histology- reproductive system
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
89 Terms
vessels, loose CT, smooth muscle
what composes the medulla of the ovaries?
exterior part- cortex
except in horses, they are interior
in what part of the ovary can you find follicles?
the follicles are interior, and the CT and vessels are exterior
(usually, it is the opposite)
what is unique about the ovary of a mare?
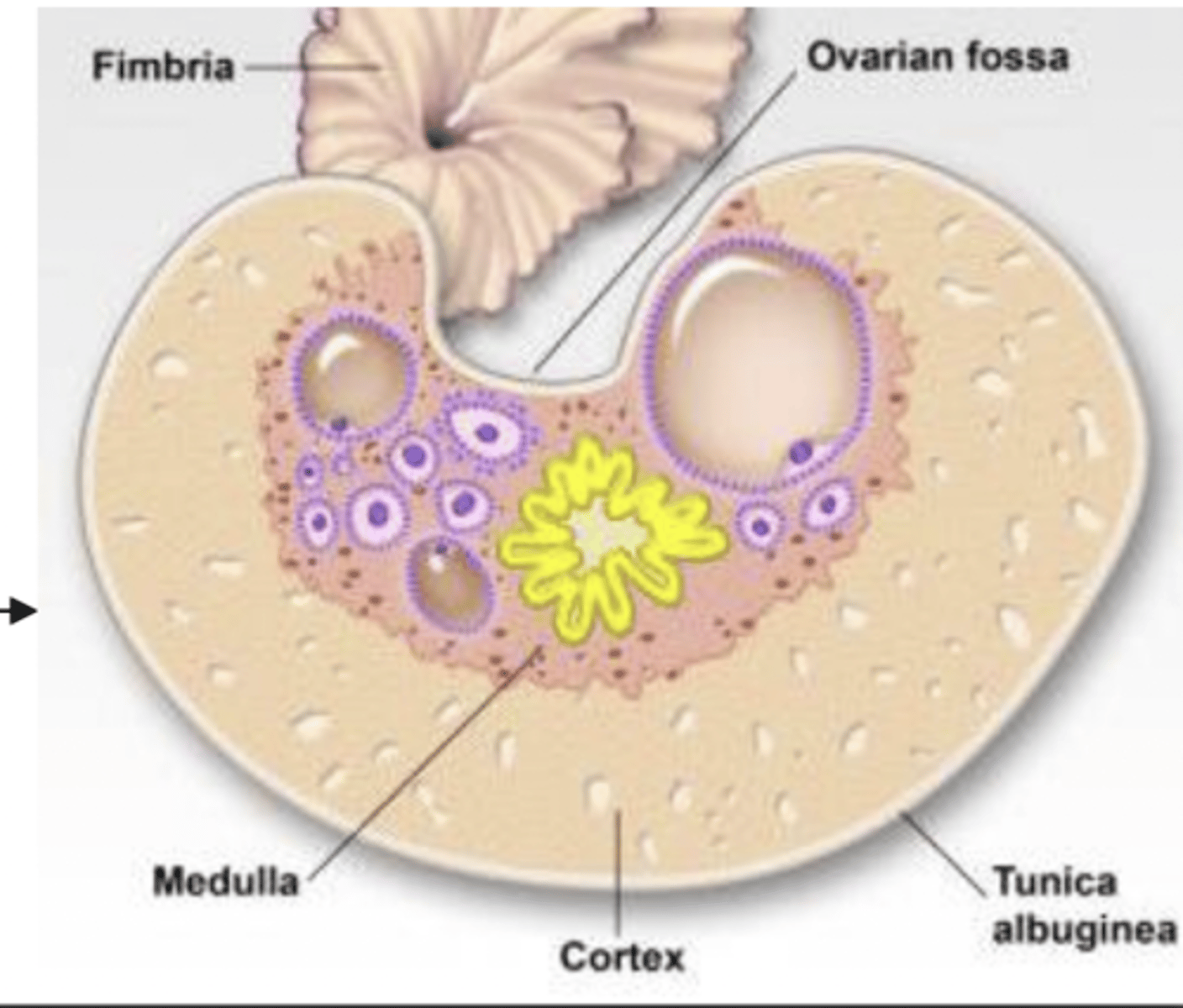
the germinal epithelium
what is the most external layer of the ovary?
tunica albuginea
if the germinal epithelium is the most external layer of the ovary, what layer is next?
dense irregular CT
what is the tunica albuginea of the ovary composed of?
follicle protection
what is the function of the tunica albuginea of the ovary?
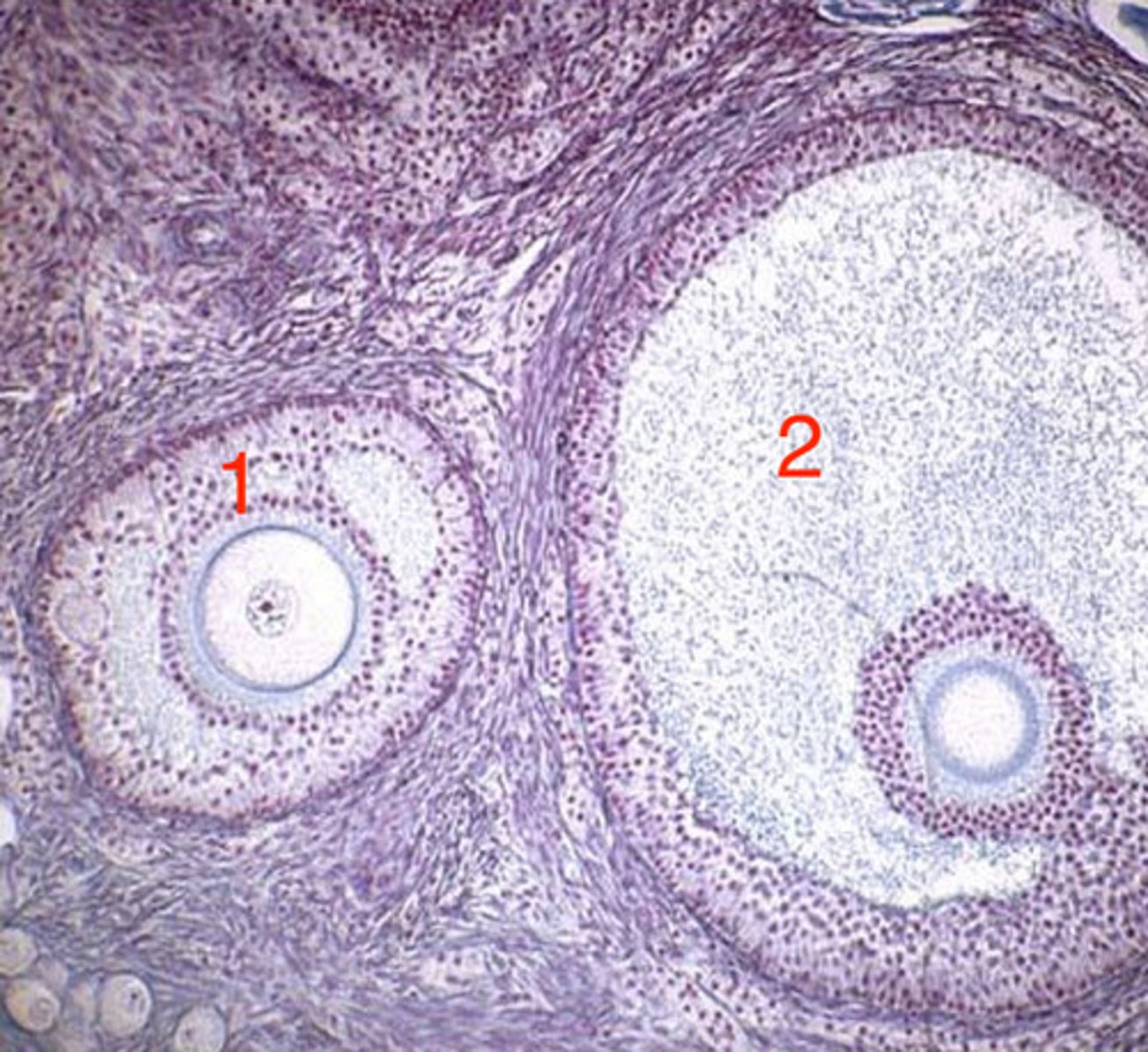
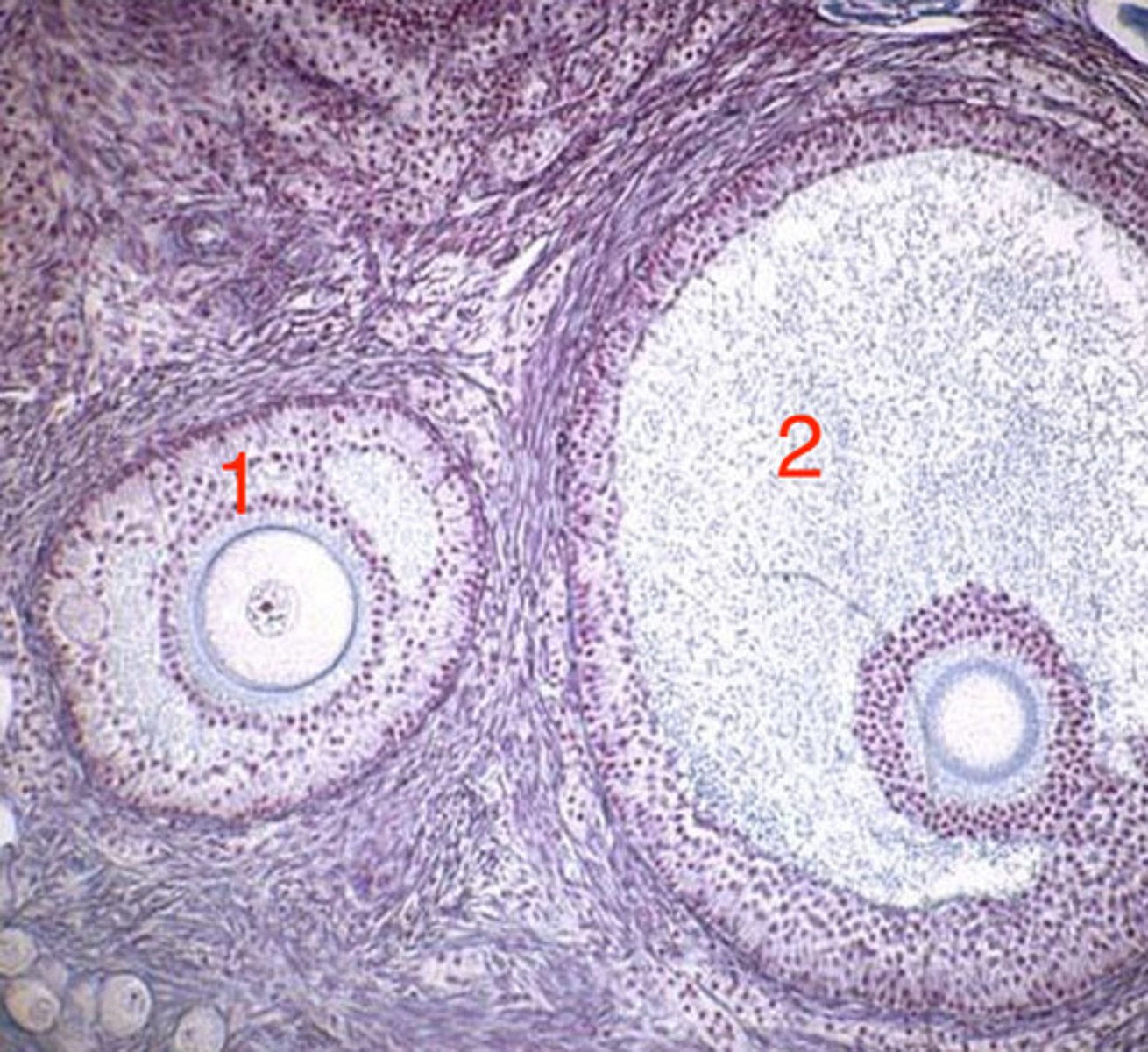
cortex
ovary- what is 1?
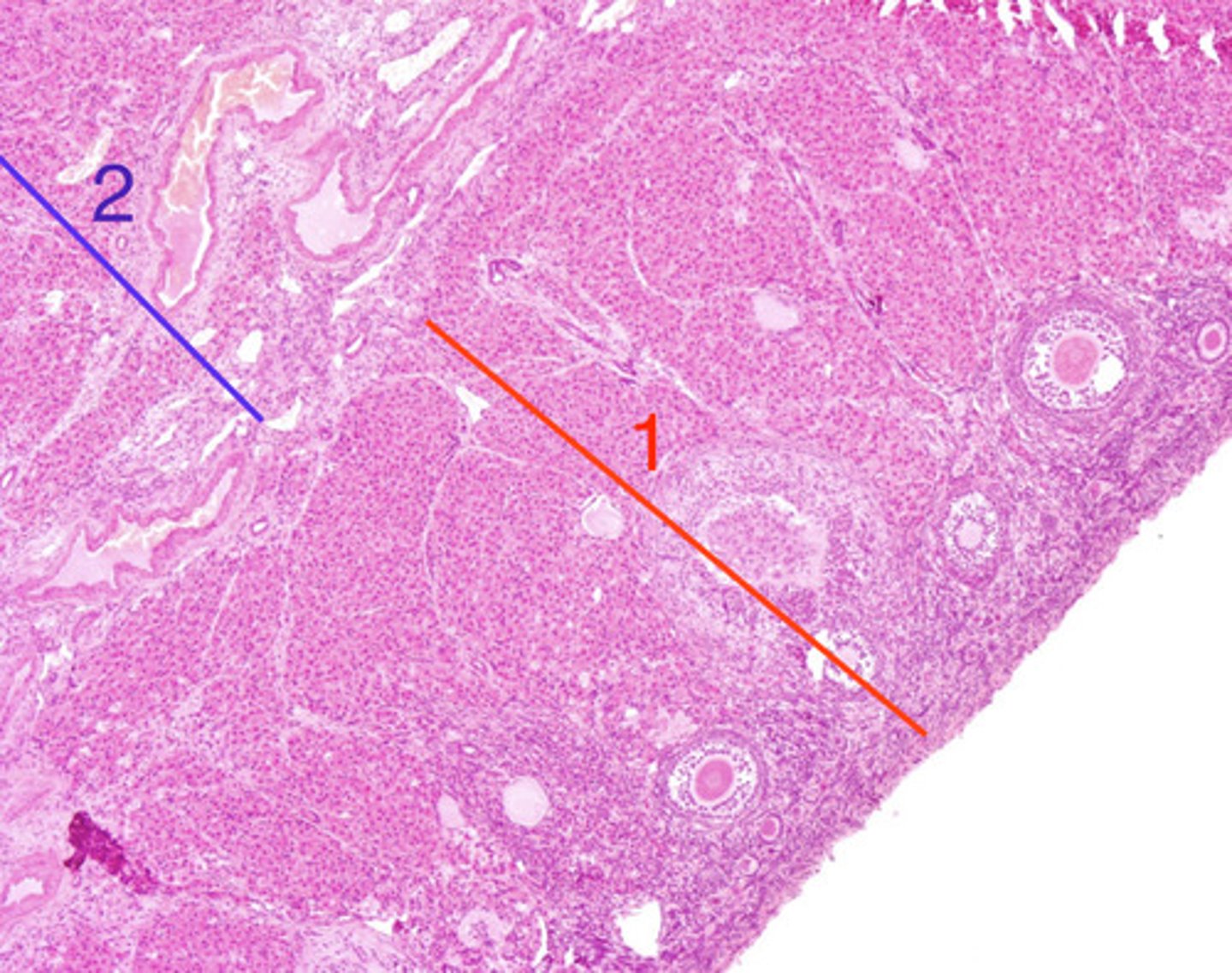
2
ovary- which is the medulla?
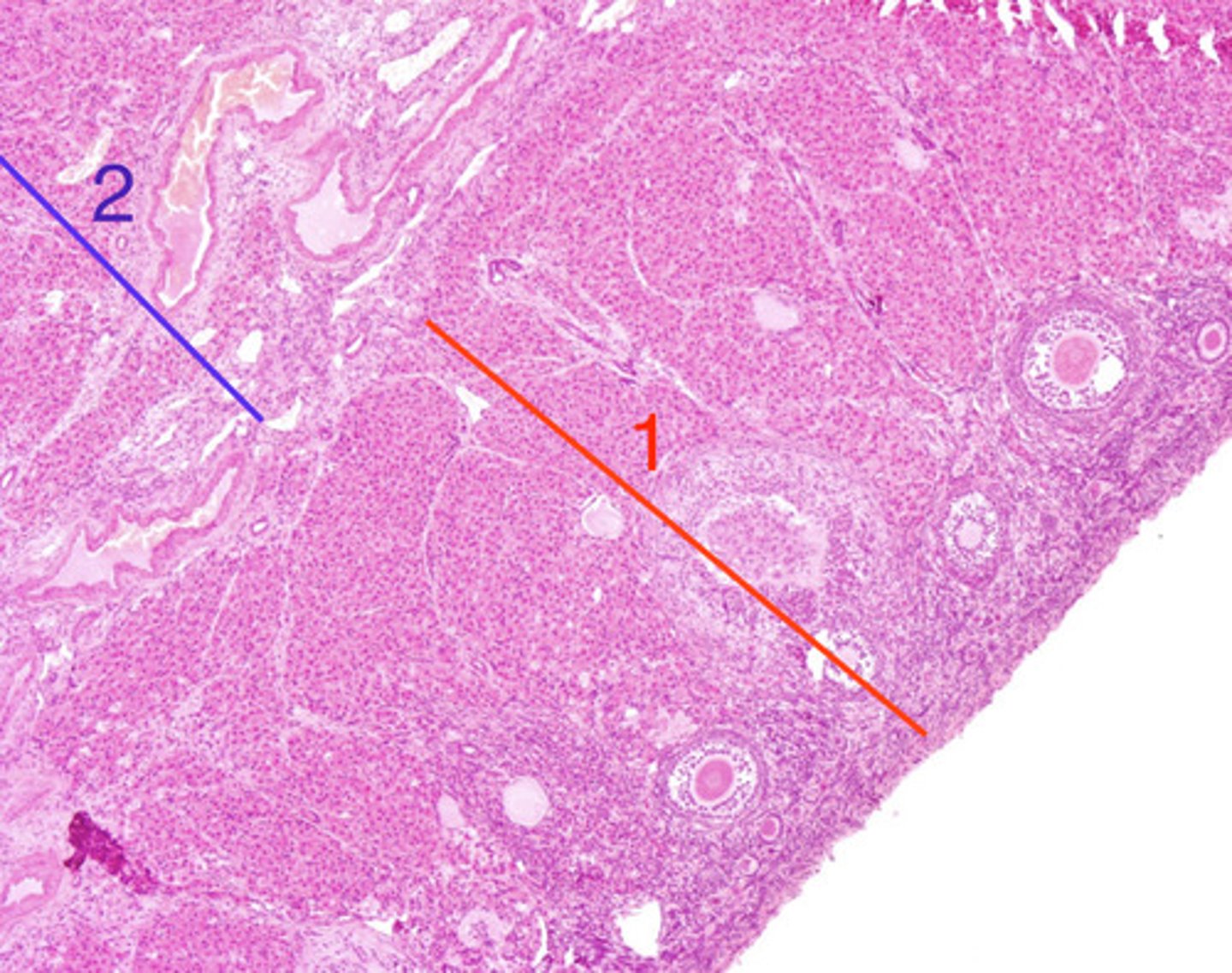
germinal epithelium
what is this layer of the ovary?
