Ch 7, Part 1: Linkage& Chr mapping in eukaryotes (OCT 3rd)
1/10
Earn XP
Description and Tags
What is linkage and how does it affect Mendelian expectations?
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
How did "the chromosomal basis of inheritance” start
Friedrich Miescher (1869): discovers DNA in bandage pus
-Contains C, H, O, N and P: Not a protein
-Appears in nucleus of all cells: named nuclein
How did “meiosis as the basis of inhertance” start
Oscar Hertwig (1876): observes movements of chromosomes in
sea urchin egg mother cells
-later observes that fertilization requires combination of
nuclein from both the egg and sperm cell
-Proposes that nuclein is the material of heredity
How did “chromosome theory of interitance” start
1902: Walter Sutton and Theodor Boveri independently
recognize correlation between segregation of
chromosomes in meiosis and segregation of Mendelian
factors (alleles)
-Boveri supposes that there are many more factors
than chromosomes; genes that appear on the same
chromosome are said to be in linkage
Thomas Hunt Morgan Lab…
what does white eyes and miniature wings classify as?
what does F1 generation turn out if recessive female x WT male?
They are both x-linked recessive mutations
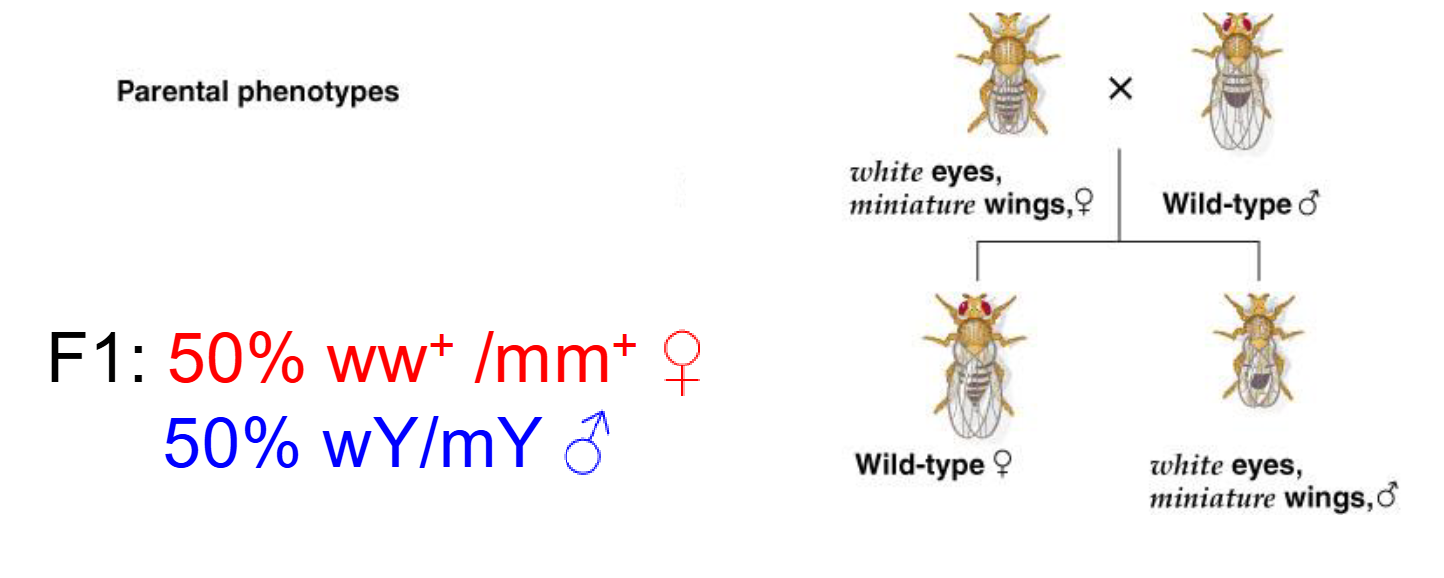
In THM lab..
what are the F2 expectations?

