FBLA Introduction to Information Technology
1/217
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
218 Terms
Open System Interconnection (OSI)
a networking framework to implement protocols in seven layers
Physical Layer
The first layer of the model. It conveys the bit stream - electrical impulse, light or radio signal — through the network at the electrical and mechanical level. It provides the hardware means of sending and receiving data on a carrier, including defining cables, cards and physical aspects.
Data Link Layer
The second layer. Data packets are encoded and decoded into bits. It furnishes transmission protocol knowledge and management and handles errors in the physical layer, flow control and frame synchronization. The data link layer is divided into two sub layers: The Media Access Control (MAC) layer and the Logical Link Control (LLC) layer. The MAC sub layer controls how a computer on the network gains access to the data and permission to transmit it. The LLC layer controls frame synchronization, flow control and error checking.
Network Layer
The third layer. It provides switching and routing technologies, creating logical paths, known as virtual circuits, for transmitting data from node to node. Routing and forwarding are functions of this layer, as well as addressing, internetworking, error handling, congestion control and packet sequencing.
Transport Layer
The fourth layer. It provides transparent transfer of data between end systems, or hosts, and is responsible for end-to-end error recovery and flow control. It ensures complete data transfer.
Session Layer
The fifth layer. It establishes, manages and terminates connections between applications. The session layer sets up, coordinates, and terminates conversations, exchanges, and dialogues between the applications at each end. It deals with session and connection coordination.
