association registry
have the tendency to be genetically homozygous
Purebred breeding advantages
Specialized business/ Purebred shows
Provides the foundation stock for crossbreeding and commercial production systems
Purebred breeding disadvantages
Appearance of undesirable recessive characteristics due to homozygosity of the genes of the parent animals
Requires a higher investment than raising market animals
Inbreeding
Mating of related animals
The mating of animals more closely related than the average of the breed or population.
Increases genetic purity and homozygosity
Desirable and undesirable genes grouped together and therefore the undesirable and desirable traits are more visible.
Inbreeding
Breeders can easily identify animals with undesirable traits and could eliminate them from the breeding program.
It is expensive because all animals with undesirable traits must be removed from the breeding program.
Average of animal breeders does not find this system desirable
2 types of inbreeding
Closebreeding
Linebreeding
Closebreeding
Most intensive form
The animals being mated are very closely related and can be traced back to more than one common ancestor.
sire to daughter, son to dam, or brother to sister
Linebreeding
It refers to mating of animals that are more distantly related and can be traced back to one common ancestor
cousins, grandparent to grandoffspring, or half-brother to half-sister
Closebreeding

Linebreeding

Outcrossing
Mating of animals of different families within the same breed.
It aims to bring traits that are desirable but not present in the original animal breeding program.
Outcrossing
It is popular with purebred breeders because it reduces the chances of undesirable traits appearing in the offspring.
Used in combination with inbreeding programs to bring in traits that are needed.
Line crossing
Mating animals from two different lines of breeding within a breed.
The purpose is to bring together desirable traits from different lines of breeding.
Some lines cross better than other lines because of different gene combinations.
Grade animal
Any animal not eligible for registry
Grading up
Mating of purebred sires to grade females
Aims to improve the quality of animals in farm
Not very expensive
It only requires purchase of Purebred sires, or their semen.