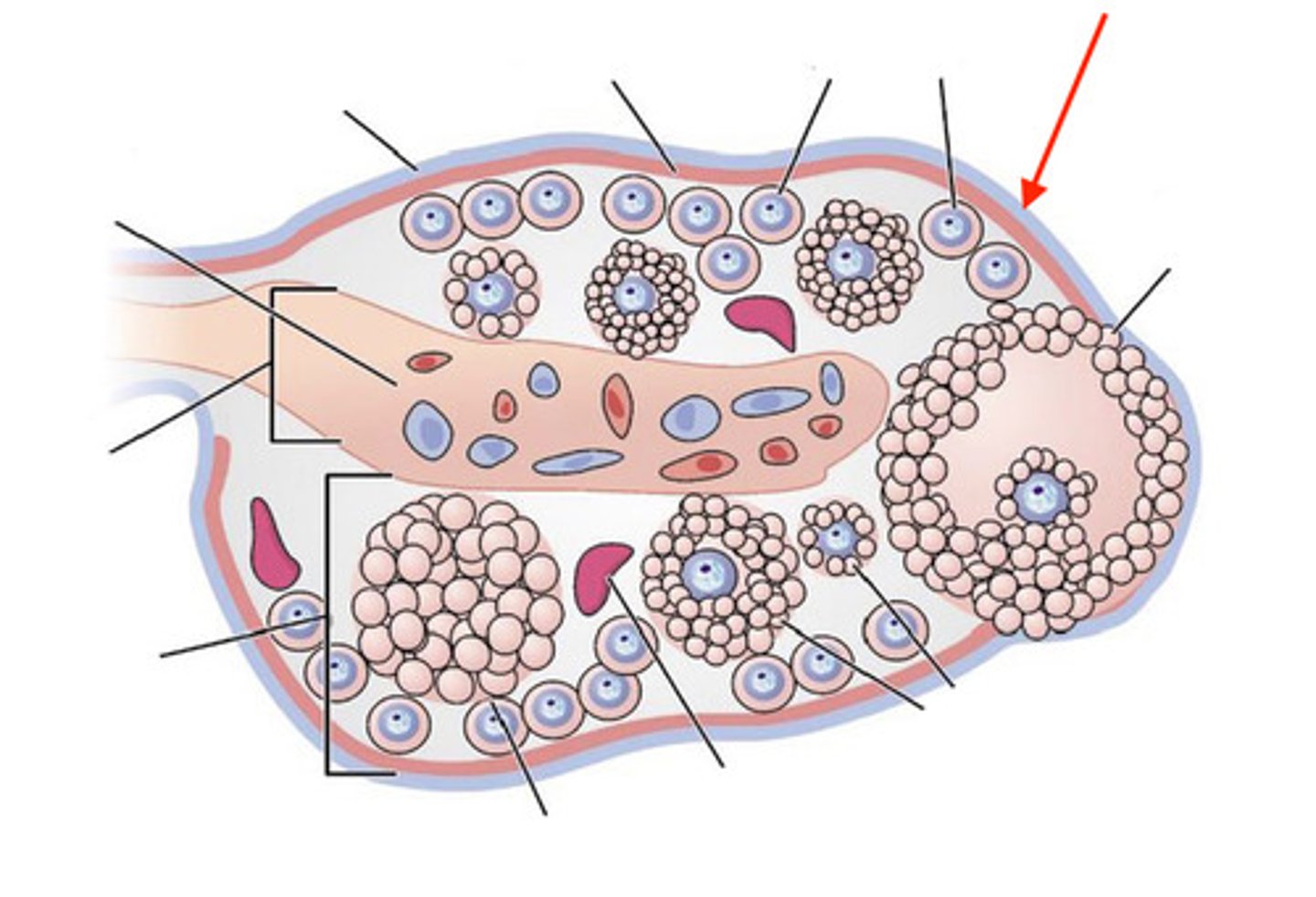
tunica albuginea
what is this layer of the ovary?
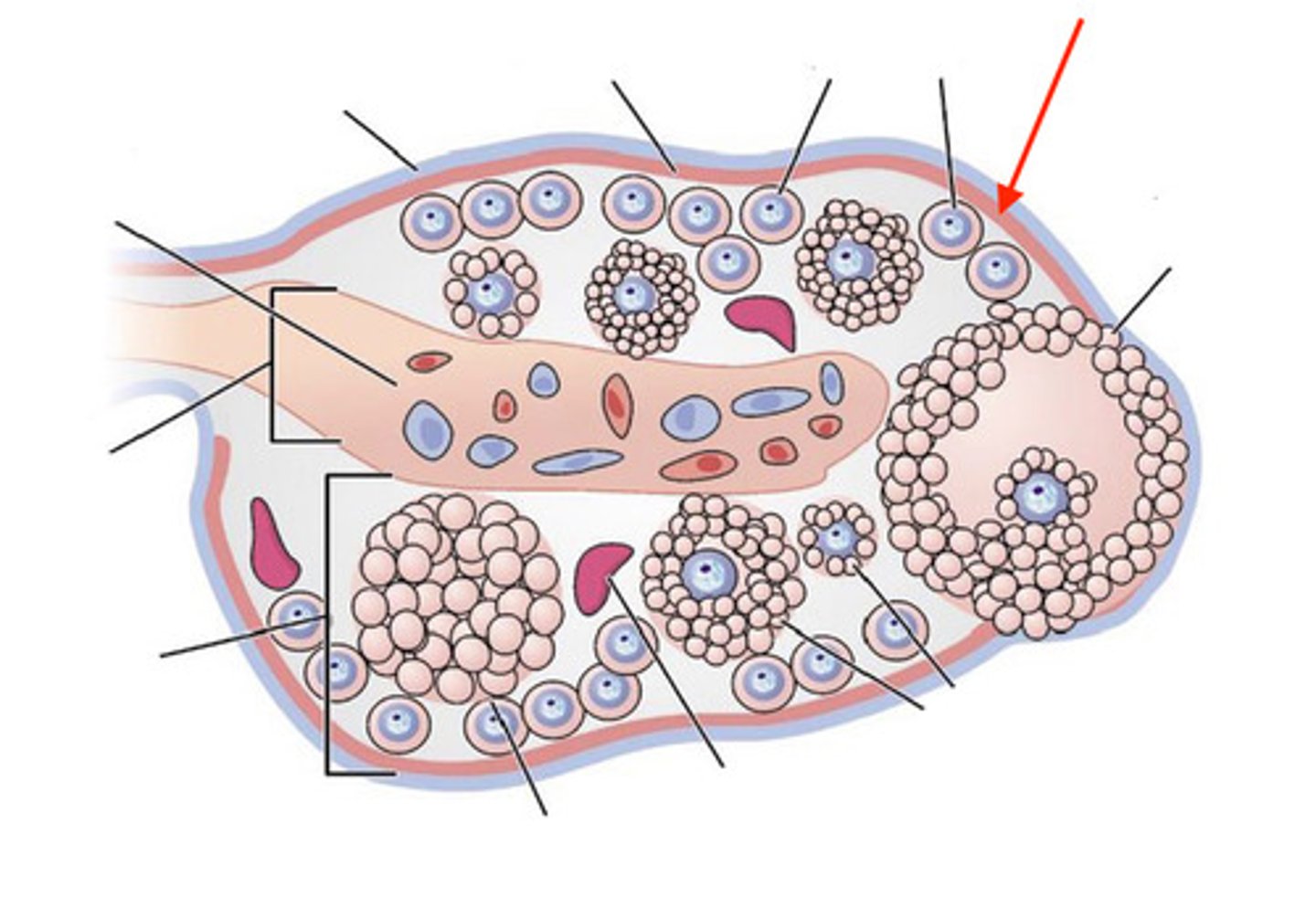
medulla (interior)
as follicles mature, they migrate towards the ______
interior- as they mature, they migrate towards the medulla
do we see more mature follicles at the interior or exterior of the ovary?
cortex
when mature follicles are ready to release the ovum, they migrate towards the_____
the loose CT of the cortex
what allows the migration of the follicles inside the ovary?
primordial and primary
which types of ovarian follicles are more abundant?
primary and primordial
which types of follicles will you find most at the periphery of the ovary?
at the periphery, the primordial follicles form clusters
what is unique about the ovaries of carnivores?
carnivore- the primordial follicles are forming clusters at the periphery
what species might this ovary belong to, and why?
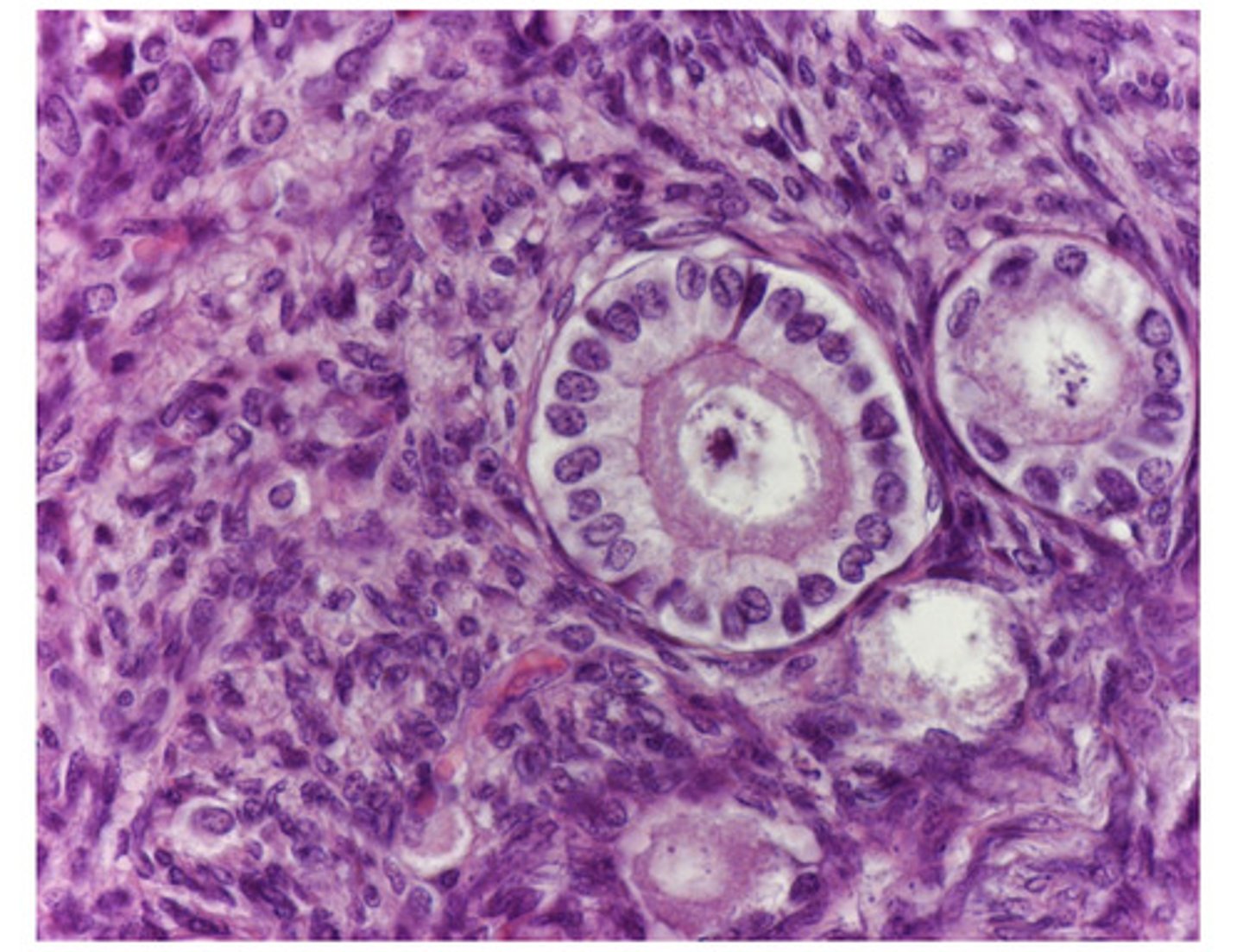
primordial
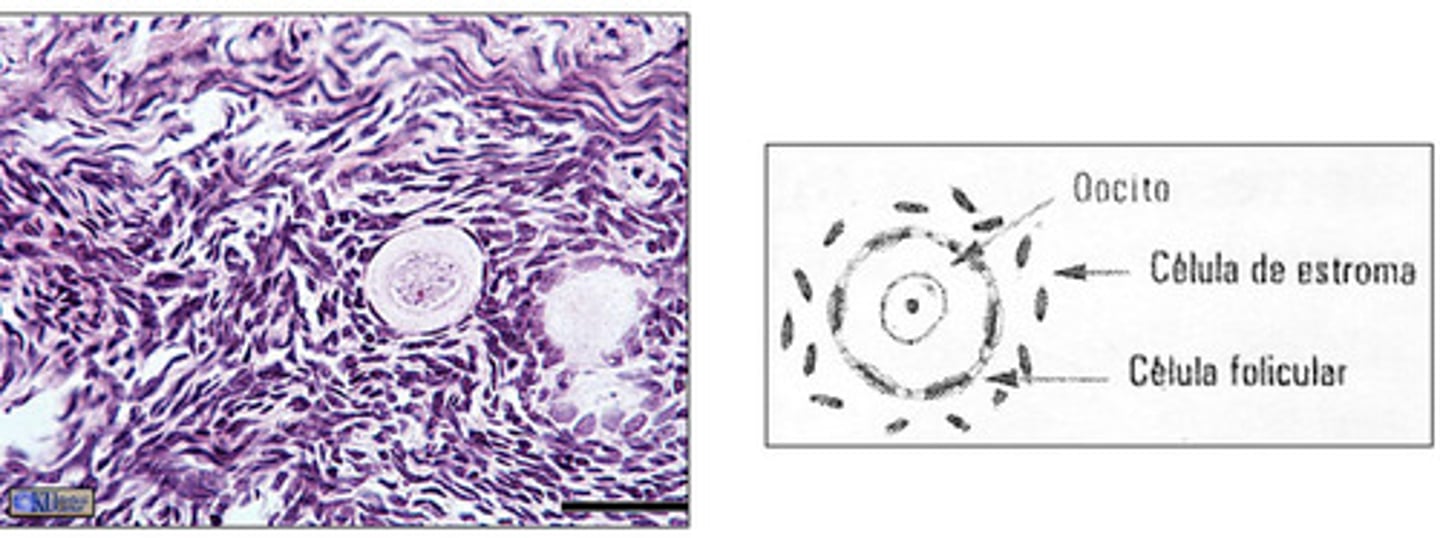
which are the smallest, most abundant follicles of the ovary?
one layer of squamous cells
primordial follicles have an oocyte that is surrounded by what cells?
primordial- small, one layer of squamous cells surround oocyte
what type of follicle is this?
