PHBioChem (Lecture) | Module 2.3-2.5: MEMBRANE LIPIDS, EMULSIFICATION LIPIDS AND MESSENGER LIPIDS
1/140
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
141 Terms
membrane
All cells are surrounded by?
80%
How many percent are lipids?
Protein
80% - lipid, the rest is?
Phospholipids, Sphingoglycolipids, and Cholesterol
Three common types of Membrane Lipids
Phospholipids
Most abundant type of membrane lipid.
Phospholipids
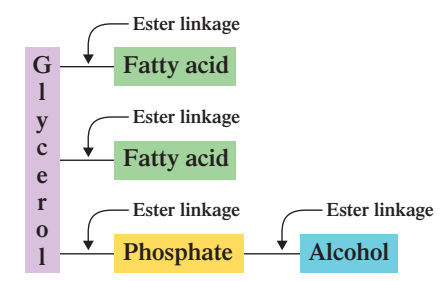
one or more FA, a phosphate group, a platform molecule, and an alcohol attached to the phosphate group.
Platform Molecule
Also known as the backbone of the lipid
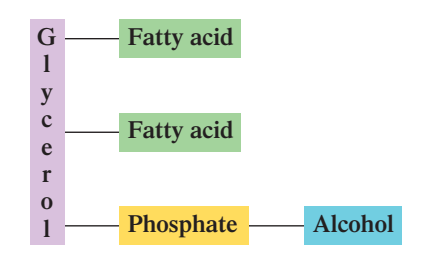
Glycerophospholipids
What is the Platform molecule: Glycerol-based phospholipids
Glycerol-based phospholipids
Its platform molecule is Glycerophospholipids
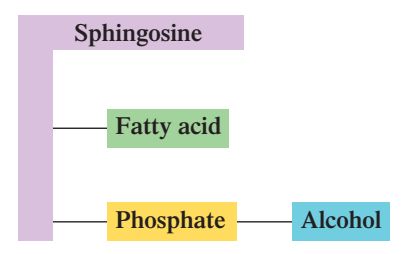
Sphingosine
What is the Platform molecule: Sphingophospholipids
Sphingophospholipids
Its platform molecule is Sphingosine
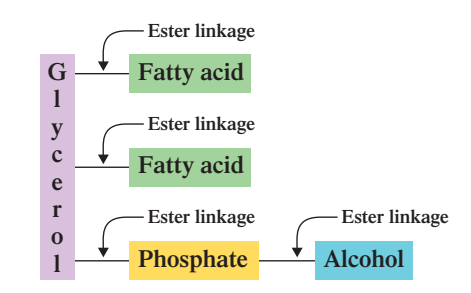
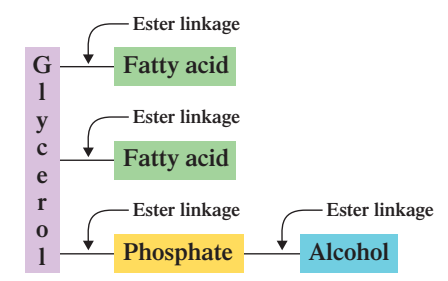
Glycerophospholipids
Glycerol + two FA + Phosphate + Alcohol (four ester linkages)
Glycerophospholipids
Sphingophospholipids
Four
however, glycerophospholipids have ______ ester linkages as contrasted to three ester linkages in triacylglycerols.
4 ester linkages
GLCEROPHOSPHOLIPIDS: What are the linkages in Glycerophospholipids ? (highest to lowest)
Glycerol
GLYCEROPHOSPHOLIPIDS: What is the BACKBONE on this Glycerophospholipids?
Two Fatty Acids
GLYCEROPHOSPHOLIPIDS: What is the NON-POLAR TAIL on this Glycerophospholipids?
Phosphate and Alcohol
GLYCEROPHOSPHOLIPIDS: What is the POLAR HEAD on this Glycerophospholipids?