Presentation Layer
The sixth layer. It provides independence from differences in data representation (e.g., encryption) by translating from application to network format, and vice versa. The presentation layer works to transform data into the form that the application layer can accept. This layer formats and encrypts data to be sent across a network, providing freedom from compatibility problems. It is sometimes called the syntax layer.
Application Layer
The seven layer. It supports application and end-user processes. Communication partners are identified, quality of service is identified, user authentication and privacy are considered, and any constraints on data syntax are identified. Everything at this layer is application-specific. This layer provides application services for file transfers, e-mail, and other network software services. Telnet and FTP are applications that exist entirely in the application level. Tiered application architectures are part of this layer.
Network Topology
It refers to layout of a network. How different nodes in a network are connected to each other and how they communicate is determined by the network's topology.
Network
A group of two or more computer systems linked together. There are many types of computer networks, including the following:
Topology
The shape of a local-area network (LAN) or other communications system.
Node
In networks, a processing location. A node can be a computer or some other device, such as a printer. Every node has a unique network address, sometimes called a Data Link Control (DLC) address or Media Access Control (MAC) address.
Physical Topology
The physical layout of devices on a network. Every LAN has a topology, or the way that the devices on a network are arranged and how they communicate with each other.
Logical Topology
Every LAN has a topology, or the way that the devices on a network are arranged and how they communicate with each other.
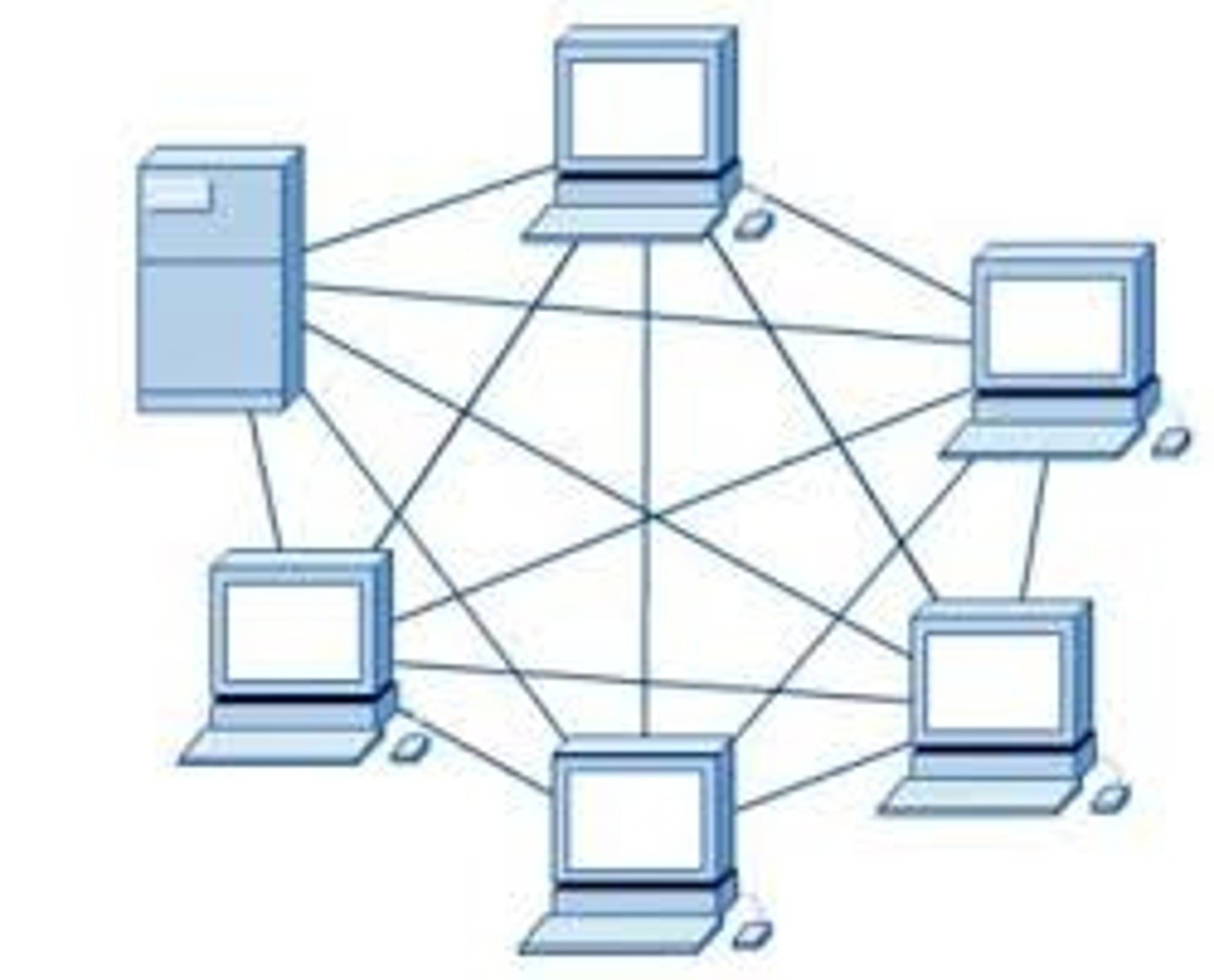
Mesh Topology
A topology where devices are connected with many redundant interconnections between network nodes. In a true mesh topology every node has a connection to every other node in the network.
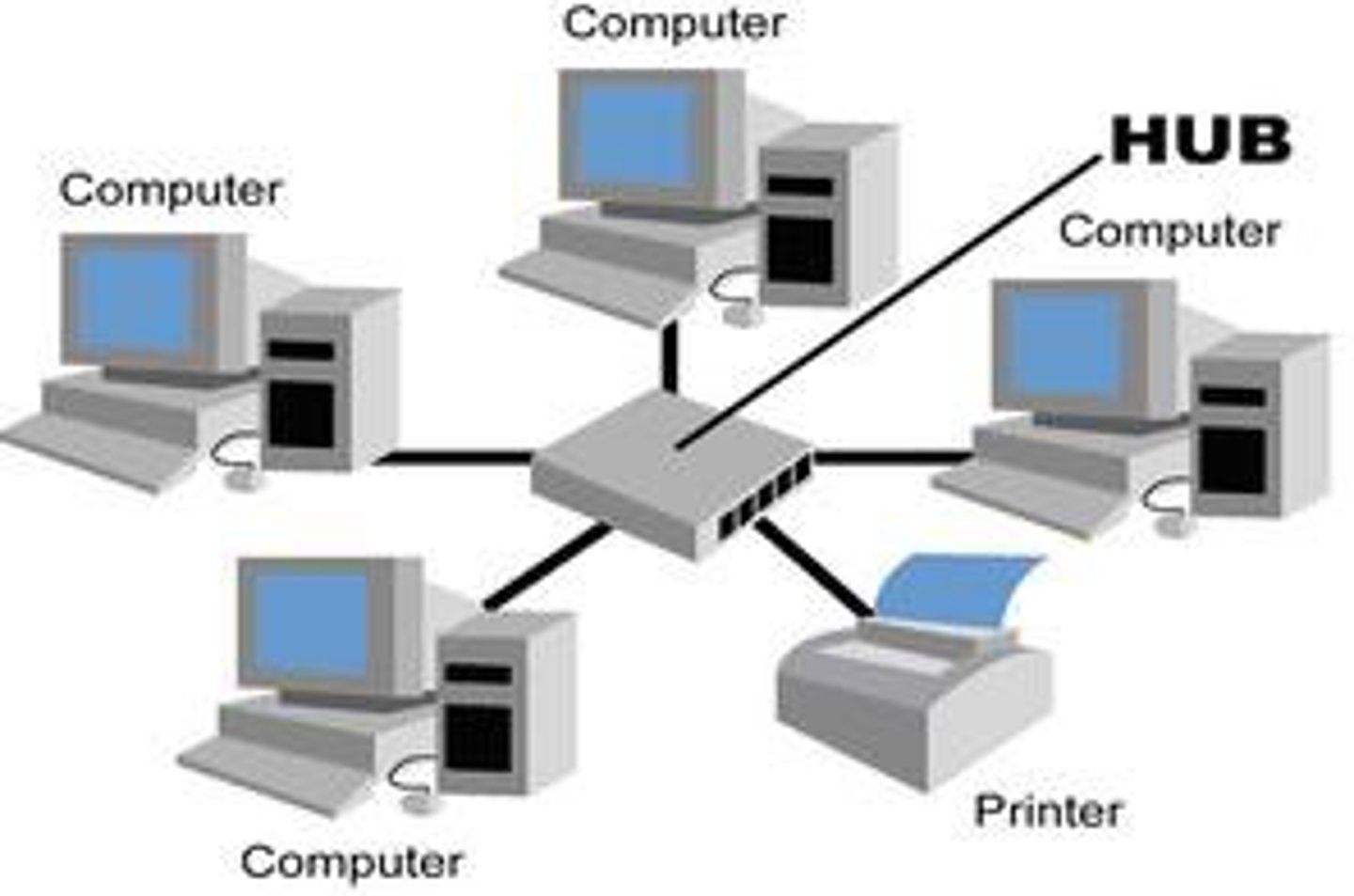
Star Topology
A topology where devices are connected to a central computer, called a hub. Nodes communicate across the network by passing data through the hub.
Main Advantage: In a star network, one malfunctioning node doesn't affect the rest of the network.
Main Disadvantage: If the central computer fails, the entire network becomes unusable
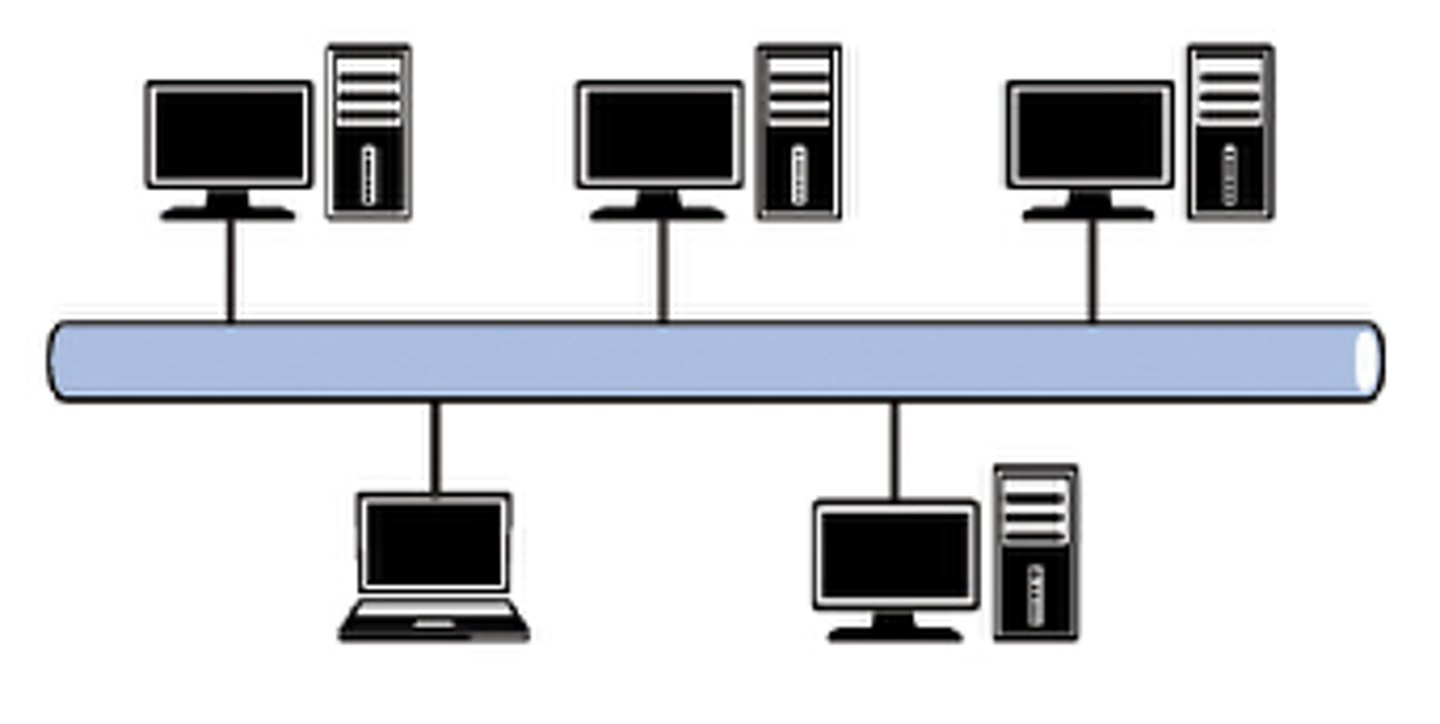
Bus Topology
A topology where a central cable -- the main wire -- that connects all devices on a local-area network (LAN). It is also called the backbone. This is often used to describe the main network connections composing the Internet. Bus networks are relatively inexpensive and easy to install for small networks. Ethernet systems use a bus topology.
Main Advantage: It's easy to connect a computer or device and typically it requires less cable than a star topology.
Main Disadvantage: The entire network shuts down if there is a break in the main wire and it can be difficult to identify the problem if the network shuts down.
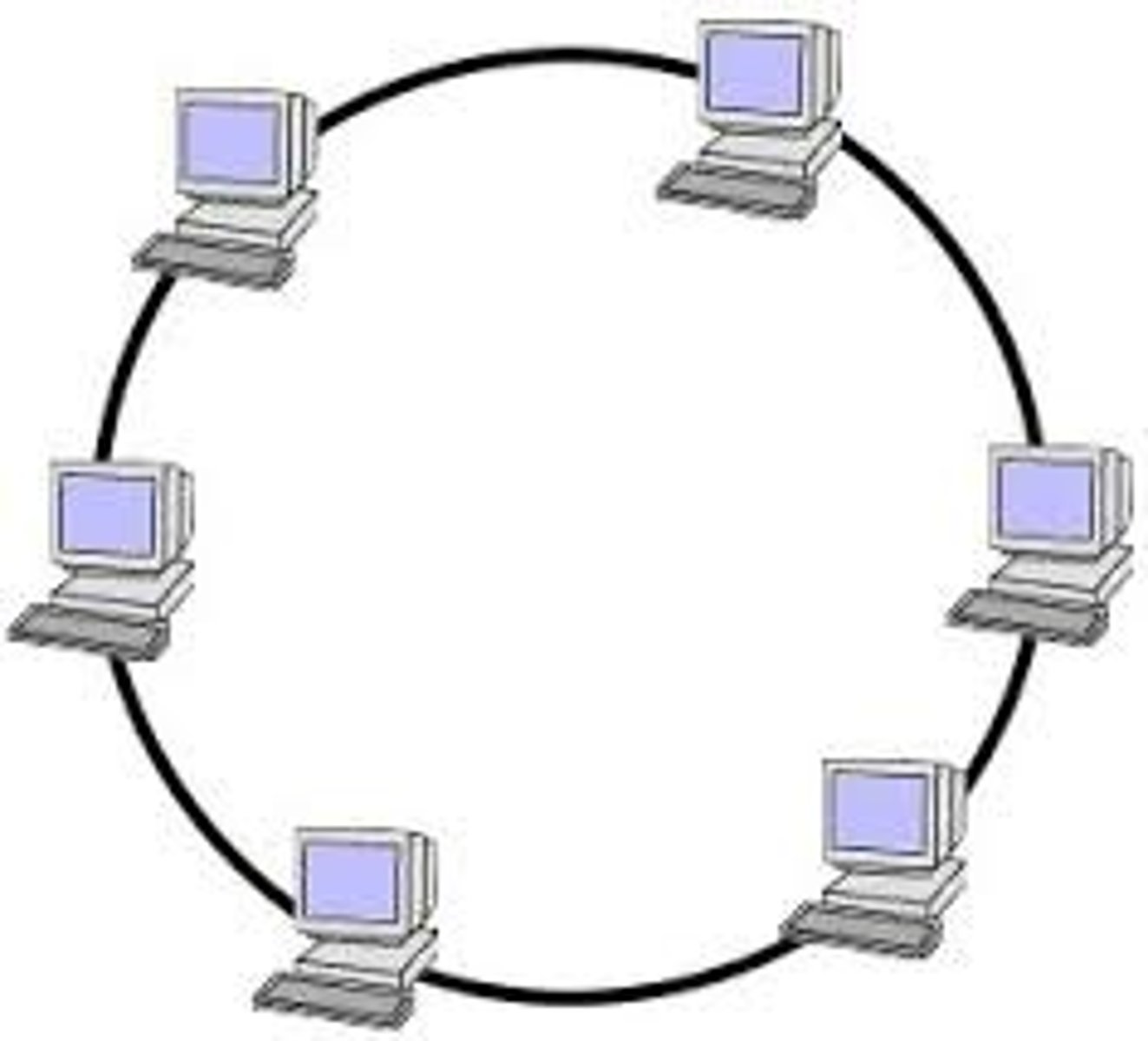
Ring Topology
A local-area network (LAN) whose topology is a ring. That is, all of the nodes are connected in a closed loop. Messages travel around the ring, with each node reading those messages addressed to it.
