GENERATING ELECTRICITY
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/42
Last updated 4:24 PM on 2/17/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
1
New cards
radioactive decay, fusion and fission all give off…
energy
2
New cards
what is radioactive decay
completely spontaneous, has one daughter nuclei product and alpha/beta particle
3
New cards
what is fission
fission is non-spontaneous
* requires a neutron fires at nucleus
it has two daughter nuclei and 3 neutrons as products
* requires a neutron fires at nucleus
it has two daughter nuclei and 3 neutrons as products
4
New cards
what is fusion
fusion happens in stars
it joins two nuclei together to make one nucleus
it joins two nuclei together to make one nucleus
5
New cards
describe the process of fission in a Uranium 235 nucleus
* a neutron is fired at the nucleus
* the U235 nucleus splits into two daughter nuclei
* a small number of individual high energy neutrons are also given off
* energy is released
* the U235 nucleus splits into two daughter nuclei
* a small number of individual high energy neutrons are also given off
* energy is released
6
New cards
what can be caused by the neutrons given off by fission
the high energy neutrons can then target more U235 nuclei causing more fission
* CHAIN REACTION
* CHAIN REACTION
7
New cards
write the chemical reaction of the fission of U235
235/95U + 1/0n -→ 140/55Cs + 93/37Rb +3(1/0n)
8
New cards
function of fuel rods in a nuclear reactor
source of the U235
9
New cards
function of shielding in a nuclear reactor
prevents any radioactive material escaping by absorbing the radioactive decay
10
New cards
function of control rods in a nuclear reactor
control the rate of reaction.
* rate of reaction is too high, the rods are lowered
* they absorb excess neutrons and reduce the rate of fission
* if the rate of reaction is too slow, the rods are lifted
* allows the rate to increase
* rate of reaction is too high, the rods are lowered
* they absorb excess neutrons and reduce the rate of fission
* if the rate of reaction is too slow, the rods are lifted
* allows the rate to increase
11
New cards
function of the moderator in a nuclear reactor
absorbs some of the energy of the high energy product neutron, slowing them down to a more moderate speed so fission can still take place but at a more controlled rate
12
New cards
describe the process of fusion
* smaller nuclei combine into a larger nuclei
* occurs in stars
* creation of a larger nucleus results in a loss in mass from the smaller nuclei and a release of energy
* requires high energy, pressure and temperature in order to overcome the electrostatic repulsion between protons
* occurs in stars
* creation of a larger nucleus results in a loss in mass from the smaller nuclei and a release of energy
* requires high energy, pressure and temperature in order to overcome the electrostatic repulsion between protons
13
New cards
the nuclei in fusion are always…
positively charged
* repel eachother
* need high kinetic energy to overcome
* repel eachother
* need high kinetic energy to overcome
14
New cards
waste products of fusion are…
still radioactive
15
New cards
waste products of fusion can cause…
cancer/mutations in humans
16
New cards
where is the waste product of fusion typically stored
in mountains/underground
17
New cards
what protects humans from the products of nuclear fission in a reactor
concrete around the core of the reactor
18
New cards
waste products of fusion can cause…
cancer in humans
19
New cards
what happens if the rate of reaction gets too high in a nuclear reactor
it explodes
20
New cards
what is the function of the live wire in a plug?
carries charge
21
New cards
what is the function of the earth wire in a plug?
grounds the plug
22
New cards
what is the function of the neutral wire in a plug?
completes the circuit back to its source
23
New cards
what is a fuse
a small piece of wire that melts and breaks the circuit if a surge occurs
24
New cards
what are 3 hazards of mains electricity
1. damaged insulation
* touching exposed wire -→ electrocution
2. overheating cables
* caused by too much current in the wire
* leads to a fire of melting of insulation
3. damp conditions
* water + wires -→ water conducts electricity
* short circuit = fire
* electrocution
25
New cards
explain differences in current and voltage in mains vs cell
cell: produces direct current, voltage is much lower than mains
mains: produces an alternating current (50hz), voltage is much higher (230V)
mains: produces an alternating current (50hz), voltage is much higher (230V)
26
New cards
describe the generator effect
* movement of a magnet through a coil
* magnetic feild ‘cuts’ the coil
* induces a voltage
* a complete circuit means there is a current
* magnetic feild ‘cuts’ the coil
* induces a voltage
* a complete circuit means there is a current
27
New cards
how to increase voltage produced by the generator effect
* increase number of coils
* increase stregth of magnet
* move it faster
* increase stregth of magnet
* move it faster
28
New cards
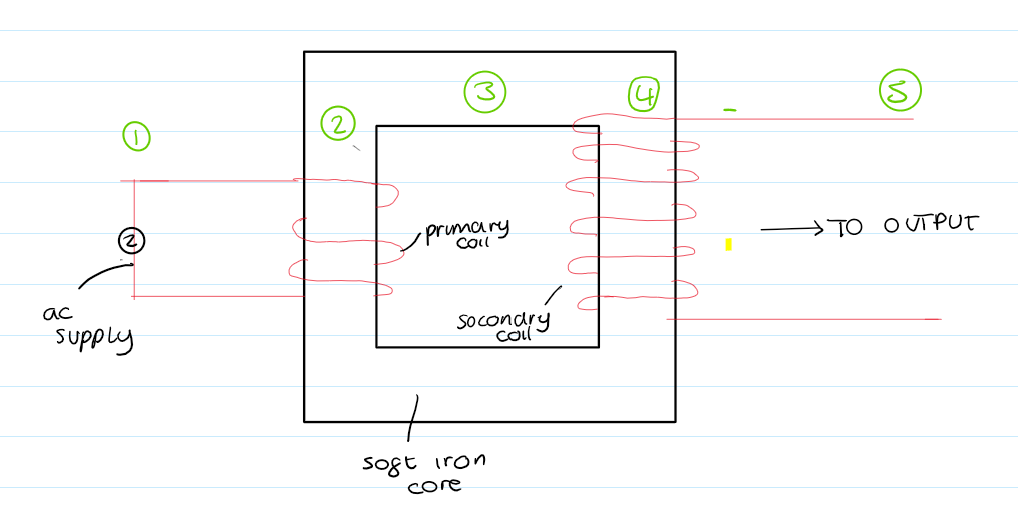
describe how a transformer works
1. the a.c supply provides an alternating current to the primary coil
2. the ac creates a changing magnetic feild around the primary coil
3. the soft iron core strengthens and channels the changing magnetic feild over to the secondary coil
4. the changing magnetic feild is being cut by the secondary coil
5. this induces a alternating/changing voltage and a current if circuit is complete
29
New cards
transformers only work with ac or dc?
