Overview of Photosynthesis and Its Processes
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Photosynthesis
Conversion of light energy to chemical energy.
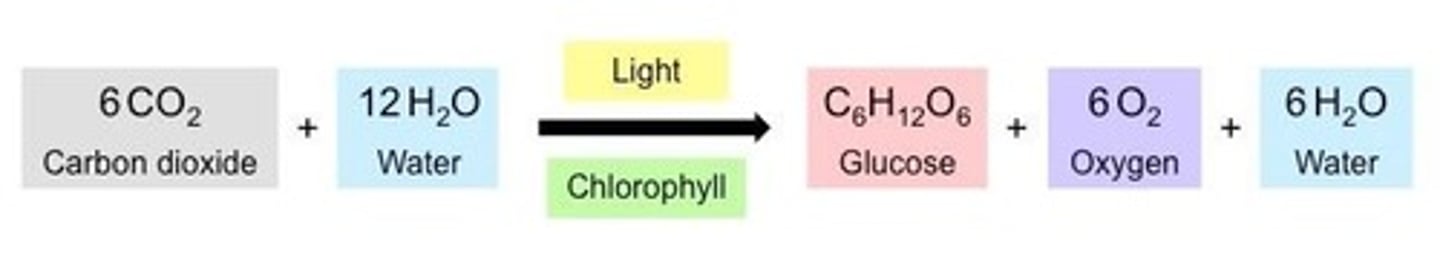
Photoautotrophs
Organisms using light to produce glucose.
Redox Reaction
Involves reduction and oxidation processes.
Electromagnetic Spectrum
Range of all types of light energy.
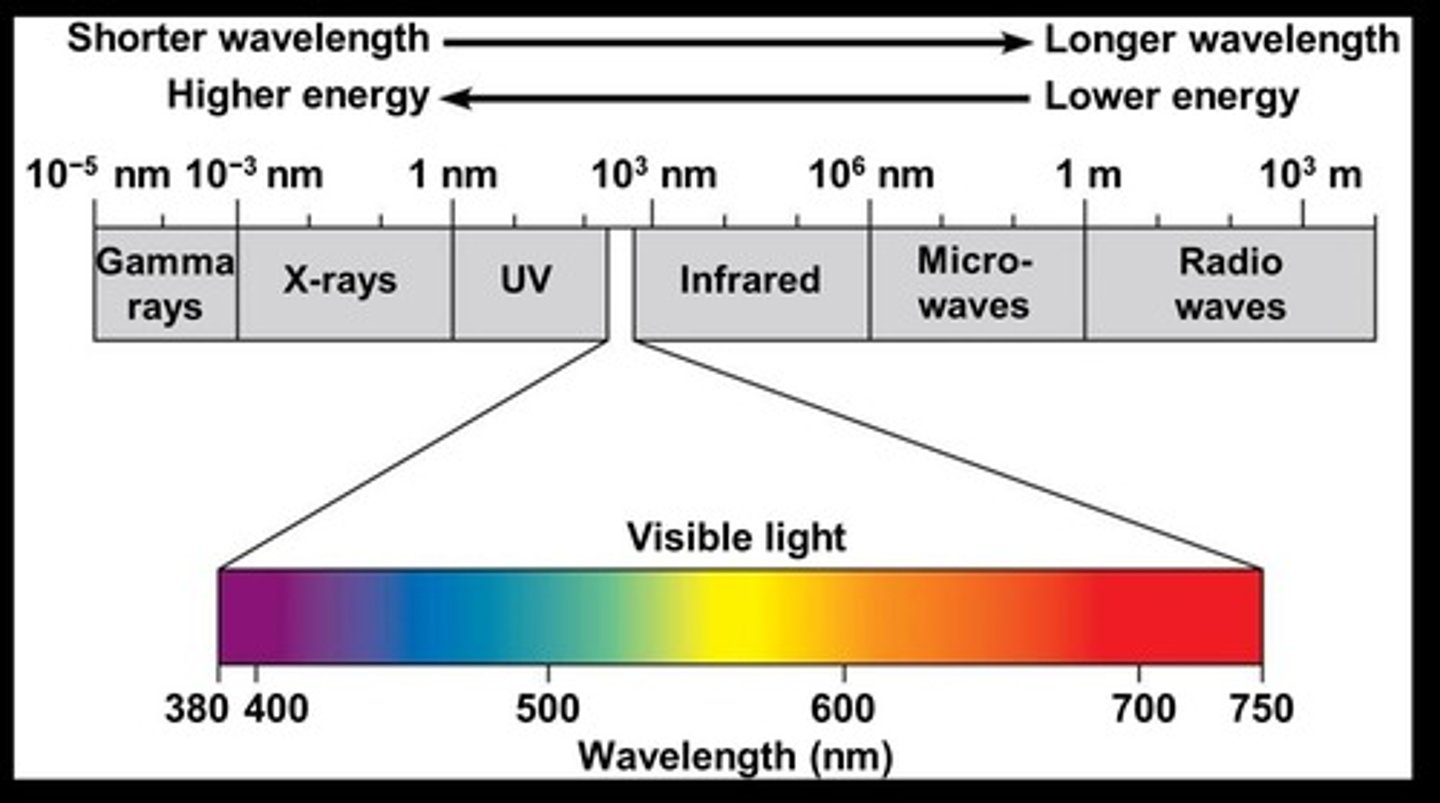
Visible Light Spectrum
Wavelength range of 380 nm to 750 nm.