primary follicle
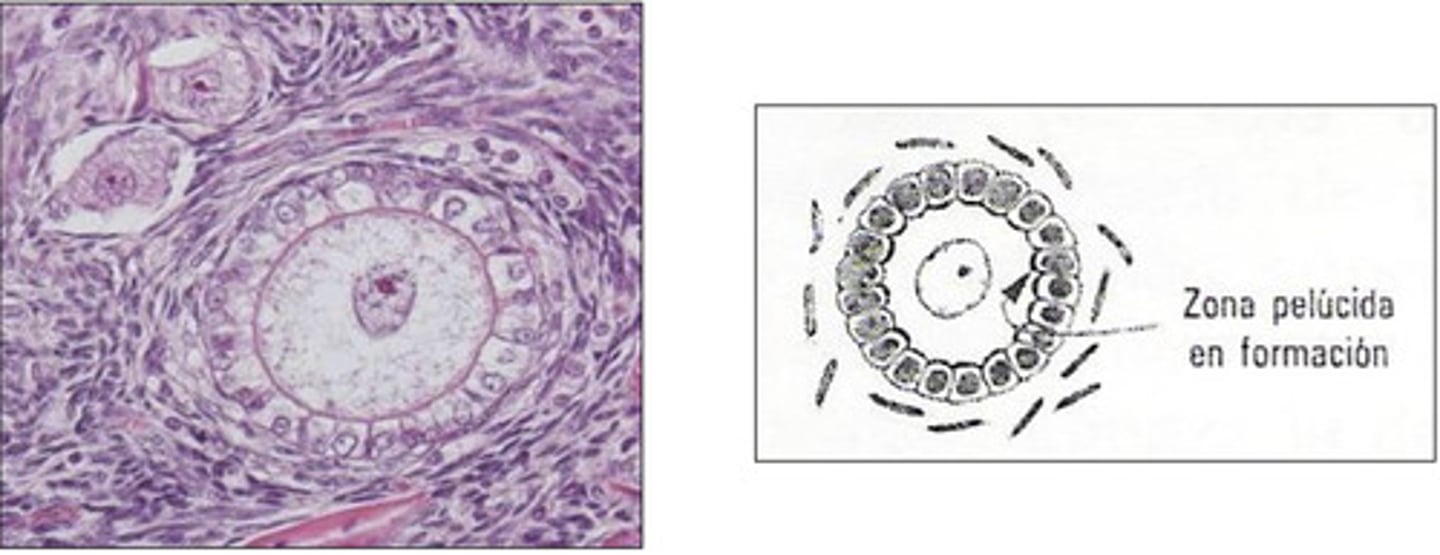
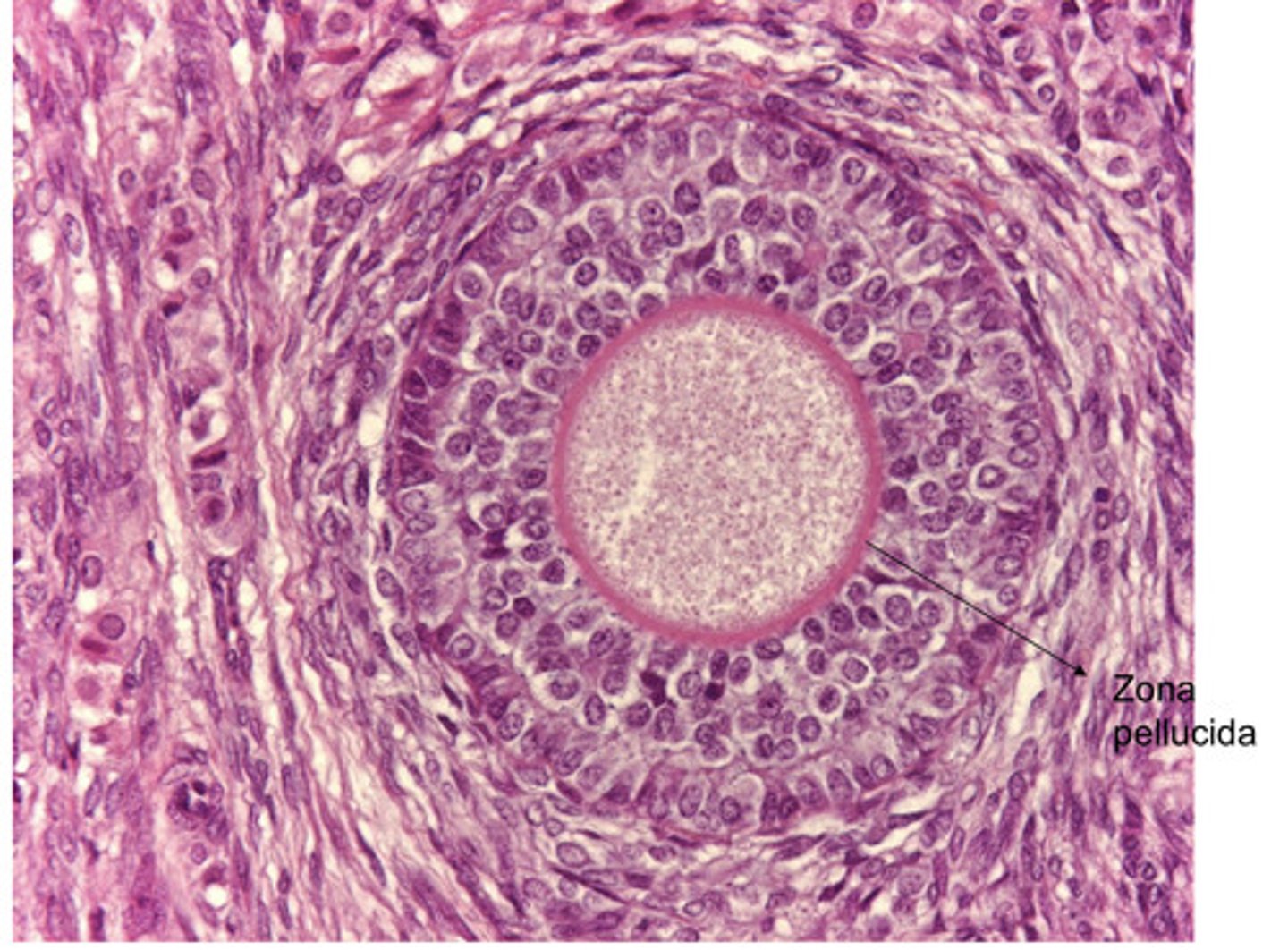
in what stage of the follicle can we begin to see the zona pellucida?
unilaminar primary- we can see zona pellucida, oocyte surrounded by cuboidal cells
what type of follicle is this?
cuboidal/columnar
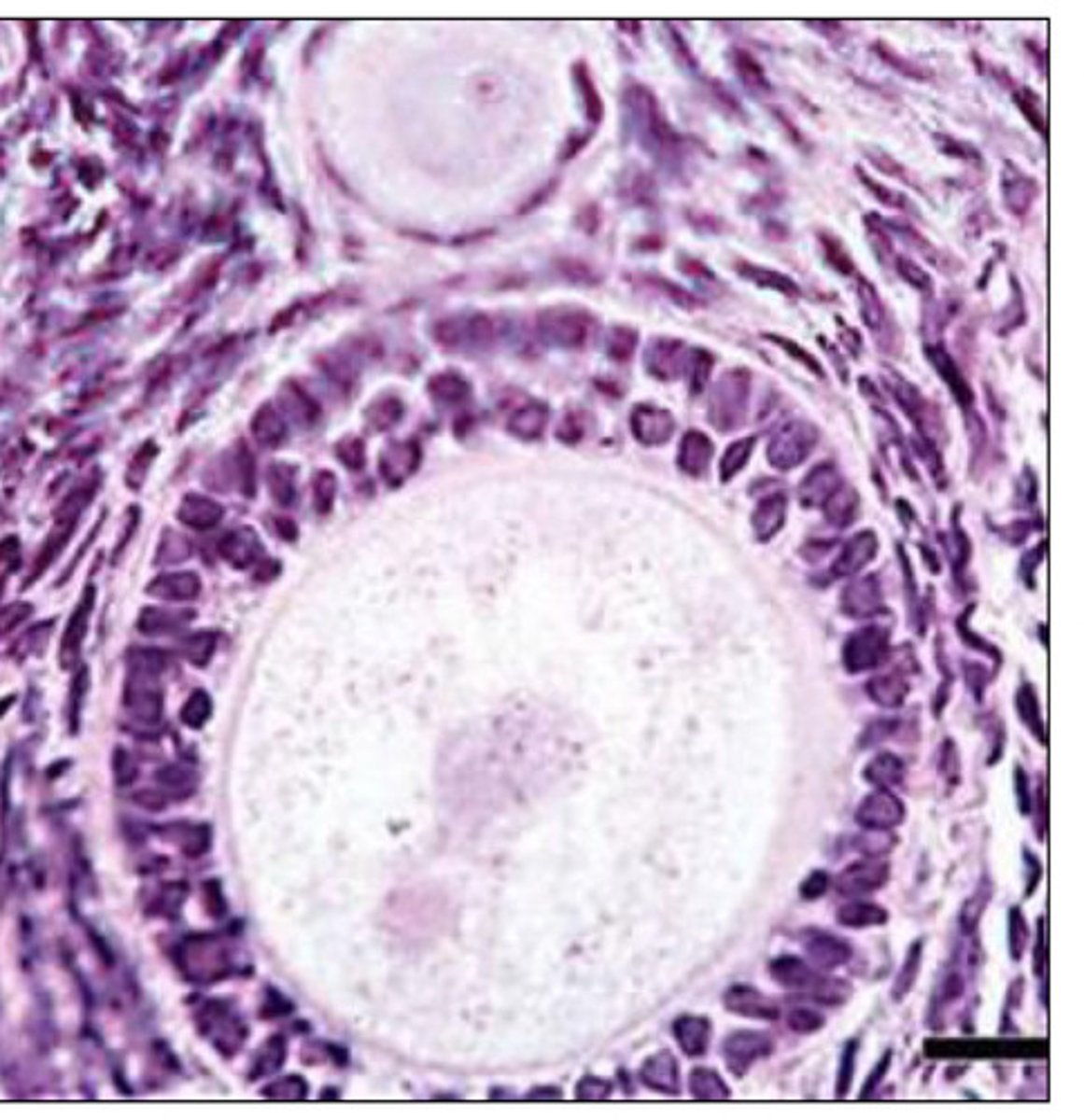
what cells surround the oocyte of a primary follicle?
unilaminar and multilaminar
what are the 2 types of primary follicles?
1 cell layers surrounds oocyte
zona pelluucida is visible
what is a unilaminar primary follicle?
2+ layers of cells surround the oocyte
zona pellucida is more visible than unilaminar
describe a multilaminar primary follicle
multilaminar primary follicle- multiple cell layers around oocyte and clear zona pellucida
what type of follicle?
unilaminar primary follicle- one cell layer around oocyte (cuboidal or columnar), slightly visible zona pellucida
what type of follicle?
multilaminar primary follicle- multiple cell layers around oocyte and clear zona pellucida
what type of follicle?
antrum beginning to form between granulosa cells
theca forming externally
follicle has migrated closer to medulla
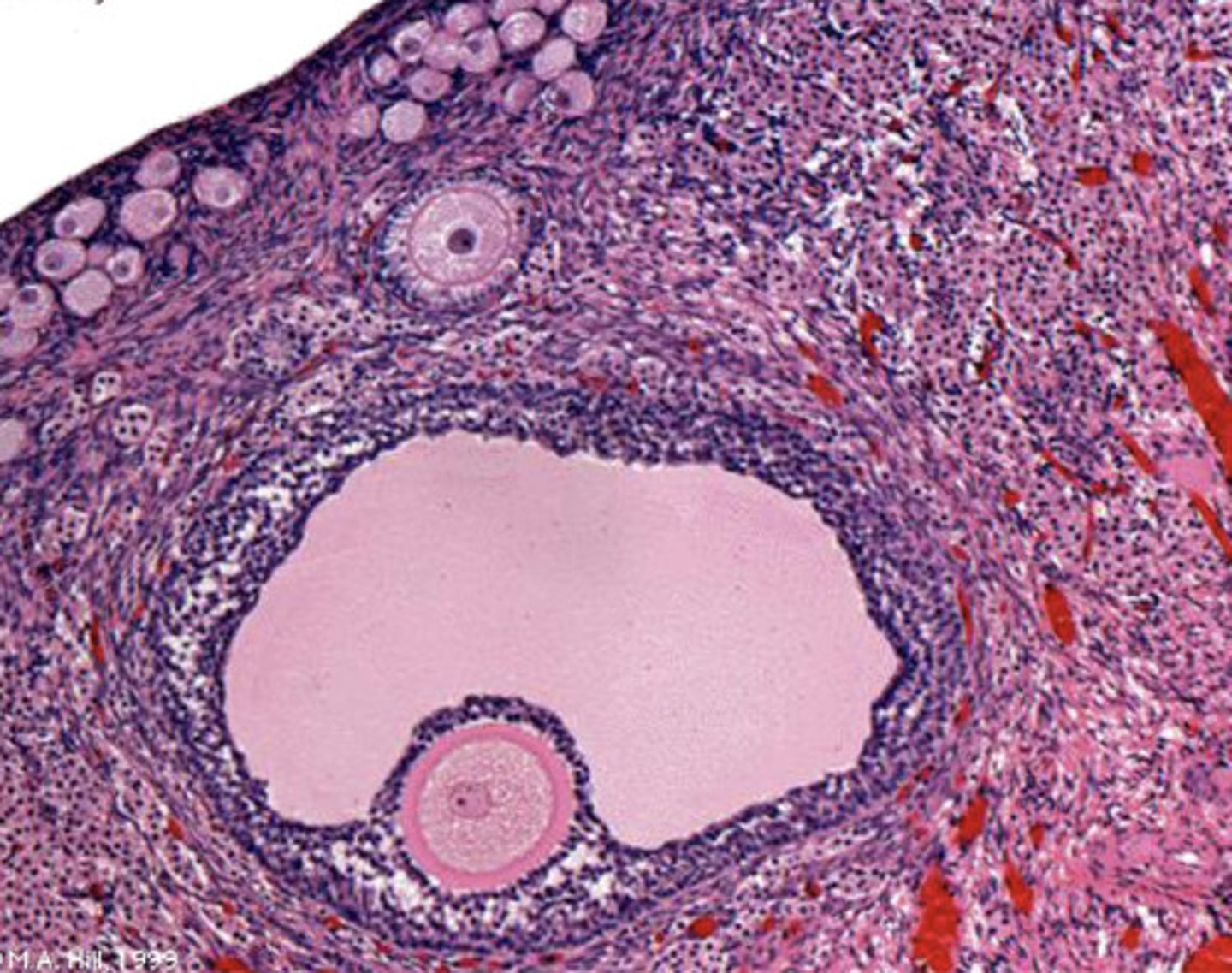
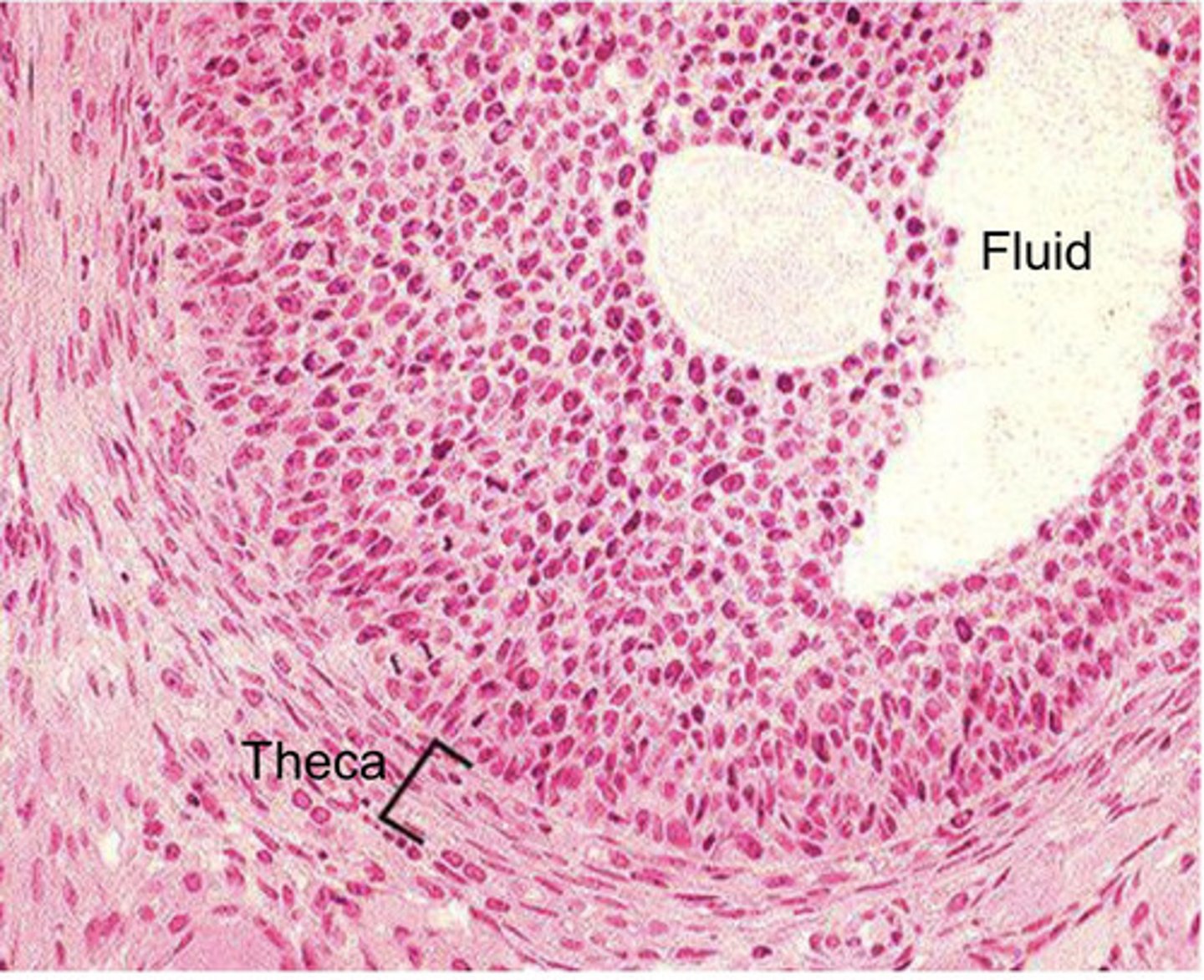
describe a secondary follicle
secondary follicle- antrum beginning to form between granulosa cells, theca forming externally
what type of follicle?
concentrical layers of squamous cells
what does the theca of a follicle look like?
secondary follicle
what stage of the follicle can you see the theca develop?
secondary follicle
what stage of the follicle can you see the antrum begin to develop?
bigger antrum
oocyte is not central, but is displaced
cumulus oophorus- cells holding oocytes to granulosa cells
corona radiata- granulosa cells surrounding oocyte
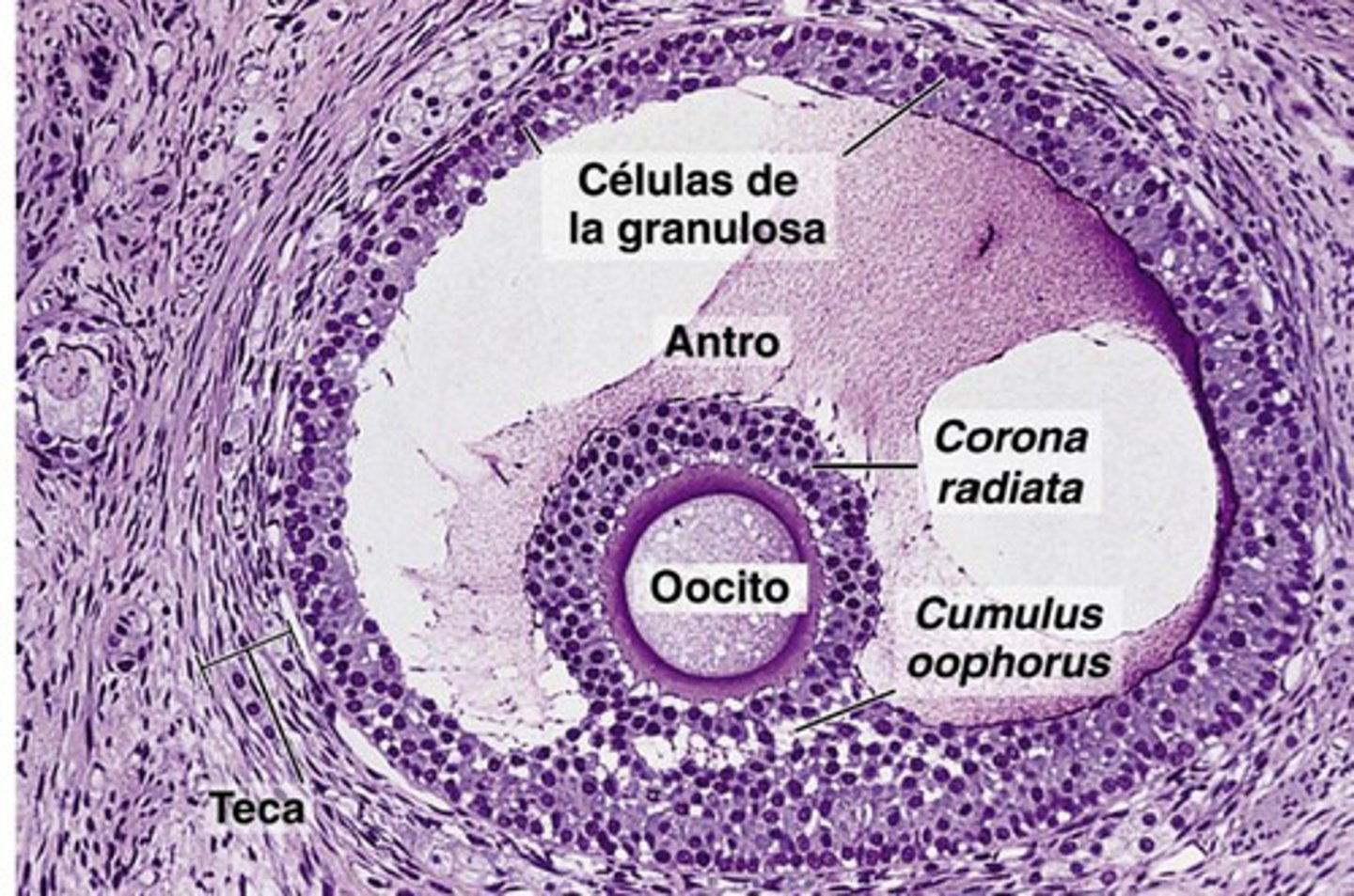
what does a graafian follicle look like?