Main Advantage: One main advantage to a ring network is that it can span larger distances than other types of networks, such as bus networks, because each node regenerates messages as they pass through it.
Tree Topology
This is a "hybrid" topology that combines characteristics of linear bus and star topologies. In a tree network, groups of star-configured networks are connected to a linear bus backbone cable.
Main Advantage: A Tree topology is a good choice for large computer networks as the tree topology "divides" the whole network into parts that are more easily manageable.
Main Disadvantage: The entire network depends on a central hub and a failure of the central hub can cripple the whole network.
Full Mesh Topology
A mesh topology occurs when every node has a circuit connecting it to every other node in a network. Full mesh is very expensive to implement but yields the greatest amount of redundancy, so in the event that one of those nodes fails, network traffic can be directed to any of the other nodes. Full mesh is usually reserved for backbone networks.
Partial Mesh Topology
A mesh topology where it is less expensive to implement and yields less redundancy than full mesh topology. With partial mesh, some nodes are organized in a full mesh scheme but others are only connected to one or two in the network. Partial mesh topology is commonly found in peripheral networks connected to a full meshed backbone.
An Algorithm
A formula or procedure that is simple for solving a problem with clear stopping point.
Windows SIM
Windows System Image Manager used for managing several disk images in a group
PCMCIA
A networking device
Application Software