Wavelength
Distance between successive peaks of a wave.
Pigments
Molecules that absorb and reflect light wavelengths.
Chlorophylls
Primary green pigments in plants and algae.
Carotenoids
Accessory pigments reflecting red, orange, yellow.
Mesophyll Cells
Cells in leaves containing chloroplasts for photosynthesis.
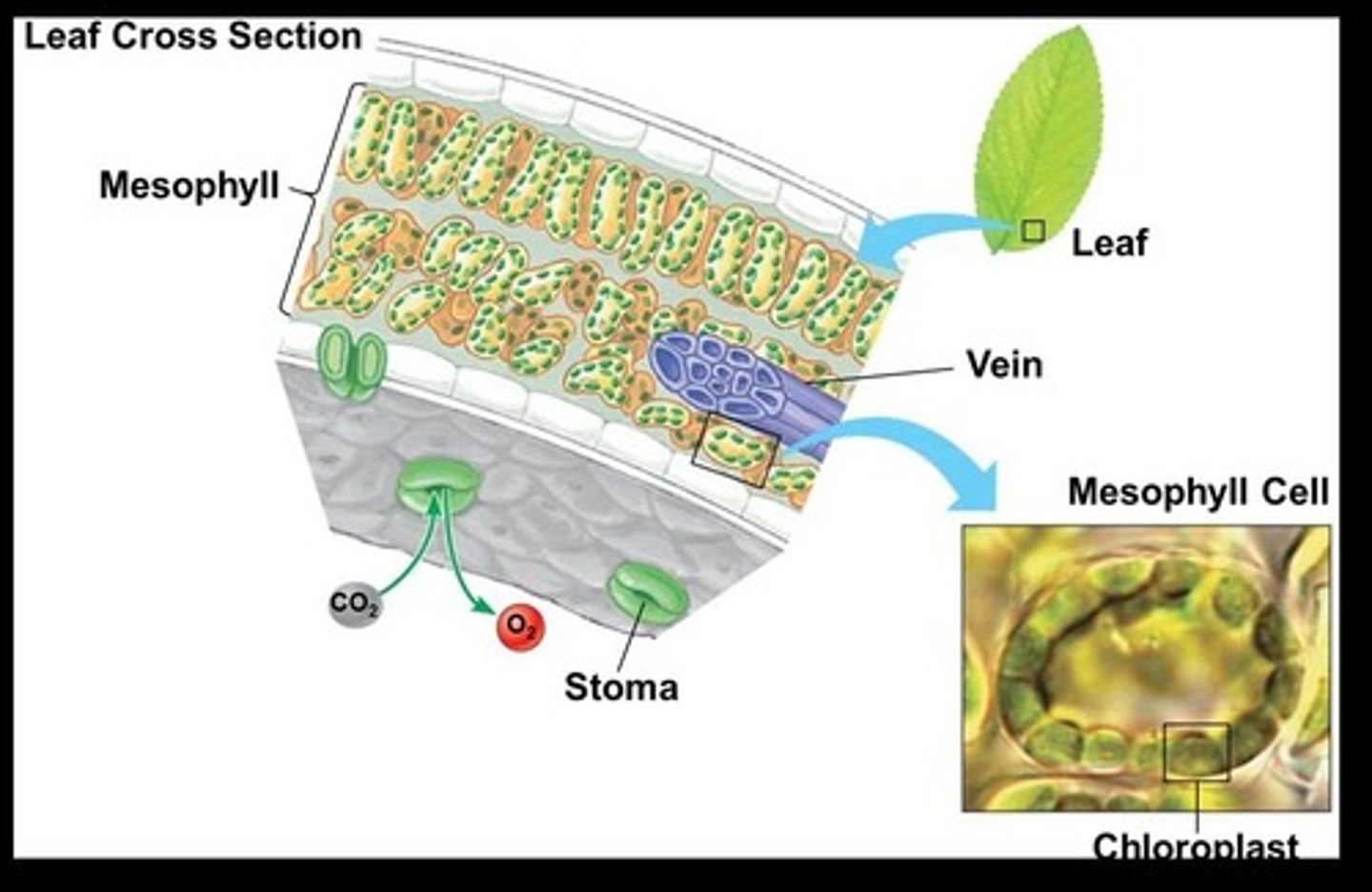
Stomata
Pores allowing gas exchange in leaves.