graafian-
oocyte is displaced, large antrum, cumulus oophorus, corona radiata
what type of follicle?
graafian
what stage of follicle has a corona radiata?
graafian
what stage of follicle has a cumulus oophorus?
corona radiata
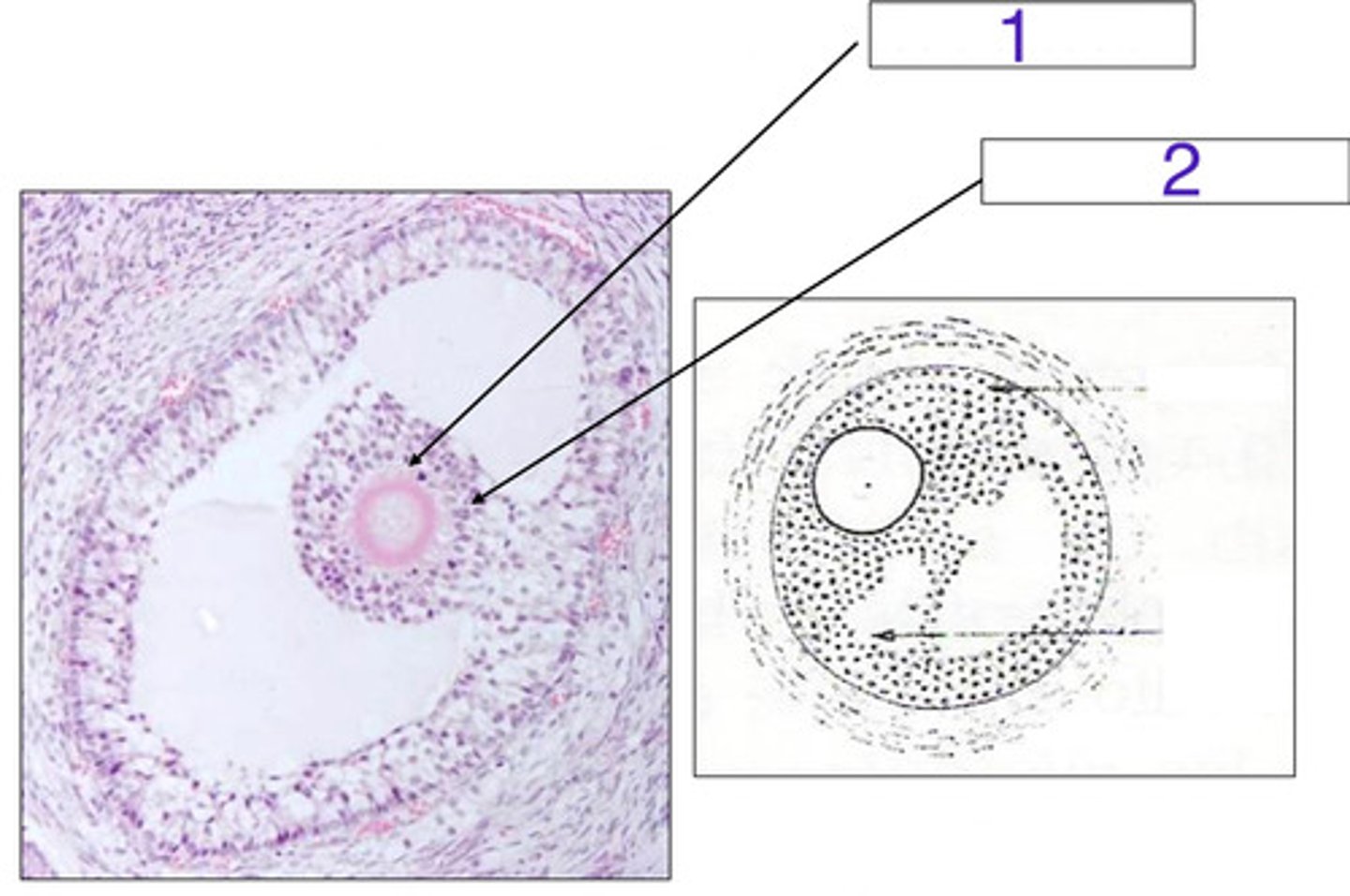
what is 1?

cumulus oophorus
what is 2?
1
which is the corona radiata?
after the follicle releases its ovum and fluid
when does the corpus luteum begin to form?
scar tissue (loose CT)
after ovulation, _____ forms inside the follicle
albicans, dense CT
the corpus luteum becomes the corpus _______, which is composed of _____
older animals
which animals can you see more corpus albicans in?
the follicles that failed to mature into graafian follicles, and instead just die
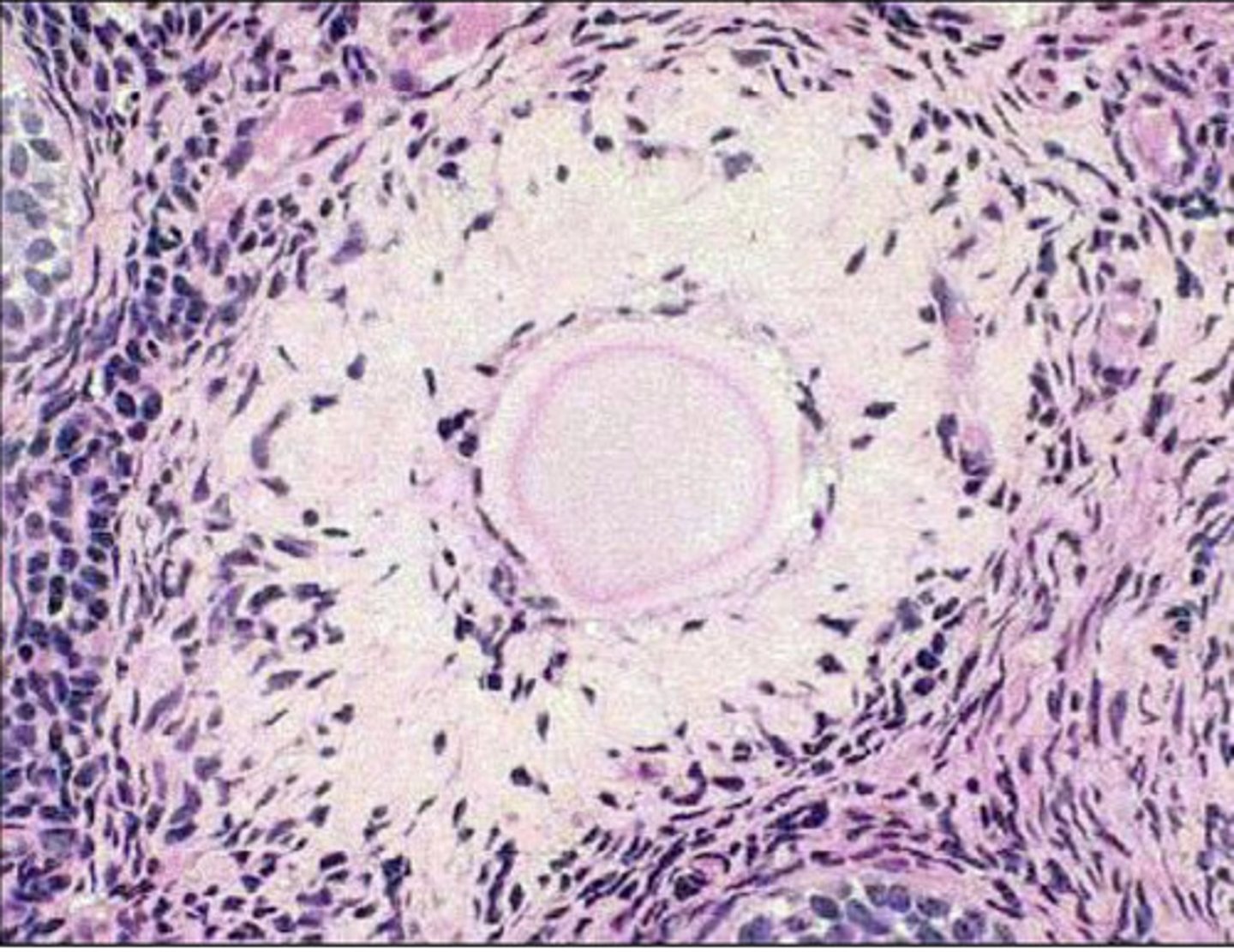
what are atresic follicles?
they degenerate and undergo phagocytosis
what happens to follicles that do not completely mature?
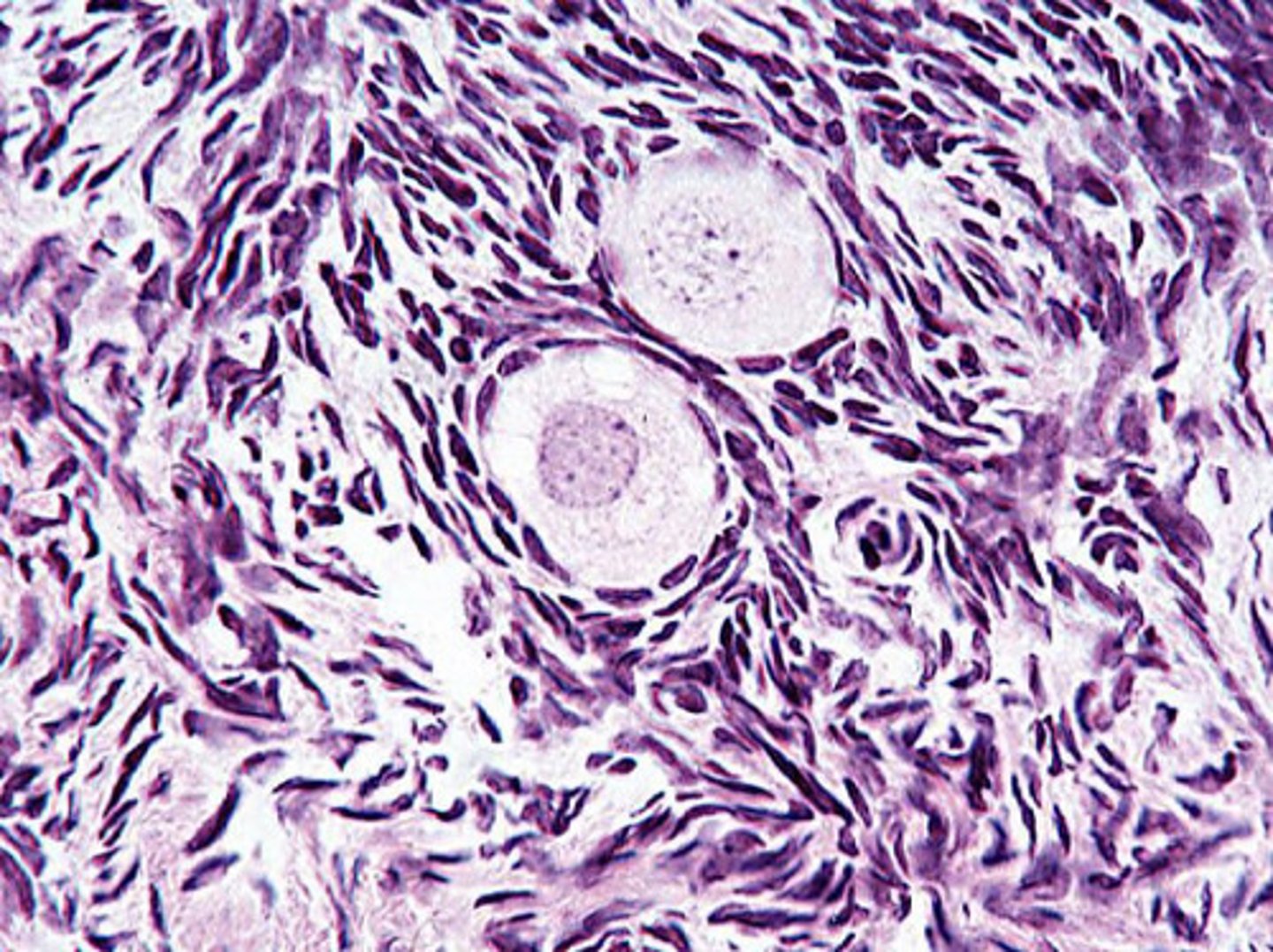
an atresic primordial follicle
what is this?
groups of tubules lined by epithelial cells for transport
in the medulla, we also see the rete ovarium- what is this?
in the medulla of the ovaries
where do we find the rete ovarium?
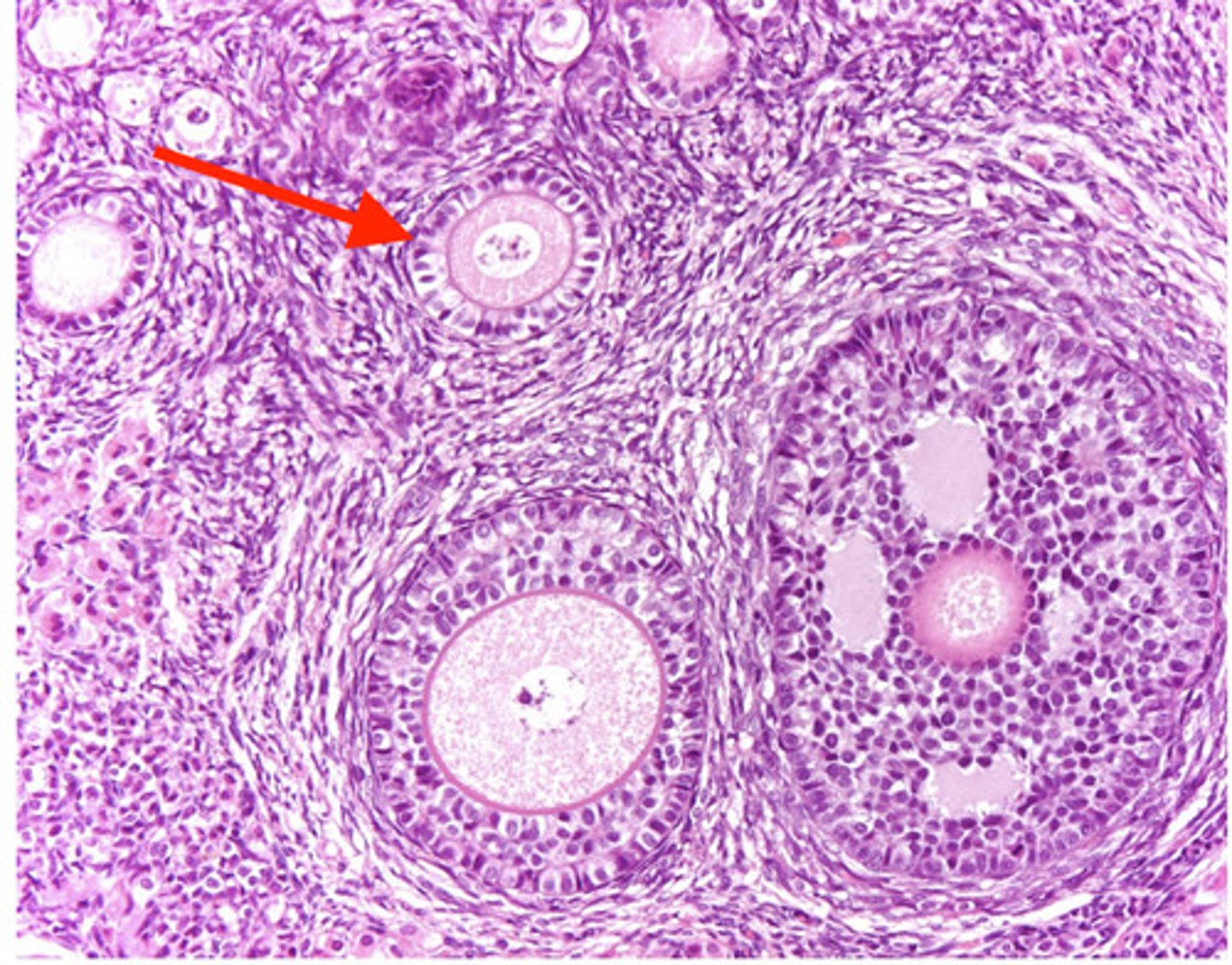
primordial
what type of follicle?