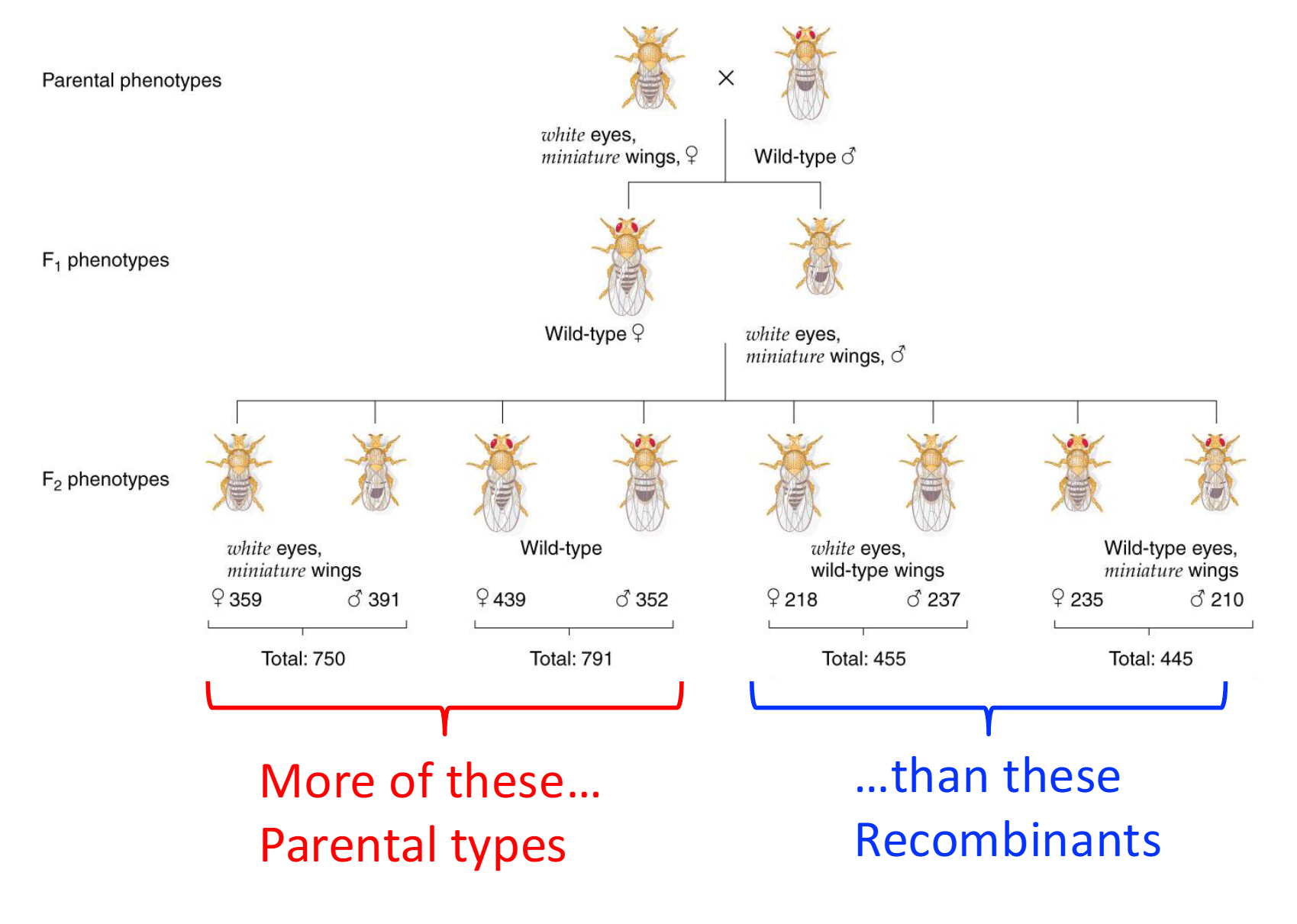
in THM lab..