Choline, Ethanolamine and Serine
GLYCEROPHOSPHOLIPIDS: The alcohol attached to the phosphate group in a glycophospholipid is usually one of three amino alcohols:
Hydrolysis and Saponification
GLYCEROPHOSPHOLIPIDS: Because of the ester linkages present, glycerophospholipids undergo _______ and ______ reactions in a manner similar to that for triacylglycerols, there are five reaction products
Phosphoric acid
GLYCEROPHOSPHOLIPIDS: This is the parent source for the minus one charged phosphate group used in the formation of glycerophospholipids
Minus one charged phosphate
GLYCEROPHOSPHOLIPIDS: Phosphoric acid is the parent source for the ____________________ group used in the formation of glycerophospholipids
choline and phosphate
GLYCEROPHOSPHOLIPIDS: Polar head (__________ and __________) and two nonpolar tails (fatty acid carbon chains).
fatty acid carbon chains
GLYCEROPHOSPHOLIPIDS: Polar head (choline and phosphate) and two nonpolar tails (___________).
Dual polarity
GLYCEROPHOSPHOLIPIDS: This is a structural characteristic of most membrane lipids.
Phosphatidylcholines, Phosphatidylethanolamines and Phosphatidylserines
GLYCEROPHOSPHOLIPIDS: Glycerophospholipids containing these three amino alcohols are respectively known as?
Glycerophospholipids
Phosphatidyl Group + Amino Alcohol = ?
Phosphatidylcholines
GLYCEROPHOSPHOLIPIDS: These are emulsifiers to promote the mixing of otherwise immiscible materials. Mayonnaise, ice cream, and custards are some of the products they are found in.
lecithins
GLYCEROPHOSPHOLIPIDS: Phosphatidylcholines are also known as?
lecithinase
GLYCEROPHOSPHOLIPIDS: The enzyme _______ in the intestine hydrolyzes most of the phosphatidylcholine taken orally before it passes into body fluids, so it does not reach body tissues
liver
GLYCEROPHOSPHOLIPIDS: The phosphatidylcholine present in cell membranes is made by the ____; thus phosphatidylcholines are not essential nutrients.
cephalins
GLYCEROPHOSPHOLIPIDS: Phosphatidylethanolamines and phosphatidylserines are also known as?
Heart, Liver and Brain
GLYCEROPHOSPHOLIPIDS: Phosphatidylethanolamines and phosphatidylserines are found in these organs
Phosphatidylethanolamines and phosphatidylserines
GLYCEROPHOSPHOLIPIDS: These compounds are found in heart and liver tissue and in high concentrations in the brain
Sphingophospholipids
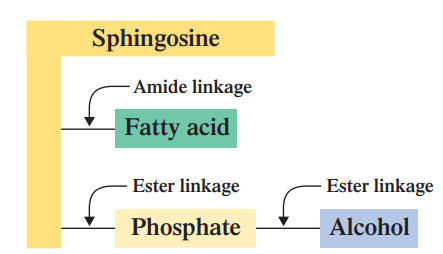
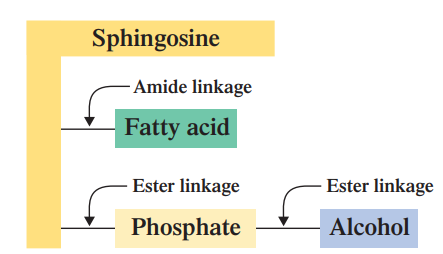
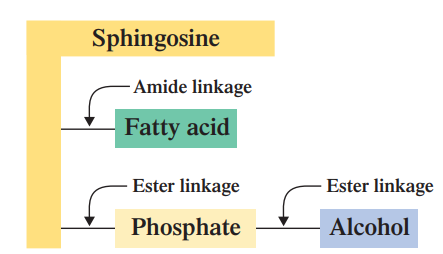
Sphingosine + one FA + Phosphate + Alcohol
1 amide linkage + 2 ester linkages
2 ester linkages and 1 amide linkage
SPHINGOPHOSPHOLIPIDS: What are the linkages in Sphingophospholipids? (highest to lowest)
Sphingosine
SPHINGOPHOSPHOLIPIDS: What is the BACKBONE on this Sphingophospholipids?