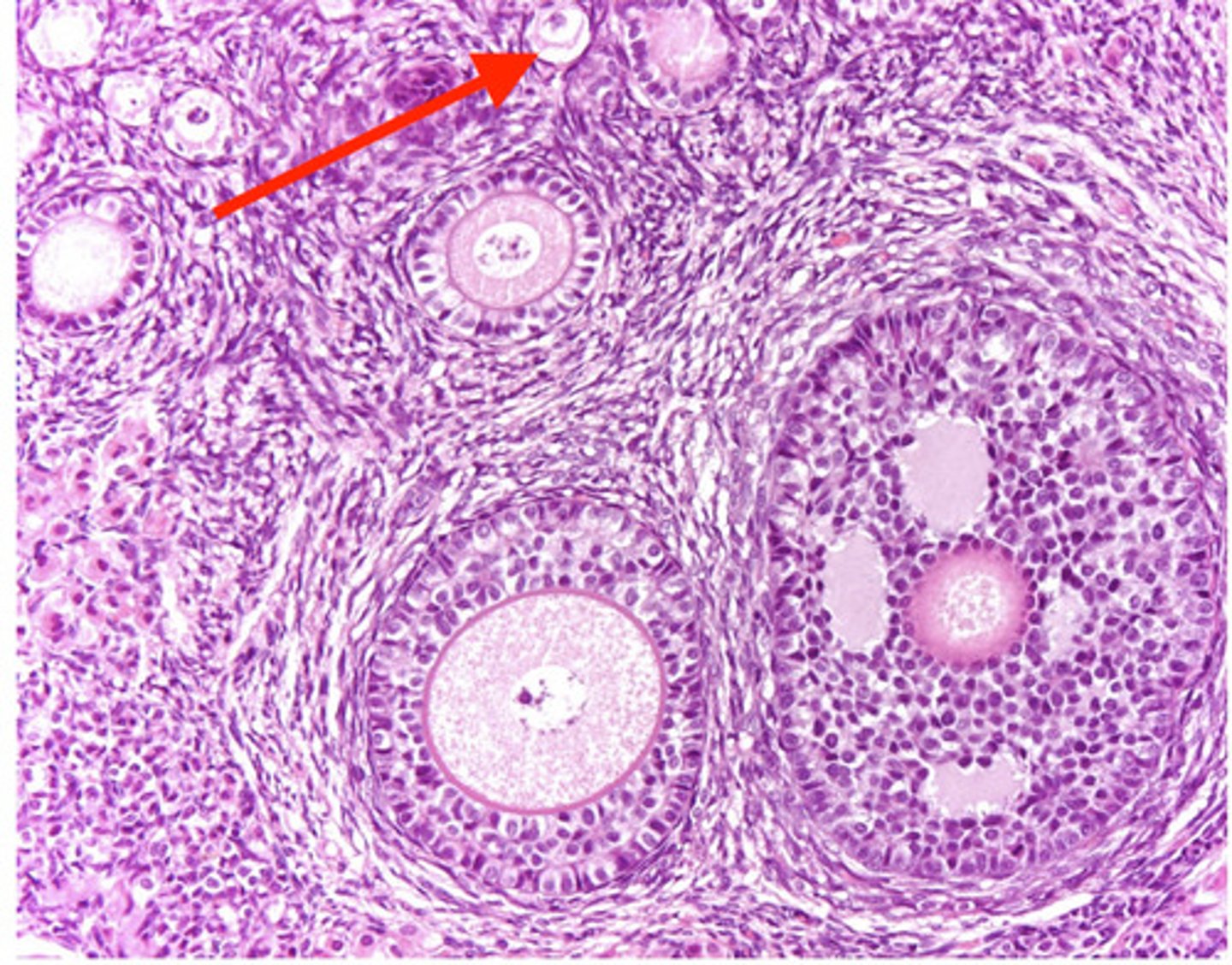
unilaminar primary follicle
what type of follicle?
multilaminar primary follicle
what type of follicle?
primordial follicles
what are these?
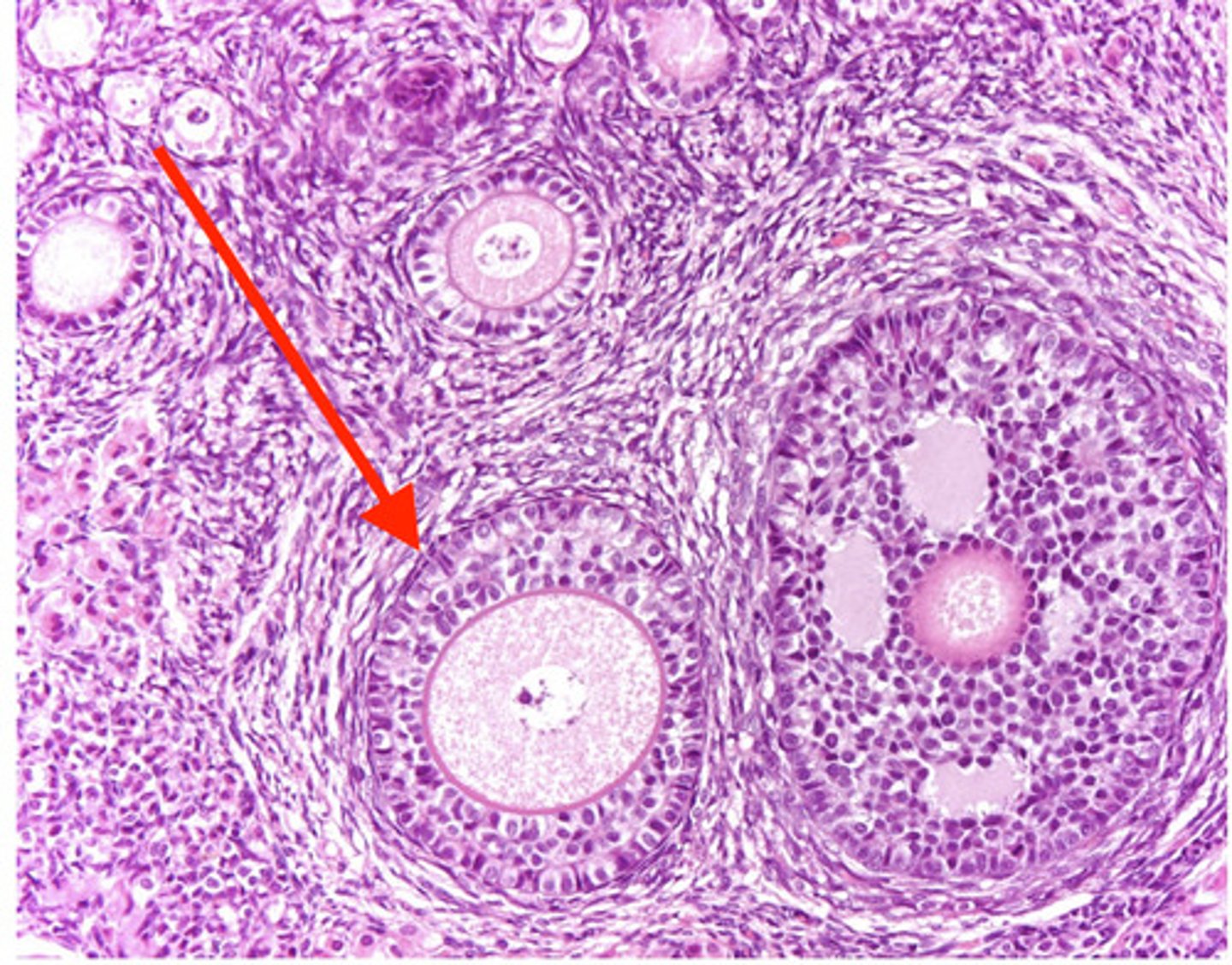
secondary follicle
what is 1?
graafian follicle
what is 2?
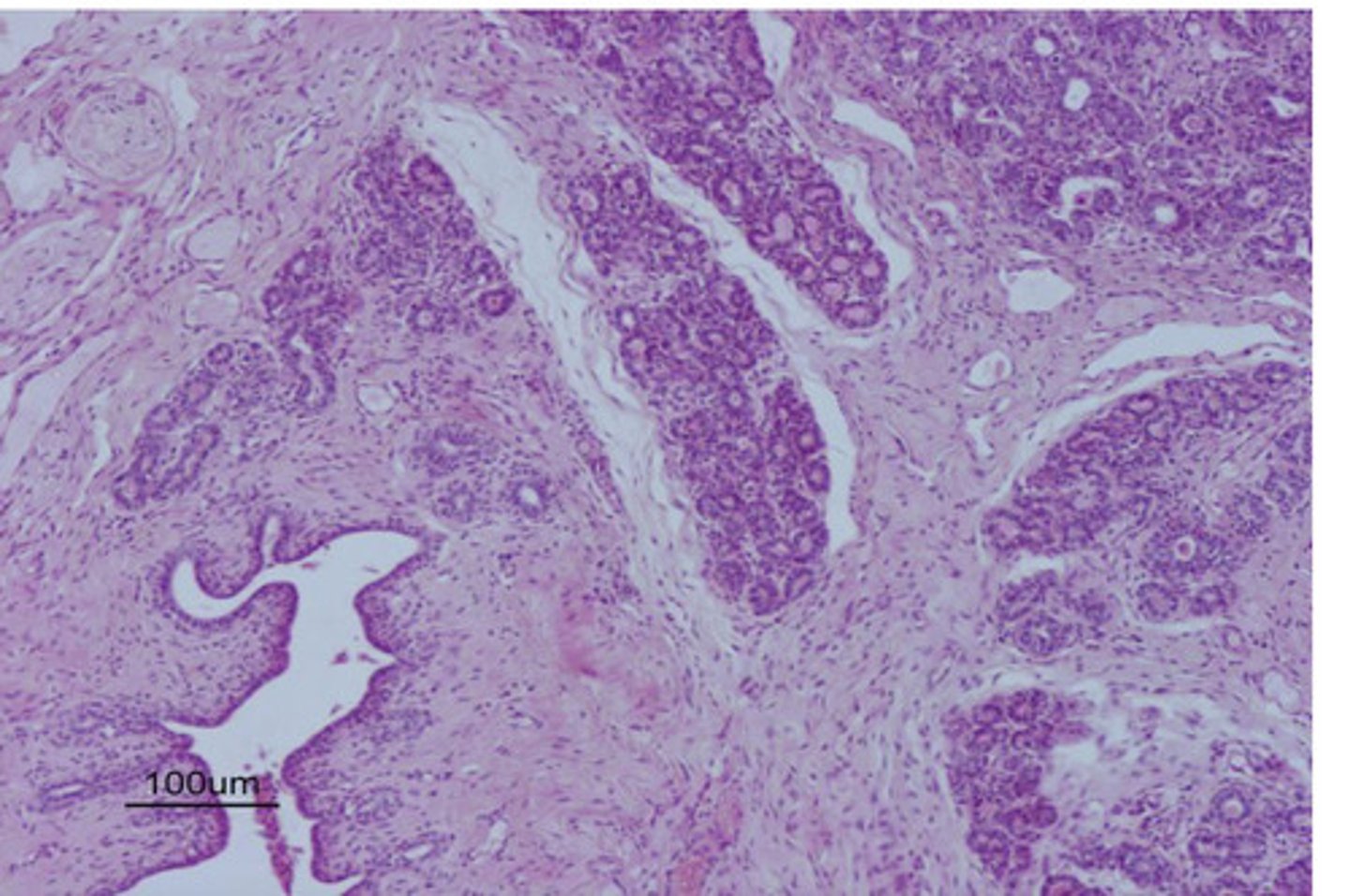
inactive
is this mammary gland active or inactive?
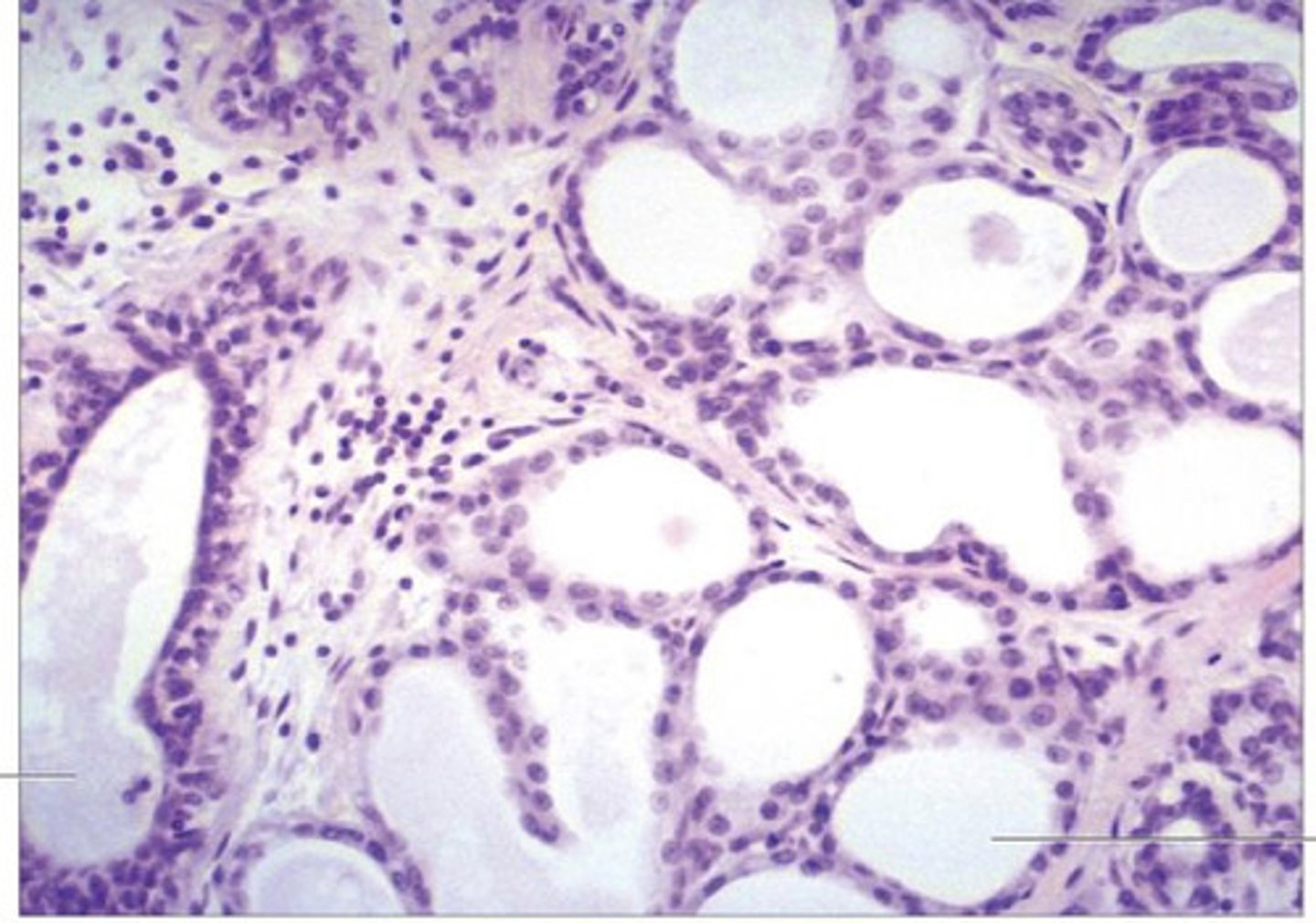
cuboidal cells surrounding alveoli, lots of CT between alveoli, clear/empty lumen
what does an inactive mammary gland look like?
squamous cells surrounding alveoli, less CT between alveoli, lumen filled with pink
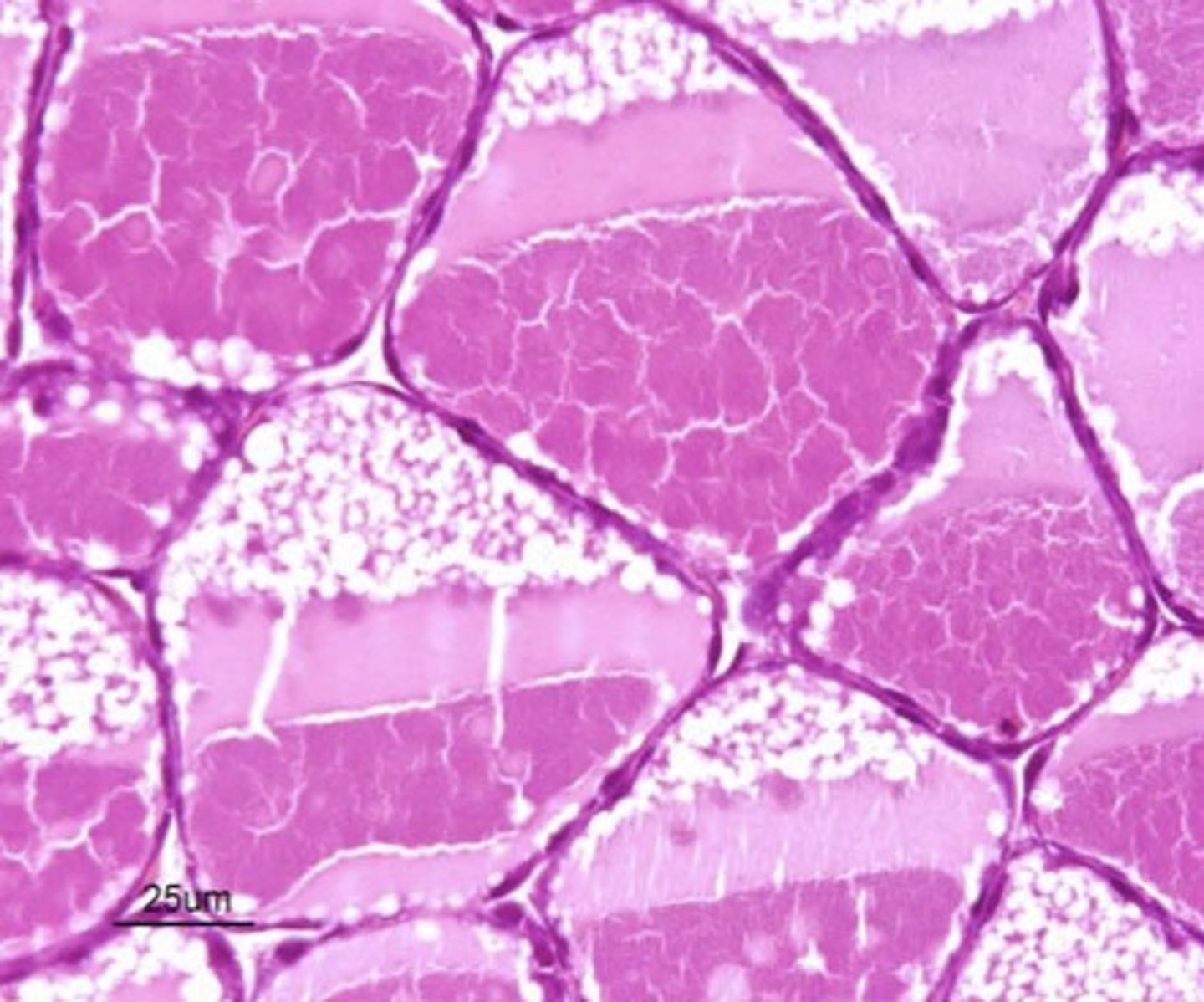
what does an active mammary gland look like?
active
is this mammary gland active or inactive?