what actually occured in the F2 generation? what was more present
There was more parental types than recombinant types
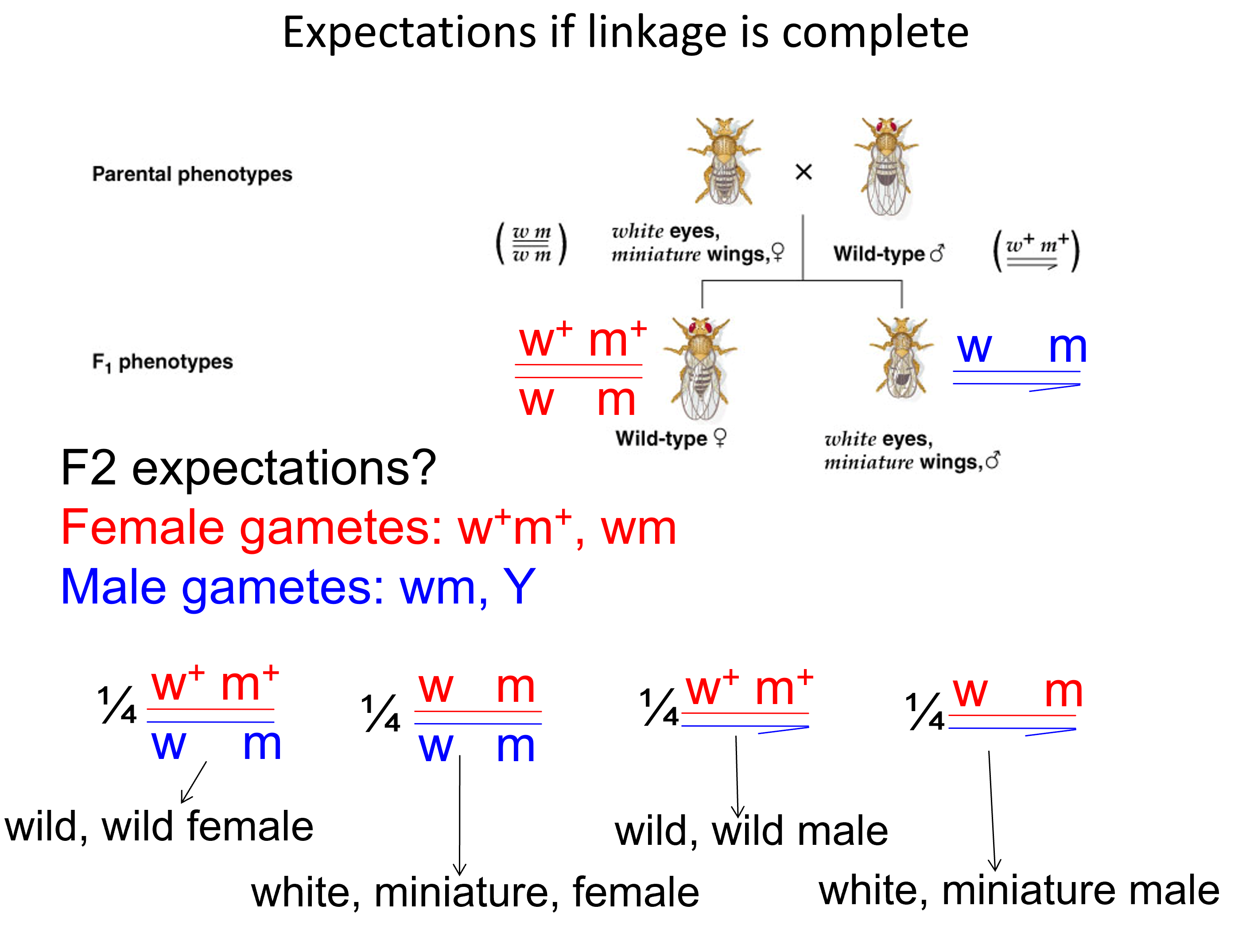
What are the expectations if: Linkage is complete
what is the noticed trend here and what is it known as?