Guard Cells
Cells regulating the opening and closing of stomata.
Epidermis
Single cell layer covering leaves' surfaces.
Cuticle
Wax layer preventing water loss from leaves.
Chloroplast Envelope
Double membrane surrounding chloroplasts.
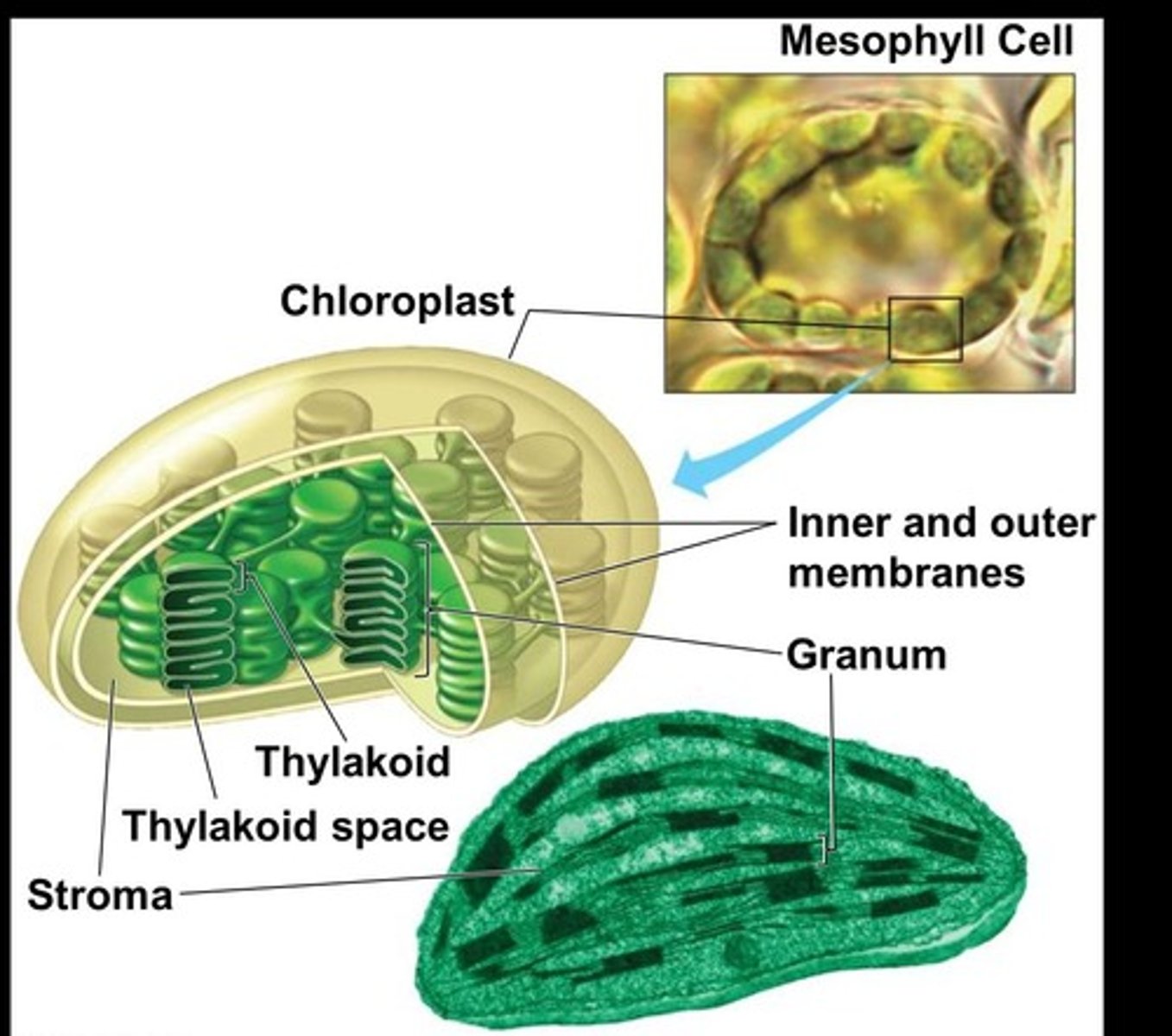
Thylakoid Disks
Structures containing photosynthetic pigments in chloroplasts.