1. lipids
2. proteins
3. calcium
what are the components inside an alveoli of a mammary gland?

a teat/nipple
what is this?
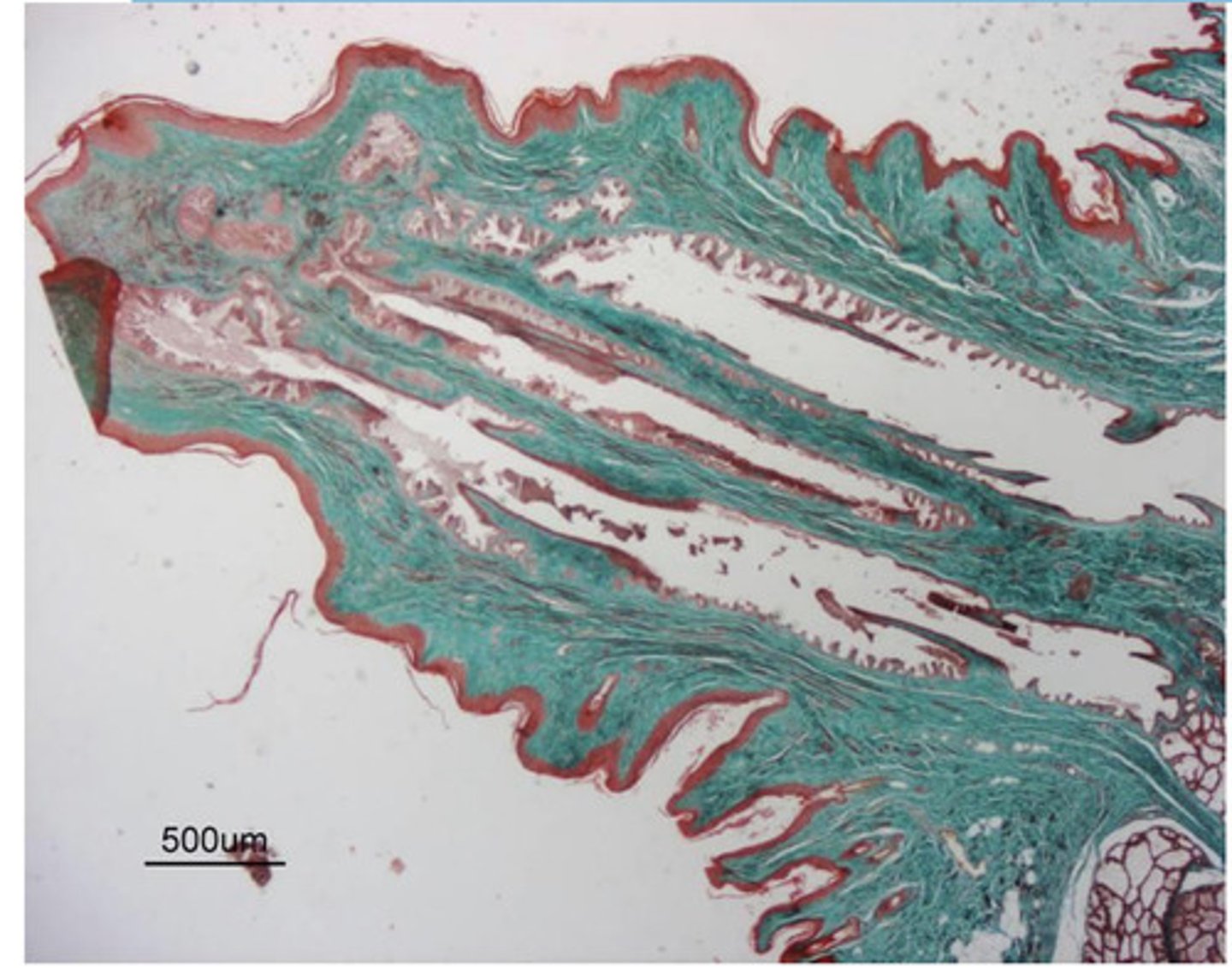
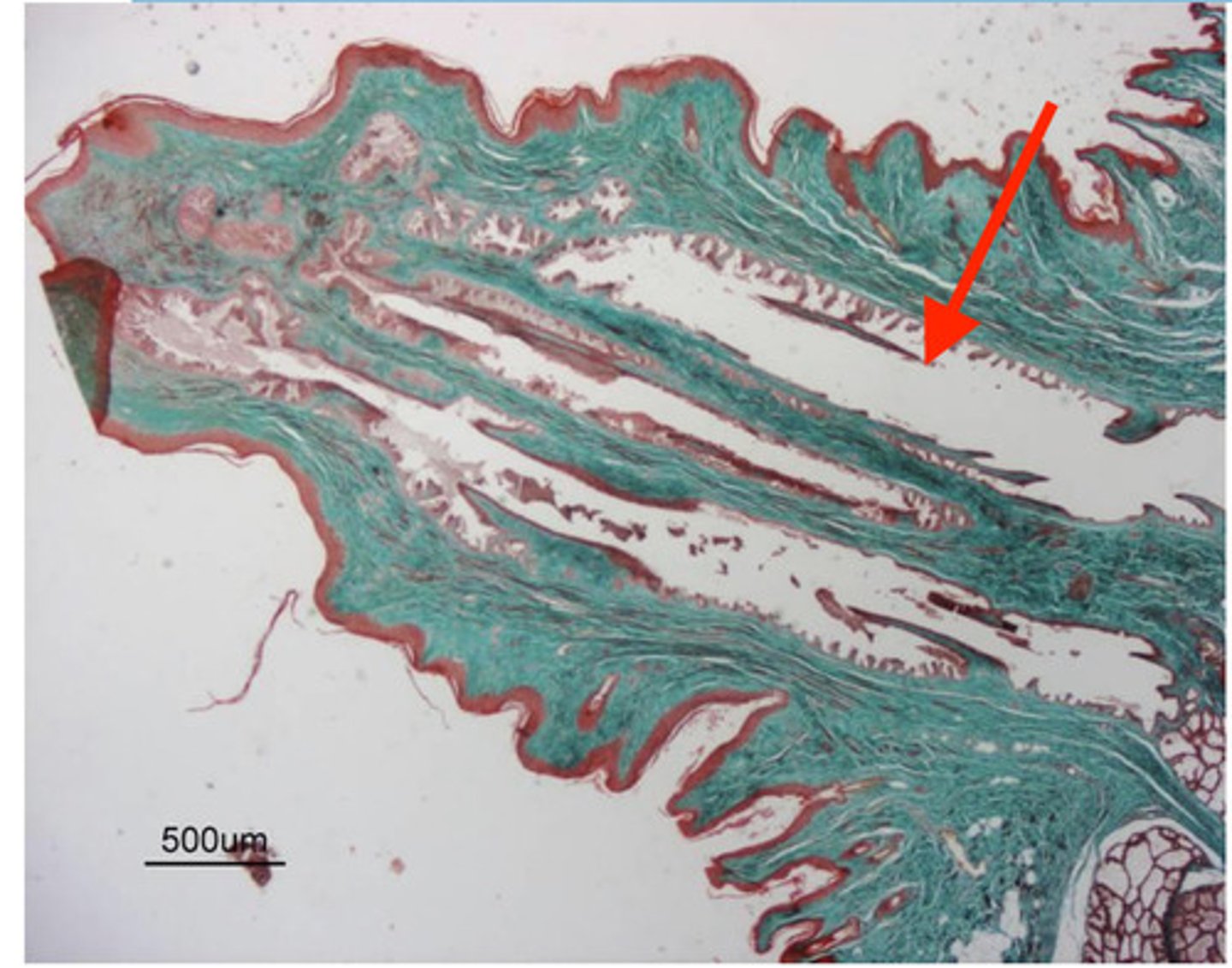
duct for transporting alveoli contents (milk)
what is this white space ?
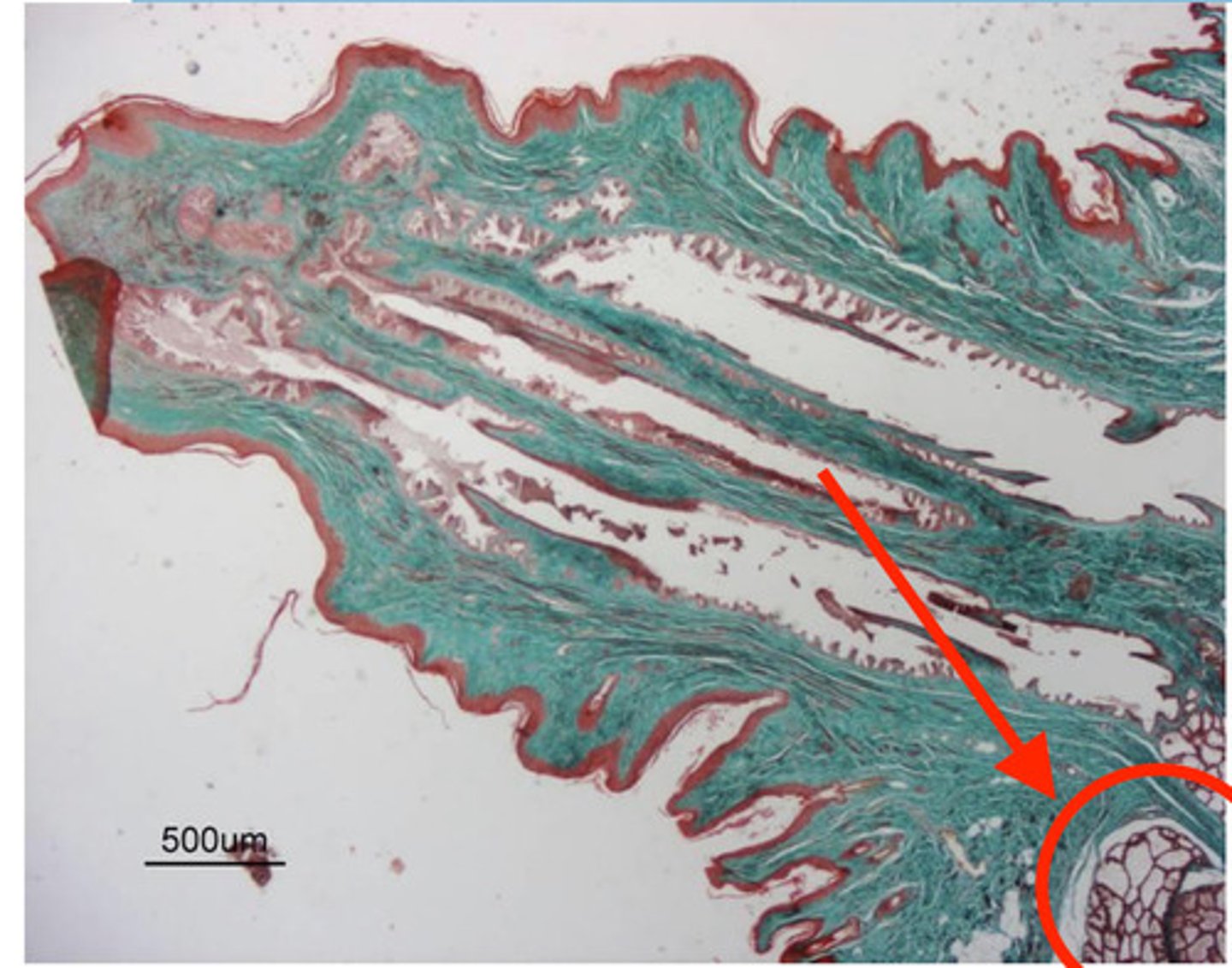
alveoli- components of mammary glands that produce milk
what are these clusters?
inactive
is this mammary gland active or inactive?
inactive
is this mammary gland active or inactive?
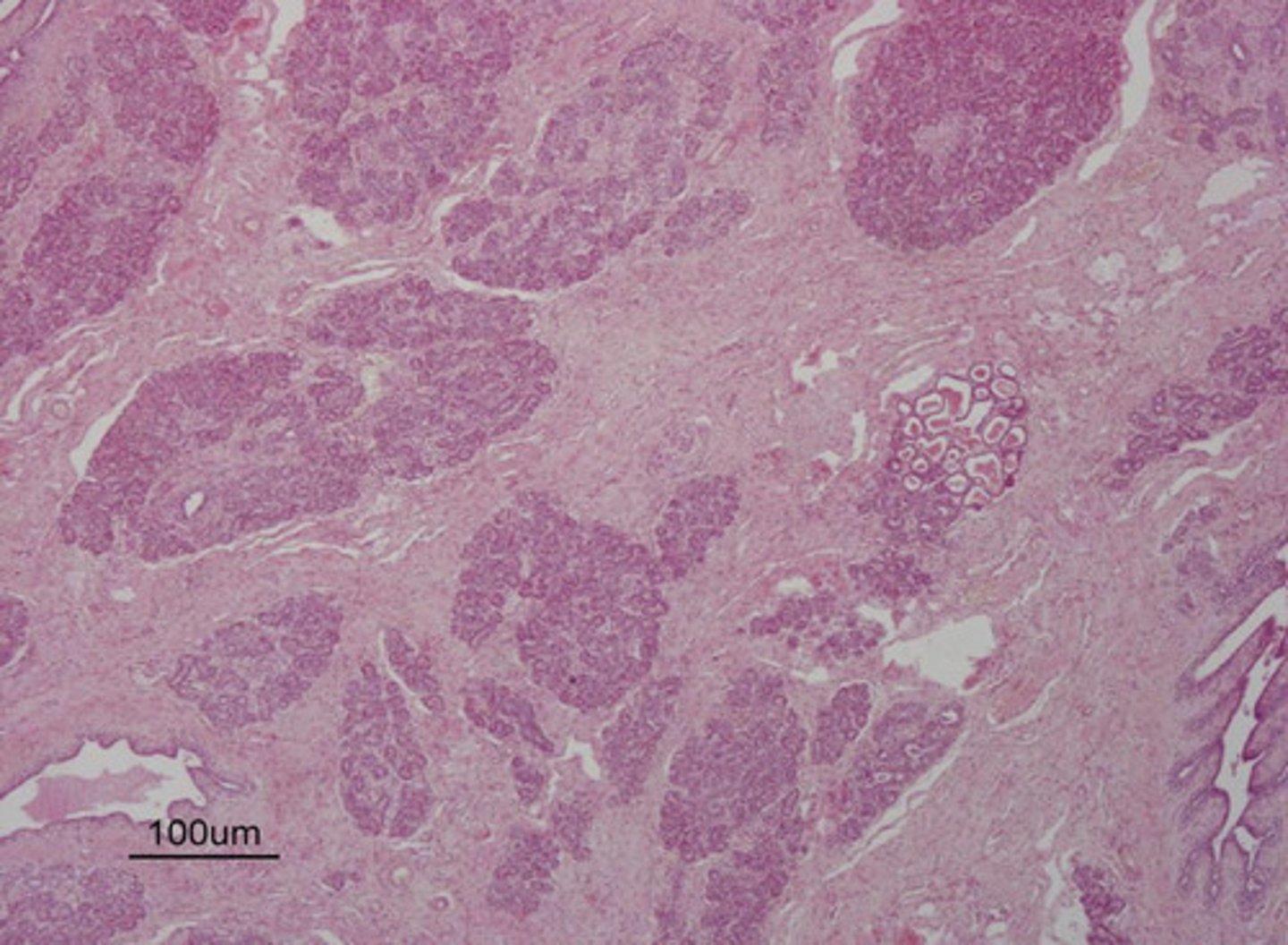
active
is this mammary gland active or inactive?
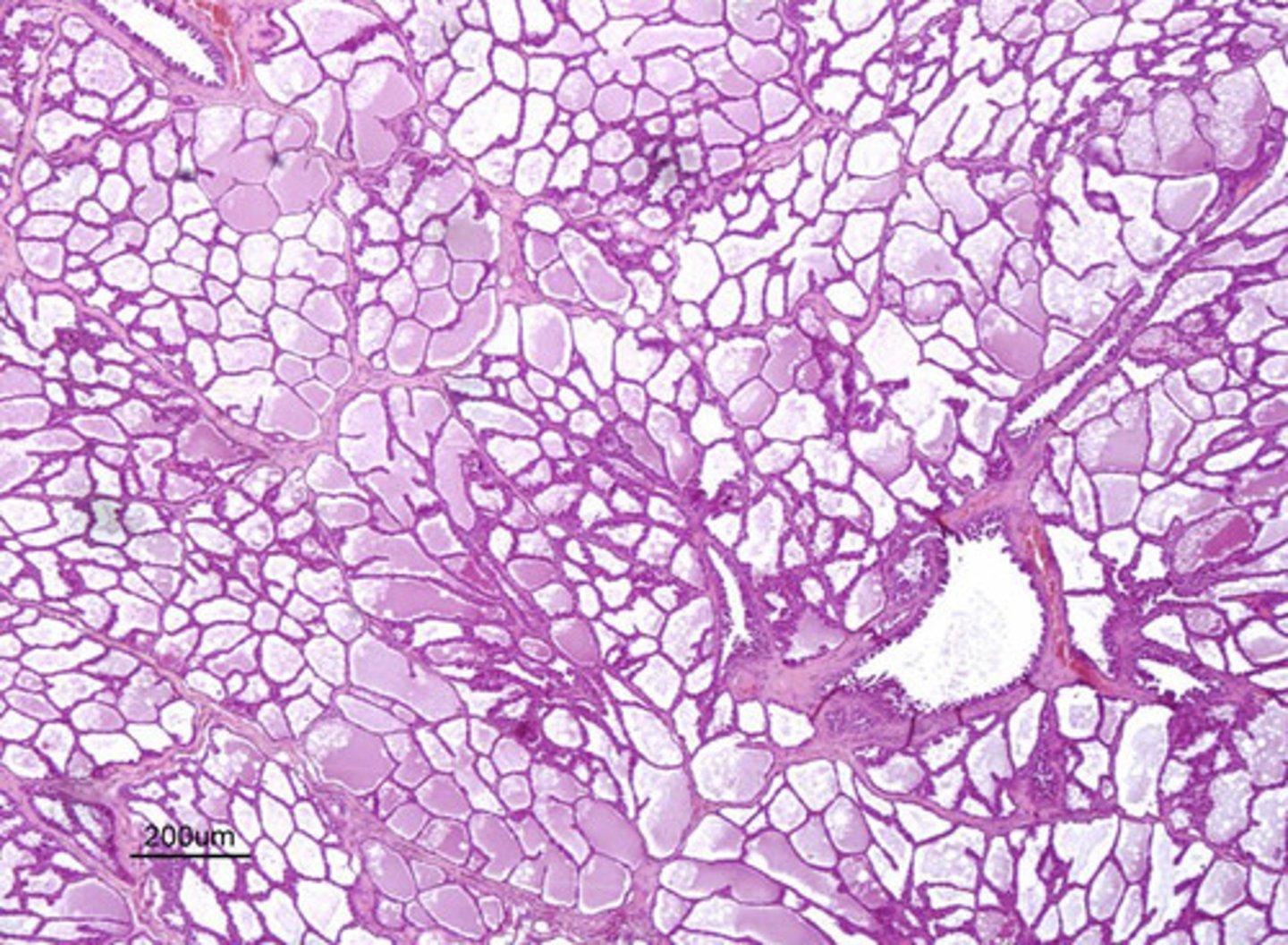
tunica vaginalis and tunica albuginea
what are the 2 histological protective layers of the testicle?
dense irregular CT
what composes the tunica albuginea of the testicle?
albuginea
the testicular septums come from the tunica ______
blood vessels and lymphatic vessels
the rete testes is composed of...
mature spermatazoa (sperm cells)
the lumen of the seminiferous tubules contain...