One Fatty Acid
SPHINGOPHOSPHOLIPIDS: What is the NON-POLAR TAIL on this Sphingophospholipids?
Phosphate and Alcohol
SPHINGOPHOSPHOLIPIDS: What is the POLAR HEAD on this Sphingophospholipids?
hydrolysis and saponification
SPHINGOPHOSPHOLIPIDS: sphingophospholipid participate in ____________ and __________ reactions. Amide linkages behave much as ester linkages do in this type of reaction
Choline
SPHINGOPHOSPHOLIPIDS: Amino alcohol is?
sphingomyelins
SPHINGOPHOSPHOLIPIDS: Sphingophospholipids in which the alcohol esterified to the phosphate group is choline are called?
myelin sheath
SPHINGOPHOSPHOLIPIDS: Sphingomyelins are found in all cell membranes and are important structural components of the ____________, the protective and insulating coating that surrounds nerves.
Sphingosine
1 tail
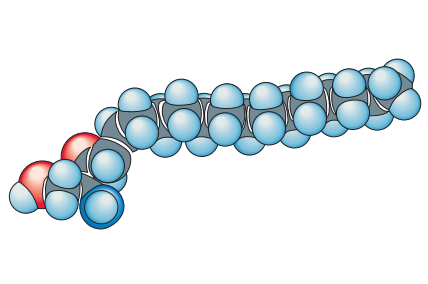
Sphingophospholipids
2 tails
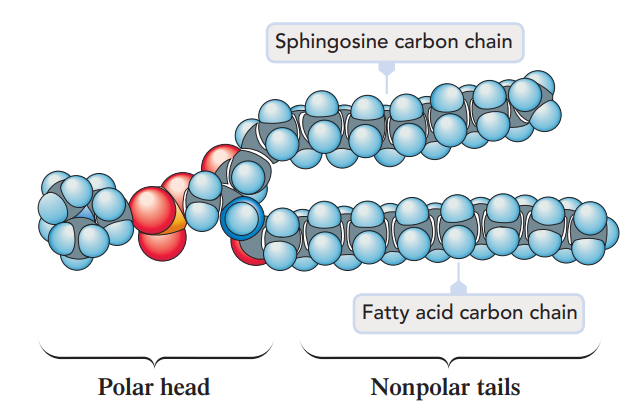
choline
SPHINGOPHOSPHOLIPIDS: What is the head group of Sphingomyelins?
cell signalling and cellular processes
SPHINGOPHOSPHOLIPIDS: Sphingomyelin is involved in __________ and ___________
Sphingoglycolipids
FA + Carbohydrate
Sphingoglycolipids
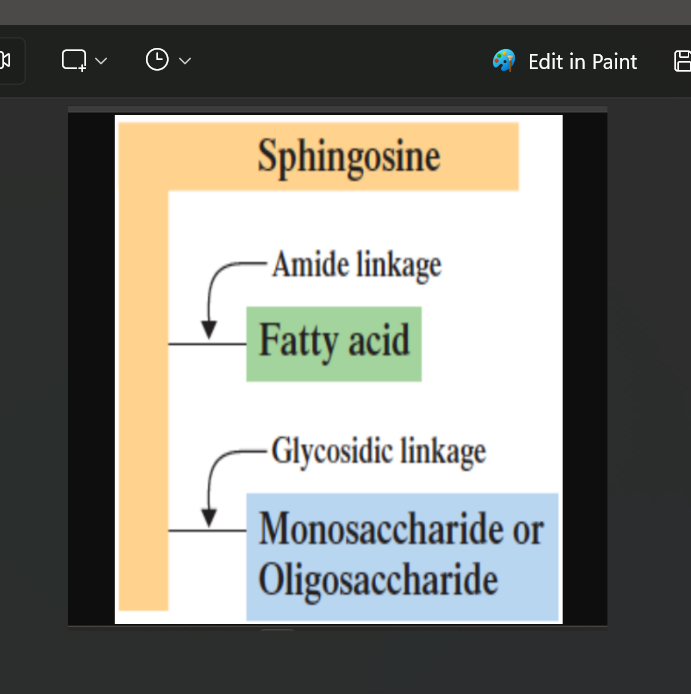
1 amide linkage and 1 glycosidic linkage
SPHINGOGLYCOLIPIDS: What are the linkages in Sphingoglycolipids? (highest to lowest)
amide linkage
SPHINGOGLYCOLIPIDS: What is linkage is between Fatty Acid and Sphingosine
glycosidic linkage
SPHINGOGLYCOLIPIDS: What is linkage is between Carbohydrates (Monosaccharide or Oligosaccharide) and Sphingosine
hydrolyzed
SPHINGOGLYCOLIPIDS: Sphingoglycolipids undergo hydrolysis and saponification reactions; both the amide and the glycosidic linkages can be?