Percent improvement per generation
First generation
50% purebred
2nd generation
75% purebred
3rd generation
87.5% purebred
Grading up

Crossbreeding
Mating of two animals from different breeds
offspring usually have improved traits and referred to as “Hybrid”.
In this system the dominant genes tend to mask undesirable recessive genes.
Production of superior traits, “Hybrid Vigor or heterosis”
Breed complementary
using benefits from breeds while hiding the flaws
Heterosis
measured by the average superiority of the hybrid offspring over the average of the parents.
Traits with a high degree of heritability…
…little improvement from crossbreeding
Traits with low heritability…
…greatest improvement as a result of crossbreeding
Forms of heterosis
individual heterosis
Maternal heterosis
Paternal heterosis
Individual heterosis
Advantages of crossbred offspring
Focuses on terminal offspring
Maternal heterosis
Advantages provided by mother
Focuses on maternal traits
maternal ability, reproduction, longevity etc.
Paternal heterosis
Advantages provided by sire
bull fertility
Systems in crossbreeding
Two-breed crosses
Three-breed crosses
Rotation breeding
3rd group
breeds the AB heifers to a terminal (T) bull selected for ability to transmit a high rate of gain.
50% of the herd
Subgroup
It is composed of AB heifers being bred for the first time.
These AB heifers are bred to a smaller breed (breed C) bull to reduce first-time calving problems.
(group four, 10 percent of the herd) of the third group
Crossbreeding systems for swine
Rotational crossbreeding
Terminal crossing systems
Rotaterminal systems
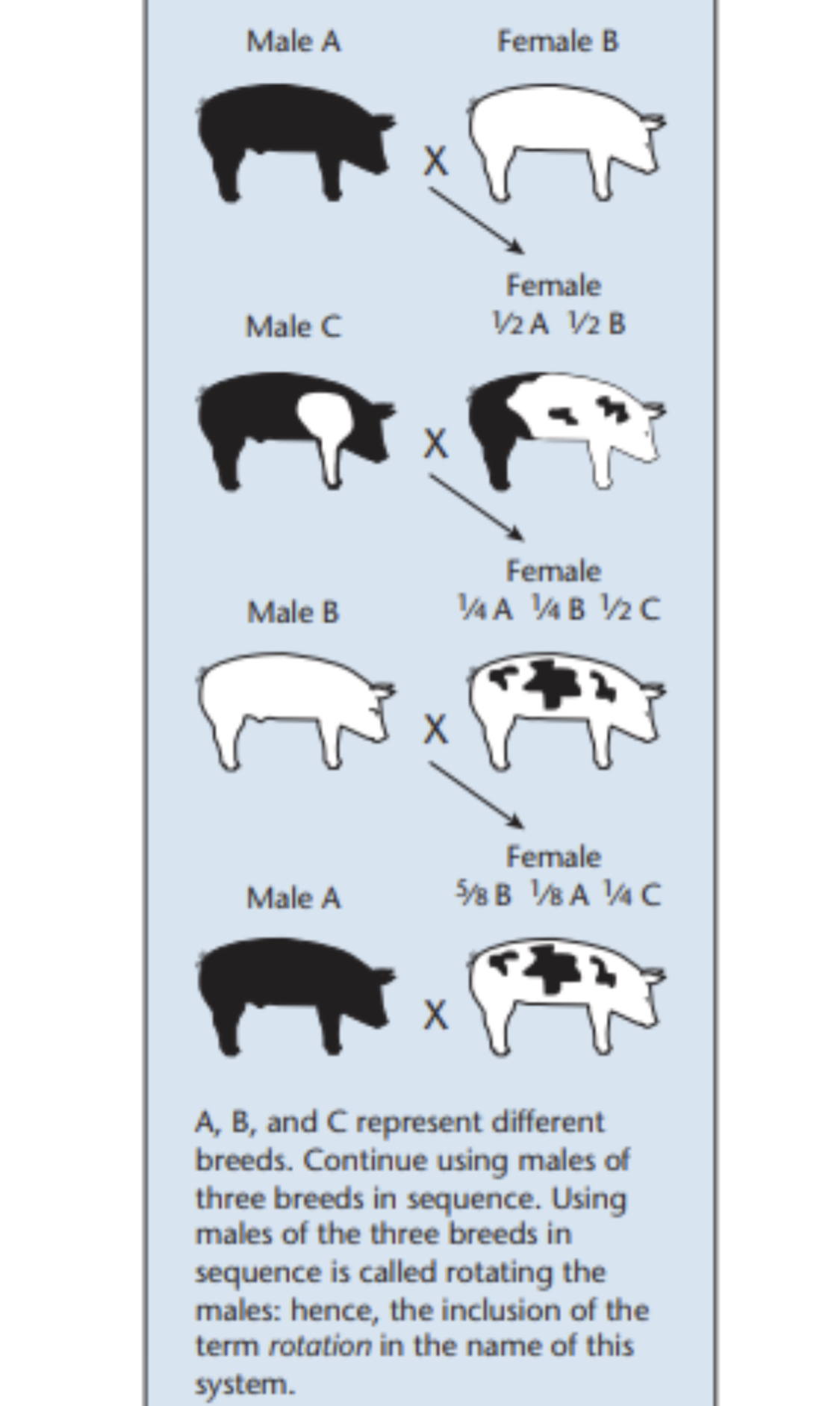
Rotational crossbreeding
In this system, A boar from breed A is mated with sows from breed B, producing offspring AB.
Selected gilts (AB) are bred to a boar from breed B.
Selected gilts from this mating are bred to a boar from breed A
Rotational crossbreeding
The pattern is repeated, switching back and forth to the breed of the most distantly related boar.
It may have two-, three-, four or five- breeding system
Reduction in heterosis if possible pattern is not followed
Rotational crossbreeding
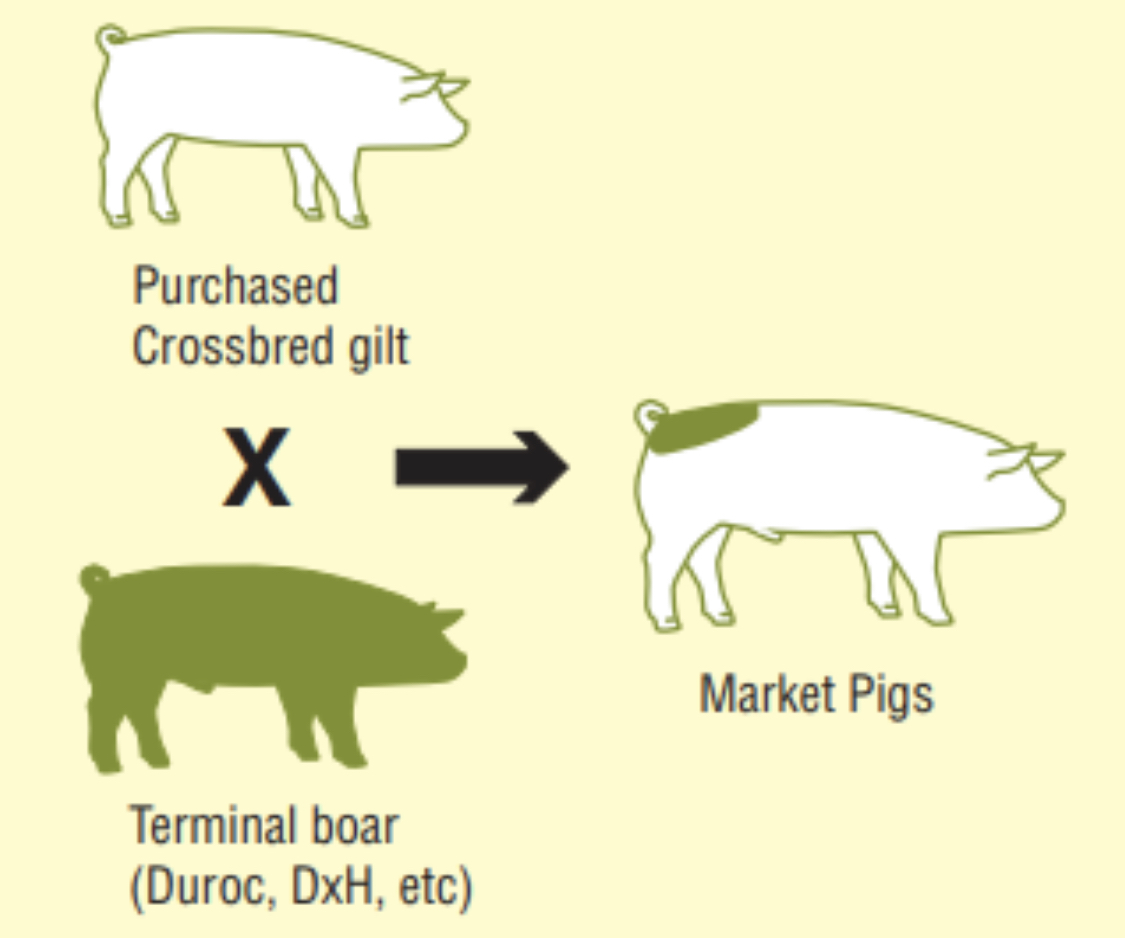
Terminal crossing system
Crossbred (F1 ) females, with superior maternal traits, are bred to boars selected for desirable back fat and rate of gain.