Granum
Stack of thylakoid disks in chloroplasts.
Stroma
Fluid inside chloroplasts where dark reactions occur.
Light Reactions
Convert light energy to ATP and NADPH.
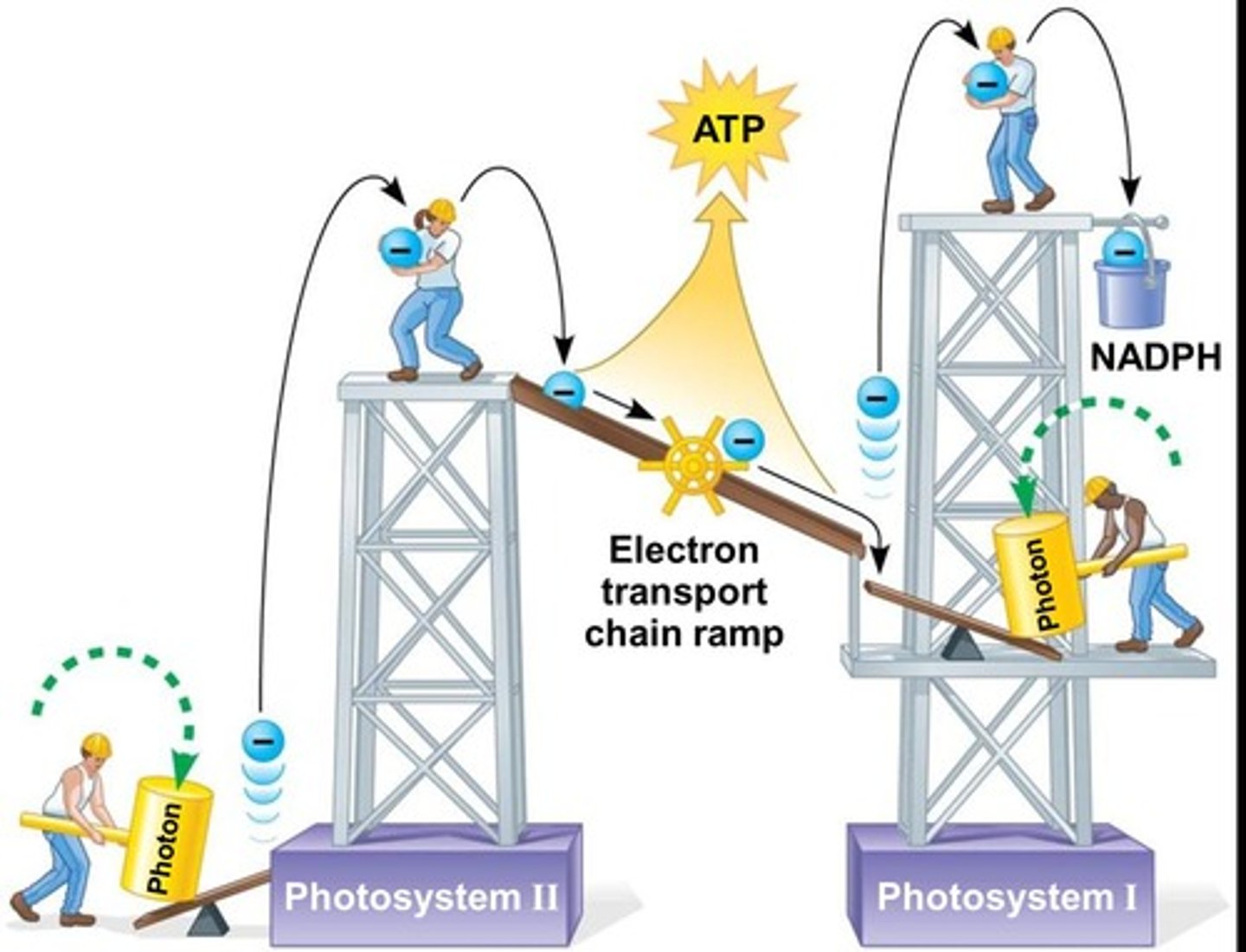
Photosystem II
Traps light at 680 nm, splits water.