A program that is designed to perform a specific task.
Assembly Language
Length in code in assembly and machine are the same and uses words.
Batch driven data warehouse
Prepare the data in advance, and then when the computer system is not busy, the information can be processed all in one batch. Payroll and credit card bills are examples.
Binary numbering system
1s and 0s
Compiled and interpreted languages are written in ?
Binary code
Broadcast devices
hubs, switches, routers, WAPs
Certificate Authority
Both the authentication proof and the encryption information.
Circuit Switched
Path exist during the entire conversation, communication in either direction can occur simultaneously.
Cloud Computing
As a Service, Platform or Software
Compiler
Translates the entire program, creating an executable, which can be run at a later time.
Confidential Risk
Information that an organization will keep secret, such as patent-able information and business plans. The government classified tags such as confidential, secret and top secret.
The Controller - MCV
Facilitates communication between the model and the view.
Database Admin
Designs DBMS
Database Admin Roles
Integration, security for remote access, procedures associated with DBMS
Database Management System Manufacturers
Microsoft Access, SQL, and its variations (MySQL, Microsoft SQL, PostgreSQL, etc..
Database Organization
Records (rows) are called tuplets. All records of the relation share the same attributes. Attributes are characteristics which are used to describe a record, and are the column headings. A field contains the data of an attribute for a record within a relation.
Database Projection
A query return of ALL records for the relation, but only selected attributes and fields.
