Exam 4
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Strength
relative amount of API in the formulation (how much drug is there).
Drug amount per volume- concentration
Potency
drug’s ability to produce a pharmacologic effect
What does NOT change when use use this equation: C₁V₁ = C₂V₂
the drug amount stays the same unless you physically add or remove drug.
used for dilution
Product Strength formula
API / Whole (total mixture).
What does Dilution do?
decrease relative amount of API (decreases strength)
Usually by adding diluent (most common in pharmacy).
Can also remove API (e.g., filter a suspension).
lowers concentration

a. What math NOT to do for dilutions and fortifications
b. what math can you use do for dilutions
a. Do NOT use proportions (C₁/V₁ = C₂/V₂) for whole problems—it’s not an equivalence after you change total volume.
b. C₁V₁ = C₂V₂ (volumes/concentrations)
What does fortification do?
Concept: increase relative API.
Usually add active (e.g., powder) → increases numerator and total mass.
Or remove diluent (e.g., evaporation) → lowers denominator.
increases concenttraion
What is stock solution?
Make a concentrated stock to use repeatedly to make to make weaker solutions by dilution
plan concentrations so later dilutions are easy.
Used for APIs and functional excipients (flavors, sweeteners, suspending agents, etc.).
IV compounding logic:
when mixing two solutions, ask “what happens to each solute’s concentration?
a. allegation define

Allegation is used when combining already-prepared formulations, not pure API powder.
Two methods in allegation
a. Alligation Medial - weighted average
b. Alligation Alternate - shortcut table used only when mixing TWO components. “parts” represent ratio units, not grams.
Anytime you mix two strengths — whether you use:
weighted average (allegation medial), or
parts method (allegation alternate),
the resulting strength must be WHAT?
must fall between the two strengths being mixed.
When one component is “0%” in allegation, what does it act like?
It acts like a it acts as a diluent (contributes no drug), only volume/mass. petrolatum = 0% drug
What happens to final strength when both components have the same API strength in allegation?
mixing does NOT change final strength.
mian difference between dilution used equation (C₁V₁=C₂V₂) and allegation?
C₁V₁=C₂V₂ assumes API amount is constant; allegation does not assume that — it calculates it.
however you can use c1V1 = c2 v2 in alligation in this situation:
Situation | Does drug amount change? | Use this |
|---|---|---|
Only adding diluent (0%) | ❌ Drug stays same | C₁V₁=C₂V₂ |
Define alligation alternative
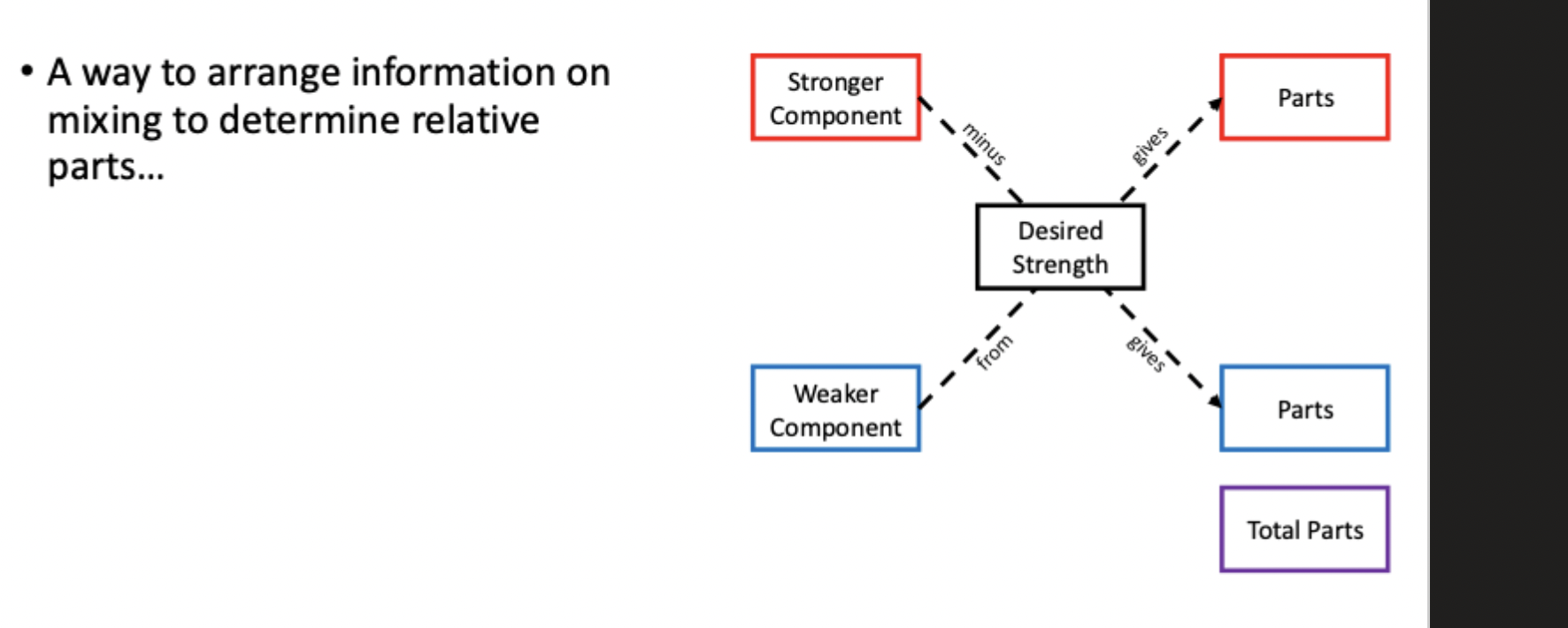
define Scaling factor
(Desired batch) / (Recipe batch); multiply every ingredient by this factor.
Reducing/enlarging can be solved by any what 3 methods
factor, proportion, dimensional analysis
when are Aliquots are required
when the weighed amount is below MWQ (~20 mg).
make a bigger mix with diluent, then take a portion.
use other math (ratio / C₁V₁=C₂V₂)
Aliquots do NOT change WHAT
the target strength
In proportional parts formulas, each part is a…
is a relative unit, not a fixed volume or weight
When all parts are liquids and compatible, we asume what
volumes are assumed to be additive
give me the different USP
USP <795> = non-sterile compounding
USP <797> = sterile compounding
USP <800> = hazardous handling
USP <1160> = pharmaceutical calculations in compounding
What is the official written recipe + math called; It must be followed exactly & documented
Master Formulation Record (MFR)
a. When do you know their power volume
b. how to find PV?
a. when label says “add X to make Y
b. PV = Y − X
Reconstitution
may contain more total drug than label dose — you withdraw the labeled dose only
Capsules:
size chosen by bulk density,
lactose used as
diluent,
tablets ≠
pure API
Suppositories
base = diluent, calibrate mold, usually prepare excess
how Capsules and suppositories connected
Mainly large mass that contains drug in a certain amount - THEN portioned into individual units.
qs ad
quantity sufficient to make total final volume/weight (not “add that amount”)
difference between ELIXIR and SPIRIT
ELIXIR = Medicinal “drink” base
Has water + low alcohol mixed
Often sweet (has syrup)
Used as something you could give to a patient directly or use to make another liquid
SPIRIT = Strong alcohol extract
Almost all alcohol, little/no water
Very strong concentration of oils/flavor or drug
NOT usually given directly — mostly used as an ingredient to mix into other things
Talc
filter aid (does not remain)
Alcohol + water contract
treat premixed 50/50 as single ingredient in problems.