Lecture 25 - Insulin Therapy
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
what are general considerations for insulin
NAPRA schedule 2 medication
usual solution strength: 100 units/mL
main source is recombinant DNA (animal sources are available but more complications)
most common delivery: insulin pen (pumps becoming more prevalent)
what are the most common adverse reactions to insulin
hypoglycemia
weight gain
lipohypertrophy
what are the main types of insulin delivery devices
syringe and vial
pens
pump and resevoir
what are factors to consider when deciding what insulin to use
age, general health, lifestyle/activity level, diet
treatment goals, motivation, ability to adhere to treatment
hypoglycemia awareness, ability to self-manage treatment
cost/coverage
NPH/regular are cheapest
analogues are expensive
pharmacodynamic profile
what is important to consider when starting an insulin regimen for someone newly diagnosed with type 1 diabetes
honeymoon period
usually transient, but can last up to 2 years
associated with low insulin requirements: <0.5 units/kg/day
what should you ask yourself when recommending an insulin dose
is it easy to remember
is it easy to prepare
what are the recommendations for total daily insulin dose
textbook: 0.4-1.0 units/kg/day
diabetes Canada: <0.5 units/kg/day during honeymoon phase
what are the recommended proportions for basal/bolus doses
textbook: 50% basal, 50% bolus
alternative for convenience: 40% basal, 60% bolus (20% before each meal)
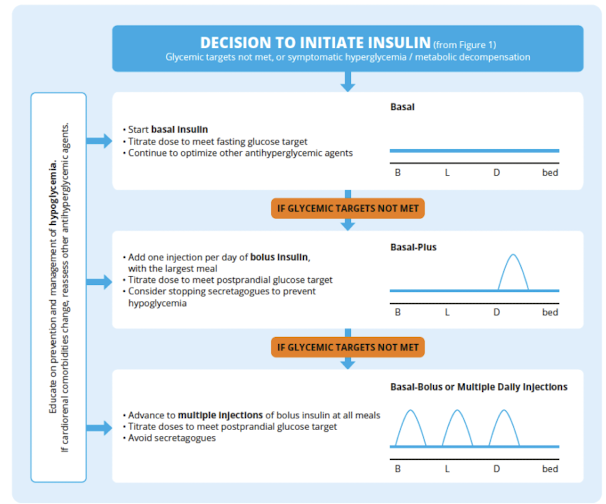
what is the recommended initial insulin management for type 2 diabetes
single daily injection of basal insulin
long-acting preferred over NPH
degludec or glargine may be considered over other long-acting analogues to reduce the risk of nocturnal hypoglycemia
incretin and/or SGLT2 inhibitor should be continued or initiated when introducing basal insulin
what are the recommendations if a bolus insulin is required for type 2 diabetes
use a step-wise approach starting with 1 bolus dose per day at the largest meal
introduce additional mealtime injections later if needed
rapid acting analogues preferred over regular insulin
insulin secretagogues (solfonylureas/meglitinides) should be discontinued
what are the sites for insulin administration
abdomen - absorption is faster, but more consistent
lateral thigh - slower and variable absorption
upper arms - slower and variable absorption, challenging to reach
superior buttocks - slowest absorption
what are counselling points for injection site rotation for the abdomen
divide the abdomen into 4 areas, inject into one area for a week then move clockwise
separate each injection within the area by 2-3cm (1-2 fingers)
why do this: minimize risk of lipohypertrophy, maintains consistent insulin absorption
do not rub the injection site after (affects absorption)
what is the general approach to insulin dose adjustment
look for lows (< 4mmol/L, symptoms of hypoglycemia)
start the day well
look for consistent highs (explanations? - exercise, skipped doses, extra meals)
change one insulin by 1-2 units
what is the clinical presentation of hypoglycemia
blood glucose <4 mmol/L
sweating, trembling, palpitations, anxiety
hunger, nausea, headache, tingling
disturbed sleep, weird dreams, weakness/dizziness, difficulty concentrating
vision changes, drowsiness, difficulty speaking, unconsciousness
how is a hypoglycemic episode managed
check blood glucose and confirm a low
consume 15 grams of a simple carbohydrate (important to carry at all times)
re-check blood glucose in 15 minutes
if still <4 repeat 15 grams of simple carbohydrates
if >4 consume a snack that includes a protein to maintain level

what are other adverse effects of insulin
weight gain
lipohypertrophy - thickened area of tissue because fat accumulates at injection site
insulin release from site is delayed and unpredictable
minimize risk by rotating sites
lipoatrophy - loss of subcutaneous fat at injection site
possibly immune-mediated inflammatory response
rare