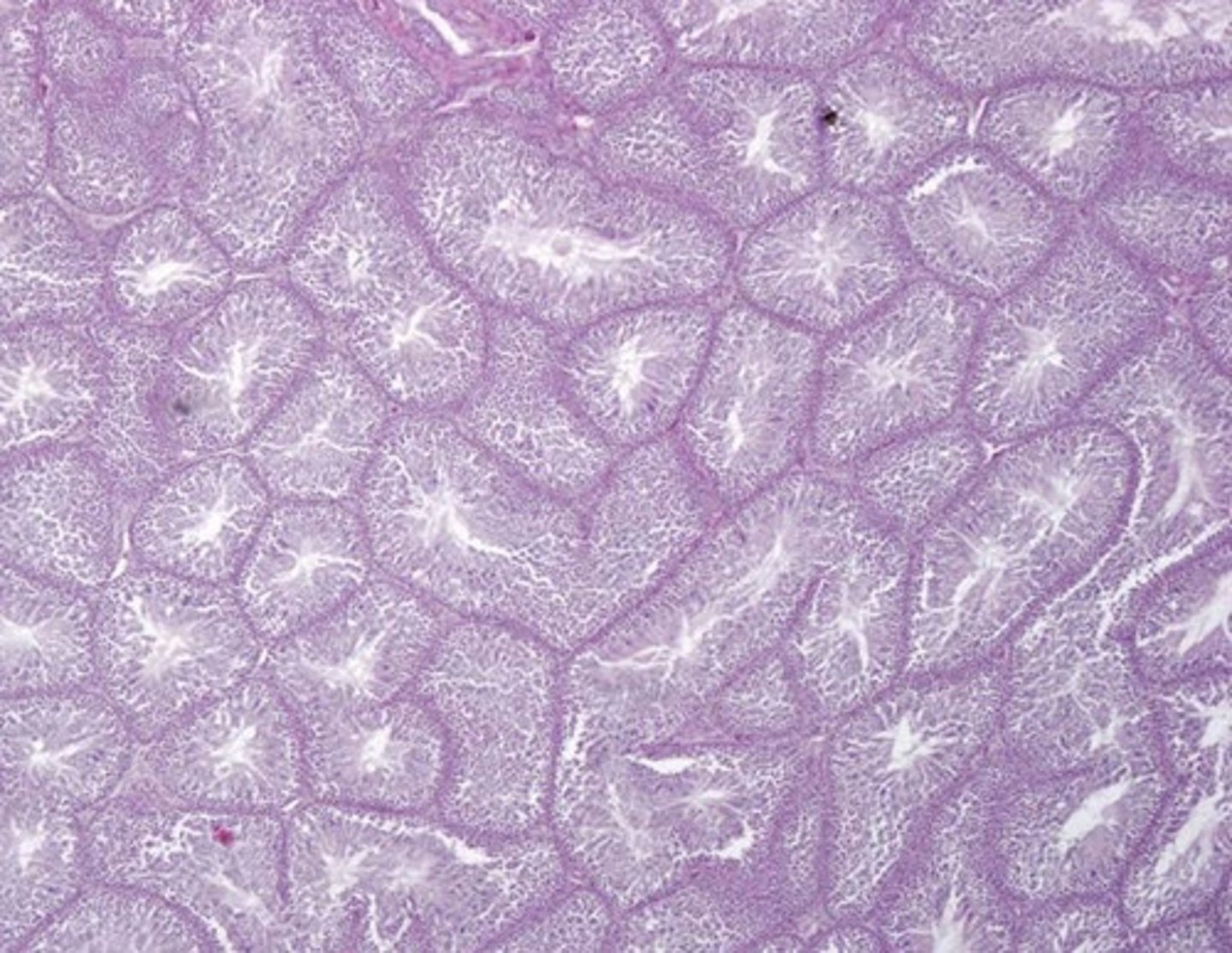
seminiferous tubules of the testicles
what are these?
sertoli cells
what are these?
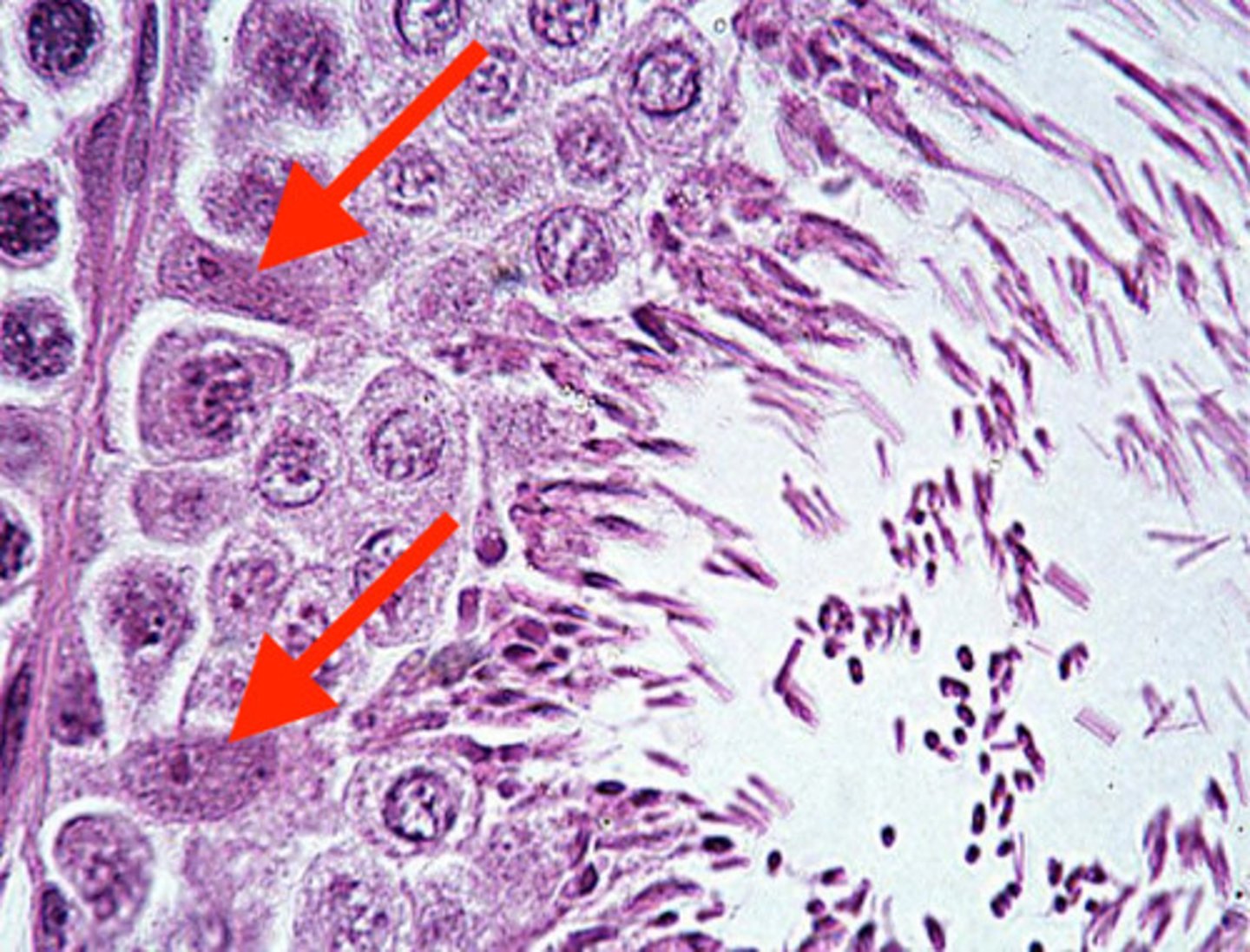
in between early stages of the spermatazoa in the walls of the seminiferous tubules
where can you find sertoli cells?
sertoli cells
what cells have the function of maintaining the structure of the seminiferous tubules?
early stages of spermatazoa, in the wall of the seminiferous tubules
what are these?
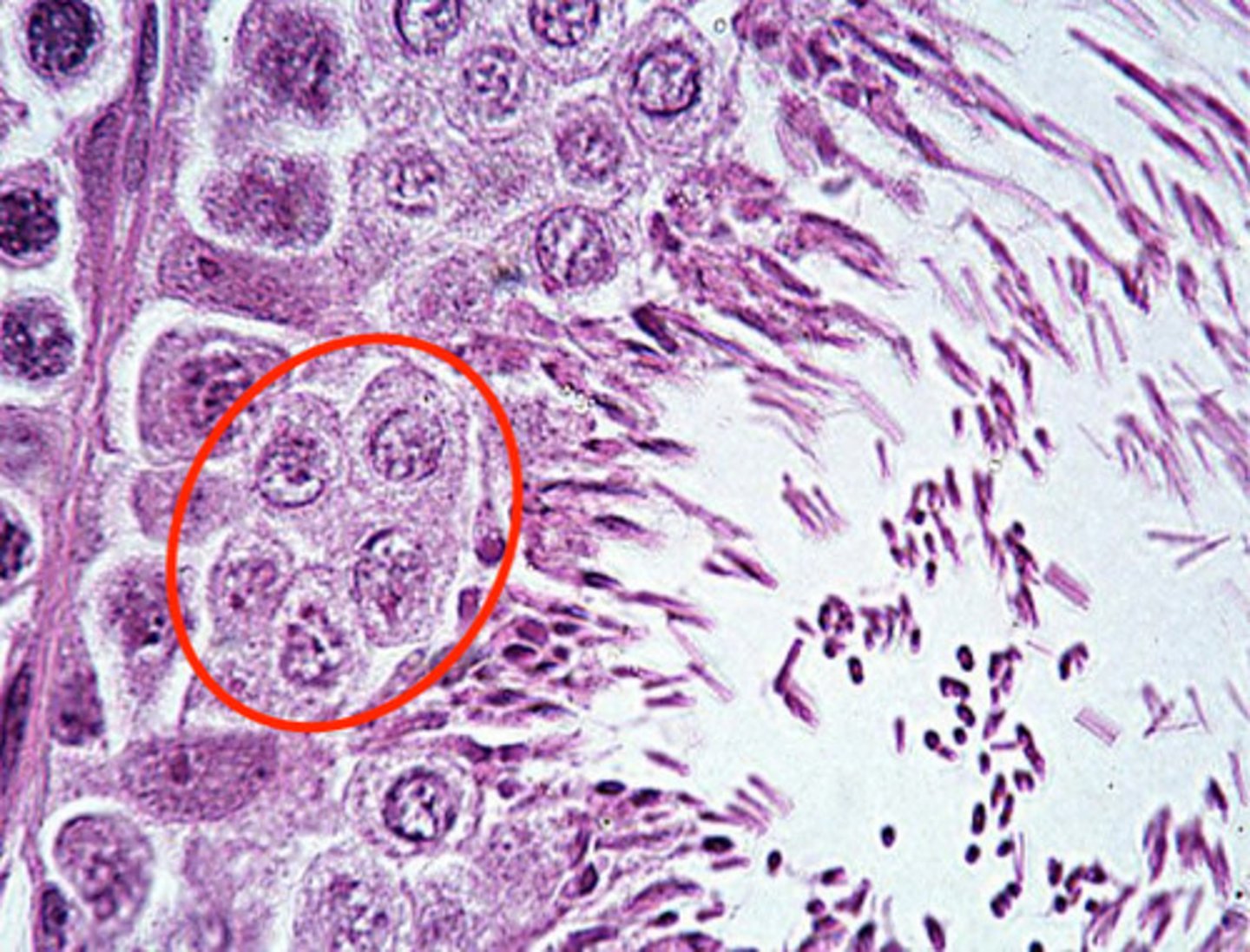
in the walls of the seminiferous tubules, maturing
they are immature spermatazoa
undergoing mitotic divisions
where are spematogenic cells found, and what are they?
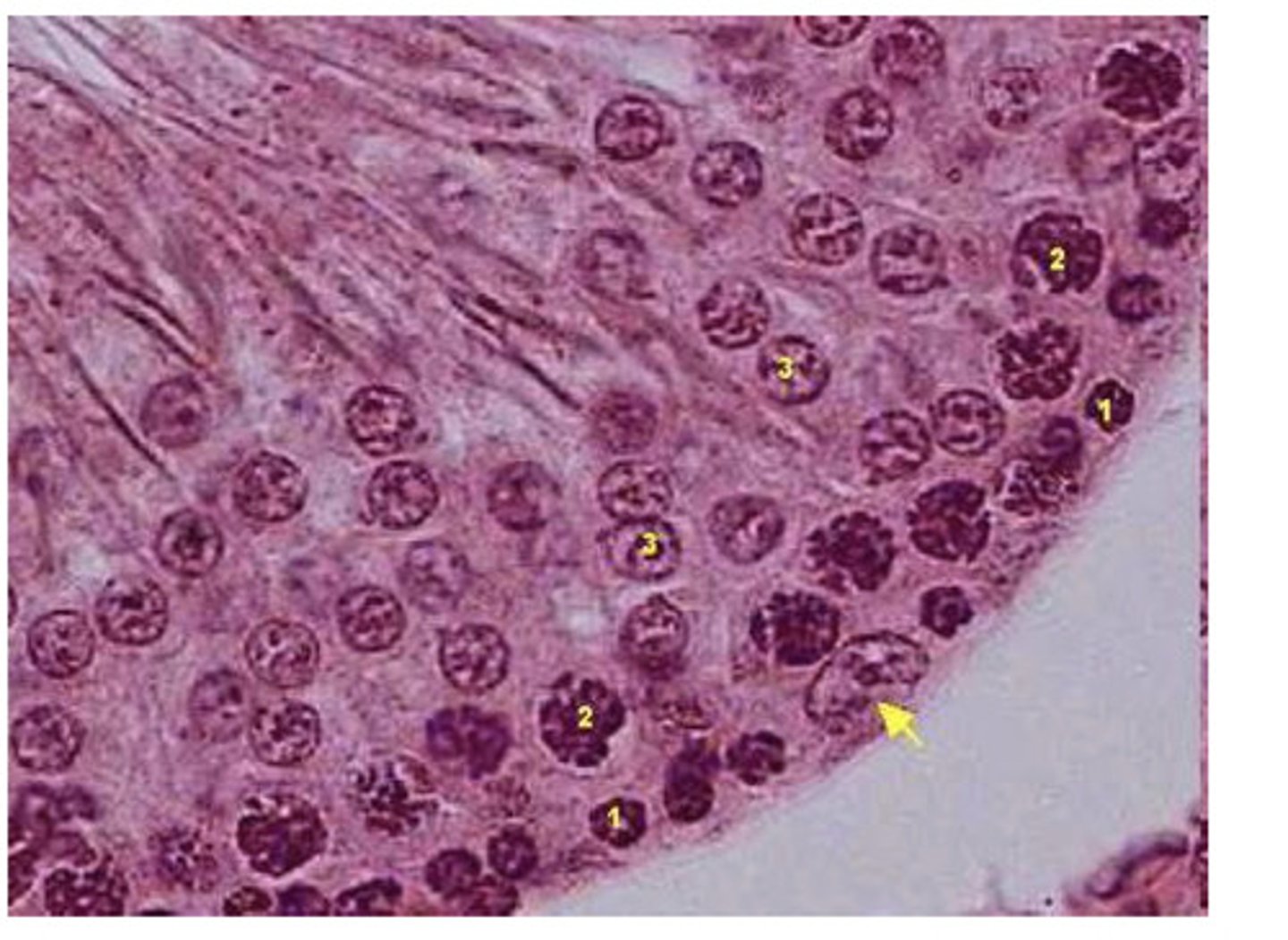
the lumen of the seminiferous tubules
spermatazoa are found in...
occupying space between the seminiferous tubules of the testes
where are leydig cells?
leydig cells
what are these?