Electron Transport Chain
Transfers electrons to synthesize ATP.
Photosystem I
Traps light at 700 nm, re-energizes electrons.
Calvin Cycle
Dark reactions producing glucose from carbon dioxide.
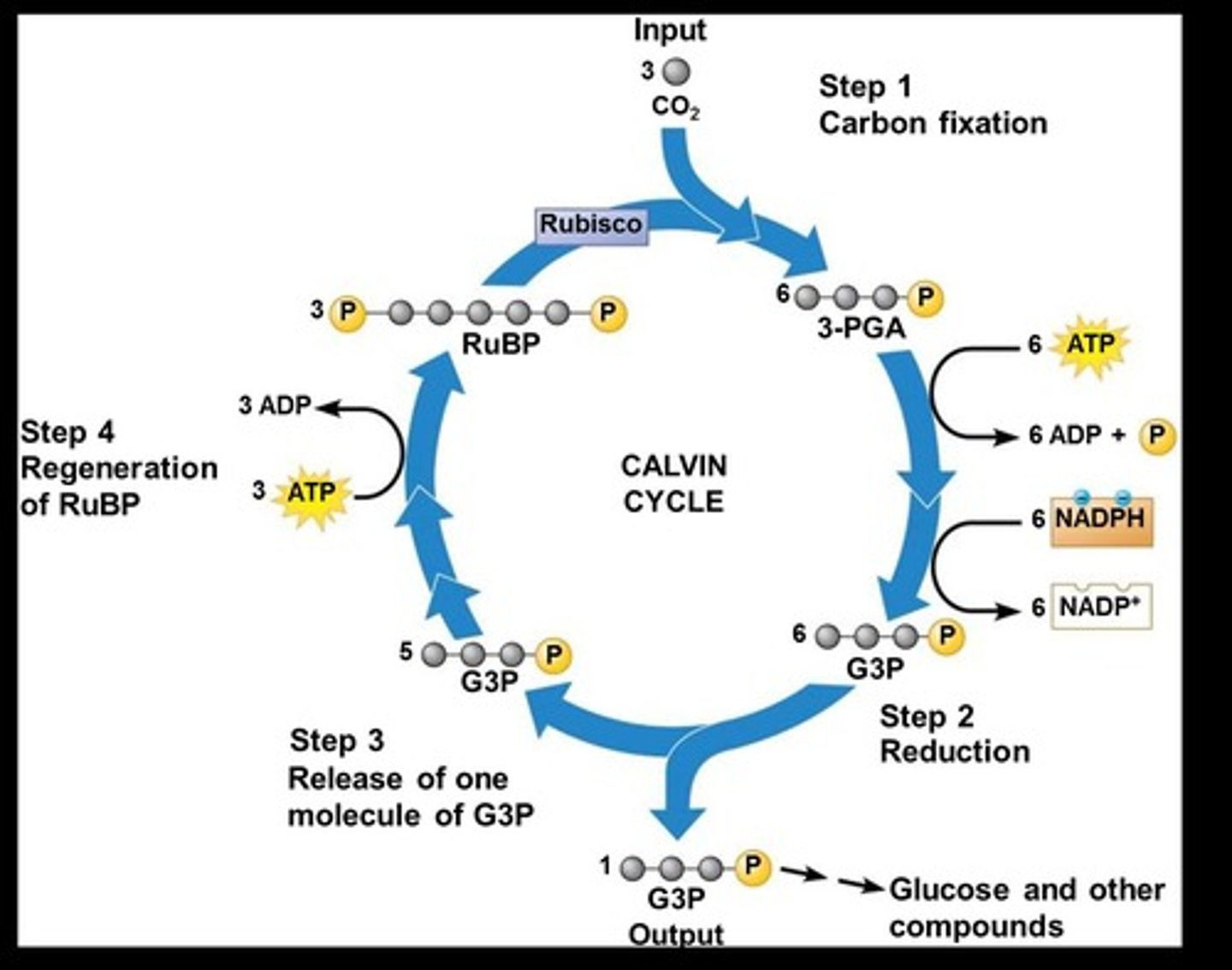
RuBP
Ribulose bisphosphate, involved in carbon fixation.
3-PGA
Three-carbon molecules formed in the Calvin Cycle.
G3P
Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate, used to produce glucose.