cerebrosides
SPHINGOGLYCOLIPIDS: The simplest sphingoglycolipids, which are called ________, contain a single monosaccharide unit—either glucose or galactose.
glucose or galactose
SPHINGOGLYCOLIPIDS: The simplest sphingoglycolipids, which are called cerebrosides, contain a single monosaccharide unit—either?
stearic acid
SPHINGOGLYCOLIPIDS: The specific structure for a cerebroside in which ___________ (18:0) is the fatty acid and galactose is the monosaccharide
gangliosides
SPHINGOGLYCOLIPIDS: More complex sphingoglycolipids, called ____________, contain a branched chain of up to seven monosaccharide residues. These substances occur in the gray matter of the brain as well as in the myelin sheath.
gray matter and myelin sheath
SPHINGOGLYCOLIPIDS: More complex sphingoglycolipids, called gangliosides, contain a branched chain of up to seven monosaccharide residues. These substances occur in the?
Seven
SPHINGOGLYCOLIPIDS: SPHINGOGLYCOLIPIDS: More complex sphingoglycolipids, called gangliosides, contain a branched chain of up to how many monosaccharide residues?
fatty acid, and glycerol nor sphingosine
CHOLESTEROL: Cholesterol’s structure differs markedly from that of other membrane lipids in that (1) there are no __________ residues present and (2) neither ______ nor ________ is present as the platform molecule.
Steroid
CHOLESTEROL: is a lipid whose structure is based on a fused ring system that involves three 6-membered rings and one 5-membered ring
6-membered rings
CHOLESTEROL: steroid is a lipid whose structure is based on a fused ring system that involves three ____________ and one 5-membered ring
5-membered ring
CHOLESTEROL: is a lipid whose structure is based on a fused ring system that involves three 6-membered rings and one __________
Cholesterol
This is a C27 steroid molecule that is a component of cell membranes and a precursor for other steroid-based lipids.
27
CHOLESTEROL: how many carbon are in steroid molecule?
Cholesterol
It is the most abundant steroid in the human body.
cell membranes, nerve tissue, brain tissue and all fluids
CHOLESTEROL: Within the human body, cholesterol is found in _____________ (up to 25% by mass), in _________, in ____________ (about 10% by dry mass), and in virtually ________
50 mg
CHOLESTEROL: Every 100 mL of human blood plasma contains about _____ of free cholesterol
170 mg
CHOLESTEROL: Every 100 mL of human blood plasma contains about 50 mg of free cholesterol and about _______ of cholesterol esterified with various fatty acids.
liver
CHOLESTEROL: Although a portion of the body’s cholesterol is obtained from dietary intake, most of it is biosynthesized by the _____ and (to a lesser extent) the intestine.
800 to 1000 mg
CHOLESTEROL: Typically, ____ to _______ are biosynthesized each day.
lipoproteins
CHOLESTEROL: Because cholesterol is only sparingly soluble in water (blood), a protein carrier system is used for its distribution. These cholesterol–protein combinations are called?
low-density lipoproteins
CHOLESTEROL: The lipoproteins that carry cholesterol from the liver to various tissues are called?
high-density lipoproteins
CHOLESTEROL: those that carry excess cholesterol from tissues back to the liver are called?
atherosclerosis
CHOLESTEROL: High blood cholesterol levels contribute to _____________, a form of cardiovascular disease characterized by the buildup of plaque along the inner walls of arteries.