ac as they depend on a changing magnetic feild
30
New cards
does the iron core conduct current in a transformer?
no it channels the changing mag feild
31
New cards
what is a step up transformer
it increases voltage in secondary coil in comparison with the primary coil (more turns in secondary coil)
32
New cards
what is a step down transformer
it decreases voltage in secondary coil in comparison with the primary coil (less turns in secondary coil)
33
New cards
what is the equation that links no of coil turns with voltage
voltage (primary)/voltage (secondary) = no of turns in coil (primary)/no of turns in coil(secondary)
34
New cards
how efficient are transformers
100%
35
New cards
what is the equation that shows the efficiency of the transformer is 100%
current (primary) x voltage (primary) = current (secondary) x voltage (secondary)
36
New cards
how do transformers work in power transmission lines
* the step up transformer drastically increases the voltage
* high voltage, low current
* current causes heating effects in wires, so a smaller current wastes less energy from heat loss
* the cables are very thick in order to decrease their resistance, reduces power loss
* the step down transformer at the end reduces the voltage to an appropriate amount for household use (240V)
\
* high voltage, low current
* current causes heating effects in wires, so a smaller current wastes less energy from heat loss
* the cables are very thick in order to decrease their resistance, reduces power loss
* the step down transformer at the end reduces the voltage to an appropriate amount for household use (240V)
\
37
New cards
how renewable is solar energy?
renewable
cost
efficiency
conditions
does it work all the time
renewable
cost
efficiency
conditions
does it work all the time
light energy -→ electrical energy
* renewable (no pollution)
* no fuel cost
* expensive to buy
* can provide energy in areas with no mains
* inefficient
* does not work at night or when its cloudy
* renewable (no pollution)
* no fuel cost
* expensive to buy
* can provide energy in areas with no mains
* inefficient
* does not work at night or when its cloudy
38
New cards
how renewable is wind energy?
renewable
cost
efficiency
conditions
does it work all the time
renewable
cost
efficiency
conditions
does it work all the time
kinetic energy -→ electrical energy
* renewable
* no fuel cost
* weather dependant (needs high wind speed)
* noisy and ruins views
* renewable
* no fuel cost
* weather dependant (needs high wind speed)
* noisy and ruins views
39
New cards
how renewable is tidal energy?
renewable
cost
efficiency
conditions
does it work all the time
renewable
cost
efficiency
conditions
does it work all the time
kinetic energy -→ electrical energy
* renewable
* no fuel cost
* reliable
* expensive to build
* destroys habitats
* easy to switch on
* renewable
* no fuel cost
* reliable
* expensive to build
* destroys habitats
* easy to switch on
40
New cards
how renewable is biomass energy?
renewable
cost
efficiency
conditions
does it work all the time
renewable
cost
efficiency
conditions
does it work all the time
chemical -→ electrical
* if replaced - sustainable
* cheap
* readily available
* no increased CO2 levels overall (biomass takes up co2 when growing)
* gives off atmospheric pollutants when burned
\
* if replaced - sustainable
* cheap
* readily available
* no increased CO2 levels overall (biomass takes up co2 when growing)
* gives off atmospheric pollutants when burned
\
41
New cards
how renewable is geothermal energy?
renewable
cost
efficiency
conditions
does it work all the time
renewable
cost
efficiency
conditions
does it work all the time
thermal -→ electrical
* renewable
* no fuel cost
* hot water + steam can heat houses directly
* only available in certain volcanic areas
\
* renewable
* no fuel cost
* hot water + steam can heat houses directly
* only available in certain volcanic areas
\
42
New cards
how renewable is hydroelectric energy?
renewable
cost
efficiency
conditions
does it work all the time
renewable
cost
efficiency
conditions
does it work all the time
gravitational potential -→ kinetic energy -→ electrical
* renewable
* no fuel cost
* easy to switch on
* reliable
* expensive to build
* floods farmland/forces poeple out of homes
* renewable
* no fuel cost
* easy to switch on
* reliable
* expensive to build
* floods farmland/forces poeple out of homes
43
New cards
how renewable is nuclear energy?
renewable
cost
efficiency
conditions
does it work all the time
renewable
cost
efficiency
conditions
does it work all the time
nuclear -→ electrical
* no pollutants
* reliable
* non renewable
* accidents lead to radioactive material in atmosphere
* no pollutants
* reliable
* non renewable
* accidents lead to radioactive material in atmosphere