notice there are no
-MT white eye & WT normal wing
-WT red eye & MT miniature wing
all F2 are either WT for both loci or mutant for both loci. This is known as parental phenotypes
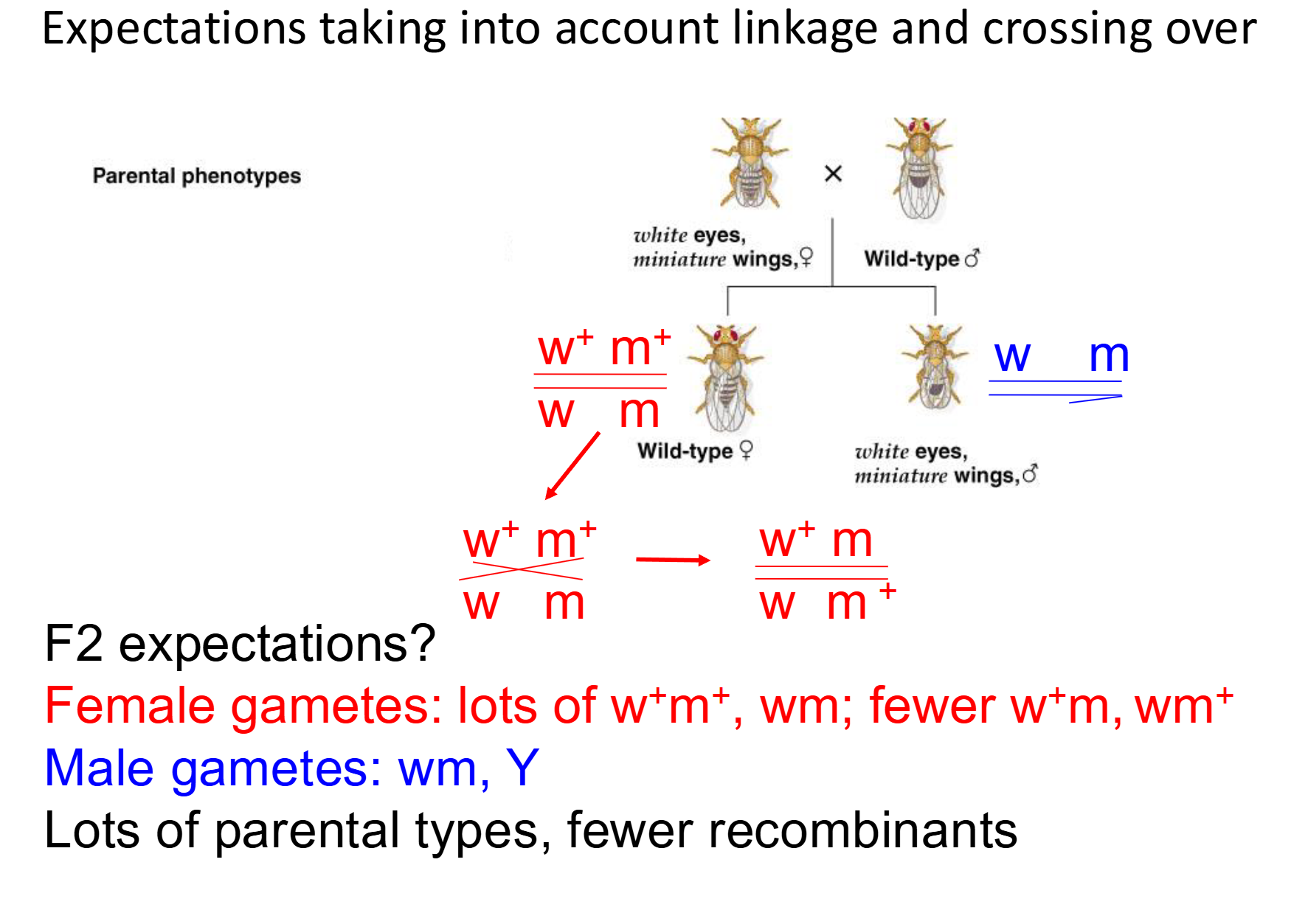
What are the expectations when: taking into account linkage and crossing over
-Based on recombinance number, you can tell how far apart genes on a chromosome are
-females have 2 x-chromosomes
Recombinant frequency and linkage,
what was discovered when genes are further apart?