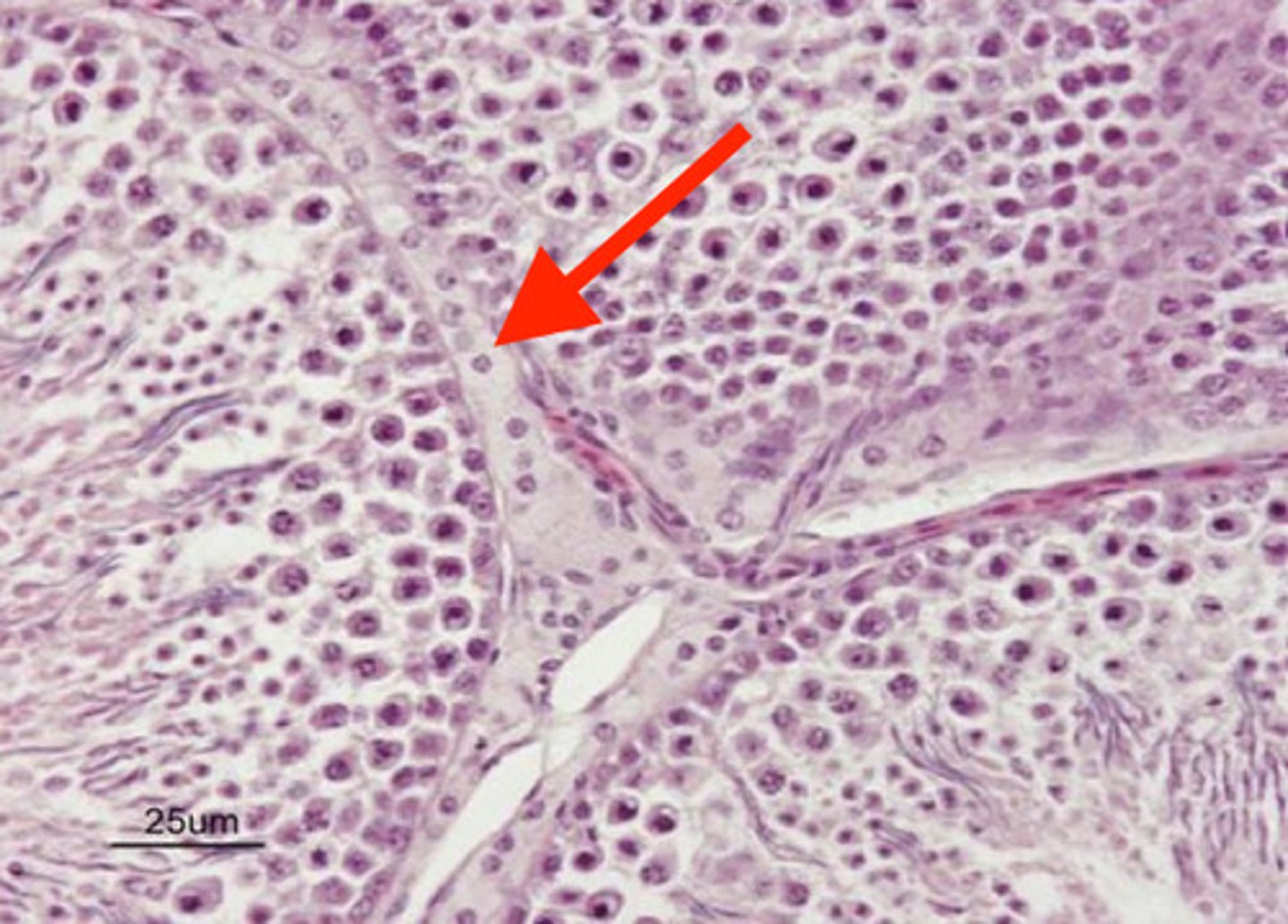
spermatazoa
what are these linear structures in the testes?
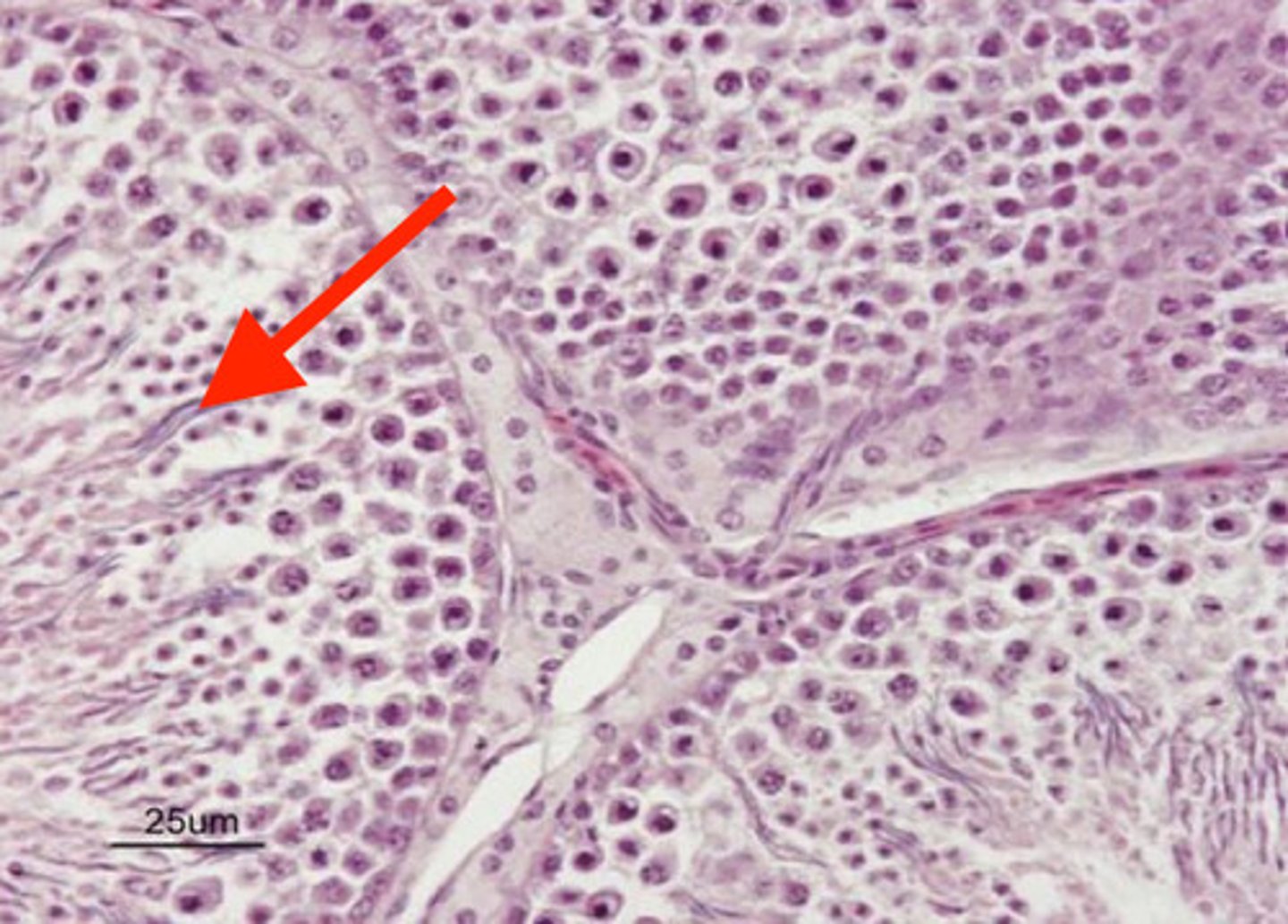
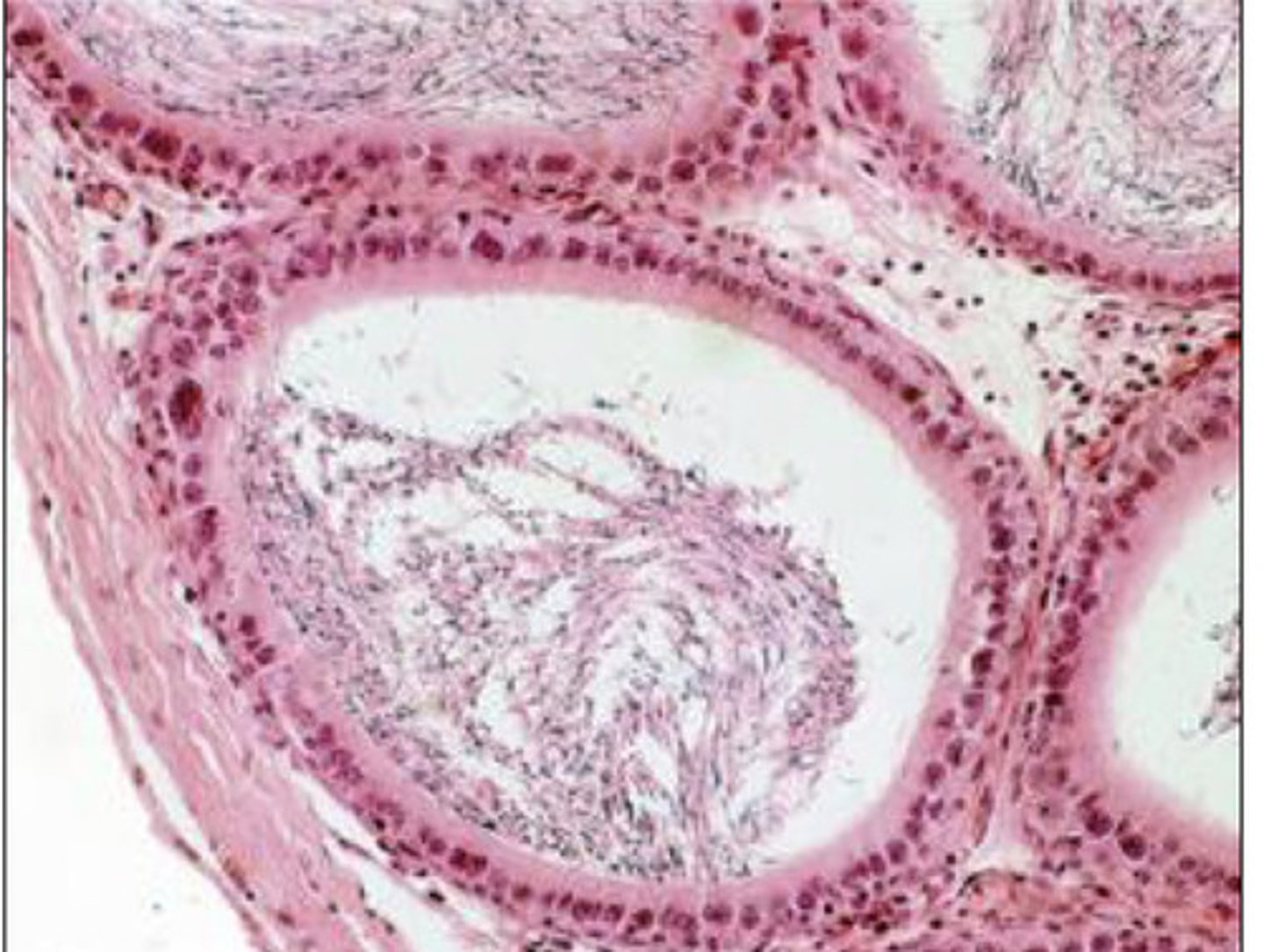
epididymis
what is this?
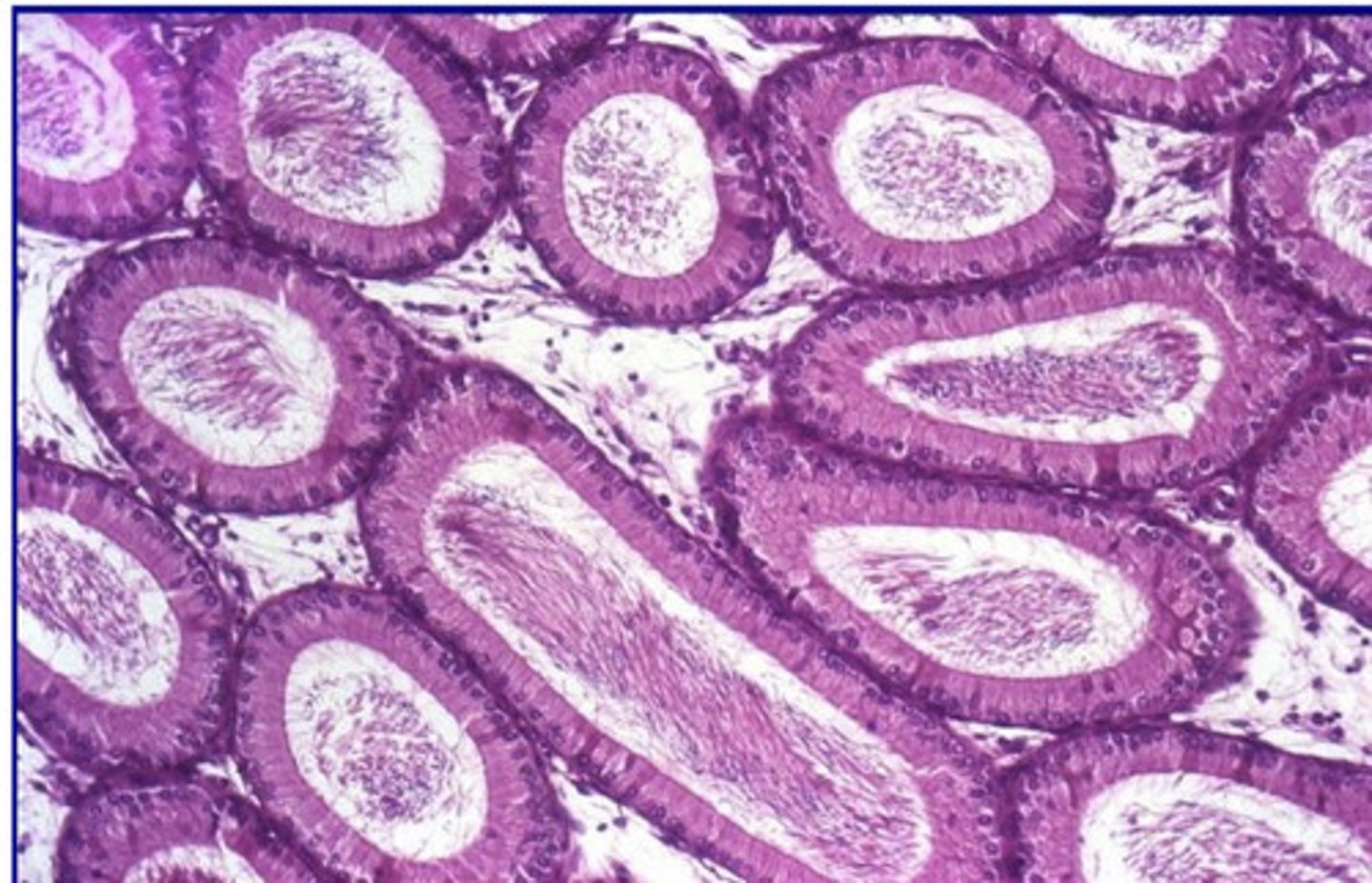
epididymis
which has a wider lumen- seminiferous tubules or epididymis?
1-2 layers of columnar cells with basal nuclei
wide lumen (with or without spermatazoa)
describe the histological morphology of the epididymis
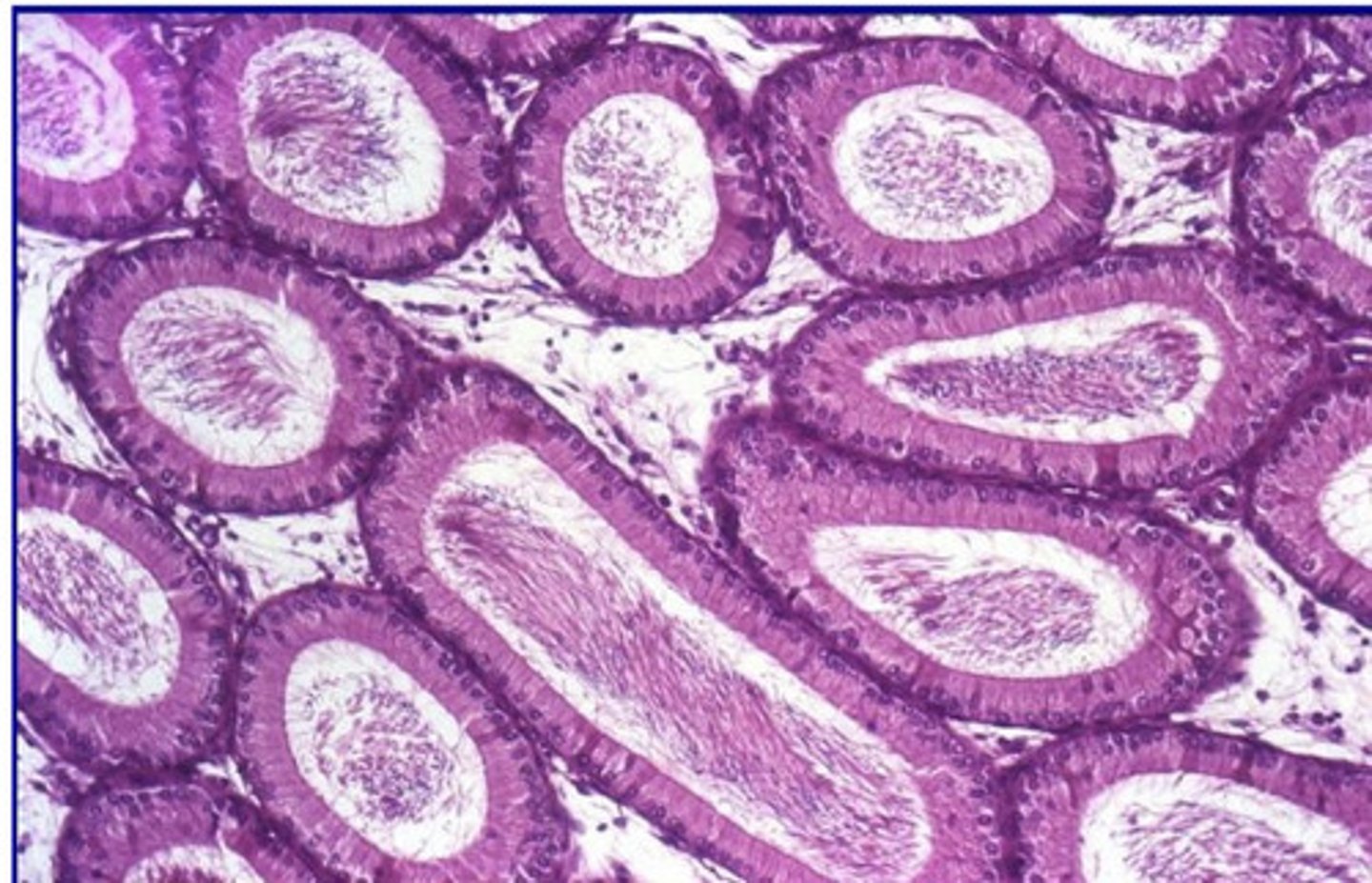
no
will you find leydig cells in the epididymis?
epididymis
what is this?