Database Query
A search of data in relation to selected parameters
Database Record
The horizontal row
Database record functionality terms
Record, Query, projection, update or modify , insert, delete and join
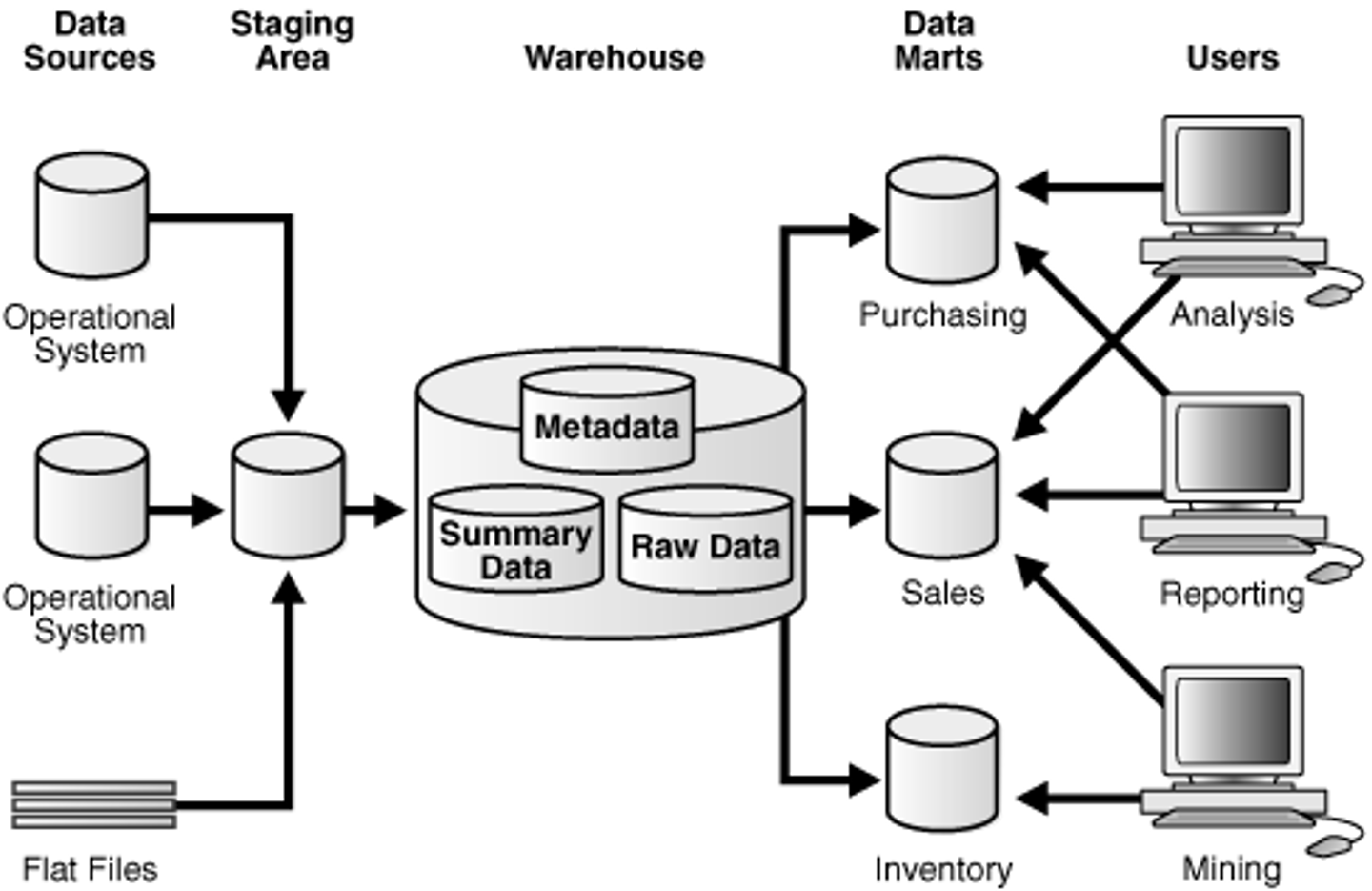
Data Marts
The means by which users obtain data or information out of the warehouse.
Data tier
In software architecture n-tier or multi-tier development -- this tier is where data are stored, retrieved and updated from database tables. The data can scale more easily.