The further apart two genes are on a chromosome, the higher the probability of recombination
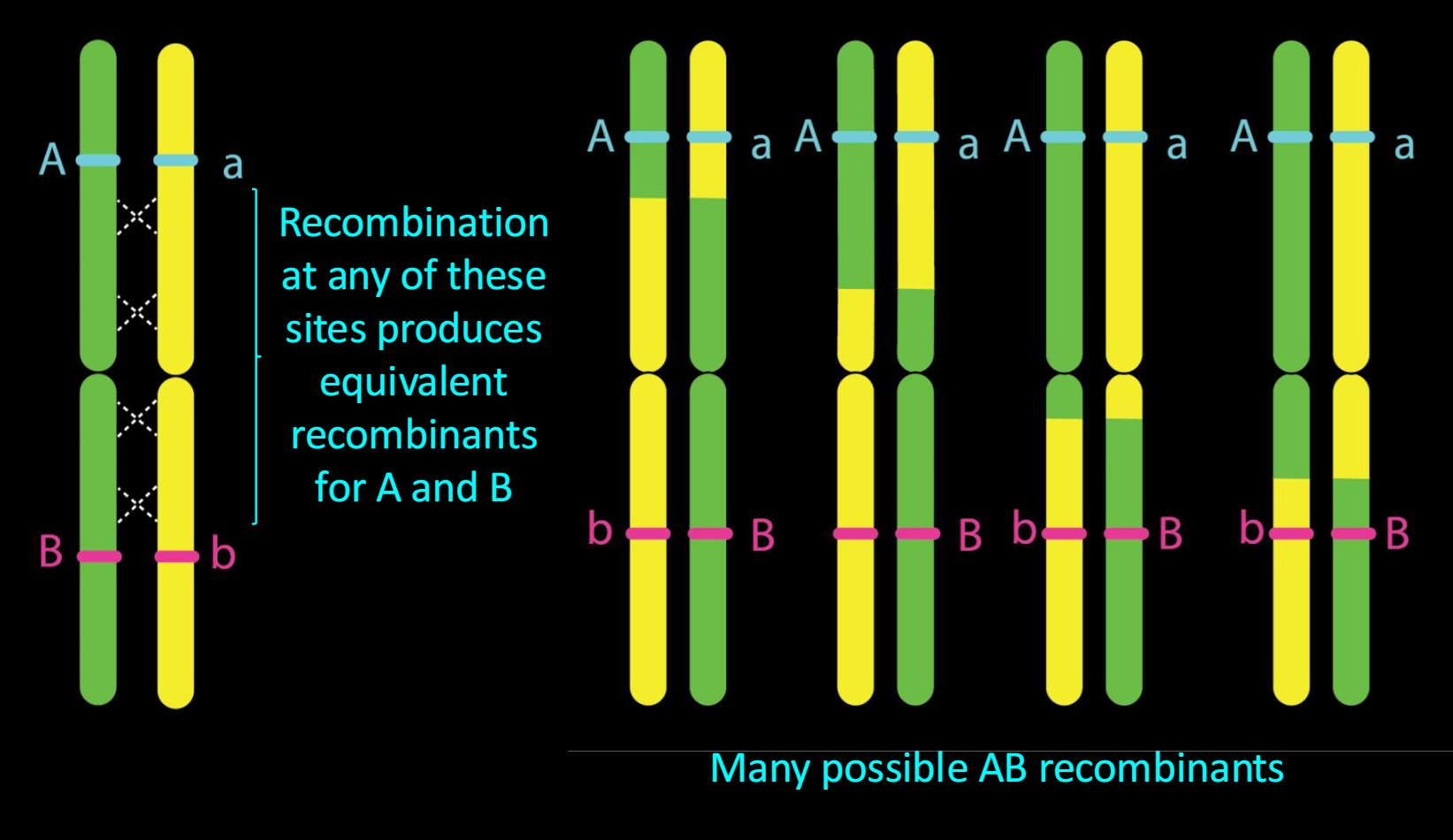
Recombinant frequency and linkage,
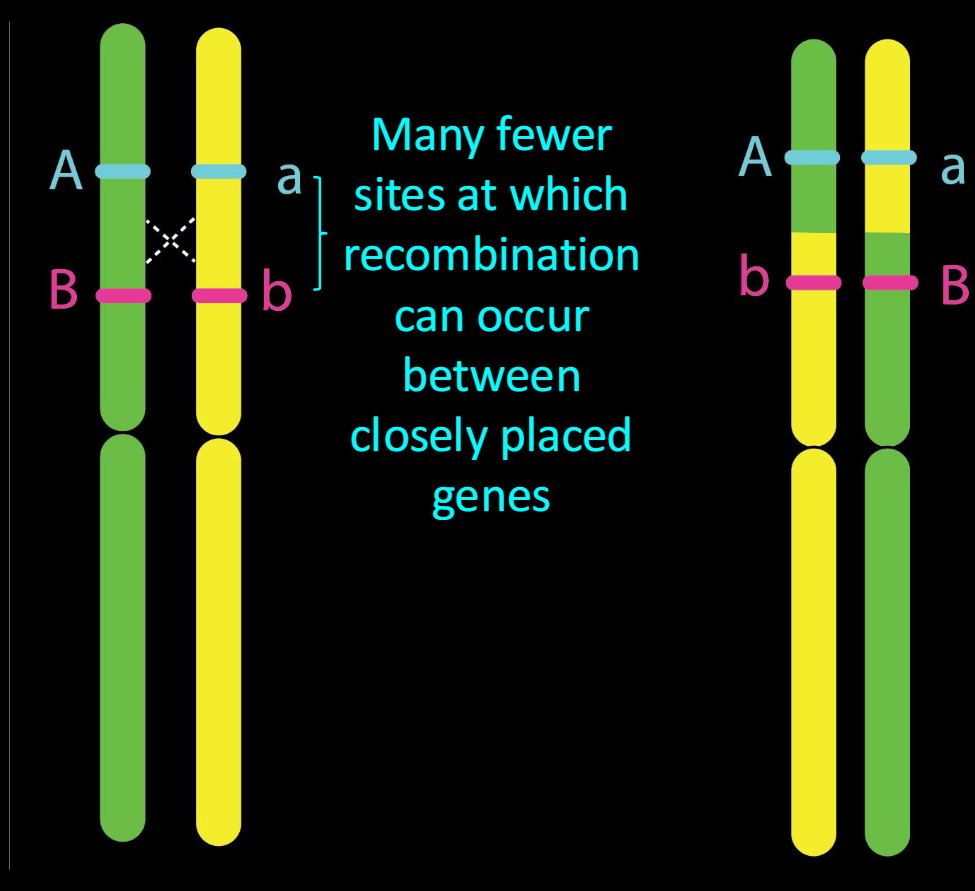
what was discovered when genes are closer together?
-The closer together two genes are on a chromosome, the lower the probability of recombination
-Much more narrow range of equivalent recombinants
The frequency of recombinants =
the distance between two loci in units called centimorgans (cM).