Plaque
CHOLESTEROL: This is a mound of lipid material, much of the lipid material in plaque is cholesterol. Plaque deposits in the arteries that serve the heart reduce blood flow to the heart muscle and can lead to a heart attack
emulsifier
This is a substance that can disperse and stabilize water-insoluble substances as colloidal particles in an aqueous solution.
colloidal particles
An emulsifier is a substance that can disperse and stabilize water-insoluble substances as __________ in an aqueous solution
bile acids
Cholesterol derivatives called ________ function as emulsifying agents that facilitate the absorption of dietary lipids in the intestine.
intestine
Cholesterol derivatives called bile acids function as emulsifying agents that facilitate the absorption of dietary lipids in the?
simple and complexed
Two types of bile acids exist:
simple
Structurally, _______ bile acids are steroid monocarboxylic acids, obtained by oxidation of cholesterol, that differ from cholesterol in two aspects:
1. they are tri- or dihydroxy cholesterol derivatives.
i 2. the carbon 17 side chain of cholesterol has been oxidized to a carboxylic acid.
cholic acid, 7-deoxycholic acid and 12-deoxycholic acid
three major types of simple bile acids produced from biochemical oxidation of cholesterol:
Taurine
BILE ACIDS:
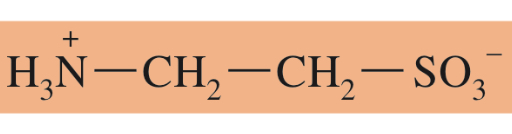
Glycine
BILE ACIDS:
pure crystallized cholesterol
A large percentage of gallstones, the causative agent for many “gallbladder attacks,” are almost __________________ that has precipitated from bile solution
Hormone
this is a biochemical substance, produced by a ductless gland, that has a messenger function.
Hormone
This serve as a means of communication between various tissues. Some of these, though not all, are lipids.
steroid hormone
it is a hormone that is a cholesterol derivative.
sex hormones and adrenocorticoid hormones
There are two major classes of steroid hormones:
adrenocorticoid hormones
included in two major classes of steroid hormones which regulate numerous biochemical processes in the body.
Cyclopentanoperhydrophenanthrene nucleus
STEROID HORMONES:
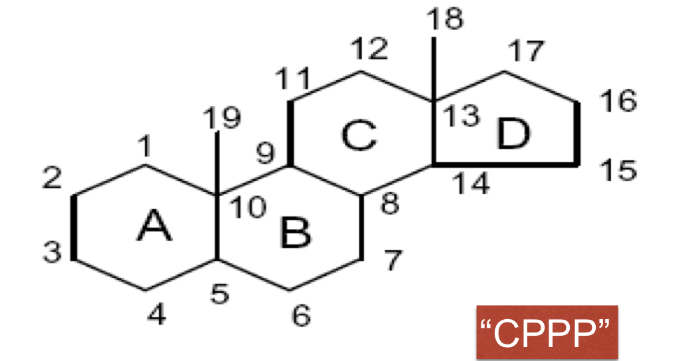
cholesterol
steroid hormones are produced from?
estrogens, androgens and progestins
The sex hormones can be classified into three major subclasses:
ovaries and adrenal cortex
STEROID HORMONES: where estrogens are synthesized?
adrenal cortex
STEROID HORMONES: estrogens are synthesized on the outer part of the adrenal glands, which are located on the top of each kidney
estrogens
STEROID HORMONES: they are synthesized in the ovaries and adrenal cortex and are responsible for the development of female secondary sex characteristics at the onset of puberty and for regulation of the menstrual cycle.
estrogens
STEROID HORMONES: They also stimulate the development of the mammary glands during pregnancy and induce estrus (heat) in animals
androgens
STEROID HORMONES: they are synthesized in the testes and adrenal cortex and promote the development of male secondary sex characteristics. They also promote muscle growth.