Data warehouse
Uses an ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) Process
DIKW
Data, Information, Knowledge and Wisdom
DQL
Data Query Language
Event Driven Data Warehouse
Processing uses business events, such as submitting an order to a vendor. receiving goods, or creating new employee records to trigger messages to send by middleware between software modules that are completely independent of one another.
Extract Data
Comes from various sources. These sources must be identified, understood and tapped
Data Warehouse
A collection of databases
Transform Data
Given the data come from different sources. it is likely that the data are not organized using the same collection attributes. Therefore, the data must be transformed to fit the model(s) of the data warehouse. This includes altering data to relations or objects, recognizing the unique identifiers and selecting the appropriate attributes.
Load Data
Into the storage facility, that is the transformed data must be stored in the data warehouse using the appropriate representation format.
Fields in SQL
Select, From, Where
First Generation
Vacuum tubes, ENIAC, punch cards, connected through cables.
Flat file database
one large single table without the relations between tables that a relational format provides
Unique Identifier or Primary key
For a database to work it must have this.
Fourth Generation
1974 IBM single chip processor, microprocessor/ microcomputer. Miniaturization still in this generation today.
Freeware or public domain
Has become obsolete or company no longer provides support
GANTT technique
Illustrated project schedule
Initiation Phase
In project management; problem definition, resource allocation and Risk assessment takes place in this phase.
Planning Phase
In project management; Objectives and activities, organize activities, time estimation and cost estimation takes place in this phase.
Executing and controlling phase
In project management; Variance reports, status reports and resource allocation takes place in this phase.
Closing phase
In project management; once all deliverables have been met, a project is consider to have reached this phase.
Gateway
An inter-networking system or device capable of joining together two networks that use different base protocols.
Hierarchical database
format organizes data using a tree-like or organization chart type structure. Main data points can have multiple sub-data points associated with them referred to as parent child model.
Information
To conclude from evidence or by reasoning. Ways to process data so it becomes information.
Interpreter
Takes the most recently entered instruction, translates it into machine language and executes it.
IT
The hardware, software and people
IT Manager
Oversees staff, communicate with upper management, understands both sides, hires and fires.
IT Support
Manager, Training, help desk
Java Database Connectivity (JDBC)
For applications written in Java, Oracle has developed this driver. This driver is orientated toward interactions with relational databases. Anyone developing in Java can use this driver in conjunction with ODBC (via a bridge) to have an application interact with any database.
Join
Withdraws information from multiple relations or field values
Kernel
Contains the core components of the operating system. Its loaded when the computer is first booted. This includes components that handle process management, resource management and memory management. It sits between the hardware and software.
Knowledge
Information that has been put to use.
Language translators
Not portable
Language translators
Assemblers, compilers and interpreters
Linux/Unix
For this operating systems the users prefer to use the command line.
Logic tier
In software architecture sits between the user and the data. This is where the system performs its logic processing, it resides on the server where the processing occurs.
MCV
Model-Control-View
Mitigation techniques
Firewall, anti-viral, anti-malware software
The model
In software architecture this layer can take different forms depending on the complexity of the application. In certain instances its an actual object that is an actual implementation of the application. This is used to retrieve information about the product. It is in this layer that the business logic is designed.
The Controller
In software architecture this layer is part of an application that interacts with the user and passes along the user requests to the model layer. It is in this layer that the input logic is designed.
The View
In software architecture this layer is the part of the application that represents the user interface. This is used to capture the input from the user to be passed via the controller to the model. It is in this layer of the application that the user interface logic is designed.
High level languages
Basic, C, C++ and java
Network Admin
Network engineer or network architects
Network admin roles
Design, edit configuration files, write shell scripts and install software and updates
Online Analytical Processing
OLAP
OLAP(Online analytical processing)
Data are processed through a suite of analysis software tools.
Online data processing
It deals with data in real time. its a "live" database
os types
workstation, mobile and server
PERT
Program evaluation and review technique
Private risk
A threat if disclosed to others such as social security and credit card numbers or health and educational information.
Project characteristics
Initiation, planning, executing and controlling and closing
Project
Temporary, unique and ends
Project management
brings a unique focus shaped by the goals, resources and schedule of each project
Public key encryption
uses two keys, a public, and a private
Public risk
Public information might include names and addresses
Quality data
Relevance, timely, accurate and reliable