All of the offspring go to market.
The costs are generally higher than in rotational breeding systems.
Terminal crossing system
Risk of introducing health issues from new breeding stock brought into the herd.
Maintain the maximum advantage of heterosis and breed differences in the breeding system.
Terminal crossing system
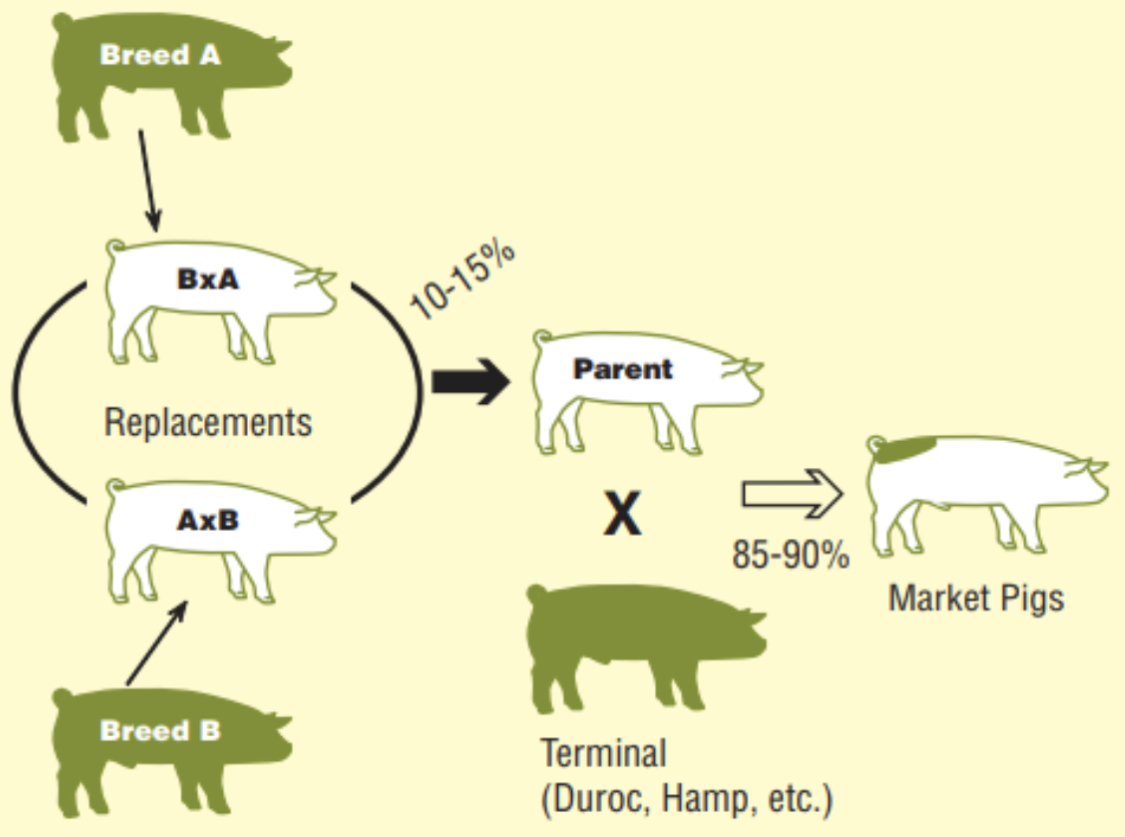
Rotaterminal system
The combination of the rotational breeding system and the terminal breeding system
Crossbred females are produced by breeding boars of different breeds in a rotating pattern to crossbred females produced by previous matings in the system.
Rotaterminal system
All the offspring produced in the terminal breeding go to market.
This system of crossbreeding maintains a high level of heterosis and allows the producer to select breeds with desirable traits.
It does require the use of more boars of different breeds.
Rotaterminal system